Divalproex
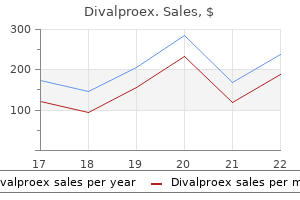
Generic divalproex 250mg overnight delivery
A good family history is very important medicine vicodin purchase genuine divalproex on-line, especially any information about other perinatal or neonatal deaths. Illustration demonstrating outer (A) and inner (B) canthal and interpupillary distances 3. The external exam is systematically performed on all fetuses regardless of gestational age (Figures 3. In macerated fetuses, it is present for a considerable length of time in skin creases, such as the axillae, groins, and behind the ears. When meconium is suspected, a cotton swab can be placed in the external auditory canal and/or the nostrils. Cottonswabdemonstratingmeconium vernix caseosa in the groin areas of a mac from the external auditory canal inastillborn erated, stillborn fetus at 37 weeks gestation. The systematic external examination should be performed with an autopsy protocol in hand. Jaundice can best be assessed in the sclera and cyanosis in the ngernail beds and vermilion border. All catheters and tubes should be left in place until the distal end can be observed or palpated during the internal examination. These can be removed and weighed and then subtracted from the initial weight of the infant to equal the true weight. ArmsoftheY(arrows)extendfromthe Indications for chromosome analysis include clinical evidence suggestive of, or tops of the shoulders. In the midline, a ver a number of anomalies suspicious for, a chromosome abnormality (Table 3. The tissue should be taken by a sterile technique, cleaning the skin with sterile saline and not alcohol. The best sources of tissue for culture are skin, fascia, lung, chorionic villi from the placenta, and cartilage. Fibroblast cultures for metabolicandenzymaticstudiesaswellaselectronmicroscopycanbeobtained by the same method. The skin ap over the chest is pulled upward while incising its attachments to the chest wall. The muscle and brous tissues should be entirely stripped to reveal the ribs and the clavicles. A vertical incision is made in the midline, from the xiphoid process to the symphysis pubis. A small nick is made near the umbilical vein and scissors are used to open the abdominal cavity. Lifting upward on the abdominal wall will eliminate cutting into the abdominal organs. Reflection of the abdominal skin flaps insertedinferiortotheumbilicusandalongtheinnerabdominalwalltopalpate with an intact umbilical arteries and vein (ar the umbilical arteries, which extend on either side of the urinary bladder. This decision can also depend on the known or suspected anomalies, to best preserve them. The skin and subcutaneous tissues are dissected away from the anterior lateral aspects of the lower ribs exposing the abdominal organs. Abnor malities in the abdominal situs very often predict the thoracic situs and the presence of congenital heart disease. The mesenteric attachments are examined and the position of the appendix is noted. The chest plate is removed by separating the sternoclavicular joint on each side(Figures3. Thechondral portionsoftheribsareincisedinanupside-downV-likepattern, approximately 4 mm from the costochondral junction. The ribs are lifted off the thoracic or gans by grasping the xiphoid process with toothed forceps and cutting away the brous attachments as close to the bone as possible. This should be per formedassoonasthechestplateisremoved, keepingthe eldassterile as possible. One or both lungs may be cultured as follows: the edge of the lung can be clamped with a hemostat and the lung pulled from the pleural cavity. With a sterile blade and forceps, a wedge of lung is removed and placed in the appropriate medium for bacterial, fungal, or viral culture. The chest plate is removed with an upside down the pericardium and thymus together. The pericardium is nicked and V-shaped incision that begins at the sternoclavicular a cut is made parallel to the diaphragm, extending to the base of joint (*) and flares laterally on each side. Note the large thymus gland (T) lying over the superior anterior portion of the heart (H) and great vessels. A continuous cut is made to the level of the left pulmonary artery with no loose pericardial aps left to obstruct the view. The pericardium, with the thymus attached, is carefully dissected off the left innominate vein. The dissection continues into the neck; the superiormost portions of the thymus often extend to the inferior aspect of the thyroid. Thethoracicsitusisdetermined, notingthelobationofthelungs, positionof the cardiac apex, and atrial morphology. Note its broad junction (dots) with the venous component of the atrium and the blunt triangular appendage. There is a broad junction between the appendage and the smooth walled portion of the atrium. The great arteries are inspected, noting the position of the aortic trunk with relationship to the pulmonary trunk. Coronary artery topography can determine the position of the ventricular septum and can be an excellent indicator as to ventricular position and size. Assessing the pulmonary venous connections, on external examination, can be done by performing the Taussig maneuver. If the heart can be lifted from the chest without movement of the lungs, there is an anomalous extracardiac pulmonary venous connection. The arrangement of the atrial appendages is of particular importance on external examination and should be classi ed as one of the following: usual arrangement (situs solitus), mirror image arrangement (situs inversus), or presence of bilateral morphologically right or left appendages (isomerism). The most consistent morphological feature of an atrium is the anatomy of its appendage and its junction with the venous component. Many features of the atrium are variable and cannot be used as a criterion of atrial morphology, such as the foramen ovale, which may be absent, along with part or all of the atrial septum (Figure 3. Note the narrow junction (dots) between the atrium and the narrow, hooked appendage. Internal exam reveals the pectinate muscles radiating from a prominent muscle bundle (crista termi nalis), which lies between the appendage and the smooth-walled portion of the atrium. Themorpho logical right bronchus is approximately half as long as the morphological left bronchus (Figure 3. The rst branch of the morphological right bronchus is eparterial (above the pulmonary artery extending to the lower lobe), in con trast to the left, where the rst branch of the morphological left bronchus is hyparterial (below the pulmonary artery extending to the lower lobe). Opening the Heart In Situ Opening the heart in situ is performed by following the ow of blood and using the coronary arteries as a guide to avoid the septum (Figure 3. This straightforward, systematic approach can be altered to accommodate each in dividual case. The aortic valve, ascending aorta, and the aortic arch are opened with this nal cut. The tricuspid valve has chordal attachments to papillary muscles (black arrow) and the septum (yellow arrows). The apical component of the ventricles is the most constant morphologic feature and will be present in even the most rudimentary or incomplete ventricles (Figure 3. When dealing with macerated stillborns this procedure is not necessary; the decision may be made on a case-by-case basis. Fetuses <20 weeks gestation typically are considered a surgical specimen and do not always require evisceration. A thorough in situ exam along with photographs and radiologic studies is often adequate.
Order divalproex 250 mg without prescription
One should keep in mind that as many as 20% of adolescents with dysfunctional uterine bleeding will have a coagulation defect symptoms thyroid cancer buy generic divalproex on line, although the most common cause is 28, 29 anovulation. Bleeding secondary to a blood dyscrasia is usually a 31 heavy flow with regular, cyclic menses (menorrhagia), and this same pattern can be seen in patients being treated with anticoagulants. Bleeding disorders are usually associated with menorrhagia since menarche and a history of bleeding with surgery or trauma. The first well-controlled studies of this issue demonstrated no change in menstrual patterns, volume, or pain. However, these authors failed to agree in their findings (a change found by one group was not confirmed by the other). Adding to the confusion, the incidence of hysterectomy for bleeding disorders in women after 37 38 tubal sterilization was reported to be increased by some, but not by others. In a large cohort of women in a group health plan, hospitalization for menstrual 39 disorders was significantly increased; however, the authors believed this reflected bias by patient and physician preference for surgical treatment. It is possible that extensive electrocoagulation of the fallopian tubes can change ovarian steroid production. Perhaps this is why menstrual changes were 39, 41, 42 detected with longer (4 years) follow-up, while no changes have been noted with the use of rings or clips. However, attempts to relate poststerilization menstrual changes with extent of tissue destruction fail to find a correlation, and an increase in hospitalization for menstrual disorders after unipolar cautery cannot be 39, 42 43 documented. This inconsistency can reflect differences in sterilization techniques, as well as the fact that a surgical solution is more likely to be chosen if continuing fertility is no longer an issue. The best answer for now is that some women experience menstrual changes, but most do not. Treatment Program for Anovulatory Bleeding the immediate objective of medical therapy in anovulatory bleeding is to retrieve the natural controlling influences missing in this tissue: universal, synchronous endometrial events, structural stability, and vasomotor rhythmicity. Progestin Therapy Most women will, at sometime during their reproductive years, either fail to ovulate or not sustain adequate corpus luteum function or duration. But this occurs with increased frequency in adolescence and in the decade prior to menopause. Women correctly seek medical advice promptly because these menstrual aberrations suggest unplanned pregnancy or uterine pathology. Under most circumstances, progestin therapy will suffice to control the abnormality once uterine pathology is ruled out. Progesterone and progestins are powerful antiestrogens when given in pharmacologic doses. Progestins stimulate 17b-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 44 sulfotransferase activity, which convert estradiol to estrone sulfate (which is rapidly excreted from the cell). Progestins also diminish estrogen effects on target cells by inhibiting the augmentation of estrogen receptors that ordinarily accompanies estrogen action (receptor replenishment inhibition). These influences account for the antimitotic, antigrowth impact of progestins on the endometrium (prevention and reversal of hyperplasia, limitation of growth postovulation, and the marked atrophy during pregnancy or in response to combined oral contraceptives). Failure of progestin to correct irregular bleeding requires diagnostic reevaluation. Oral Contraceptive Therapy In young women, anovulatory bleeding may be associated with prolonged endometrial buildup, delayed diagnosis, and heavy blood loss. In these cases, combined progestin-estrogen therapy is used in the form of combined oral contraceptives. If flow does not abate, other diagnostic possibilities (polyps, incomplete abortion, and neoplasia) should be reevaluated. If flow does diminish rapidly, the remainder of the week of treatment can be given over to the evaluation of causes of anovulation, investigation of hemorrhagic tendencies, and blood replacement or initiation of iron therapy. In addition, the week provides time to prepare the patient for the estrogen-progestin withdrawal flow that will soon be induced. For the moment, therapy has produced the structural rigidity intrinsic to the compact pseudodecidual reaction. Continued random breakdown of formerly fragile tissue is avoided and blood loss stopped. However, a large amount of tissue remains to react to estrogen-progestin withdrawal. If not prepared in this way, it is certain that the patient will view the problem as recurrent disease or failure of hormonal therapy. In successful therapy, on the 5th day of flow or in the usual Sunday start fashion, a low dose combination oral contraceptive medication (one pill a day) is started. This will be repeated for several (usually three) 3-week treatments, punctuated by 1-week withdrawal flow intervals. Early application of the estrogen-progestin combination limits growth and allows orderly regression of excessive endometrial height to normal controllable levels. If the estrogen-progestin combination is not applied, abnormal endometrial height and persistent excessive flow will recur. In the patient not requiring contraception, in whom cyclic estrogen-progestin for 3 months has reduced endometrial tissue to normal height, the oral contraceptive can be discontinued and unopposed endogenous estrogen permitted to reactivate the endometrium. In the absence of spontaneous menses, the recurrence of the anovulatory state is suspected, and a brief preemptive course of an orally active progestin is administered to counter endometrial proliferation. With this therapy, excessive endometrial buildup is avoided, and an increased risk of endometrial and possibly breast cancer is avoided. If contraception is desired, routine use of oral contraception is warranted and will also be of prophylactic value. Depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate in the dose used for contraception, 150 mg intramuscularly every 3 months, is a useful option for poorly compliant patients. Estrogen Therapy Intermittent vaginal spotting is frequently associated with minimal (low) estrogen stimulation (estrogen breakthrough bleeding). In this circumstance, where minimal endometrium exists, the beneficial effect of progestin treatment is not achieved, because there is insufficient tissue on which the progestin can exert action. A similar circumstance also exists in the younger anovulatory patient in whom prolonged hemorrhagic desquamation leaves little residual tissue. In these circumstances, when bleeding is acute and heavy, high-dose estrogen therapy is applied by using as much as 25 mg conjugated estrogen intravenously 47 every 4 hours until bleeding abates or for 24 hours. The mechanism of action for 48 estrogen is believed to be a stimulus to clotting at the capillary level. When bleeding is moderately heavy, a more intensive oral program can be utilized, 1. All estrogen therapy must be followed by progestin coverage and a withdrawal bleed. Estrogen therapy is also useful in two examples of problems associated with progestin breakthrough bleeding. These are the breakthrough bleeding episodes occurring with use of oral contraception or with depot forms of progestational agents. In the absence of sufficient endogenous and exogenous estrogen, the endometrium shrinks by pharmacologically induced pseudoatrophy. Furthermore, it is composed almost exclusively of pseudodecidual stroma and blood vessels with minimal glands. Peculiarly, experience indicates that this type of endometrium also leads to the fragility bleeding more typical of pure estrogen stimulation. The usual clinical story is a patient on long-standing oral contraception who, after experiencing marked diminution or absence of withdrawal flow in the pill-free interval, begins to see breakthrough bleeding while on medication.
Order cheapest divalproex
Certainly gonadotropin stimulation and withdrawal are important medications during labor order divalproex paypal, but ovarian steroids and autocrine and paracrine factors are also involved. The consequence of these unfavorable changes, atresia, is a process called apoptosis, 51 programmed cell death. Indeed, the process is a consequence of an orderly expression of key gene products that either promote or repress the apoptotic events. This neuronal network innervates the ovarian vasculature, interstitial tissue, and developing follicles. However, nerve fibers (not in an organized network) are present in nonprimate ovaries. During the reproductive years, the typical cycle of follicle maturation, including ovulation and corpus luteum formation, will be realized. This results from the complex but well defined sequence of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal interactions in which follicle and corpus luteum steroid hormones, pituitary gonadotropins, and autocrine and paracrine factors are integrated to yield ovulation. For the moment, our attention will be exclusively directed to a description of the events as the gonad is driven inexorably to final and complete exhaustion of its germ cell supply. For every follicle that ovulates, close to 1000 will pursue abortive growth periods of variable length. Follicular Growth In the adult ovary, the stages of follicle development observed even in the prenatal period are repeated but to a more complete degree. Emma Call was the first woman elected to the Massachusetts Medical Society (in 1884). Soon a liquor accumulates, which is essentially a transudation of blood filtered through the avascular granulosa from the thecal vessels. With antral formation, the theca interna develops more fully, expressed by increased cell mass, increased vascularity, and the formation of lipid-rich cytoplasmic vacuoles within the theca cells. As the follicle expands, the surrounding stroma is compressed and is called the theca externa. The granulosa cells that surround the oocyte are avascular and separated from the surrounding stroma by a basement membrane. Deprived of a vascular supply until after ovulation, the granulosa cells depend on specialized gap junctions that connect cells and communicate with the oocyte for the purpose of metabolic exchange and the transport of signaling molecules. It is this structure that allows repression and stimulation for the correct timing of meiosis. At any point in this development, individual follicles become arrested and eventually regress in the apoptotic process known as atresia. The antral cavity constituents are resorbed, and the cavity collapses and obliterates. Eventually this theca mass loses its lipid and becomes indistinguishable from the growing mass of stroma. Thus, the process of apoptosis is extensive in the granulosa, and the thecal layer is largely spared to be incorporated into the interstitial tissue. Prior to regression, cystic follicles can be retained in the cortex for variable periods of time. Ovulation If gonadotropin stimulation is adequate, one of the several follicle units propelled to varying degrees of maturity will advance to ovulation. Morphologically, these events include distension of the antrum by increments of antral fluid and compression of the granulosa against the limiting membrane separating the avascular granulosa and the luteinized, vascularized theca interna. In addition, the antral fluid increment gradually pinches off the cumulus oophorous, the mound of granulosa enveloping the oocyte. The mechanisms of the thinning of the theca over the surface of the now protruding, distended follicle, the creation of an avascular area weakening the ovarian capsule, and the final acute dissension of the antrum with rupture and extrusion of the oocyte in its cumulus, are multiple and complex (discussed in Chapter 6). Repeated evaluation of intrafollicular pressures has failed to indict an explosive factor in this crucial event. As demonstrated in a variety of animal experiments, the physical expulsion of the oocyte is dependent on a preovulatory surge in prostaglandin synthesis within the follicle. Inhibition of this prostaglandin synthesis produces a corpus luteum with an entrapped oocyte. Both prostaglandins and the midcycle surge of gonadotropins are thought to increase the concentration and activity of local proteases, such as plasminogen conversion to plasmin. As a result of generalized tissue weakening (loss of intercellular gap junction integrity and disruption of elastic fibers), there is swift accumulation of antral fluid followed by rupture of the weakened tissue envelope surrounding the follicle. Corpus Luteum Shortly after ovulation, profound alterations in cellular organization occur in the ruptured follicle that go well beyond simple repair. After tissue integrity and continuity are retrieved, the granulosa cells hypertrophy markedly, gradually filling in the cystic, sometimes hemorrhagic, cavity of the early corpus luteum. In addition, for the first time, the granulosa becomes markedly luteinized by incorporation of lipid-rich vacuoles within its cytoplasm. Both these properties had been the exclusive features of the theca prior to ovulation. For its part, the theca of the corpus luteum becomes less prominent, vestiges being noted eventually only in the interstices of the typical scalloping of the mature corpus luteum. As a result, a new yellow body is formed, now dominated by the enlarged, lipid-rich, fully vascularized granulosa. Its vascularity and lipid content wane, and the sequence of scarification (albicantia) ensues. Modulators of Function the complex events that yield an ovum for fertilization and ovarian structures that provide hormonal support are the products of essentially every regulating mechanism in human biology. This includes classic endocrine signals, autocrine and paracrine/intracrine regulation, neuronal input, and immune system contributions. Representatives of the white blood cell series constitute a major component of the ovarian stromal (interstitial) compartment. Macrophages present in 59 permanent, noncyclic numbers may influence ovarian function through the secretion of regulatory cytokines. During the adult ovarian cycle, there is an infiltration of white blood cells in a pattern characterized by increasing numbers of mast cells culminating in degranulation and release of histamine that is associated with 60 hyperemia at ovulation. The corpus luteum attracts eosinophils and T lymphocytes, that signal and activate monocytes and macrophages involved in luteolysis. However, this immune mechanism should not be viewed just as a healing and resolving response, but also as an important regulatory system (involving the secretion 59 of cytokines and growth factors) for ovarian function. Graham H, Eternal Eve, the History of Gynaecology & Obstetrics, Doubleday & Company, Inc. The natural history of the female germ cell: origin, migration and differentiation inside the developing ovary, Hum Reprod Update 3:281, 1997. Gondos B, Bhiraleus P, Hobel C, Ultrastructural observations on germ cells in human fetal ovaries, Am J Obstet Gynecol 110:644, 1971. Gondos B, Westergaard L, Byskov A, Initiation of oogenesis in the human fetal ovary: ultrastructural and squash preparation study, Am J Obstet Gynecol 155:189, 1986. A three-dimensional microanatomical study by scanning and transmission electron microscopy, J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 18:271, 1986. Mittwoch U, Mahadevaiah S, Comparison of development of human fetal gonads and kidneys, J Reprod Fertil 58:463, 1980. Hengster P, Menardi G, Ovarian cysts in the newborn, Pediatr Surg Int 7:372, 1992. Block E, Quantitative morphological investigations of the follicular system in women, Acta Anat 14:108, 1952. Gougeon A, Dynamics of follicular growth in the human: a model from preliminary results, Hum Reprod 1:81, 1986. Gougeon A, Regulation of ovarian follicular development in primates: facts and hypotheses, Endocrin Rev 17:121, 1996. Speert H, Obstetric & Gynecologic Milestones Illustrated, the Parthenon Publishing Group, New York, 1996.
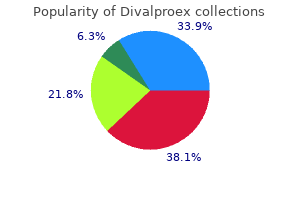
Purchase divalproex 250mg fast delivery
The femurs tend to bend from front to back and the tibiae from side to side treatment laryngomalacia infant buy divalproex 500mg low cost, but this con guration is by no means invariable. In the case of the femurs, the bone is frequently buttressed by a bar on the concave surface. However, there are also many other diseases in which osteomalacia occurs as a complication, notably gastro-intestinal and renal disorders. They are often surrounded by a sclerotic margin and there may be overlying periosteal new bone. It is this inability to store the vitamin that made scurvy such a scourge on long sea voyages, 66 during times of famine67 or in other circumstances when the supply of fresh fruit and vegetables was inadequate. This must presumably have been the case in the past when stocks of stored vegetables were exhausted and before fresh ones were harvested. The disease may still assume epidemic proportions in those parts of the world where the diet remains poor. The ship had been at sea for eight weeks when he started his experiment, choosing twelve of the sailors with scurvy as his subjects. Twomenwere given two oranges and one lemon a day for six days and they were the only ones fully to recover, although those given cider also derived some bene t. In this way, it tended to be a middle-class disease, rather than a disease of poverty as it is now. For many years, scurvy and rickets were not clearly distinguished and this was not nally achieved until Barlow clari ed the position in 1883. Untreated scurvy is frequently fatal due to effects on the heart causing sudden death. In the adult, osteoporosis is the most prominent radiological sign but in children, the changes interference with growth and characteristic signs can frequently be seen at the ends of the long bones76 which are often enlarged and may appear porous, as they do in rickets. The skull may also become bossed with deposits of periosteal new bone on the external surface. The radiographic changes can be related to histopathological ndings, as shown in Table 7. In the skeletons of Dutch whalers buried on the island of Zeeusche, Maat found black staining on the long bones that he considered was the result of sub-periosteal bleeding caused by scurvy. Some will be considered brie y here, others are men tioned elsewhere in this book. The disease is rare, slightly more common in women than in men, and increases with increasing age. If it were, the extraction and characterisation of haemoglobin would con rm the diagnosis. In thalassaemia there is reduced synthesis of either the or the chains while in sickle cell disease, there is a single mutation in which glutamic acid is substituted for valine in the chains. However, at certain times, evidence of wounding is quite common, and in later periods, signs of surgical or anatomical intervention may be apparent. It may be dif cult to differentiate trauma that occurred at or around the time of death from that suffered after burial and there is no doubt that some peri-mortem trauma will not be recognised. Breaks to bones that occur during or after recovery should present no dif culty, however, as the broken surfaces will be of a much lighter colour than the rest of the skeleton. A dislocation results from the complete loss of contact between two bone surfaces that should normally be in contact. Thus, they may be simple, when there are only two fragments, or comminuted when there are more than two. Classi cation of fractures Type Appearance Transverse Fracture at right angles to long axis of bone Oblique Fracture at oblique angle to long axis of bone Spiral Fracture winds around long axis of bone Depressed Skull fracture in which the table(s) of the skull are forced inwards Crush Vertebral fracture usually caused by a fall Wedge Vertebral fracture secondary to vertebral collapse such as caused by infection or malignant disease; typically seen in osteoporosis Greenstick Incomplete fracture seen in children Pathological Fracture occurring in a bone affected by some pathological process Stress Fracture occurring as the result of repeated loading 140 palaeopathology Table 8. Of the ankle: Vertical fracture of anterior medial portion of distal bula with avulsion of anterior tibio bular ligament Lisfranc Fracture-dislocation (or fracture-subluxation) of tarsometatarsal joints Maisonneuve Spiral fracture of upper third of bula and medial malleolus Malgaigne Fracture through ipsilateral ilium and pubic rami Monteggia Fracture of proximal third of ulna with anterior dislocation of radial head Piedmont Another name for the Galeazzi fracture Pott Any type of bimalleolar fracture Pouteau Identical with the Colles fracture Rolando Comminuted Y or T-shaped fracture-dislocation of base of rst metacarpal (continued) trauma 141 Table 8. Falls from a height onto the feet may result in crush fractures of the vertebrae or the pelvis, while a direct blow to the head may cause a depressed fracture. For example, in fractures of the forearm in which only one of the two bones is broken, the intact one will prevent the other becoming displaced. Similarly, if one or two ribs are fractured, the rest of the rib cage splints those that are broken and they do not usually lose their normal position. Reduction is achieved by putting the fractured bone back into its normal anatomical position. Nowadays this is done with the patient anaesthetised and relaxed and with X-ray guidance. The means of immobilisation by the application of splints has been in use for thousands of years. The period of immobilisation required to allow healing depends on a number of factors, including inter alia the age of the patient, the bone fractured and the quality of the bone, as will be discussed later. What is particularly noticeable about fractures that are found in skeletal assemblages is that the majority are well healed and in good alignment and few are found with signs of infection. In this condition, a large segment of the rib cage may become detached from the remainder and be drawn inwards during inspira tion and outwards during expiration, thus impairing the entry of air into the lungs. Non-union: If a fracture fails to heal, this is known as non-union and the brous joint formed between the broken ends of the bones is known as a pseudarthrosis. Shortening and deformity:3 If a broken limb is not properly reduced, it will heal with shortening or angulation (Figure 8. As we have seen earlier, a wide variety of organisms may 3 this is sometimes also referred to as mal-union. Theobliquefractureline(arrowed)isclearly visible and has entered the ankle joint; there is also a good deal of heterotopic ossi cation aroundthefracture. Thefracturewasnotreducedandthereisconsiderableangulationwhich would have caused some dif culty with walking during life. It is remarkable how few fractures seen in a skeletal assemblage show signs of infection, another testimony to the care with which they were treated, or to the robust natural immunity enjoyed by our ancestors in the days before we were overcome by pathological cleanliness. Necrosis may also be caused by what is known as the tamponade effect, that is, by raised pressure within the joint capsule which is suf cient to disrupt the blood supply to the head of the femur. Femoral neck fractures may be seen in skeletal assemblages with the loss of the head. The stump of the femoral neck may remain in articulation with the acetabulum or make a pseudarthrosis with the ilium. The proximal three-quarters of the bone is supplied by dorsal vessels and the distal quarter by palmar branches. The proximal pole of the scaphoid has only a limited blood supply, and large areas of it are reliant on a single vessel which may be damaged by a fracture. Lunate: the lunate receives its blood supply from the dorsal radiocarpal arch and the palmar intercarpal arch; the proximal pole is relatively less well supplied than the remainder of the bone. Fractures of the lunate are not common but may compromise the blood supply with subsequent necrosis. Since osteoarthritis will take many years to develop, its presence in the skeleton will indicate that the individual survived for some considerable time after the injury that caused the fracture. Ankylosis: A fracture that extends into a joint, or a fracture-dislocation of a joint will almost certainly result in blood entering the joint, which greatly increases theriskthatthejointwillbecomeankylosed. Anyjointthatisfoundtobefused in the skeleton and in which there is no obvious sign of infection, or some concomitant disease such as a sero-negative arthropathy, is very likely to have been subject to injury of one kind or another.
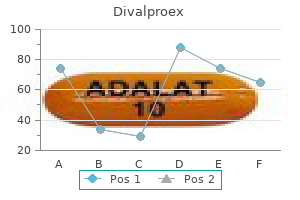
Buy divalproex overnight
Face cases provide a useful framework to illustrate the issues: masks for noninvasive ventilation: Fit medications during labor buy 500 mg divalproex free shipping, excess skin hydration, and pressure ulcers. Inhibitory Effect of Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure was found to be azospermic. Repeated the apical surface of epithelial cells which controls the flux of chloride, sweat tests revealed chlorides between 35 and 49 mmol/l and first line bicarbonate and sodium thereby regulating airway surface hydration. Diagnostic cut-offs are estab possess an additional mutation D1152H on his other allele. There are now >2, 000 mutations described, many of A well 4-week old baby girl was referred following a positive newborn which are extremely rare and have not yet been fully understood. The baby was diarrhea due to pancreatic exocrine dysfunction, respiratory symp well-grown and had normal stools; there were no parental concerns. Consensus in Europe is that such babies and later complications of diabetes mellitus and arthropathy. Some will develop lung complications in later life, so and the diagnosis may even be suspected prenatally with echogenic a degree of follow up is advised. Thiocyanate is critical for epithelial generation of hypoth so further investigation should be considered in these cases. Cystic fibrosis: loss of airway surface liquid homeostasis increases mucus viscosity terminology and diagnostic algorithms. Arachidonic acid is the precursor for mutations may predispose to cystic fibrosis-like disease. Furthermore, other sphingolipids such as sphingosine bations of bronchitis with opportunistic organisms and neutrophil play important roles in response to microbes in the lung. The relentless cycle of infection and affects cell membrane lipid raft composition, receptor clustering and inflammation results in airway injury and bronchiectasis leading cell signaling. Ceramide also increases epithelial cell permeability and ultimately to respiratory failure, the most common cause of death. To date, none of these drugs has moved forward that further promote infection and impair bacterial phagocytosis and to Phase 3 trials. Furthermore, other alarmins, S100A8, markers would facilitate determination of anti-inflammatory efficacy S100A9, and S100A12, the calgranulins, released from neutrophils in vivo. Third, it is important the airway, releasing non-heme iron that is required for bacterial to select the correct population that is likely to respond to therapy a growth and biofilm formation and also is taken up by epithelial cells personalized medicine approach to anti-inflammatory therapy. Aureli M, Schiumarini D, Loberto N, Bassi R, Tamanini A, Mancini G, prevent infection and inflammation. Unravelling the role Importantly, an early prospective, randomized and double blind study of sphingolipids in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Chem Phys Lipids using oral glucocorticoids every other day for a year in patients with 2016;200:94-103. Inflammation in cystic prospective trial over 4 years, particularly in patients with chronic P. J Cyst Fibros 2015;14 aeruginosa infection, it has not been widely accepted due to difficulties (4):419-430. Association of cystic fibrosis with target specific inflammatory mediators: proteases, reactive oxygen abnormalities in fatty acid metabolism. N Engl J Med 2004;350: species, neutrophil chemoattractants, abnormal intracellular signals, 560-569. During the last decades the cornerstone of any resuscitation or management of respiratory failure. In other situations, endotracheal which combined bronchoalveolar lavage and serological results at high intubation may be chosen as an elective procedure to secure the rates even in children younger than three years of age, indicating that airwaysand provide positive pressure ventilation. A chronic P ae infection necessitates regular suppression intubation is a respiratory failure requiring artificial ventilation. There therapy with antimicrobials in order to prevent deterioration of lung is a broad spectrum of disorders that may lead to respiratory function. Common approaches to address these directly associated with respiratory pathology (meconium aspiration, microbacteria will be discussed. In the study of Qvist, clearing atelectasis, transient tachypnea of a newborn) or as a complication of M. Current techniques of artificial ventilation based on by non-culture based techniques in a given patient, dosages, synchronized and volume guaranteed regimes provide effective pharmacodynamics and interactions of drugs applied, comprehensive support that fully respects the physiological requirements of a treatment including airway clearance, upper airway reservoir and newborn and assures adequate oxygenation while reducing the risks implementation into everyday life need to be considered, when associated with positive pressure ventilation. Nevertheless, even with proper preparation, about 1/3 of ventilated children present with extubation failure and need to be reintubated. It may also be associated with the switch from a desirable to keep the intubation period as short as possible to reduce positive pressure ventilation to spontaneous breathing and change of risk of possible complications. Such problems are mostly observed inevitably carries risk of cardiopulmonary instability and often in tracheo/bronchomalacia, external compression of the airways or results in need for reintubation and reinstitution of artificial some congenital airway defects. On the other hand, prolonged intubation has been may also lead to quick onset of respiratory problems. It may be helpful associated with increased risk of airway or lung injury, with to evaluate the airways with an ultrathin bronchoscope after increasing incidence of infectious complications, such as ventilator stabilization and reinstitution of adequate ventilation. Careful associated pneumonia and neurodevelopmental impairment mainly 1 extubation on the bronchoscope may help to reveal the location of in extremely low birth weight children. Continuous monitoring and obstruction in many cases; however, this is not 100% reliable. The decision to extubate should be taken after careful evaluation of cardiorespira studies to define reintubation as extubation failure, therefore the tory stability, the oxygen requirement and its trend and the overall comparison of published results is rather difficult. From a practical point of view, as status of the baby and its readiness for a switch to spontaneous ventilation. Extubation should be always properly planned and failure of extubation, we should understand a need for reintubation in prepared. The worst scenario is an unexpected accidental extubation a child with no new pathology that could explain the imminent respiratory failure. Indications for reintubation usually are that usually leads to emergency reintubation and carries significant risk of hypoxemia, instability and even airway injury during rapid frequent or major apneas, emergency reintubation. The recommended tidal volume that should maintain adequate ventilation and at the same time prevent Failed extubation represents a high risk situation especially in very low any lung injury is at the level of 4. It has been associated with high morbidity and and resistance of the respiratory tract should also be taken in even increased risk of death. Before extubation, the tube should be used for last successful extubation have been published, most of them based on direct suctioning, if needed. If the monitoring of blood gases and scoring some of the physiological signs that characterize respiratory vital signs and functions provides stable results, the child can be drive and respiratory strength. While they may improve the rate of successful ventilation homogeneity and thus prevent the risk of reintubation. Thus, they should be aware of the recent Conclusion trends in Neonatology, as reflected in the published literature in the field of Neonatal Pulmonology. The most recent large multicenter, randomized trial, well judged based on the assessment of respiratory stability and explored prenatal betamethasone treatment at 34 to 36 weeks of gestation. The Low Birthweight Neonates with Protracted Ventilation: Mortality and rate of primary outcome was lower in the betamethasone group 18-Month Neurodevelopmental Outcomes. In the Neurosis study, 2 863 infants (gestational age, 23 weeks 0 days to Preterm Infants: Predictors of Success and Outcomes following Failure. Risk factors associated with failure of early inhaled budesonide than among those who received placebo, but extubation in very-low-birth-weight newborns. Inhaled corticosteroids were extubation in very-low-birth-weight infants: a feasibility study. Data on long-term Pediatric Pulmonologist respiratory, growth, anddevelopmentaloutcomesare eagerlyawaited. The analysis included only 2 studies better indicator of chronic respiratory insufficiency.
Generic divalproex 500 mg with mastercard
It is to determine the extent to which osteoporosis is related to argued that more active individuals are less likely to fall the glucocorticoid or to other factors medicine x boston order generic divalproex pills, as treatment is super and are more capable of protecting themselves upon imposed on the effects of the primary disease, which may falling, thereby reducing fracture risk. Excessive doses of thyroid hormone can acceler ate bone remodeling and result in bone loss. Patients undergoing transplantation are at different manufacturers, the output varies in absolute high risk for rapid bone loss and fracture, not only from terms. In addition, these patients often have underly population that is matched for race and gender. Z-scores ing metabolic abnormalities, such as hepatic or renal compare individual results to those of an age-matched failure, that predispose to bone loss. These effects may be mediated lyze trabecular bone and cortical bone content and volume directly, by toxic effects on osteoblasts, or indirectly by separately. Though it can be used for measurements Z and T-Scores of any skeletal site, clinical determinations are usually 3 made of the lumbar spine and hip. In younger individuals, such as perimenopausal or the perimenopausal transition is a good opportunity early postmenopausal women, spine measurements may be to initiate discussion about risk factors for osteoporo the most sensitive indicator of bone loss. A careful history and physical examination should be performed to identify risk factors for osteoporosis. The For patients who present with fractures, it is important guidelines further recommend that bone mass measure to ensure that the fractures are not caused by an under ment be considered in all women by age 65, a position lying malignancy. It is impor serum calcium level may re ect malnutrition and osteo tant to consider the risk of fracture for individuals, includ malacia. Treatment thresholds depend on malabsorption; a high urine calcium (>300 mg/24 h) is cost-effectiveness analyses but will likely be ~1% per year indicative of hypercalciuria and must be investigated of risk in the United States. Vitamin D levels frequently, if medically justi ed should be optimized in all individuals being treated for osteoporosis. Hyperthyroidism should be evalu aCriteria adapted from the 1998 Bone Mass Measurement Act. These tests measure cortisol should be measured after overnight dexam the overall state of bone remodeling at a single point ethasone. Clinical use of these tests has been hampered nutrition is suspected, serum albumin, cholesterol, and a by biologic variability (in part related to circadian complete blood count should be checked. Asympto rhythm) as well as to analytical variability, although matic malabsorption might be heralded by anemia the latter is improving. Asymptomatic help in the prediction of fracture risk, independently of celiac disease with selective malabsorption is being bone density, particularly in older individuals. In women found with increasing frequency; the diagnosis can be 65 years, when bone density results are greater than made by testing for antigliadin, antiendomysial, or trans the usual treatment thresholds noted above, a high glutaminase antibodies but may require endoscopic level of bone resorption should prompt consideration biopsy. The primary use of biochemical markers When osteoporosis is found associated with symptoms is for monitoring the response to treatment. With the of rash, multiple allergies, diarrhea, or ushing, mastocy introduction of antiresorptive therapeutic agents, bone tosis should be excluded using 24-h urine histamine remodeling declines rapidly, with the fall in resorption collection or serum tryptase. Serum and urine electrophoresis and earlier estimate of patient response than does bone den evaluation for light chains in urine are required to sitometry. A bone marrow biopsy may be tained after treatment with bisphosphonates or estrogen; required to rule out myeloma (in patients with equiv this effect is less marked after treatment with either ocal electrophoretic results) and can also be used to raloxifene or intranasal calcitonin. Biochemical markers quently involves management of acute fractures as well as treatment of the underlying disease. These surgical Serum osteocalcin procedures are followed by intense rehabilitation in an Serum propeptide of type I procollagen attempt to return patients to their prefracture functional Bone resorption level. Long bone fractures often require either external or Urine and serum cross-linked N-telopeptide internal xation. A few small, randomized clini oughly educated to reduce the impact of modi able risk cal trials suggest that calcitonin may reduce pain related to factors associated with bone loss and falling. A recently developed tions should be reviewed to ensure that all are neces technique involves percutaneous injection of arti cial sary. Glucocorticoid medication, if present, should be cement (polymethylmethacrylate) into the vertebral evaluated to determine that it is truly indicated and is body (vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty); this offers signi being given in doses as low as possible. There have been no long-term randomized should be made to facilitate smoking cessation. Reduc controlled trials of either vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty ing risk factors for falling also includes alcohol abuse to date. Short periods of bed rest may be helpful for treatment and a review of the medical regimen for any pain management, but, in general, early mobilization is drugs that might be associated with orthostatic recommended as it helps prevent further bone loss hypotension and/or sedation, including hypnotics and associated with immobilization. If nocturia occurs, the frequency should be soft elastic-style brace may facilitate earlier mobiliza reduced, if possible. Muscle spasms often occur with acute compression diuretic use), as arising in the middle of sleep is a com fractures and can be treated with muscle relaxants and mon precipitant of a fall. Avoiding stocking feet on wood oors, checking related to abnormal strain on muscles, ligaments, and carpet condition (particularly on stairs), and providing tendons and to secondary facet-joint arthritis associated good light in paths to bathrooms and outside the home with alterations in thoracic and/or abdominal shape. Treatment for Chronic pain is dif cult to treat effectively and may impaired vision is recommended, particularly a problem require analgesics, sometimes including narcotic anal with depth perception, which is speci cally associated gesics. Elderly patients with neuro clining position is often required to allow the soft tissues, logic impairment. Various physical modalities, such as ultra Nutritional Recommendations sound and transcutaneous nerve stimulation, may be Calcium A large body of data indicates that optimal bene cial in some patients. Pain also occurs in the neck calcium intake reduces bone loss and suppresses bone region, not as a result of compression fractures (which turnover. Recommended intakes from an Institute of almost never occur in the cervical spine as a result of Medicine report are shown in Table 28-6. The preferred source of calcium is from dairy prod with psychological symptoms, not always commonly ucts and other foods, but many patients require calcium appreciated. Food sources of calcium are dairy back pain can lead to marked loss of self-image and a products (milk, yogurt, and cheese) and forti ed foods secondary depression. Altered balance, precipitated such as certain cereals, waf es, snacks, juices, and crack by the kyphosis and the anterior movement of the ers. These symptoms can sometimes be in doses 600 mg at a time, as the calcium absorption alleviated by family support and/or psychotherapy. Since vitamin D supplementation at doses that would achieve these serum levels is safe and Note: Pregnancy and lactation needs are the same as for nonpregnant inexpensive, the Institute of Medicine recommends daily women. Adequate ing carbonate are best taken with food since they vitamin K status is required for optimal carboxylation of require acid for solubility. To confirm bioavailability, lism is impaired, such as with long-term warfarin therapy, calcium supplements can be placed in distilled vinegar. Magnesium supplementation may be warranted in standard practice to ensure an adequate calcium and vita patients with in ammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, min D intake in patients with osteoporosis, whether they chemotherapy, severe diarrhea, malnutrition, or alcoholism. Excessive protein intake Calcium citrate 60 mg/300 mg can increase renal calcium excretion, but this can be cor Calcium lactate 80 mg/600 mg rected by an adequate calcium intake. Meta-analyses of studies (OsCal 250) performed in postmenopausal women indicate that Calcium carbonate 500 mg/tablet weight-bearing exercise prevents bone loss but does (Tums 500) not appear to result in substantial gain of bone mass. Exercise also has bene cial effects on available in many countries, obviating the problem of neuromuscular function, and it improves coordination, taking two tablets or using a patch and oral progestin.
Order divalproex cheap
Guideline: Updates on the Management Faltering: Revisiting Implications for Interventions Using of Severe Acute Malnutrition in Infants and Children symptoms stroke order line divalproex. Nutrition during Pregnancy and the Module 4 focuses on anthropometry of Postpartum Period: Why Does it pregnant and postpartum women and girls. Children born to undernourished women girls and girls are more likely to be small for their gestational age, be born Users are encouraged to review Module 1 preterm, die in the frst month of life, and be stunted by age 2 (ibid). Improving the nutritional status of pregnant and postpartum women and girls, as well as all women of reproductive age, will contribute to improved health of women and reduce their risk of mortality, while enhancing the health, growth, and development of their children. Weighing and measuring women and adolescent girls early in pregnancy can help determine their nutritional status and how well their bodies can cope with pregnancy. This information can identify women who may beneft from interventions or enhanced clinical care and can guide counseling and support to promote a healthy pregnancy and improve fetal growth. At the population level, anthropometric data can be used to evaluate trends in nutritional status among pregnant and lactating women and girls, helping to determine whether an intervention is needed. This section provides a brief description of the most common nutrition-related conditions afecting pregnant and postpartum women and girls that can be identifed using anthropometry. The anthropometric measurements and indices used to determine these nutrition conditions are described in the Measurements section. Women of short stature were often stunted as children (meaning they were too short for their age as identifed by the length/height-for-age index). However, surgical delivery is often not available in low-resource settings and, when available, increases risk of maternal morbidity and mortality (Black et al. Since short stature refects past environmental infuence on growth, there are no associated dietary recommendations to address short stature since the condition cannot be reversed. Short stature, which commonly refers to women <145 cm tall, is identifed through height measurement. The result is that she is shorter than would be expected for a healthy girl of her age. Stunting detected during adolescence is usually a result of poor growth during the frst 1, 000 days of life, from pregnancy through age 2, after which it is difcult to regain lost growth and fully recover from the efects of stunting (Victora et al. As with a woman of short stature, if a girl still lives in the same nutritionally poor conditions in which her growth was stunted, she may be at increased nutritional risk. Dietary or other nutritional assessments may help to determine nutritional risk and delivering in a health facility may help reduce the risks of a complicated delivery. A woman or adolescent girl may be underweight/thin because of a rapid deterioration in nutritional status over a short time or chronic (long-term) malnutrition. Thinness may be a result of an inadequate diet; severe, repeated, or chronic illness or infection; or a combination of diet and illness. Some studies have found an association between maternal thinness and maternal mortality, although there is limited research on this association (Black et al. Children of underweight/thin women are at higher risk of intrauterine growth restriction, low birth weight, and preterm birth. In addition, maternal overweight and obesity during pregnancy increase the risk that the child will be overweight or obese (Black et al. Although there have been limited studies exploring the efects of overweight and obesity among pregnant adolescents, evidence suggests that they sufer similar risks, including increased risk of gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and cesarean delivery (Sukalich et al. In addition, although some women lose weight or return to their pre-pregnancy weight, many women retain weight after pregnancy, with an average weight gain of 0. The amount of weight gain (or loss) varies widely, and there is evidence that women who gain excessive weight during pregnancy or were overweight before pregnancy are more likely to retain more weight postpartum (Gore et al. This section describes the anthropometric measurements and indices commonly used to identify nutrition-related conditions in pregnant and postpartum women and girls, as well as the challenges with using them. In addition, bilateral pitting edema, a clinical measure of severe malnutrition, is included because it is frequently assessed alongside anthropometry. Anthropometry measurements can also help to indirectly monitor the growth of the fetus, as good maternal nutritional status and appropriate weight gain during pregnancy contribute to normal/optimal fetal growth. There is no global agreement on the best measures to use, and evidence to to the establish standard measures or cutofs for use in developing countries is insufcient. The guidance Interpretation here refects the current knowledge of the most commonly used anthropometric measurements section. It can be a proxy indicator for pelvic size, which can predict challenges such as obstructed labor. In pregnant women, height can be used to identify women with short stature who may need specialized medical care for a safe delivery. To date, stunting has not routinely been measured among school-age children and adolescents. Height-for-age can be applied to adolescent girls at any time during pregnancy or postpartum. Gaining a healthy amount of weight during pregnancy contributes to a healthy birth for mother and child. Gestational weight gain, also called pregnancy weight gain, is afected by pre-pregnancy weight as well as genetics, health, dietary choices, socioeconomic status, and culture, among other factors. If a woman gains too little weight, she may have a preterm or low birth weight infant; gaining too much weight in pregnancy is associated with retaining excessive weight postpartum, delivering large-for-gestational-age infants, and cesarean delivery, and it may lead to the child being overweight later in life (Siega-Riz et al. To maintain a healthy pregnancy, it is recommended that underweight women gain more weight than their healthy/normal and overweight/obese counterparts, and that overweight and obese women gain less than women of normal weight. Using the adult ranges will probably classify the adolescents as thin more readily and therefore adolescents will be advised to gain more weight. Postpartum women who lose weight return to their pre-pregnancy weight at varying rates because of a number of factors including their pre-pregnancy weight, type of delivery, gestational weight gain, breastfeeding status, and age. Excessive postpartum weight retention is a concern, and evidence suggests it is associated with longer-term overweight and obesity (Endres et al. There is no specifc guideline for how soon after birth to monitor postpartum weight loss and the exact timing of when a woman should return to her pre-pregnancy weight. Bilateral pitting edema can be a clinical sign of a specifc form of severe malnutrition known as nutritional edema, edematous malnutrition, severe malnutrition with edema, or kwashiorkor. However, edema is quite common during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester due to the additional blood and body fuid needed to support the fetus, and typically does not indicate malnutrition. Therefore, edema during pregnancy can be normal or it can indicate other medical conditions, such as pre-eclampsia (particularly if the edema is sudden and in the hands and face) (Swamy and Heine n. It is recommended that pregnant women and girls with edema be assessed further to determine the cause and provided with appropriate treatment as needed.
250mg divalproex with visa
A control group of adoptees whose parents 39 this document is a research report submitted to the U treatment of strep throat divalproex 500 mg without a prescription. This group was viewed as not having a genetic/biological vulnerability to criminal conduct. Four different outcome measures were used to determine the role of GxEs in the development of aggression. Second, adolescent aggressivity was a retrospective scale indexing the aggressiveness of the adoptee during adolescence. Fourth, items pertaining to an adult diagnosis of antisocial personality disorder were used to construct an adult antisocial behavior scale. The results of the multivariate analyses revealed that the biological predisposition measures and the adverse home environment scale had significant main effects on all four outcome measures. The GxE measures also exerted 40 this document is a research report submitted to the U. In this study, GxEs were shown to influence early childhood and adolescent risk of antisocial conduct. Jaffee and her colleagues (2005) also employed an innovative research design to examine the interaction between genetic vulnerabilities and physical maltreatment on conduct problems. Unlike the early studies that used samples of adoptive children to test for GxEs, Jaffee et al. The E-Risk Study is a longitudinal sample of 1, 116 families with twin children born in England and Wales in 1994 and 1995 (two consecutive birth cohorts). The families were interviewed when the twin children were five years old and two years later when the children were seven years old. To assess physical maltreatment, mothers completed an in interview protocol from the Multisite Child Development project. Children were categorized as conduct disordered if their mothers or their teachers indicated that the child displayed three more symptoms of conduct disorder; children scoring below three on the checklist were considered not to have conduct disorder. The unique aspect of their research, however, was the way in which they measured genetic risk. One twin from each twin pair was selected as the target twin and their sibling was included as the co-twin. Jaffee and her associates calculated ordinary least squares regression equations with the continuous measure of conduct disorder as the dependent variable. The measure of genetic risk and the measure of physical maltreatment were included as predictor variables in the models. An interaction term was also created by multiplying the genetic risk score by the physical maltreatment variable. The results of these models revealed a significant main effect for genetic risk (=. The significant interaction term was interpreted as empirical documentation of a GxE in the etiology of conduct disorder. Beaver and Wright (2005) also examined the effect of GxEs on adolescent delinquency. Importantly, Beaver and Wright conceptualized the pubertal development scale as a genetic measure and the delinquent peers scale as the environmental measure. In addition to the main effects of the independent variables, they also included an interaction term 42 this document is a research report submitted to the U. Data for their study came from the publicly available version of the Add Health sample (N=6, 504). However, there was also a significant effect for their proxy GxE measure: the interaction term for pubertal development X delinquent peers exerted a statistically significant effect on delinquency (=. Lastly, Button and her colleagues (2005) examined whether family dysfunction interacted with genes in the creation of antisocial conduct. They measured conduct problems by using five items extracted from the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire. Family dysfunction was indexed by using twelve questions from the General Functioning subscale of the McMasters Family Assessment Device. These questions tapped two dimensions of the home life: family pathology and family health. In general, the results generated from studies indirectly testing for GxEs have revealed the importance of examining the interactive effects of genetic and environmental factors in the development of antisocial behaviors. While useful, these studies have been unable to identify the precise genes that may be implicated in GxEs. To test for a GxE, they employed the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, a prospective study of 1, 037 children born in New Zealand between April of 1972 and March of 1973. Thus far, data have been collected from the participants when they were ages 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, and 26. Remarkably, 96 percent of the original sample was contacted and re-interviewed in the latest wave of data collection. Four different dependent variables indexing antisocial behaviors were used in their analysis. Dunedin participants were assessed for conduct disorder at ages 11, 13, 15, and 18. The third dependent variable used in the analysis was a disposition towards violence scale. Questions such as, when I get angry, I am ready to hit someone, were included in the scale (alpha=. For this scale, male study members nominated one person who knew them very well. These nominated individuals were then contacted and asked a series of questions pertaining to antisocial personality symptoms exhibited by the Dunedin participants. The responses to these items were then summed together to form an additive scale of antisocial personality symptoms (alpha=. The interrelationships among these four different scales were then analyzed and results demonstrated moderate inter-scale correlations. Additional model-fitting techniques revealed that a common factor accounted for the four antisocial behavior measures. As a result a composite index was created by summing together scores for these four scales. Physical maltreatment was measured by using behavioral observations, parental reports, and retrospective reports reported on by Dunedin participants. At the age 3 assessment, independent observers watched the mother and the child interact. Observers who indicated that the mother engaged in two or more of these negative actions were characterized as rejecting their child. Second, at the age 7 and age 9 interviews, parents were presented with a checklist of disciplinary behaviors, including items that tapped physical punishment. Parents who were in the top ten percent of on this scale were coded as unusually harsh disciplinarians. Those children who had more than two primary caregivers were classified as having suffered disruptive caregiver changes. Fourth, at the age 26 assessment, study members completed a retrospective questionnaire asking about incidents of physical abuse occurring before the age of 11. Finally, during the age 26 interviews, Dunedin participants were asked about unwanted sexual abuse. Based on this information, study members were grouped as either having been sexually abused or not having been sexually abused.

