Nootropil
Nootropil 800 mg online
One such condition is the congenital vascular malformation medicine 48 12 nootropil 800mg on line, which results from an abnormal maturing of blood vessels as the baby develops the motherwomb. The doctor will know how to tell the difference and when more testing or treatment is needed. My doctor thinks that my baby had a congenital venous malformation, what does this mean A congenital venous malformation means that some of the blood vessels which should have matured into normal veins did not make it to the final stage of growth. If this happens early, the abnormal blood vessels do not have the form usually seen with blood vessels and appears more like a spongy mass which can involve neighboring body parts. If this happens later in the pregnancy, the blood vessels look more normal but are abnormally small, abnormally large or have unusually connections with other blood vessels. How bad the symptoms related to the malformation are will determine the need for further study and/or treatment. Your child might have a syndrome called the Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome which involves an abnormal maturing of veins, lymph blood vessels and the normal connection between arteries and veins (the capillary blood vessels). It is a congenital vascular malformation which has been present since birth but just noticed now because your child is up walking and playing. X-ray studies may find lower leg deep vein abnormalities like too small or an absent vein in the leg or abdomen and/or the presence of a vein which should have been replaced during the pregnancy but remains to help get blood out of the leg. The lateral varicose vein my also be helping to remove blood from the leg so is important to have. Early on all that is needed to take care of symptoms is the use of support stockings. Your doctor will be able to tell you if this is the problem and, if so, if other treatment will be needed. My child has a congenital venous malformation, are we at risk for other children with the same problem Most congenital venous malformations do not run in the family, in other words, are not genetically determined. You would have to discuss this with your doctor to know for sure if this is a concern for your family. It is uncommon in blood cell), may also increase, but is not a cause of individuals younger than 30 years. All clonal diseases are types of more viscous (thick) so the blood does not fow efciently. The growth of marrow red cell precursors of 150 grams/liter (g/L) of blood would also be increased by can also be studied to examine their ability to grow in the one-third to 200 g/L of blood. Eventually, however, phlebotomy evaluated individually by a hematologist/oncologist, a doctor results in iron defciency. Patients may feel tired after a For more information about choosing a doctor or a treatment phlebotomy and need to rest for a short time. Aspirin is given by mouth and the most common supervision and therapy to keep the hematocrit concentration side efects include upset stomach and heartburn. The drug can reduce Treatment goals for the disease are the rate of platelet formation in the marrow. Patients taking anagrelide l To control symptoms may experience side efects including fuid retention, heart l To decrease the risk of complications and blood pressure problems, headaches, dizziness, nausea and diarrhea. To help prevent pruritus, it is suggested alone cannot control the overproduction of red cells and that patients bathe less frequently. The spleen may some controversial evidence that after long-term therapy become further enlarged. However, it is thought to have much less potential more precisely, post-polycythemia vera myelofbrosis. Immature white cells such as radiophosphorus and alkylating agents, which include may be released from the marrow into the blood. When discontinuing Secondary polycythemia is limited to overproduction of therapy for reasons other than thrombocytopenia, gradual red cells. Development of sustained-release The individual side efects of specifc drugs are discussed in preparations provides a new option for patients; injections the treatment section on pages 3 and 4. Clinical trials are designed to be any reason, treatment should be put in place to bring the accurate and very safe. Patient participation in clinical trials hematocrit to a normal concentration before surgery. Some people may survive longer after diagnosis, perhaps For more information, please visit It is important to know that outcome data can show how groups of people with Telephone/Web Education Programs. The organization also provides information and support to people who have Advocacy. It is set up to coordinate, facilitate and perform basic CancerCare and clinical research on Philadelphia chromosome-negative This publication is designed to provide accurate and authoritative information in regard to the subject matter covered. Hilson7 1Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts; 2Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina; 3Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Illinois; 4Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, St. Its 16,000 members are physicians, physician or medical physicist in light of all the circum technologists, and scientists specializing in the research stances presented. To the contrary, a conscientious international meetings and workshops designed to in practitioner may responsibly adopt a course of action dif crease the competencies of nuclear medicine practitioners ferent from that set forth in the guidelines when, in the andtopromotenewadvancesinthescienceofnuclear reasonable judgment of the practitioner, such course of action medicine. Existing also the art, of dealing with the prevention, diagnosis, alle practice guidelines will be reviewed for revision or renewal, viation, and treatment of disease. The variety and complexity as appropriate, on their fth anniversary or sooner, if of human conditions make it impossible to always reach the indicated. Reproduction or modica guidelines is to assist practitioners in achieving this objective. This guideline describes the technique of performing and interpreting ventilation and perfusion scintigraphy. Results of D-dimer test, if obtained, should be Lung scintigraphy is a diagnostic imaging procedure that noted. History of prior deep venous thrombosis or pul both to evaluate cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders. Pertinent chest radiographic ndings include, but pulmonary distribution of a radioactive gas during breath are not limited to , consolidation, atelectasis, effu ing. Pulmonary perfusion scintigraphy is a diagnostic sions, masses, cardiomegaly, and decreased pul imaging test that records the distribution of pulmonary monary vasculature. Radiographic pulmonary evaluation is be normal in patients with pulmonary embolism. Patient preparation and precautions the most common clinical indication for lung 1. Document the degree of resolution of pulmonary changes in signs or symptoms, a chest radiograph embolism. Radiopharmaceuticals cardiac shunts, pulmonary arterial stenoses, and 99mTc has a half-life of 6 h, a photopeak of 140 keV, arteriovenous stulae and their treatment (6). Nuclear medicine study request but is currently not available in the United States. In women of childbearing age, pregnancy and lac Aerosol imaging is usually performed before tation status should be noted and the procedure perfusion imaging because it is more difficult to performed in a manner to minimize radiation ex deliver a larger dose of the 99mTc aerosol than it is posure. Because both agents are labeled probability of pulmonary embolism may be help with 99mTc, it is extremely important that the ful. Use of validated tools such as the Wells (12) counting rate of the second study is at least 3 to score is preferred. The usual pediatric administered An advantage of aerosol imaging is that images activity is 1.
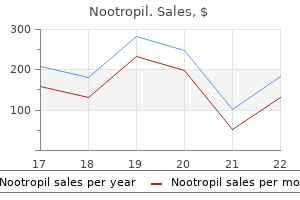
Discount nootropil 800 mg without a prescription
Stone is not only crucial to the Olivia enterprise but plays a very dominant role there medicine quest order line nootropil. This only serves to enhance his previously dominant role and to divide women, as men frequently do, when they make their presence necessary and vital to women. Tus, like Stone, he exhibits a high degree of visibility and also divides women, in the name of lesbian-feminism. Pat Hynes has suggested that there is only an apparent similarity between a strong lesbian, woman identifed self and a transsexual who fashions himself in a lesbian-feminist image. Hynes especially points to the body language of transsexuals where she notes subtle but perceptible diferences between, for example, the way lesbians interact with other women and the way transsexuals interact with women. However, in the fnal analysis, he can only play the part, although the part may at times seem as, or more, plausible than the real woman (as is also the case with the male-to-constructed-female transsexual who appears more feminine than most feminine women). Obviously, women who are in the process of moving out of patriarchal institutions, consciousness, and modes of living are very vulnerable and have gaps. I would imagine that it would be difcult, for example, for Olivia Records to fnd a female sound engineer and that such a person would be absolutely necessary to the survival of Olivia. The question of deception must also be raised in the context of how transsexuals who claim to be lesbian-feminists obtained surgery in the frst place. Deception reaches a tragic point for all concerned if transsexuals become lesbian-feminists because they regret what they have done and cannot back of from the efects of irreversible surgery (for ex ample, castration). Transsexuals merely cut of the most obvious means of invading women so that they seem noninvasive. Tere is a long tradition of eunuchs who were used by rulers, heads of state, and magistrates as keepers of women. One fnds eunuchs associated with temples dedicated to the goddesses from at least 2000 B. The political implications of historical eunuchism and its potential for female control should not be lost upon woman-identifed women. This myth was prevalent in many religious traditions, including the Jewish, Greek, and Christian. Eve was born of Adam; Dionysus and Athena were born of Zeus; and Jesus was generated by God the Father in his godly birth. Mary Daly has written at length in her most recent work, Gyn/Ecology: The Metaethics of Medical Feminism, about the myth of Dionysus. Tese can shed much light on the mythic implications of the transsexually constructed lesbian-feminist. Tus Zeus exterminates the woman and bears his own son, and we have single-parent fatherhood (read mother hood). Whether we are talking about being born of the father, or the self (son), which in the myth are one and the same person (as in the Christian trinity), we are still talking about male mothering. Transsexuals illustrate the way in which men do this, by acquiring the artifacts of female biology. Even though they cannot give birth they acquire the organs that are representative of this female power. He shows that female bio logy, whether exercised in giving birth or simply by virtue of its existence, is representative of female creativity on a profound mythic level. It is he who recognizes that if female spirit, mind, creativity, and sexuality exist anywhere in a powerful way, it is here, among lesbian-feminists. I am not saying that the lesbian-feminist is the only self and woman-identifed woman. It is understandable that if men want to become women to obtain female creativity, then they will also want to assimilate those women who have withdrawn their energies from men at the most intimate and emotional levels. Most ofen, lesbian existence is simply not acknowledged, as evidenced in the laws against homosexuality, which legislate against male homosexuals, but not lesbians. It has been simply assumed that all women relate to men, and that women need men to survive.
Diseases
- Kallmann syndrome with Spastic paraplegia
- Wilms tumor and pseudohermaphroditism
- Mental retardation short stature scoliosis
- Hyperimmunoglobulin E - reccurrent infection syndrome
- Adrenal gland hypofunction
- Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans
- Tinnitus
Discount 800mg nootropil with mastercard
It is helpful to use the patients pre-intubation respiratory rate and depth of ventilation to gauge the post-intubation Vm requirements medicine abbreviations order nootropil online from canada. Some data even suggest that mild hypercapnea is pro tective against lung injury30 and improves red blood cell oxygen delivery. Whether this was causal or coincidental and whether a lower Pplat should be actively sought by lowering Tvis currently unclear. In obese patients or patients with stiff chest walls, Pplat may not accurately reflect transpulmonary pressure or the pres sure distending the alveoli. Shunts are caused by pulmonary (pneumonia, pulmonary contu sion, pulmonary edema, and so forth) or cardiac (patent foramen oval, atrial or ventric ular septal defects) causes. A transthoracic echocardiogram (or ideally transesopha geal echocardiography) bubble study can help to detect cardiac shunts. The treatment of patients with unilateral lung shunts and cardiac shunts is different than the standard open lung recruitment strategies used in most patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure. Ventilation with lower tidal vol umes compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respira tory distress syndrome. When supine, the inferior and posterior portions of the lung can become atelectatic from compression by the heart, thorax, and dia phragm. Atelectasis can worsen gas exchange, decrease compliance, and increase the risk for volutrauma because the Tv prescribed is now directed to a smaller lung vol ume. Preemptively developing multidisciplinary treatment protocols assists in treating this complicated patient population. Mechanical ventilation and acute lung injury in emergency department patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: an observational study. Mechanical ventilation in the emergency department: a call to ac tion in a resource-constrained era. Association between early hyperoxia and worse outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity: early reversible changes in human alveolar structures induced by hyperoxia. Development of fine structural damage to alveolar and capillary lining cells in oxygen-poisoned rat lungs. Association between hyperoxia and mor tality after stroke: a multicenter cohort study. Association between arterial hyperoxia following resuscitation from cardiac arrest and in-hospital mortality. Hypoxemia due to increased venous admixture: influence of cardiac output on oxygenation. Predicting dead space ventilation in critically ill patients using clinically available data. Physiologic rationale for ventilator setting in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. High tidal volumes in mechanically venti lated patients increase organ dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Association between use of lung protective ventilation with lower tidal volumes and clinical outcomes among pa tients without acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. Hypercapnic acidosis is protective in an in vivo model of ventilator-induced lung injury. Low tidal volume ventilation should be the routine ventila tion strategy of choice for all emergency department patients. Low tidal volume should not routinely by used for emer gency department patients requiring mechanical ventilation. Tidal volume reduction in patients with acute lung injury when plateau pressures are not high. Monitoring right-to-left intracardiac shunt in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Prevalence and prognosis of shunting across patent foramen ovale during acute respiratory distress syndrome. Neuromuscular blockade and skel etal muscle weakness in critically ill patients: time to rethink the evidence Inhaled nitric oxide and inhaled prostacyclin in acute res piratory distress syndrome: what is the evidence Effect of prone positioning on the survival of patients with acute respiratory failure. Effect of mechanical ventilation in the prone position on clinical outcomes in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory fail ure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prone positioning in patients with moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome: rationale, indications and limits. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for 2009 influenza A (H1N1) acute respiratory distress syndrome. Reducing the burden of acute respira tory distress syndrome: the case for early intervention and the potential role of the emergency department. Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. Histopathology incidence indicating the number of animals affected following phosgene exposure (from Kodavanti et al. Pulmonary histopathology severity score in rats following subchronic phosgene exposure (from Kodavanti et al. Results of CatReg analysis of severity-graded lung lesions reported by Kodavanti et al. Increased collagen staining of terminal bronchiole/peribronchiolar region (multistage model). It is not intended to be a comprehensive treatise on the chemical or toxicological nature of phosgene. The discussion is intended to convey the limitations of the assessment and to aid and guide the risk assessor in the ensuing steps of the risk assessment process. Comments from all peer reviewers were evaluated carefully and considered by the Agency during the finalization of this assessment. The RfD and RfC provide quantitative information for use in risk assessments for health effects known or assumed to be produced through a nonlinear (possibly threshold) mode of action. The RfD (expressed in units of mg/kg-day) is defined as an estimate (with uncertainty spanning perhaps an order of magnitude) of a daily exposure to the human population (including sensitive subgroups) that is likely to be without an appreciable risk of deleterious effects during a 3 lifetime. The inhalation RfC (expressed in units of mg/m) is analogous to the oral RfD, but provides a continuous inhalation exposure estimate. The inhalation RfC considers toxic effects for both the respiratory system (portal-of-entry) and for effects peripheral to the respiratory system (extrarespiratory or systemic effects). This document does not attempt to develop concentration values protective of acute toxicity. The carcinogenicity assessment provides information on the carcinogenic hazard potential of the substance in question and quantitative estimates of risk from oral and inhalation exposure. The information includes a weight-of-evidence judgment of the likelihood that the agent is a human carcinogen and the conditions under which the carcinogenic effects may be expressed. The quantitative risk estimates are derived from the application of a low-dose extrapolation procedure, and are presented in two ways to better facilitate their use. Second, the estimated concentration of the chemical substance in drinking water or air when associated with cancer risks of 1 in 10,000, 1 in 100,000, or 1 in 1,000,000 is also provided.
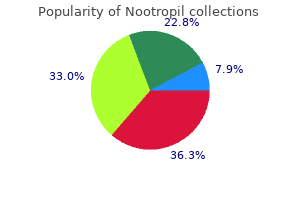
Purchase nootropil 800 mg
Performanceofarectilin and rectilinear biphasic waveform in a short ventricular brillation pig model medications list form buy generic nootropil on-line. Inuence of the headjaw position upon upper national randomized, double-blind multicenter trial. Cervical spine movement monophasic waveform on the incidence and severity of cutaneous burns fol during orotracheal intubation. A comparison of rectilinear spinal motion during intubation: efficacy of stabilization maneuvers in the and truncated exponential biphasic waveforms in elective cardioversion of setting of complete segmental instability. Hyperventilation of transthoracic cardioversion of atrial brillation using a biphasic, truncated induced hypotension during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Ventricular tachycardia rate and self-inatable bags with three different ventilatory devices. Prehospital trial management techniques in a bench model simulating a cardiac arrest patient. The incidence of regurgitation during car nal cardiac pacing: a prospective, controlled clinical trial. Effect of three emergency pacing modalities on of oxygen combined with active cardiac compression-decompression during cardiac output in cardiac arrest due to ventricular asystole. Br J Anaesth 2008;100: of endotracheal intubation: implication for emergency medicine. Endotracheal intubation versus and adopt second-generation supraglottic airway devices as rst choice. Comparison of neurological outcome the Combitube: comparison with the endotracheal airway. The impact of video laryn associated with the use of the esophageal-tracheal Combitube. Can J Anaesth goscopy use during urgent endotracheal intubation in the critically ill. Esophagealgas tracheal intubation during in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resus tric tube airway vs endotracheal tube in prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest. The use of laryngeal tube by nurses in ofthreemethodstoidentifytrachealtubeplacementintheemergencysetting. Aclinicalstudyofimpedancegraph tors for unsuccessful prehospital laryngeal tube placement. Evaluation of the size 4 i-gel airway in one of impedance respirometry distinguish oesophageal from tracheal intubation. Effect of out-of-hospital pediatric endo tracheal tubes may be detected by the debrillator during cardiopulmonary trachealintubationonsurvivalandneurologicaloutcome:acontrolledclinical resuscitation. Advanced cardiac life support before for conrming endotracheal tube placement during emergency intubation. Comparisonofthreedifferentmethodstoconrmtrachealtubeplace cheal tube placement assessment in out-of hospital setting. Real-time tracheal ultrasonography for monary resuscitation from paramedic endotracheal intubation. Ann Emerg conrmation of endotracheal tube placement during cardiopulmonary resus Med 2009;54, 645-52 e1. Reduced effectiveness of vaso dioxide detection in emergency intubation in four groups of patients. Vasopressin versus epinephrine for misplaced intubation within a regional emergency medical services system. Vasopressin for cardiac arrest: meta-analysis of randomized controlled venting gastric ination during bag-mask ventilation in pediatric patients. Am J Cardiol cricoid pressure on preventing gastric insuffiation in infants and children. The effect of cricoid pressure on the cricoid cartilage and corticosteroids for in-hospital cardiac arrest. Airway difficulties caused by epinephrine and neurologically favorable survival after in-hospital cardiac improperly applied cricoid pressure. Amiodarone as Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists and the Difficult Airway compared with lidocaine for shock-resistant ventricular brillation. Successful resuscitation of ventricular brilla with out of hospital cardiac arrest in Japan: controlled propensity matched tion after low-dose amiodarone. Is epinephrine during cardiac arrest recurrent sustained hypotensive ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Microvascular blood venous amiodarone (in a new aqueous formulation) for incessant ventricular ow during cardiopulmonary resuscitation is predictive of outcome. Progressivemyocardialdysfunc administration of a new aqueous formulation of intravenous amiodarone. Arandomisedtrialtoinvestigatetheefficacyof on survival after cardiac arrest: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Randomized clinical trial of magnesium, diazepam, or both after out-of with unfavourable functional outcome and increased in-hospital mortality. Developingavasopressorcombination myocardial infarct size via enhancement of adenosine mechanism in rabbits. Thrombolysis during resuscita tiveness of calcium chloride in refractory electromechanical dissociation. Calcium chloride: cutaneous mechanical thrombectomy during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Use of calcium in prehos tissue plasminogen activator during out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Rescue systemic thrombolysis during cardiopulmonary resuscita cardiac life support drugs increase resuscitation rates from in-hospital cardiac tion. Buffer therapy during out-of-hospital cardiopul sive pulmonary embolism with cardiopulmonary resuscitation: management monary resuscitation. The effects of sodium ery after rescue thrombolysis of presumed pulmonary embolism despite prior bicarbonateduringprolongedcardiopulmonaryresuscitation. A review of 100 cases of cardiac arrest and the relation of Electrolyte abnormalities, poisoning, drowning, accidental hypothermia, potassium, glucose, and haemoglobin levels to survival. The effect of dextran and streptokinase on cerebral function and blood cose concentration after cardiopulmonary resuscitation inuences functional ow after cardiac arrest. A multiple logistic regres plasminogenactivatorandheparinreducescerebralno-reowafterresuscita sion analysis of in-hospital factors related to survival at six months in tion from cardiac arrest: an experimental study in the cat. Intensive Care Med patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital ventricular brillation. Efficacy and safety of thrombolytic ther on perfusion of vital organs during closed-chest resuscitation. Pulmonary embolism as a cause of cardiac hypothermiawithandwithoutvolumeloadinginanischemicmodelofcardiac arrest: presentation and outcome.
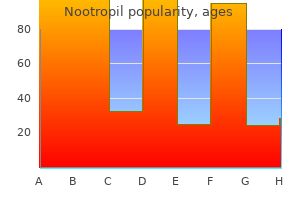
Order cheapest nootropil and nootropil
Recurrence mg/kg) provides effective maintenance therapy for moderate rate may be less in patients with disease limited to the colon symptoms gerd best 800 mg nootropil. These medications are used for frequently Surgery to correct growth retardation must be performed relapsing disease or when high-dose corticosteroids are nec before the completion of puberty. Testing prior to initiating therapy is high-grade mucosal dysplasia, or malignant tumors. Several indicated to identify patients at risk for serious side effects surgical approaches (ileoanal anastomosis, Koch-type conti such as bone marrow failure. Web Resources Bariol C et al: Early studies on the safety and effectiveness of. Differentiating ulcerative colitis from Crohn disease in children and young adults: Report of the working group of the North Ameri General References can Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition and the Crohn and Colitis Foundation of America. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography > 20% of total bilirubin), (2) variably acholic stools, (3) dark in infants is of limited use and highly dependent on the urine, and (4) hepatomegaly. Prolonged neonatal cholestasis (conditions with de creased bile flow) has intrahepatic and extrahepatic causes. Histologic examination of tissue obtained by percutaneous liver this diagnosis is considered in infants with jaundice, hepa biopsy increases the accuracy of differentiation to 95% tomegaly, vomiting, lethargy, fever, and petechiae. Infectious agents associated with neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis include herpes simplex Elevated total and conjugated bilirubin. Although hep atitis C may be transmitted vertically, it rarely causes neona General Considerations tal cholestasis. The degree of liver cell injury caused by these Intrahepatic cholestasis is characterized by hepatocyte dys agents is variable, ranging from massive hepatic necrosis function and patency of the extrahepatic biliary system. A (herpes simplex, enteroviruses) to focal necrosis and mild specific cause can be identified in about 50% of cases. It can be confirmed least invasively by hepatobiliary is jaundiced, may have petechiae or rash, and generally scintigraphy using technetium-99m (99mTc)-diethyliminodi appears ill. Characteristic histologic features of intrahepatic and extrahepatic neonatal cholestasis. Intrahepatic Extrahepatic Intrahepatic Extrahepatic Preterm infant, small for gesta Full-term infant, seems well Giant cells +++ + tional age, appears ill Lobules Disarray Normal Hepatosplenomegaly, other Hepatomegaly (firm to hard) Portal reaction Inflammation, minimal Fibrosis, lymphocytic organ or system involvement fibrosis infiltrate Incomplete cholestasis (stools Complete cholestasis (acholic Neoductular Rare Marked with some pigment) stools) proliferation Associated cause identified Polysplenia syndrome, equal right Other Steatosis, extramedul Portal bile duct plug (infections, metabolic, and left hepatic lobes lary hematopoiesis ging, bile lakes familial, etc) Stools may be normal to pale in color but are seldom acholic. Macular, papular, vesicular, or petechial Clinical symptoms usually appear in the first 2 weeks of life, rashes may occur. Poor oral intake, natal liver failure, hypoproteinemia, anasarca (nonhemolytic poor sucking reflex, lethargy, and vomiting are frequent. Diagnostic Studies Treatment Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and signs of mild hemoly Most forms of viral neonatal hepatitis are treated symptomat sis are common. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy shows decreased hepatic Prognosis clearance of the circulating isotope with excretion into the Multiple organ involvement is commonly associated with gut. Careful ophthalmologic examination may be useful for neonatal infectious hepatitis and has a poor outcome. Persistent liver disease results in mild chronic hepa lial cells, the presence of intranuclear acidophilic inclusions titis, portal fibrosis, or cirrhosis. The liver in most infants of herpes simplex, or positive immunohistochemical stains who recover from congenital viral infection is left without for several viruses can be diagnostic. Chronic cholestasis, although rare following infec lobular disarray characterized by focal necrosis, multinucle tions, may lead to dental enamel hypoplasia, failure to thrive, ated giant-cell transformation, and ballooned pale hepato biliary rickets, severe pruritus, and xanthoma. Portal changes are not striking, but modest neoductular proliferation and mild fibrosis may occur. Galac transmission occurs occasionally transplacentally and pri tosemia, congenital fructose intolerance, and tyrosinemia marily from exposure to maternal blood at delivery. These infants may also have concomi ers, fetal and infant acquisition risk is greatest if the mother tant bacteremia. These findings are neonatal hepatitis may be indistinguishable from infectious markers for circulating infectious virus; however, hepatitis B causes. In such cases, progressive jaundice, massive hepatocyte necrosis, collapse of the reticulum frame stupor, shrinking liver size, and coagulation abnormalities work, minimal inflammation, and occasional pseudoacinar dominate the clinical picture. Survival without liver transplantation is rare, but is renal failure usually follow. Histologically, the liver shows associated with reasonable repair of liver architecture. If not ciencies, other genetic disorders, or certain precipitants asso given at birth it can be administered as late as 7 days ciated with neonatal liver disease feature intrahepatic postpartum as long as the infant has received the vaccine. Enzyme Deficiencies and Other Inherited Disorders Most bacterial liver infections in newborns are acquired by transplacental invasion from amnionitis with ascending Early specific diagnosis is important because dietary or spread from maternal vaginal or cervical infection. Jaundice appears early and is of the permanent in several disorders as long as the diet is main mixed type. As with other genetic disorders, parents of the picture is that of diffuse hepatitis with or without microab affected infant should be offered genetic counseling. The most common organisms involved are Escherichia some disorders, prenatal genetic diagnosis is available. Isolated Cholestasis caused by metabolic diseases such as galac neonatal liver abscess caused by E coli or Staphylococcus aureus tosemia, fructose intolerance, and tyrosinemia may be is associated with omphalitis or umbilical vein catheterization. Neonatal screening programs for galactosemia usually detect the disorder before cholestasis C. This on bile secretion produced by bacterial products (endotox occurs in premature infants with respiratory distress, severe ins) and inflammatory cytokines. When these Treatment of the infection leads to prompt resolution of perinatal conditions develop in association with gastrointes the cholestasis without hepatic sequelae. Contributing fac disorder may be indistinguishable from extrahepatic causes in tors may include toxicity of intravenous amino acids, dimin 10% of cases. Early introduction of feedings has Intrauterine growth retardation, prematurity, poor feed reduced the frequency of this disorder. The prognosis is ing, emesis, poor growth, and partially or intermittently generally good. Occasional cases of cirrhosis, liver failure, acholic stools are characteristic of intrahepatic cholestasis. A recent study suggests that oral rash, or congenital heart block is usually also present.
Syndromes
- Is there nausea?
- Light-headedness
- The type of spider
- Know how much you or your child weighs before giving these medicines.
- Convulsions
- Occupational therapy
- Nerve conduction velocity test may also be done.
- Tube from the mouth into the stomach to empty the stomach (gastric lavage)
- Your groin or neck area will be cleaned and numbing medicine (anesthetic) will be applied to the skin.
- Chronic unilateral obstructive uropathy
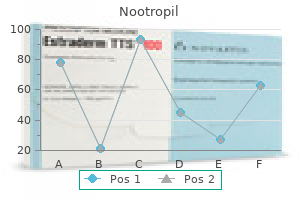
Cheap nootropil 800mg fast delivery
Appendicitis Patient is septic (see sepsis) Arterial Occlusion Requiring immediate surgery nature medicine purchase 800 mg nootropil free shipping, transfer or infusion of blood thinners. Conditions Key Indicators Status Epilepticus Continuous seizure or repeated seizures without returning to an alert baseline of over 20 minutes. Critical care is usually, but not always, given in a critical care area, such as the coronary care unit, intensive care unit, pediatric intensive care unit, respiratory care unit, or the emergency department. It should be used only once per date even if the time spent by the individual is not continuous on that date. More fluid is appropriate only if patient is dehydrated or if insensible losses are increased. After 72 hours of the initiation of the therapy, the patient will be evaluated by the respiratory therapist for pulmonary stability. If baseline hemoglobin is 9 g/dL or higher, may require red cell exchange transfusion. If effective (improved working of breathing, respiratory rate, Albuterol Increased work of breathing wheezing, aeration) order scheduled albuterol 2-4 puffs with spacer or 2. Management of sickle cell disease: Summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members. Corticosteroids for acute chest syndrome in children with sickle cell disease: Variation in use and association with length of stay and readmission. The use of incentive spirometry in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease to reduce the incidence of acute chest syndrome. Incentive spirometry to prevent acute pulmonary complications in sickle cell diseases. Comparison of automated red cell exchange transfusion and simple transfusion for the treatment of children with sickle cell disease acute chest syndrome. Exchange versus simple transfusion for acute chest syndrome in sickle cell anemia adults. Erythrocytapheresis in children with sickle cell disease and acute chest syndrome. They are current at the date of publication and are reviewed on a regular basis to align with the best available evidence. External viewers are encouraged to consult other available sources if needed to confirm and supplement the content presented in the clinical pathways. The information should not be used in place of a visit, call, consultation or advice of a physician or other health care provider. Thus, we ventilate our patients with pressure differences Volume which are minute in comparison to the total pressures in play in the environment around them, or even to the pressures in their own cardiovascular system. Venous return pressure will overcome intrathoracic pressure, and the heart will fill normally. The collaborative protocols have been developed to serve all the levels of certification within New York State. Each region will determine which levels will be credentialed to practice within their jurisdiction. Advanced providers are also responsible for, and may implement, the standing orders indicated for the preceding levels of care. There is a training module available that must be reviewed by every advanced provider prior to utilizing these protocols. The collaborative protocol formulary exists as a minimum guideline for all agencies operating within these protocols. Pursuant to the provisions of Public Health Law, the individual having the highest level of prehospital medical certification, and who is responding with authority (duty to act) is responsible for providing and/or directing the emergency medical care and the transportation of a patient. These protocols are not intended to be absolute treatment documents; they are principles and directives, which are sufficiently flexible to accommodate the complexity of patient management. No protocol can be written to cover every situation that a provider may encounter and this set of protocols is not a substitute for the judgment and experience of providers. Providers are expected to utilize their best clinical judgment and deliver care and procedures, according to what is reasonable and prudent for specific situations. It is expected that any deviations from protocol shall be documented and reviewed, according to regional procedure. The patient may be covered and, if allowed by law enforcement, may be moved to an adjacent private location. The provider must have the ability to immediately remove any mechanical restraints that hinder patient care at all times 2016 26 (2-5) General: Airway Management and Oxygen Delivery Criteria Providers may operate as outlined below. Do not remove or unscrew the cap, unless no other means of accessing the device is possible o Remove any clamps on the vascular access device, and slowly withdraw 10 mL of fluid from the port o Inject 5 mL normal saline. Treat medical or traumatic condition per protocol o Assess pump function and circulation by listening to the motor of the pump over the heart and observing the green light on the system control device o Assess perfusion, based on mental status, capillary refill, and skin color. In cases of obesity, utilize the ideal weight (as indicated by the length) for dose calculations. Delmonico n international conference of transplant physicians, sur recipient bilateral pneumonectomy and lobar implantation. A geons, and allied health professionals was held in Van the use of live donors is occurring in cases in which the po couver, Canada, on September 15 and 16, 2005 to address the tential recipient mortality is high while awaiting for lung al care of the live lung, liver, pancreas, and intestine organ do lografts from a deceased donor. The Vancouver Forum was convened under the auspices however, the practice may expand to include elective patients of the Ethics Committee of the Transplantation Society. Donor Evaluation world, including participants from the following continents: the goals of donor selection are to identify donors with Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North and South America. This Vancouver Forum fol unrelated individuals with emotional attachment to recipient lowed a conference convened in Amsterdam on the care of and/or family. Each organ the necessity of two live lung donors for a single recip work group addressed the following topics in concert and ient also brings a consideration of both parents as donors for reported their findings in a plenary presentation to all partic the potential recipient. The Vancouver Forum also provided an opportunity the donor evaluation is a multi-phased process that for the Ethics Committee of the Transplantation Society to begins with the potential recipient and family providing the address issues of informed consent, the responsibilities of the names of potential donors with basic health information and transplant team, live donor selection, autonomy and satisfac height, weight, age, relationship, and smoking history. An ethics statement of the liminary psychosocial evaluation of selected donors is per Vancouver Forum pertaining to these issues will be published formed to assess the desire to donate. This evaluation in separately by the Ethics Committee of the Transplantation cludes a determination of the donor motivation, pain Society. The transplant community has a responsibility for tolerance, feelings regarding the possible death of the poten the care of the live organ donor. The death of a live donor is a tial recipient (and the donor) and the ability of the potential tragedy of immeasurable proportion that brings an ethical donor to be separated from family responsibilities and career dimension distinct from the complications that might be ex obligations. Report from the Thoracic Group Prospective donors should be informed of the morbid Live donor lung transplantation generally involves ity associated with lobectomy and the potential for mortality, three simultaneous operations: two donor lobectomies and a as well as for potential negative recipient outcomes in regard to life expectancy and quality of life after transplantation.
Buy nootropil overnight
Audiologic Evaluation of Infants and Children steroid therapy may reverse the loss if initiated right away symptoms 4dp3dt proven nootropil 800 mg. If hearing impairment is suspected, the child should be Sounds are presented at various intensity levels, and the referred to an audiologist for testing, and to an otolaryngolo audiologist watches closely for a reaction, such as change gist for further evaluation and treatment. The management of in respiratory rate, starting or stopping of activity, startle, hearing loss depends on the type and severity of impairment. This method is highly Conductive hearing loss is typically correctable by addressing tester-dependent and error-prone. For example, hearing loss due to chronic effusions Auditory stimulus is paired with positive reinforcement. Cochlear implantation is an option for some responds to sound stimulus by performing an activity, children with severe-profound loss, and at the time of this such as putting a peg into a board. The child indi Unlike hearing aids, the cochlear implant does not amplify cates when he or she hears a sound. Children with hearing loss should receive and otoacoustic emission testing may be used if a child ongoing audiologic monitoring. Referral Joint Committee on Infant Hearing: Year 2000 position statement: A child who fails newborn hearing screening or has a Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and inter suspected hearing loss should be referred for further audio vention programs. Available at: be tested in children with a history of developmental delay, Other culprits include adenoviruses, coronavi Characteristics of illness and antibody response. Clinical Findings insufficient evidence of benefit to warrant the use of antibi the patient usually experiences a sudden onset of clear or otics for common cold symptoms. Oral decongestants have mucoid rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, sneezing, and sore been found to provide some symptomatic relief in adults but throat. Cough suppression at usually not a prominent feature in older children and adults, night is the number one goal of many parents; however, the in the first 5 or 6 years of life it can be as high as 40. The nose, throat, and tympanic most experts to be effective in adults and adolescents, but membranes may appear red and inflamed. Use of shows the duration of cough, sore throat, and rhinorrhea in narcotic antitussives is discouraged, as these have been asso adults with rhinovirus-proven infections. Parents should be informed due to shedding of epithelial cells and influx of neutrophils. Rhi should be added to the water or the device should be cleaned nosinusitis acknowledges that the nasal and sinus mucosa are at least every 3 days. Available scientific data suggest that cold and cough med ications are generally not effective in children, and may be associated with serious adverse effects. It is almost always S pneumoniae, H influenzae (nontypeable), M catarrhalis, preceded by a viral upper respiratory infection (cold). The maxillary and ethmoid and may commonly include nasal drainage, nasal conges sinuses are most commonly involved. These sinuses are tion, facial pressure or pain, postnasal drainage, hyposmia or present at birth, forming in the third to fourth gestational anosmia, fever, cough, fatigue, maxillary dental pain, and ear month. Frontal helpful in making the diagnosis, as the findings are essen sinusitis is unusual before age 10 years. Occasionally, sinuses may be tender to percussion, but immune pathogenic processes is believed to underlie the this is typically seen only in older children and is of question development of rhinosinusitis in children. Transillumination of the sinuses is difficult to bacterial infections play integral roles in the pathogenesis. If the patient is hospitalized because of nate is recommended as first-line therapy. Cefuroxime, cef rhinosinusitis-related complications, blood cultures should podoxime, and cefdinir are recommended for patients with a also be obtained. Macrolides should Imaging of the sinuses during acute illness is not indi be reserved for patients with an anaphylactic reaction to cated except when evaluating for possible complications, or penicillin. Intravenous therapy with nafcillin or clindamy as a preseptal cellulitis, but can progress to postseptal celluli cin plus a third-generation cephalosporin such as cefotaxime tis, subperiosteal abscess, orbital abscess, and cavernous should be initiated until culture results become available. Associated signs and symptoms include Topical decongestants and oral combinations are fre eyelid edema, restricted extraocular movements, proptosis, quently used in acute rhinosinusitis to promote drainage. The most common maxillary Patients with underlying allergic rhinitis may benefit from complication is overlying cheek cellulites. For reasons that are unclear, nasal decongestants should not be used for more than 3 days male adolescents seem to be at higher risk for intracranial due to risk of rebound edema. Frequently, children with complicated rhinosinusitis have no prior history of sinus infection. No information is American Academy of Pediatrics: Clinical practice guidelines: available on the rate of complications in ambulatory patients Management of sinusitis. Sinus and Allergy Health Partnership: Antimicrobial treatment Treatment guidelines for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis. Chronic rhinosinusitis is diagnosed To minimize the number of children who receive antimi when the child has not cleared the infection in the expected crobial therapy for uncomplicated viral upper respiratory time but has not developed acute complications. Important factors to consider include aller in day care, and have not been on recent antibiotic therapy, gies, anatomic variations, and disorders in host immunity. Physician prescribes: Amoxicillin/clavulanate No 9 (high dose) 8 Physician prescribes: Cefuroxime Cefuroxime Cefpodoxime Are there allergies Cefpodoxime Cefdinir to penicillin Yes Cefdinir A Azithromycin No Clarithromycin C 16 17 10 Is patient Clinician provides Physician prescribes cured or Yes appropriate usual to high-dose Improved High-dose amoxicillin = 90 mg/kg/d in 2 divided doses No High-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate = 90 mg/kg/d amoxicillin; 21 6. If allergy manifests as anaphylaxis, 22 macrolides should be prescribed instead of cephalosporins: Subsequent modifications 1. Bilateral atresia results in severe respiratory distress at birth and requires immediate placement of an oral airway, Treatment and otolaryngology consultation for a more permanent surgi A. In the very young child, this may be Recurrent rhinitis is frequently seen in the office practice of the only procedure that should be performed. Allergic Rhinitis films have been reported in the adenoids of children with Allergic rhinitis has significant morbidity and may contrib chronic rhinosinusitis, and may explain the resistance of ute to the development of rhinosinusitis and asthma exacer these infections to standard antibiotic therapy. Symptoms include nasal congestion, frequent sneez ing, rubbing of the nose, and clear rhinorrhea. Treatment with nasal corticosteroids is effective of developing sinuses and impairment of midface growth. Montelukast, a leukotriene antagonist, has children, and may be indicated in addition to adenoidectomy.

Purchase nootropil cheap online
Key strategies for success symptoms joint pain fatigue buy nootropil mastercard, arrived at over time, included targeting all adult inpatients, adding forcing functions with hard stops to guarantee a risk assessment was done, using algorithmic logic, grouping risk factors for the convenience of providers, and auto-populating some risk factors. Importantly, the addition of risk score points is performed behind the scenes, with options appropriate for the point total displayed as the default prophylaxis choice. In addition, a full suite of educational and faculty engagement techniques were used. Certain key elements, such as weight and creatinine clearance, were pulled into the order set and made available to the ordering provider at the point of care. Mandatory selection of high, moderate, or low risk was mandated on admission and transfer. Opting out of anticoagulant prophylaxis for moderate or high-risk patients led to capture of anticoagulant contraindications and default choices for mechanical prophylaxis. Track Performance With Metrics this chapter addresses the importance of measurement in tracking and preventing hospital associated venous thromboembolism and discusses key metrics and strategies for using them effectively. The previous chapter discussed how to plan for measurement; this chapter explains measurement more fully and how to use it to meet your goals. This inability may reflect lack of institutional support and prioritization, failure to create a protocol with measurable operational definitions, or failure to appreciate which particular metrics can drive improvement efforts and effect real change. It is required to assess baseline performance and understand the health care delivery process. Many measures also satisfy public reporting and the reporting requirements of regulatory bodies, many of which are increasingly tied to reimbursement. Good measurement also informs ongoing improvement efforts and illuminates pockets of strengths and weaknesses (opportunities for improvement) within the system, allowing for smarter deployment of precious time and resources and concurrent remediation of failures in the health care delivery process. Categories of Measurement Measures are commonly categorized as assessing structure, process, or outcomes, complemented by balancing measures that monitor for unintended negative consequences. Process measures examine the reliability of crucial steps in health care delivery. This clinical endpoint is unsuitable as a lone metric for performance tracking, however, because the events are too infrequent, subclinical, or delayed in onset to provide timely and useful feedback to the team. Thus, it should be coupled with process and structural measures to accurately track performance. Balancing measures monitor for potential unintended adverse consequences of interventions. This is a fourth category of measures that improvement teams may want to consider. Individual hospitals may already be collecting data on most if not all of these measures. Exclusion criteria are patients <18 years of age, a length of stay <2 days or >120 days, patients with comfort measures only, and patients enrolled in clinical trials. First, the use of any prophylaxis equates with appropriate prophylaxis in these measures. Therefore, hospitals can appear to have very high performance on these measures even if the majority of patients do not receive adequate prophylaxis. In addition, hospitals with radically different prophylaxis patterns and different levels of adequate prophylaxis might look exactly the same under this measurement approach. The ability to adjust prophylaxis after these time intervals pass is not assessed. Ideally, measures will capture prophylaxis across the patient stay, not during narrow 24-hour time periods. Third, this approach uses retrospective data collection, leaving no opportunity to address deficits in care proactively. The following strategies have been successfully used in a wide variety of hospitals in large-scale national collaborative 5,6 efforts. Improvement teams can review and prioritize which options are most feasible and impactful in their setting. This additional information can also help the team understand where the process is failing so they can make appropriate adjustments. A review could quickly identify whether a patient is on an anticoagulant, mechanical prophylaxis, both, or neither. Many hospitals can pull those data elements into the report itself; others have a unit champion perform this review. Scripted phone calls, pages, or notes can then be used, if appropriate, to contact the responsible prescribing provider to ask for clarification or a prophylaxis order. In addition, providers can be alerted to prophylaxis oversights, which might create opportunities to improve care as well as to educate staff. Moreover, sampling active inpatients may allow insights into process barriers and valid reasons to amend the new processes to emerge more readily. A sampling strategy that uses 20 to 30 randomly selected patient charts per month can be statistically appropriate for most hospitals; it is also relatively quick and easy. To make the time commitment more manageable, charts can be audited each week with the results rolled up into monthly reports. Available data collection resources in any given hospital may dictate methods and definitions. It is often helpful to pilot the metric definitions and steps in data collection to identify and solve stumbling blocks. When you assess audit results, questions that should be answered include: Did the reviewers arrive at the same risk level There are also questions that sequential pilots of the audit tool should help answer: How much time is acceptable in perioperative or trauma settings for a patient not to be on pharmacologic prophylaxis Depending on the scope of the initiative, it may make sense to exclude: o Patients receiving obstetric care. As an example, a roster of all adult inpatients hospitalized for more than 48 hours could be assigned a random number (a number of free random number generators are available on the Internet). The main disadvantage is the potential that some small but important patient group could be underrepresented. The need for unambiguous operational definitions of ambulation and mobility, bleeding risk factors, and a host of other terms will become apparent during the piloting process. There are a number of variations, depending on local resources and the sophistication of the reporting tool. The orange color represents patients with a lab contraindication within the last 2 days who are on mechanical prophylaxis only. The automation allows monitoring of virtually every inpatient on a daily basis as opposed to focusing only on the first hospital day or on a relatively small subset of patients captured by sampling techniques. This method of audit or measurement can spur concurrent intervention (aka measure-vention), which will be discussed in more detail in the next chapter. Patterns of prophylaxis by service and unit will very quickly become apparent, focusing the attention of the improvement team on underperforming units. Thus, a few point-in-time assessments have the potential to lead to under-prophylaxis as well as over-prophylaxis.

Buy 800 mg nootropil free shipping
Pituitary microadenomas may respond to pituitary surgical removal if a tumor is present 1950s medications purchase nootropil 800mg with amex. Hood S et al: Prevalence of primary hyperaldosteronism assessed Prognosis by aldosterone/renin ratio and spironolactone testing. If it is benign, cure is to be expected Mulatero P et al: Diagnosis of primary aldosteronism: From screening to subtype differentiation. Potency/mg Compared with Potency/mg Compared with Cortisol Adrenocorticosteroid Trade Names Cortisol (Glucocorticoid Effect) (Sodium-Retaining Effect) Glucocorticoids Hydrocortisone (cortisol) Cortef 1 1 Cortisone Cortone Acetate 0. Glucocorticoids exert a direct or permissive effect on virtu ally every tissue of the body; major known effects include the A. Stimulation of fat breakdown (lipolysis) and redistribu stress with resultant hypoadrenocorticism tion of body fat B. Marked retention of sodium and water, producing edema, phosphorus excretion increased blood volume, and hypertension (more common in endogenous hyperadrenal states) 4. Potassium loss with symptoms of hypokalemia cellular response to inflammation and hypersensitivity 3. Negative nitrogen balance, with loss of body protein and bone decreased wound healing protein, resulting in osteoporosis, pathologic fractures, and aseptic bone necrosis 7. Suppression of growth, retarded skeletal maturation partment volume and pressure 3. Excessive appetite and intake of food When prolonged use of pharmacologic doses of glucocorti 2. Activation or production of peptic ulcer coids is necessary, clinical manifestations of Cushing syn 3. Side effects may occur with the use of (particularly in children with hepatic disease) synthetic exogenous agents by any route, including inhala 4. Lowering of resistance to infectious agents; silent infection; decreased inflammatory reaction Use of a larger dose of glucocorticoids given once every 48 1. Susceptibility to fungal infections; intestinal parasitic infections hours (alternate-day therapy) lessens the incidence and 2. Euphoria, excitability, psychotic behavior, and status epilepticus with electroencephalographic changes Prolonged use of pharmacologic doses of glucocorticoids 2. Thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, cerebral hemorrhage ally does not restart until the administered steroid has been 2 H. Myocarditis, pleuritis, and arteritis following abrupt cessation of several weeks. Nephrosclerosis, proteinuria abruptly (if the condition for which it was prescribed allows) 4. Acne (in older children), hirsutism, amenorrhea, irregular menses because adrenal suppression will be short-lived. Posterior subcapsular cataracts; glaucoma is advisable to educate the patient and family about the signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency in case problems arise. If tapering is not required for the underlying 5 mg/m2/d given only in the morning. This will allow the disease, the dosage can be rapidly decreased safely to the adrenal axis to recover. The symptoms of pheochromocytoma are generally When an alternate-day schedule is followed, plasma cortisol caused by excessive secretion of epinephrine or norepineph is measured the morning before treatment. Plasma cortisol rine and most commonly include headache, sweating, tachy concentration in the physiologic range (> 10 mg/dL) indi cardia, and hypertension. Exogenous hypertension, dizziness, weakness, nausea and vomiting, steroids may then be discontinued safely, although it is diarrhea, dilated pupils, blurred vision, abdominal and pre advisable to continue giving stress doses of glucocorticoids cordial pain, and vasomotor instability (flushing and pos when appropriate until recovery of the response to stress has tural hypotension). After basal physiologic adrenal function returns, the Laboratory diagnosis is possible in more than 90% of adrenal reserve or capacity to respond to stress and infection cases. A blockers can create false-positive results) is the most sensitive plasma cortisol concentration greater than 18 mg/dL at 60 test and the gold standard for diagnosis. Intermediate values may Even if the results of testing are normal, patients who require additional testing, with urinary vanillylmandelic acid have received prolonged treatment with glucocorticoids may and urinary total metanephrines providing the highest spec develop signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency during ificity. Provocative tests using histamine, tyramine, or gluca acute stress, infection, or surgery for months to years after gon and the phentolamine tests may be abnormal but are treatment has been stopped. Gulliver T, Eid N: Effects of glucocorticoids on the hypothalamic Laparoscopic tumor removal is the treatment of choice; pituitary-adrenal axis in children and adults. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program: Long-term caution and with the patient properly stabilized. Oral phe management of asthma in children: Safety of inhaled cortico noxybenzamine or intravenous phentolamine is used preop steroids. The tumor can be nosis is poor in patients with metastases, which occur more located wherever chromaffin tissue (adrenal medulla, sym commonly with large, extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas. Ilias I, Pacak K: Current approaches and recommended algorithm It may be multiple, recurrent, and sometimes malignant. Type 1 diabetes results from immunologic damage to the insulin-producing cells of the pancreatic islets. It is associated with islet cell About 6% of siblings or offspring of persons with type 1 antibodies (immunologic markers), diminished insulin pro diabetes also develop diabetes (compared with prevalence in duction, and being ketosis-prone. It occurs most frequently in over because not all second identical twins develop diabetes. However, renal damage from cyclosporin pre antibodies and often is associated with a family history of cludes its use. White blood cells are found in the islets of newly diabetes in several generations. Others have specific mutations and are months to years prior to diagnosis in the serum of over 90% of best treated with sulfonylurea medications after receiving patients who will develop type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes has a strong genetic component, although the inherited defects vary in different families. Obesity (particu larly central) and lack of exercise are often major environ Treatment mental contributing factors. The prevalence is increased among treatment are (1) insulin type and dosage, (2) diet, (3) exer females, which may be related to its association with the cise, (4) stress management, and (5) blood glucose and polycystic ovary syndrome. All must be considered to obtain safe and darkening of the skin over the posterior neck, armpits, or and effective metabolic control. Type 1 Diabetes reliably administer insulin without adult supervision because Free antibody screening is now available for families having they lack fine motor control and may not understand the a relative with type 1 diabetes (1-800-425-8361). Type 2 Diabetes Education about diabetes for all family members is essential for the home management of diabetes. The use of an educa the prevention of type 2 diabetes was evaluated in a large tional book (see Understanding Diabetes in the references) can study, the Diabetes Prevention Program. All caregivers need to learn about that 30 minutes of exercise per day (5 days/wk) and a low-fat diabetes, how to give insulin injections, perform home blood diet reduced the risk of diabetes by 58%. Meeting with a counselor to express these feelings at the classic symptoms of polyuria, polydipsia, and weight the time of diagnosis helps with long-term adaptation. Other cases may be detected by finding Insulin has three key functions: (1) it allows glucose to pass glucosuria on routine office urinalysis. Up to 50% of new into the cell; (2) it decreases the physiologic production of cases of diabetes used to be diagnosed in patients presenting glucose, particularly in the liver; and (3) it turns off ketone in coma, but most are now diagnosed before the individuals production.
Purchase nootropil overnight delivery
Determination of risk factors for deep venous thrombosis in Not specific to 2008 hospitalized children surgical patients Does not address Ansari et Risk stratification and utilisation of thrombo-embolism prophylaxis question of al treatment junctional tachycardia buy nootropil on line. Multimodal thromboprophylaxis for total hip and knee arthroplasty Not best available 2007 based on risk assessment evidence Not best available Gangired Risk factors and clinical impact of postoperative symptomatic evidence (not dy et al. Factors leading to decreased rates of deep vein thrombosis and Not best available 2007 pulmonary embolism after total knee arthroplasty evidence the 2007 John Charnley Award. Patients reported Soohoo et Factors predicting complication rates following total knee in a more recent al. Not best available Surgery: Effects of Timing of First Dose and Risk Factors for 2005 evidence Thromboembolism and Bleeding Complications on Efficacy and Safety Gray et al. Outcome of hip arthroplasty in octogenarians compared with Not best available 2005 younger patients evidence Gregory Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in hip and knee arthroplasty Not best available et al. Piovella evidence (not An epidemiological study based on postoperative screening with et al. Lower-limb deep-vein thrombosis in a general hospital: risk factors, Not specific to 2005 outcomes and the contribution of intravenous drug use surgical patients Systematic Edmonds review, Evidence-based risk factors for postoperative deep vein thrombosis et al. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip Not best available 2003 arthroplasty. A prospective and randomised clinical study evidence Kinkel et Revision total hip arthroplasty: the influence of gender and age on Not best available al. Incidence and natural history of deep-vein thrombosis after total Not best available 2002 knee arthroplasty. Perioperative deep vein thrombosis in Chinese patients undergoing evidence (not 2002 craniotomy specific to elective arthroplasty) Wahlande Factor V Leiden (G1691A) and prothrombin gene G20210A Not best available r et al. Factors leading to low incidence of deep vein thrombosis after Not best available 1991 cementless and cemented total knee arthroplasty evidence the incidence of deep vein thrombosis after cementless and Not best available Kim 1990 cemented knee replacement evidence Stern et Not best available Total knee arthroplasty in obese patients al. Evaluation of low-dose warfarin therapy evidence 1989 Not best available Hu 1989 Prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis in total hip surgery evidence Not best available Stringer et Deep vein thrombosis after elective knee surgery. Low incidence of deep-vein thrombosis after cementless total hip Insufficient data 1988 replacement Lynch et Deep-vein thrombosis and continuous passive motion after total Not best available al. An incidence study evidence Sikorski the natural history and aetiology of deep vein thrombosis after total Not best available et al. Not best available subcutaneous heparin in the prevention of postoperative deep vein 1977 evidence thrombosis Kelsey et Not best available Prediction of thromboembolism following total hip replacement al. Excluded Studies Considered for Risk Factors for Bleeding Author Title Reason for Exclusion Goddard et al. Total knee replacement in patients with end-stage Not best available 2010 haemophilic arthropathy: 25-year results evidence the influence of perioperative coagulation status on Excludes patients with Karkouti et postoperative blood loss in complex cardiac surgery: a pre-existing al. Risk factors for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal Does not investigate 2010 dissection for gastric lesions risk factor of interest Assessment of the risk of bleeding in patients undergoing Cosmi et al. Does not address percutaneous coronary interventions-incidence, predictors, 2009 question of interest and prognostic implications Kinnaird et Bleeding during percutaneous intervention: Tailoring the Systematic review, al. Not best available with type 1 von Willebrand disease undergoing 2009 evidence adenotonsillar procedures High-volume surgeons in regard to reductions in operating Yasunaga et Does not examine risk time, blood loss, and postoperative complications for total al. The outcome of cementless total hip arthroplasty in evidence (retrospective 2009 haemophilic hip arthropathy case series) Perioperative international normalized ratio level is a poor Not best available Blasdale et al. Excluded Studies Considered for Risk Factors for Bleeding Author Title Reason for Exclusion Guidelines on the assessment of bleeding risk prior to Chee et al. British Committee for 2008 bibliography screened Standards in Haematology Chiang et al. Total knee arthroplasty for severe haemophilic arthropathy: Insufficient data 2008 long-term experience in Taiwan the incidence of and risk factors for venous Gerber et al. The impact of haemophilia on the success of total hip evidence (retrospective 2008 arthroplasty case series) Not best available Modig et al. Template bleeding time for preoperative screening in evidence (coagulation 2008 patients having orthognathic surgery screening) Not best available Beiderlinden Risk factors associated with bleeding during and after evidence (coagulation et al. A 30 years single center experience case series) Factors predicting early postoperative liver cirrhosis-related Not best available Iwata et al. Modified Child-Pugh score as a marker for postoperative evidence (coagulation 2007 bleeding from invasive dental procedures screening) Excludes patients with Welsby et al. Excluded Studies Considered for Risk Factors for Bleeding Author Title Reason for Exclusion Not best available Gerrah et al. Using cone and plate(let) analyzer to predict bleeding in evidence (coagulation 2006 cardiac surgery screening) Routine coagulation screening in children undergoing Not best available Giles et al. Long-term postoperative bleeding after dentoalveolar evidence (coagulation 2006 surgery in the pretransplant liver failure patient screening) Not best available Welsby et al. The kaolin-activated Thrombelastograph predicts bleeding evidence (coagulation 2006 after cardiac surgery screening) Not best available Bae et al. Postpartum hemorrhage after cesarean delivery: an analysis Not best available 2005 of risk factors evidence Ohta et al. Analysis of risk factors for massive intraoperative bleeding Not best available 2005 during laparoscopic splenectomy evidence Paucity of studies to support that abnormal coagulation test Segal et al. Systematic review, results predict bleeding in the setting of invasive 2005 bibliography screened procedures: An evidence-based review Sirichindakul Risk factors associated with major intraoperative blood loss Not best available et al. Reexploration for bleeding after coronary artery bypass Does not investigate 2004 surgery: risk factors, outcomes, and the effect of time delay risk factor of interest Kukreja et al. Factors affecting blood loss during percutaneous Does not investigate 2004 nephrolithotomy: prospective study risk factor of interest 302 Table 59. Excluded Studies Considered for Risk Factors for Bleeding Author Title Reason for Exclusion Not best available Castellano et American Society of Anesthesiology classification may evidence (coagulation al. Hip arthroplasty in patients with cirrhosis of the liver evidence (retrospective 2003 case series) Legroux Not best available Gerot et al. Total knee arthroplasty in hemophilic arthropathy evidence (retrospective 2003 case series) Terjung et al. An Not best available 2003 analysis of risk factors evidence Not best available Winkelmayer Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for bleeding evidence (coagulation et al. Platelet glass bead retention predicts bleeding after cardiac Insufficient data 2001 surgery Not best available Friedman et Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after supratentorial surgery evidence (coagulation al. Systematic review, Post-tonsillectomy bleeding: a meta-analysis 2001 bibliography screened Lehman et al. Discontinuation of the bleeding time test without detectable Not best available 2001 adverse clinical impact evidence Nevo et al. Acute bleeding and thrombocytopenia after bone marrow Does not address 2001 transplantation question of interest 303 Table 59. Excluded Studies Considered for Risk Factors for Bleeding Author Title Reason for Exclusion Not best available Steib et al. Intraoperative blood losses and transfusion requirements evidence (coagulation 2001 during adult liver transplantation remain difficult to predict screening) the impact of bleeding times on major complication rates Not best available Stiles et al. Orthopaedic outcome of total knee replacement in evidence (retrospective 2000 haemophilia A case series) Relationship between clinical history, coagulation tests, Not best available Gabriel et al. Is a prolonged bleeding time associated with an increased Not best available 1999 risk of hemorrhage after liver biopsy Haemophilic; arthropathy: Assessment of quality of life evidence (retrospective 1999 after total knee arthroplasty case series) Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsies: measurement Bjortuft et al. Not best available of bleeding volume and evaluation of the predictive value 1998 evidence of coagulation tests Reexploration for hemorrhage following coronary artery Dacey et al. Northern New 1998 evidence England Cardiovascular Disease Study Group the relation between the platelet-activated clotting test Not best available Ereth et al. Modifiable risk factors for vascular access site Does not address 1998 complications in the question of interest Not best available Wahba et al. Are in-vitro platelet function tests useful in predicting evidence (coagulation 1998 blood loss following open heart surgery The clinical usefulness of the preoperative bleeding time evidence (coagulation 1996 screening) Not best available Lofqvist et al. Preoperative platelet count and postoperative blood loss in Not best available 1996 patients undergoing hip surgery: an inverse correlation evidence Moulton et al.

