Terramycin
Discount terramycin 250 mg on line
Do some ways of improving performance change the actual character of the activity Different Ways of Enhancing Performance As already indicated antibiotics for sinus infection nausea purchase genuine terramycin on-line, there are multiple ways to improve athletic performance, from the elementary to the sophisti cated, from the old to the new. Anabolic steroids permitted greater weight training leading to enlarged muscle mass. Someday, insertion of syn thetic muscle-enhancing genes may make muscles * stronger, quicker, and less prone to damage. Where in this sequence of devices to improve running do we acquire any disquiet regarding the means used Such changes, of course, would transform the activity into something other than running. They fall generally into three categories: better equipment, better training, and better native powers. Pole-vaulting used to be done with rigid bamboo poles and vaults of fifteen feet high seemed virtually superhuman; now flexible fiberglass poles are used, and vaults go over nineteen feet. Baseball gloves were once little more than shaped padding for the hand; now, more than twice their original size, they resemble small bushel baskets. Curved hockey sticks, replacing the straight ones, make possible greater puck control and faster shots. With such equipment now an accepted part of the sport, used by virtually everyone in competitive and pro fessional athletics, players who did not use them would be looked upon as foolish, and they would likely never make it to the highest levels of competition. Corked baseball bats, for example, are believed to permit increased bat speed and thus hitting power. Yet they are considered an unacceptable form of cheating and are illegal in professional baseball. Players who use them are looked down upon by many fans as cheaters or seen as fools for believing they could get such an unfair advantage without getting caught. Were someone to propose that the rules be changed, so that everyone could use corked bats, many people would probably still object. Some of these rules are not matters of principle but of taste, while others involve particular discernments about what is best for individual sports that cannot be uni versalized. It could become more rigorous, the athlete working harder and longer than he did before or harder and longer than his teammates or his rivals. Training could be more effective (better, not nec essarily harder), the athlete training more intelligently or scientifically. And training could be better coached, the ath lete practicing under the guidance of someone with supe rior wisdom or know-how regarding nutrition, general fit ness, or specialized skills such as batting or pitching. All of these forms of improving performance through training proceed through habituation, practice, and instruc tion, consciously and conscientiously undertaken. Yet the effects of the training are often written into the bodies of the athletes, in the form of increased strength, longer en durance, greater quickness, improved coordination, and smoother performance. Similar bodily changes might also be produced not through active training or active training alone, but by direct biotechnical intervention into the body of the athlete, seeking to improve his native capacities by altering his underlying genetic or biochemical make-up. Direct biological means of improving the powers of our bodies range from the small and familiar to the large and novel. Least dramatic are special diets, for example, diets high in protein, known for decreasing body fat and increas ing muscle mass. Some prominent athletes (including Tiger Woods) have used this surgery to get better-than-normal eyesight, a practice that is fully legal and considered by all professional sports to be an acceptable enhancement. Off in the future, but already visible on the drawing board, are pros pects of genetic enhancement of bodily strength and resil ience through the insertion into muscles of genes for erythropoietin or more specific muscle growth factors. Be cause so much of athletic excellence is based on strength and swiftness, the muscle-enhancing technologies are un der special scrutiny by the sports authorities. To illustrate how present and pro spective biotechnologies can enhance native bodily powers, we turn next to various technological approaches to direct muscle enhancement, both pharmacologic and genetic. They are central agents of physical strength and speed, at tributes admired and celebrated in most human cultures. As basic elements of physical vigor, they also play a role in human attractiveness and in our sense of well-being and even our sense of who we are. Our path through the life cy cle is displayed most vividly in the changes of our muscula ture. When we are young, the active use of our muscles in play and in sports strengthens and develops them. At puberty, production of estrogen and testosterone enhances these processes, so that the peak of human muscular develop ment usually occurs between ages 20 and 30. As we age, we gradually lose the ability to do various * physical tasks, sometimes in part, sometimes altogether. Some people suffer from muscle diseases, often caused by specific genetic mutations (for example, muscu lar dystrophy), that render them unable to develop their muscles to the same extent as the healthy. Others manage through exercise and fitness training to maintain peak mus cular strength and endurance much longer than the aver age. Still others, sedentary and inactive, neglect those maintenance functions altogether and fall weaker earlier than most. They need to be physically integrated with, and function harmoniously through their attachments to , nerves, tendons, ligaments, and bones. While our attention will be on enhancing the activities of muscles and their cells, this fact reminds us that any biotechnological intervention that strengthens only muscles may unbalance the interactions with these other body parts, with serious malfunction as a possible consequence. Though not exactly a matter of athletic performance, the perfection of our musculature and body build is a matter of great concern to many people intent on improving their body image. Muscles have always played a prominent role in the idealizations of male human form. The mus culature is well developed and well proportioned but with out much articulation of individual muscles; indeed, the in tegrated physique points not to itself but to some impend ing action. A more contemporary idealization of the male human form is the modern bodybuilding champion, such as Arnold * the age-related loss of muscle size and strength has been named sarcopenia. Through specialized weight training, per haps with the help of anabolic steroids, all the muscles (es pecially the biceps and pectoral muscles) become much lar ger than those in the statue of David, and the different groups of skeletal muscles are individually articulated. The picture is less one of measured and proportionate strength in the service of splendid activity, more one of muscle * bound power, to be admired for its own sake. As embodied agents of our innermost will, muscles not only work our purposes on the world, but make manifest the deep qualities of our character, our dispositions and in tentions, our self-discipline, self-development, and self image. We are highly attentive to posture and motion in others, and muscular actions make possible the communi cation and cooperative coordination essential for human so ciety. Muscle Cell Growth and Development Scientists have learned a great deal about the cellular structure and development of skeletal muscles, as well as about how genes important to muscle cells function and are regulated. The following brief discussion of muscle cell bi ology will reveal targets for biotechnical interventions aimed at improving muscle strength and resilience. The major cell type present in skeletal muscle fibers is the multinucleated myotube, a long cylindrical cell that * the very idea of muscle-bound looks away from activity, and implies restricted freedom of motion; the hypertrophied muscles cut down somewhat the range of possible motion around some joints. The result was women bodybuilding champions with smaller but similarly indi vidually developed and articulated skeletal muscles. These myotubes arise from precursor cells, mononucleated myoblasts, by means of their fusion with each other and with pre-existing myotubes. Myoblasts, in turn, are formed by differentiation of a particular stem cell found in muscle tissue, called a satellite 2 cell. This proc ess is also influenced by hormones such as growth hor mone, testosterone, and estrogen. Schematic diagram of some important processes in skeletal muscle fiber growth and repair.
Purchase 250 mg terramycin otc
Genotype: genetic makeup of a given organism antibiotics for acne forum buy terramycin 250mg fast delivery, usually related to a given characteristic. Germ cells: the reproductive cells which contain the genetic material passed on to the offspring. Life history: the changes organisms undergo from conception to death, focusing particularly on the schedule of reproduction and survival. Lifespan: the period of time in which the life events of a species or sub-species. Can sometimes be used interchangeably with longevity even though they have slightly different meanings. Can sometimes be used interchangeably with lifespan even though they have slightly different meanings. Maximum lifespan (tmax): the maximum period of time organisms of a given species or sub-species. Usually refers to the longevity of the longest-lived individual of a given species or sub-species. Mechanical senescence: age-related changes that are a consequence of mechanical usage. Mutation accumulation theory: theory by Peter Medawar that explains the existence of aging by the accumulation of mutations with harmful effects at later ages. Negligible senescence: organisms in which the aging process has not been detected in spite of detailed studies, as observed in some animals. Oocyte: a female gametocyte that develops into an ovum after two meiotic divisions. Oxidative stress: damage caused by reactive oxygen species; oxidative stress has been implicated in aging. Phenotype: the characteristics of an organism as determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences. Phylogeny: the evolutionary development and history of a species or taxonomic group of species. Polyphenism: the ability of a single genome to give rise to two or more morphologies. Polyphyodont: an animal that develops several sets of teeth successively throughout its life, as observed in many species. Progeria: genetic disease resembling accelerated aging which typically affects children. Rate of living theory: theory that argues that lifespan inversely correlates with metabolic rates. It is also characterized by various biomarkers and can or not be accompanied by cell death. Semelparous: organisms that reproduce only once, usually followed by death, as observed in several animals. Senescent cell: normally dividing cell that is irreversibly growth arrested and exhibits a number of other biomarkers associated with cellular senescence. Stem cell: an undifferentiated cell that can divide, differentiate into specialized cells, and can self renew to give rise to more stem cells. Telomerase: enzyme that adds telomeric sequences to the telomeres and has been associated with cellular immortality. Trait: a particular characteristic of an organism that can have different phenotypes. I often cite my own academic publications for the simple reason that I am more familiar with them, though I always aim to provide a broad overview of the literature on any given topic. For the sake of brevity I do not cite every single paper related to a given topic, and I frequently cite review papers and books-yet I try to cite the most important primary research papers. Lastly, please see my list of links and books for additional sources of information. A theory of aging based on the modulation of cell cycle signaling by reproductive hormones. Open discussions in the biogerontology community would attract public interest and influence funding policy. Lessons from the history of the oral contraceptive pill and hormone replacement therapy. The incomplete copying of template margin in enzymic synthesis of polynucleotides and biological significance of the phenomenon. Partitioning mean longevity differences in terms of age-specific mortality parameters. An historical perspective emphasizing the surgical solutions to the design of these classical models. Budgets will automatically adjust in InfoEd to reflect the new rate for proposals submitted Monday and thereafter. Although the overall fringe assessment on non-government grant accounts is not changing, the split between accounts 59010 and 59020 will shift. In the academic year 2016-2017, 1 position will be offered: One member of the Columbia faculty will be selected to spend one semester as a visiting professor at Sciences Po. The visiting professorship program is open to full-time officers of instruction of professorial rank. Professors on sabbatical or on leave will be preferred to participate in this exchange. Please note that, for the visiting professorship in France, by French law, faculty members above the age of 65 years-old are not eligible to the stipend. They are also expected to deliver two academic lectures or seminar presentations, and to attend two dinners or events hosted by the Alliance Program. The Alliance Visiting Professorship aims to foster research linkages among the faculty and to increase the range of educational experiences available to stu-dents in the participating institutions. Maples, PhD; Scientific Program Officer; Office of Extramural Programs; National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health; 1600 Clifton Road, N. Ag Centers are expected to conduct high quality research and help translate scientific discoveries into practical applications to improve worker safety and health in the areas of agriculture, forestry, and fishing. Center functions should include developing integrated approaches that link basic science with translation and outreach activities. Center structure should take advantage of diverse scientific resources and focus on local, regional, and/or national worker safety and health issues. Centers should place emphasis on the creation and implementation of evidence-based solutions that address important agricultural safety and health problems. Collaborations with other academic institutions, nonprofit organizations, and other occupational safety and health focused groups are expected. Applicants must concisely describe the occupational health burden within their service area and directly link research and outreach activities to help alleviate the burden. Applicants should also clearly articulate the anticipated impacts of the proposed work, both during the project period and beyond. To be considered for a internship, applications are accepted before September 30 each year. The application process is very simple and requires filling a questionnaire that covers your education, current studies, language skills and experience. Please feel free to refer your fellows, graduate students, medical students, and residents to well respected programme. Centralized linkage of clinical data and cancer registry data to corresponding tissue and biospecimen data from these resources will be a huge asset to the organization, and prove to facilitate research. Please direct any additional questions to our Database Manager, Natalie Peart, at (212) 305-7409 or email us at dbsr@columbia. We would like to invite you to circulate it within your institution (epidemiology and beyond). Other datasets are used internally and may be accessed through data use agreements. Proposals should be submitted electronically in a single Adobe file to Craig Kandell (ckk7); ckk7@columbia. We anticipate funding four R01 pilots at a level of $25,000 and two program project/center pilots at a level of $75,000. Priority will be given to pilot proposals which are interdisciplinary in nature and that cross departments within the Mailman School of Public Health.
Diseases
- Barrett syndrome
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
- 17 alpha hydroxylase deficiency
- Myelofibrosis-osteosclerosis
- D-minus hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Wolcott Rallison syndrome
- Ollier disease
- X-linked mental retardation and macroorchidism
- Familial band heterotopia
- Mental retardation u Mental retardation x
Purchase terramycin with paypal
Isolating all the relevant genetic vari ants steroids and antibiotics for sinus infection buy discount terramycin 250 mg online, and knowing how to work with them to produce the desired result, will therefore prove immensely difficult. To be sure, not every trait for which parents might wish to se lect need turn out to be highly polygenic: for example, height, skin color, eye color, or even the genetic contribu tions to sexual orientation or basic temperament might be heavily influenced by a very few genes. As we will see more fully in Chapter Four, one mutation in a single gene has been shown to result in enormous increases in the lifespan of flies, worms, and mice, and the same gene has been identified in humans. Yet even here there would be no guarantee that the predisposing genes, even if correctly and safely introduced into the zygote or early embryo, would necessarily express themselves as desired, to yield the sought-for improvement. Even more of an obstacle to successful genetic engineer ing is the practical difficulty of inserting genes into embryos (or gametes) in ways that would produce the desired result and only the desired result. Getting the genes into the right place in the cell, able to function yet without disturbing regular cellular functions, is an enormously challenging task. Insertion of genes into the host genome can cause ab normalities, either by activating harmful genes or by inacti vating useful ones. Recently, for example, children undergo ing experimental gene therapy for immune system deficien cies have developed leukemia after retroviral gene transfer into bone marrow stem cells, very likely the result of activa * Growing recognition of the complexity of gene interactions, the importance of epigenetic and other environmental influences on gene expression, and the impact of stochastic events is producing a strong challenge to strict genetic determinism. Straightforward genetic engineering of better children may prove impossible, not only in practice but even in principle. And should intro duced genes become inserted into inappropriate locations, normal host genes could be inactivated. Running such risks might be justified in gene therapy ef forts for already existing individuals, where the genes hold out the only hope of cure for an otherwise deadly disease. But these safety risks will pose formidable obstacles to all interventions in gametes or embryos, especially nonthera peutic interventions aimed at producing children who would allegedly be, in one respect or another, better than well. As a possible way around the hazards of gene insertion, some researchers have proposed the assembly and injection of artificial chromosomes: the new better genes could be packaged in small, manufactured chromosomal elements that, on introduction into cells, would not integrate into any of the normal forty-six human chromosomes. Such artificial chromosomes could, in theory, be introduced into ova or zy gotes without fear of causing new mutations. But methods would have to be found to guarantee the synchronized rep lication and normal segregation of such artificial chromo somes. Otherwise, the package of improved genes, once introduced into the embryo, would not be conserved in all cells after normal mitotic division. Even more dauntingly, any gene introduced on such a chromosome would now be present in three copies (one from mother, one from father, and one on the extra chromosome) instead of the usual two, throwing off the normal balance of gene copies among all the genes. The consequences of such triploidy can be deleterious (for example, Down syndrome). All in all, safety and efficacy standards would seem to preclude doing such experiments with human subjects, at least in the United * States, for the foreseeable future. But, at least for the time being, we believe that we may set this prospect safely to the side. Unlike the prospect for precise genetic engineering through directed genetic change, the possibility of genetic enhancement of children through embryo selection cannot be easily dismissed. This approach, less radical or complete in its power to control, would not introduce new genes but would merely select positively among those that occur naturally. A dozen or more eggs are fertilized and the embryos are grown to the four-cell or the eight-to-ten cell stage. One or two of the embryonic cells (blastomeres) are removed for chromosomal analysis and genetic testing. Only the embryos free of the ge ing any proposals that seek to modify gametes or embryos. This decision produces an effective moratorium on all such research (at least that supported by federal funding). Collins also pointed out to the Council, there are numerous practical difficulties with this scenario. Of course, because of the complex relationship between genes and traits, the mere ability to screen for multiple genetic variants in no way guarantees that numerous pheno typic traits will soon be detectable. Also, selecting for highly polygenic traits would require screening a large number of embryos in order to find one that had the desir able complement. With only a dozen or so embryos to choose from, it will not be possible to optimize for the many * necessary variants. Because many of the desirable human phenotypic traits are very likely polygenic, the contribution of any single gene identifiable by blastomere testing is likely to be small, and the likelihood of finding all the de sired genetic variants in a single embryo is exponentially smaller still. And should some of the desirable genes come grouped in clus * If, for example, a desired trait required the concurrence of only seven specific genetic alleles and (to take the simplest case) there were only two alternate vari ants of each gene, one would need (on the average) 128 embryos (and even more eggs) to get the full complement (2 to the seventh power). Of course, if the oocyte supply could be increased, say by deriving oocytes from embryonic stem cells, this problem might be soluble. The inter play of nature and nurture (genes and environment) in hu man development is too complex and too little understood to make such results predictable. More realistically, the question that parents would face would be something like this: Would you opt for a traumatic and expensive procedure that might give you a very slightly happier and more tal ented child, might give you a less happy, less talented child, might give you a deformed child, and probably 9 would do nothing Under these circumstances, should genu ine and significant improvements be achieved for a few highly desired attributes (say, in maximum lifespan; see Chapter Four), one can easily imagine that there would be an increased demand for the practice, inconvenient or not. In the meantime, we would do well to consider the ethical implications not only of such future prospects but also of our current practices that make use of genetic knowledge. Ethical Analysis the technologies we have just considered range from the well-established (prenatal screening out, using amnio centesis and abortion) to the speculative (embryonic fixing up, using direct genetic modification of embryos or gam etes), with special attention to the new and growing (choosing in, using preimplantation genetic diagnosis fol lowed by selective embryo transfer). As we have suggested, we have our doubts whether these powers will soon be widely employed for any other purpose. Yet there are ample reasons why we should not become complacent or take these matters lightly. Powers to screen and select for one purpose are immedi ately available to screen and select for another purpose; the same is true for powers of directed genetic change. And, as already noted, it is sometimes hard to distinguish between desirable traits that one would call healthy and those that one would call good in some other way: consider the case of leanness (non-obesity) or perfect pitch (non-tone deafness) or attentiveness (non-distractibility). Moreover, there is ample reason to take stock of the ethical and social issues related to present and anticipated practices of screening and selection even if, as we have indicated, there is no reason for alarm regarding designer babies. In addition to welcome consequences for the health of children, such practices may have more ambiguous or worrisome consequences for our ideas about the relation of sex and procreation, parents and children, the requirements of responsible parenthood, and beliefs in the equal worth of all human beings regardless of genetic (or other) disability. In what follows, we shall examine, first, the reasons why many people welcome these technologies; second, concerns that might be raised about the safety of these pro cedures and about equality of access to their use; and, fi nally, more profound ethical questions regarding how these technologies might affect family life and society as a whole. The widespread practice of prena tal screening in high-risk pregnancies has enabled numer ous couples to terminate pregnancies when severe genetic disorders have been detected. It is the natural aspiration of couples not only to have children, but to have healthy chil dren, and these procedures have in many cases lent crucial assistance to that aspiration. People welcome these tech nologies for multiple reasons: compassion for the suffering of those afflicted with genetic diseases; the wish to spare families the tragedy and burden of caring for children with deadly and devastating illnesses; sympathy for those cou ples who might otherwise forego having children, for fear of passing on heritable disorders; an interest in reducing the economic and social costs of caring for the incurable; and hopes for progress in the overall health and fitness of hu * man society. Should it become feasible, many people would have rea son to welcome the use of these technologies to select or produce children with improved natural endowments, above and beyond being free of disease. Parents, after all, hope not only for healthy children, but for children best en dowed to live fulfilling lives. Assuming that it became possible * Not all Members of this Council agree that it is obviously and simply good to assist people in avoiding the need to care for children who are not healthy. One Member comments: It would be good to live in paradise, but, given that we dont, I am not sure that it is necessarily a good not to have to care for children who are not healthy. And they would likely regard it as an extension of their reproductive freedom to be able to do so; they might even regard it as their parental obligation. In a word, parents would enjoy enlarged freedom of choice, greater mastery of fortune, and satisfaction of their desires to have better children. As with all biomedical interventions, a primary ethical concern is the matter of safety: the risks of bodily harm incurred by those subject to the procedures involved in genetic screen ing and manipulation.
Buy cheap terramycin on line
Understanding the pathophysiology of the event peg 400 antimicrobial generic terramycin 250 mg with amex, particularly in relation to its onset, is invaluable. History the typical story is of gradual emergence of unusual behaviour and/or social withdrawal together with falling school performance. Examination the presence of motor signs (pyramidal, extrapyramidal, or cerebellar) is incompatible with a diagnosis of primary psychosis. Unwanted drug effects Tardive dyskinesia this is most often associated with neuroleptics (phenothiazine, haloperidol), atypical antipsychotics (olanzapine) and, more rarely, with anti-emetics (metaclopromide or prochlorperazine), but it can also occur with theo phylline. Behavioural management in difficult to control epilepsy Children with poorly-controlled seizures may have difficulties with behaviour and attention interictally. Episodic behavioural episodes may be mistaken for seizures and (for example) lead to excessive and inappropriate use of emergency seizure medication. In the latter, a distinction between socialized (with preservation of peer relationships) and socialized (offending alone with little guilt or concern) is useful. For most children with autism and epilepsy, antiepileptic therapy should be long term even if seizure freedom has been achieved. Typically food borne, initially though person-to-person spread, a risk as it may be shed in the stool for several weeks after resolution of symptoms. Sudden drops in blood pressure risk focal infarction particularly of the optic nerve. Rhabdomyolysis/myoglobinuria Rarely presents primarily to the renal team, although nephrological input may be required for uid management and/or acute secondary renal failure. Decisions on the use of long-term ventilation must be preceded by clear discussions with the child and family, on the aims of treatment and a frank exchange of views on end of life issues (see b p. The respiratory/long-term ventilation team will advise on mask tting and ventilator type. An inspiratory positive airway pressure is set together with a back-up rate for when the child does not trigger a breath. Mask or mouthpiece used with a portable volume ventilator, set in the assist-control mode. A breath is activated by drawing air through the mouthpiece, thus creating a small negative pres sure in the circuit by with sipping or inhaling. Generally, a problem of infancy, but may be seen later in childhood due to acquired brain injury. Idiopathic congenital central hypoventilation syndrome Unexplained by any of the listed possible causes. Late-onset central hypoventilation syndrome Presents following respiratory infection or anaesthesia, which may trigger the need for nocturnal ventilator support. Often preceded by chronic pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, or respiratory infections with seizures or need for mechanical ventilation. History and examination give diagnostic clues, but endoscopy is usually, and imaging may be required. Inspiratory stridor suggests a laryngeal obstruction, expiratory stridor implies tracheobron chial obstruction, and a biphasic stridor suggests a subglottic or glottic abnormality. Most neurological stridor is chronic; other causes include congenital or acquired stenosis or other compressive abnormalities, including webs, rings aberrant vessels, etc. Parenteral haloperidol can cause acute oculogyric crisis or dystonia (treat with procyclidine). Antipsychotics and benzodiazepines can aggravate delirium, exacerbate underlying causes (for example, benzodi azepines worsening respiratory failure) and cause signi cant unwanted effects. Intubation and ventilation of the unconscious child will be either for the purpose of securing a safe airway due to an inadequate cough and gag re ex, or for the management of raised intracranial pressure. Borderline cases should be discussed urgently with an intensivist or anaesthetist. Non-accidental (in icted) traumatic brain injury the forensic evaluation of suspected non-accidental head injury is beyond the scope of this book. Acute management of seizures can also be challenging, although this typically abates after a few days. Treatment algorithm A seizure that has not stopped spontaneously within 5 min is less likely to do so; therefore, start drug treatment. Airway and oxygen Breathing and circulation Glucose Vascular access No vascular access Diazepam 0. Fosphenytoin is prescribed in with phenytoin equivalents (fosphenytoin 75 mg is equivalent to phenytoin 50 mg); take care as mistakes can easily be made. The child should be managed in a high dependency setting with the facility to support airway and breathing rapidly if needed. Most neonatal seizures are subtle, mani festing with combinations of motor, behavioural, and autonomic symptoms, making them difficult to recognize clinically. More recent evidence indicates an adverse effect of neonatal seizures themselves on long-term neurodevelopmental outcome and increased epilepsy in later life. Acute control of dystonia Non-pharmacological interventions Many children with dystonia may be quite physically disabled, but with intact cognition. In addition, positioning can be very helpful in aborting the spasms in some children. Physiotherapy assessment may provide additional strategies to improve spasm-free periods and sleep. In some children, handling may exacerbate dystonia and this should be minimized to necessary cares. The risks of complications from severe dystonia need to be measured against the risk of unwanted effects from the high doses of speci c anti-dystonia drugs often required (Table 6. Consider use of objective dystonia scales and serial video to assess response to treatment. Extreme care should be taken to monitor children when using combinations of drugs with sedating properties. Acute brain injury After severe acquired brain injury particularly involving basal ganglia, both traumatic and non-traumatic. Same side are derivatives of the same drug effects, but less gastric irritation Alimemazine 2 mg/kg/dose (max.
Buy terramycin 250 mg without a prescription
Most low and no adverse effects were reported antibiotic word parts purchase terramycin in united states online, this children born to mothers on low-dose may not be the case in younger infants. The treatment (<10mg/week) seem normal at manufacturers currently advise to avoid use birth. There does not seem to be any during breastfeeding, but with careful dosing association between later pregnancy exposure combined with planned timing of feeding, and fetal abnormalities. Limited preconcep Metolazone tion and first trimester use was largely associ It is not known if metolazone crosses the pla ated with normal pregnancy outcomes. Rodent teratogenicity studies are reas 8-methoxypsoralen during breastfeeding does suring. Because of there are no clinically significant effects on the its role as a photosensitiser, it is recommended infant. While metolazone does appear to be Maternal medication and the baby 587 safe during pregnancy and lactation, there are significant maternal systemic concentrations; few clinical indications for its use, and if these however, other tetracyclines can cross the pla are present, there are other, better studied, centa, and their use is associated with tooth alternatives. Black discolouration of breast milk is reported (and was postulated to Metoprolol be an iron chelate of minocycline or one of its Metoprolol crosses the placenta; however, it derivatives). Rodent teratogenicity studies are reassuring but high doses may cause embryo Minoxidil toxicity. Only small quantities of metoprolol It is not known whether minoxidil crosses the are found in breast milk, and the neonatal placenta. No reported when a mother had used minoxidil adverse effects are seen in the breastfed infant. Minoxidil enters breast milk at It is not known whether miconazole crosses concentrations that are too small to produce a the placenta. It does not appear to carry any increased risk of malformations when Mifepristone used during the first and second trimesters. Mifepristone is a potent antiprogestogenic There is one case report of neonatal hypo steroid used in with medical termination of preg thermia through the first 10 days of life that nancy. Mirtazapine abort after its use, and while many will then enters breast milk but only small amounts are choose to have a with surgical termination of detected in the breastfed infant. They should be are available with a better studied safety pro warned that mifepristone is teratogenic in file during both pregnancy and lactation. Although there are concerns about the potential for hormonal Mitomycin effects in the breastfed infant, these appear not Mitomycin is used to treat a variety of cancers. Use during lactation has not been Minocycline reported, and it is not known if mitomycin It is not known whether minocycline crosses enters breast milk. In the single report of use during reported in the literature, appears to be safe. It should probably be considered incompatible Moxifloxacin with breastfeeding pending additional study. This Modafinil has led to the restricted use of quinolones in Modafinil is used to treat narcolepsy. It is not known if moxiflox animal data suggest moderate risk of skeletal acin enters breast milk in humans (it is and renal malformations. There is a cause fetal renal failure and are generally con lack of experience during lactation, and it is sidered contraindicated during pregnancy. Nadolol It is not known if nadolol crosses the Mometasone placenta (similar drugs in this class do). It is not known if mometasone crosses the pla Propranolol and labetalol are better studied centa. Inhaled steroids are used widely during blockers that can be used during preg pregnancy and are not associated with malfor nancy. There is mometasone enters breast milk, considering some evidence of growth restriction in the dose and route, it is unlikely that breastfed animal studies, and reports of cardiorespira neonates ingest clinically relevant amounts. It is not associated with any known ter Nalidixic acid crosses the placenta, and rodent atogenic effect in animals. While a number of and canine teratogenicity studies report an malformations have been reported in humans, association of older quinolones, like nalidixic the association with montelukast is unclear. This has led to the restricted use of these use during pregnancy appears to be an effect agents during pregnancy. A recent meta-analy on fetal growth, with more women having sis did not seem to bear out many of the con smaller babies. Nalidixic acid is Maternal medication and the baby 589 excreted into breast milk, but only minimal are generally reassuring, although there is an amounts are ingested by the breastfed neonate. There is no published experience of use during In general, the newer quinolones are preferred. Rodent tera unlikely that maternal systemic concentration togenicity studies are generally reassuring, reaches a clinically relevant level. Rodent and there appears to be no behavioural teratogenicity studies are reassuring. The potential for during breastfeeding due to toxicity, one harm in a nursing infant is probably negligible exposed breastfed infant had plasma levels of given the dose and route of administration. As a but this has not been reported after naproxen group, aminoglycosides have been associated use. Rodent teratogenicity studies are reassur with irreversible deafness after in utero ing, as are cohort studies in humans. They should generally be avoided appears in breast milk in small quantities that during pregnancy, and if used, therapeutic are unlikely to cause any clinical effects in the monitoring should be undertaken. Jamali and Stevens: Drug Intell Clin Pharm teratogenicity studies have not been per 1983;17:910. Sumatriptan (which enters breast Nicardipine milk in small amounts) may be a better Nicardipine crosses the placenta (F/M ratio alternative to use until more information is 0. Nicardipine passes into breast milk limited to a single case report where it was used in only tiny amounts that are unlikely to until 24-week gestation (after which, treatment cause any problems in the breastfed infant. Nicotine fetal risks have been identified from limited replacement therapy may prevent exposure to exposure during human pregnancies. Only some of the other chemicals and is therefore small amounts of nizatidine pass into breast probably preferable to continued smoking; milk and are unlikely to affect the breastfed nonetheless, it carries its own risks. The Norethisterone is found in combined oral con long-term effects of nicotine replacement traceptive and progestogen-only pills. Nicotine passes into Masculinisation (mainly clitoral hypertrophy) breast milk (whether from smoking or from is reported in between 0. Nimodipine crosses the placenta (F/M ratio Jacobson: Am J Obstet Gynecol 1962;84:962. Nimodipine enters breast milk, It is not known if norfloxacin crosses the pla but the breastfed newborn ingests clinically centa, and while limited human experience is insignificant amounts. Although appearing to reassuring, there is conflicting data from be safe during lactation, there are alternative animal studies. Arthropathy is a concern fol agents for which there is more experience lowing use of other quinolones. With Nitrofurantoin limited data, it is not possible to determine if It is not known whether nitrofurantoin crosses use during breastfeeding is safe; alternatives the placenta. Nitrofurantoin is excreted in exposure is probably limited due to its lipophi breast milk in small amounts. Case Maternal medication and the baby 591 series of nortriptyline use during pregnancies Olsalazine sodium have not shown any increase in fetal adverse Active inflammatory bowel disease can events. It is facturers advise that ofloxacin and other qui not known if it crosses the placenta; however, nolones should be avoided in pregnancy there is very little maternal systemic because of this, the risk is probably not as great absorption, meaning that at most the fetus will as originally thought.
Buy terramycin online pills
Very low levels of Protamine sulphate quinapril are found in breast milk; they would Protamine is used to correct the anticoagulant not be expected to cause any adverse effects in effect of heparin virus that causes hives generic terramycin 250mg with visa. Limited human There is no published experience with rabe data from first trimester use suggest an prazole during pregnancy, and it is not known increased risk of gastroschisis and small bowel if it crosses the placenta. It is not known whether milk in small amounts that are unlikely to rabeprazole enters breast milk. It would pregnancy (especially during the second and appear to cross the placenta, but rodent tera third trimesters) because of fetal risks. Most ramipril is used in pregnancy, the mother reports of use in human pregnancy are simi should be monitored closely for oligohydram larly reassuring, but arthrogryposis multiplex nios; however, this may not appear until after congenita has been reported after use. Rodent teratogenicity Quetiapine crosses the placenta (F/M ratio studies are reassuring, but data in humans are ~0. Rodent teratogenicity studies are too limited to allow meaningful analysis of mostly reassuring as is very limited evidence risk. In some all better studied alternatives during preg women, the psychiatric risks of coming off que nancy. Small ing breastfeeding, and it is not known if amounts are excreted into breast milk. It is not known Rifabutin whether it crosses the placenta in humans Rifabutin is indicated for prophylaxis against (there is low transfer in rats). It is reports of adverse fetal outcomes associated not known if rifabutin crosses the placenta. It enters breast milk, but the breastfed infant is is not known whether rifabutin enters breast unlikely to receive clinical significant amounts. It is, therefore, unlikely to pose a Risedronate sodium significant risk to the fetus. Rodent teratoge There is no published experience with risedro nicity studies are reassuring, as are reports of nate during pregnancy (etidronate is a slightly use during human pregnancies. Rodent teratoge known whether saquinavir enters human nicity studies are generally reassuring. Risperidone It is not known if risperidone crosses the Saxagliptin placenta (it does in rodents). Rodent teratoge Saxagliptin inhibits dipeptidylpeptidase-4 to nicity studies are generally reassuring, as are increase insulin secretion and lower glucagon reports of exposures during human preg secretion. Rodent teratogenicity studies are bility, feeding problems and somnolence, reassuring, but there is no reported experience which may represent a withdrawal-emergent during human pregnancy. Risperidone enters available on the use of saxagliptin during breast milk in amounts that are not expected breastfeeding or whether it passes into breast to cause effects in the breastfed infant. Rizatriptan It is not known whether rizatriptan crosses the Selegiline hydrochloride placenta. Rodent teratogenicity studies are It is not known whether selegiline crosses the generally reassuring as is limited use (of all placenta. There are no data important for the development of the imma on the transfer of rizatriptan to breast milk. It is suggested that if rizatriptan any change in enzyme activity could have a is used, breastfeeding is best avoided for the profound effect on brain development. However, because There are very limited data on use during lac cholesterol and other products of the cholesterol tation, and it is not known if selegiline passes biosynthesis pathway are essential components into breast milk. It is not known if it crosses the hypercholesterolaemia and will avoid exposing placenta; however, it is not teratogenic in ani the fetus/infant to drugs at a critical time. There is no evidence of teratogenicity although one in vitro study suggested that it may adversely Sertraline affect the growth of the fetal and infant heart. Sertraline crosses the placenta (F/M ratio No clinically significant cardiac effects have ~0. It is not association with omphalocoele and septal known if sirolimus enters breast milk. Sertraline is found in breast milk in amounts that are affected by timing and size of the Sitagliptin maternal dose. The breastfed infant should be Sitagliptin inhibits dipeptidylpeptidase-4 to monitored for possible adverse effects; giving increase insulin secretion and lower glucagon the drug in the lowest effective dose and secretion. It is not known if sitagliptin crosses avoiding feeds at times of peak drug levels the placenta in humans (it does in rodents). Simethicone Sodium aurothiomalate While it is not known if simethicone crosses It is not known whether sodium aurothioma the placenta, it is unlikely that maternal late crosses the placenta. Rodent studies reveal systemic concentrations reach clinically rele increased risk of embryo and fetotoxicity, gas vant levels. There are no dose may be an option in those women who reports of use during lactation, and the low are unable to stop their treatment. Sodium maternal levels mean that even if transfer into aurothiomalate is excreted into breast milk, breast milk did occur, it would be unlikely but no convincing cases of infant toxicity have that the breastfed infant would be adversely been reported. It may not be necessary to withdraw if well Simvastatin controlled, but alternatives exist for which It is not known if simvastatin crosses the pla there is more experience during both preg centa. Rodent studies are reas humans has not shown any increased fetal suring with no evidence of teratogenicity. The concentrations in breast milk are against food allergies, exclusive breastfeeding too small to be clinically significant. Rodent teratogenicity Sucralfate is only minimally absorbed across studies have not been performed. It is not known whether sucralfate enters maternal cyanide toxicity can be reversed by breast milk; low maternal levels means that it sodium thiosulphate, this does not cross the should pose no risk to the breastfed infant. Use Ali and Egan: Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol in humans is limited to case reports of 2007;21:793. There are no reports Sufentanil of use during lactation, the thiocyanate metab Sufentanil crosses the placenta (F/M 1. It is olite has a long life, and breastfeeding is best used for fetal analgesia during a variety of pro avoided if the mother has received sodium cedures. Both sulfasalazine and reported use during pregnancy is restricted to sulfapyridine cross the placenta (M/F ratio ~1). Sotalol Large epidemiologic studies identify no evidence crosses the placenta (F/M ratio ~1), and it has of teratogenicity or an increased prevalence of been used to treat fetal tachyarrhythmia with a adverse fetal outcomes. Rodent teratogenicity moderately high response rate (flecainide and studies are also reassuring. Moffatt and Bernstein: Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol although there were no adverse events in this 2007;21:835. Maternal medication and the baby 601 Sumatriptan Tazarotene Only small amounts of sumatriptan cross the Tazarotene is a third-generation prescription placenta, and it should pose only minimal risk topical retinoid cream or gel. The manufacturer reports teratogenic skeletal abnormalities (these were not seen at and embryotoxic effects after oral levels equivalent to therapeutic doses used in administration in rodents, and skeletal alter humans). A small amount of sumatriptan ations and decreased pup weight at birth after enters breast milk, but the quantity ingested topical application. There are insufficient gestational morphism, developmental delay and polymi animal studies. Reports of use in humans do crogyria to concurrent use of a statin, and the not reveal obvious evidence of teratogenicity. At least 15 case centrations with the breastfed infant receiving reports describe oligohydramnios, fetal growth negligible amounts. This and the poor oral bio retardation, pulmonary hypoplasia, limb con availability would mean that the infant should tractures and calvarial hypoplasia after not experience any adverse effects.
L-HISTIDINE (Histidine). Terramycin.
- Allergic diseases, ulcers, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Histidine.
- Anemia associated with kidney failure or kidney dialysis.
- What is Histidine?
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96476
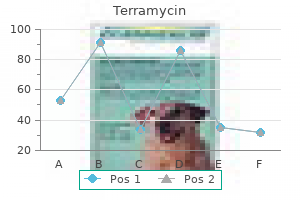
Purchase terramycin discount
When there is nothing in the lung cavity antibiotic resistance in india cheap 250mg terramycin otc, such as with a pneumothorax, there is hyperresonance. When there is fluid accumulation, such as when there is a pneumonia or effusion, there is decreased resonance (ie Dullness). Think of a drum with and without water inside to visualize what is inside the lung. A pneumothorax will push the trachea away from the affected side, while a bronchial obstruction will pull the trachea towards the side of the lesion. Leads to hemoptysis as the primary lung finding, with hematuria/anemia/ and crescentic glomerulonephritis as the kidney findings. Caused by anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies, which produce linear staining on immunofluorescence. Signs/Symptoms: Progressive dementia Chorea of the limbs, face, head/neck, and trunk Behavior disturbances such as: Depression, aggression, psychosis, changes in personality. The Berry aneurysm is seen at the bifurcation of the anterior communicating artery. The two types clinically encountered are Expressive Aphasia (Brocas), and Receptive Aphasia (Wernickes). Patient will experience all symptoms associated with dorsal column malfunction (lack of proprioception, ataxia during locomotion). This causes damage to the spinothalamic tract, which then results in a bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation in the upper extremities in a cape-like distribution. The causes of renal failure: Pre-renal Azotemia a is when there is a decrease in renal blood flow, which leads to a decrease in the glomerular filtration, and thus retention of water and sodium in the kidneys. Renal failure leads to a build-up of toxins and leads to the inability to excrete nitrogenous bases. Acute renal failure is usually due to hypoxemia, while chronic renal failure is usually caused by either hypertension or diabetes. These have a tendency to form staghorn calculi and get stuck in the urinary system. These stones are also produced when there are conditions of increased cell turnover, such as with leukemia. The following numbers describe the appropriate compensation dependent on each metabolic disturbance. Ultimately this is a condition that occurs as a result of purine metabolism disorder. The plaques that develop are known as psoriatic plaques, and are caused by excessive production of skin and a faster skin cycle than normal skin. It is caused by IgG antibodies against the epidermal cell surface, causes breakdown of the cellular junction of the epithelial cell. The most common site of presentation is the skin, however it may affect the kidneys, cardiac, and gastrointestinal systems. May also be due to renal failure, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, and congestive heart failure. The most common cause is autoimmune, infectious, and as a result of metastatic disease. Signs/Symptoms: Palpitations Anxiety Headache Diaphoresis Significant hypertension Tachycardia Diagnosis is based on checking urine metanephrines, and treatment is surgical removal after adequate management of the hypertension. While most commonly found in the adrenal medulla, it can be found anywhere along the sympathetic chain. This condition will cause an excess of androgens and a decrease in mineralocorticoids. The ease by which tetany occurs can be tested by certain maneuvers that cause muscular spasms. Patient will have enlargement of hands, feet, facial features, deepening of voice, etc. A defect in T4 formation or the failure of thyroid development during development causes sporatic cretinism. Patients are puffy-faced, pale, pot-bellied with protruding umbilicus and a protruding tongue. There is an increased need for insulin that doesnt get met, and is usually caused by an illness/infection that increases the stress level of the person. Common problems: Vertebral crush fractures Pelvic fractures Fractures of the distal radius Vertebral wedge fractures Management: Bisphosphonates are recommended, whereas estrogen replacement works well but comes with side effects that are concerning. This condition is suspected whenever there are recurring ulcers that are not treated conservatively. Characterized by benign lesions and diffuse breast pain that is often related to hormonal changes associated with her menstrual cycle. Mammogram is not required to make this diagnosis, but fine-needle aspiration is commonly done to check the characteristics of the fluid. Treatment is not necessary, however pain relief should be done **There is no increased risk of breast cancer in fibrocystic disease. Arising from mammary duct epithelium or lobular glands, and overexpression of estrogen/progesterone receptors. Contains Call-Exner bodies, which are small follicles filled with eosinophilic secretions. Presents with severe pain related to menstruation and produces chocolate cysts (blood in the ovary). Tendency to protrude from cervix, is highly aggressive and has a tendency to recur. Eclampsia = Triad above + seizure * If pre-eclampsia is present, patient requires bedrest, salt-restriction, and monitoring. Characterized by nodular enlargement of the lateral and middle lobes (ie periurethral), which compresses the urethra into a vertical slit. The most common site of adenocarcinoma is the posterior lobe (aka peripheral zone). Digital rectal exam is the best way to detect the cancer, as hard nodules can be detected on exam. The most worrisome adverse effect is osteoblastic metastasis (detect by increased alkaline phosphatase). Pediatric Endocrinology Each Pediatric Endocrinology exam is built to the same specifications, also known as the blueprint. The table below shows the percentage of questions from each of the content domains that will appear on an exam. Know effects of insulin on protein synthesis and proteolysis; lipolysis and ketogenesis; glucose production and utilization. Know the effects of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity on beta cell function and insulin resistance 2. Know the duration of time glycogen stores and gluconeogenesis can maintain normal blood glucose concentrations in normal neonates, children and adolescents B. Know the importance of the sulfonylurea receptor, chromium picolinate, the potassium channel, and the role of calcium flux in insulin secretion 3. Recognize histologic appearance of islets early and late in the course of type 1 diabetes with preferential destruction of beta cells and late persistence of alpha and delta cells 3.
Quality 250 mg terramycin
Keratolytic agents are effec tive and mostly contain salicylic acid infection journal cheap terramycin 250mg amex, sometimes lactic acid, bichloroacetic acid, or trichloroace tic acid. Virucidal agents contain glutaraldehyde or formaldehyde and are as effective as keratolytic agents. A more time-consuming and also an effective approach is topical immunotherapy with squaric acid dibutylether or diphenylcyclopropenone. Topical immunomodulatory therapy using imiquimod 5% cream may be considered in more recalcitrant cases. Cryotherapy in the vicinity of the matrix should be performed carefully to prevent permanent damage of this nail-forming organ. Excision is less favor able due to the high rate of recurrence and resultant deformity. A wait-and-see policy or use of mild topical keratolytics is justifed in most of the cases. Aggressive treatments should be used with reluctance, because recurrences and permanent scarring of the nail unit are not uncommon. However, suspicion is justifed in those situations in which the nail plate is damaged, because a common wart does not invade the nail matrix. Other risk factors for malignant transformation are radiation therapy, immunodefciency, arsenic, pesticides, and subungual tumors of incontinentia pigmenti22,23 (see also the section Ollier Disease and Chapters 1 and 9. Because of their benign appearance they are often misdiagnosed as a viral wart (Figure 15. Lesions mostly are present for several years before the correct diagnosis can be made. The integrity of the nail is lost because this squamous cell carcinoma infltrates the nail matrix. The commonest clinical signs are, in decreasing order, subungual hyperkeratosis, onycholysis, oozing, and nail plate destruction. It should be noted, however, that an incisional biopsy specimen may only reveal an in situ carcinoma but examination of the whole residual lesion may show overt invasive or microinvasive clusters. The preoperative evaluation should include radiography to exclude osseous involvement because bony invasion is reported regularly in invasive squamous cell carcinoma. The value of Mohs micrographic surgery in invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the nail unit is a matter of debate. Some authors prefer this treatment to prevent amputation,19,24 while others fnd rather high recurrence rates, up to 56%. Another reason is because radiation therapy has been associated with bone necrosis. Linear erythronychia,28 linear leuk onychia,29 or linear melanonychia30 are all clinical signs seen in onychopapilloma. The streak mostly has interrupted splinter hemorrhages and distally, it ends in a visible hyperkeratotic papule that sticks out from under the nail plate (Figure 15. The hyperkeratotic plug at the distal end of the nail often is painful when pulled or clipped. Nail Tumors in Children 201 Mostly, the clinical expression mostly is very suggestive for onychopapilloma. Punch biopsies can miss the diagnostic pathology or contribute to the recurrence of a lesion if only a portion of the tumor is sampled. Complete excision with a longitudinal nail unit biopsy from matrix to hyponychium that include the length of the lesion is recommended for these lesions. Mostly, they are skin-colored but hyper pigmentation or hypopigmentation has also been observed. The proximal interphalangeal joints are most frequently involved, but they have also been noted on the distal interphalangeal joints, metacarpophalan geal joints, and may occasionally occur on the thumbs and toes. Primary knuckle pads appear as a spontaneous fnding unassociated with other cutaneous disorders. Knuckle pads secondary to repeated trauma are called pseudo-knuckle pads,33 or chewing pads in children. The diagnosis of knuckle pads is primarily based on the clinical morphology of the skin lesions; biopsy of suspected lesions may be considered to exclude conditions with similar appearing morphology. Onychomatricoma Onychomatricoma is a rare benign tumor of the nail matrix presenting as a symptomless, slowly develop ing, focally or completely thickening of the nail plate. Very typical are flamentous extensions originating from the matrix, which become visible on nail avulsion and correspond with the funnel-shaped deformity of the nail plate. Onychomatricoma have some preference for fngernails above toenails but have no sex preference. The mean age of presen tation is approximately 51 years38 but a pediatric case has been reported. Onychocytic Matricoma An onychocytic matricoma is a recently described rare tumor of the nail matrix. So far, fve cases have been described but only one in a child, a 17-year-old adolescent. Acanthoma: Acantholytic Dyskeratotic Acanthoma Acantholytic dyskeratosis is a histologic pattern de ned by a hyperkeratotic and parakeratotic epidermis with intraepidermal clefts containing acantholytic and dyskeratotic keratinocytes. Nail Cysts the nail cysts represent a broad group of lesions that differ in histogenesis and clinical picture. Others are indistinguishable from epi dermal inclusion cysts of the skin and are known as implantation epidermoid cysts. Finally, some cysts may contain epithelium that resembles that of the nail bed and are called onycholemmal cysts. Clinically, in subungual epidermoid inclusions the distal phalanx of the digit gradually increases in size with marked hyperplasia of the bed epithelium, resulting in subungual keratosis, onycholysis, or dystrophic nail plate. Other clinical presentations include shooting pain or even an acquired pincer nail. A nail bed biopsy is required for diagnosis because the reported inclusions are rather microscopic than macroscopic. Once the diagnosis on subungual epi dermoid inclusions has been made, no clear treatment is curative, although simply making an accurate diagnosis may prevent inappropriate treatment. The occurrence of the cyst in children is very rare but an 8-year-old girl with two implantation epi dermoid cysts of the distal phalanx following nail surgery has been reported by Baran and Bureau. Epithelioid Hemangioma of Bone Epithelioid hemangioma, previously designated angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia and his tiocytoid hemangioma, is a vascular tumor mostly occurring in the skin and subcutis. Angioma Subungual angioma often present as painful swellings with focal blue-red discoloration, mostly beneath the lunula. Capillary Malformations Capillary malformations, port-wine stains, or nevus fammeus are the most common congenital vascular malformations, frequently occurring on the extremities. Digital Arteriovenous Malformations Arteriovenous malformation is usually congenital but an acquired type is also known, of which most are due to an injury. Pyogenic Granuloma Pyogenic granuloma mostly are reactive tumors occurring in the lateral nail folds. Malignant Hemangioendothelioma Retiform hemangioendothelioma, epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, and congenital hemangioendo thelioma are rare malignant tumors that may arise in the vicinity of the nail. Retiform Hemangioendothelioma Locally aggressive, low-grade angiosarcoma of unknown etiology that was frst described in 1994. In 2011, Keiler reported of an 11-year-old girl with a rapidly enlarging and intermittently painful swelling of her left distal fourth fnger. Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma A borderline malignant vascular tumor that occurs mainly during the second and third decades of life. Only one case describing an infant with a con genital lesion on the right index fnger has been reported. It occurs in infancy or early childhood but the fnger is an extremely unusual site.
Buy terramycin 250mg lowest price
Consider the following two digital messages: Build a red brick wall 910 cm wide treatment for sinus infection in adults purchase terramycin 250mg without a prescription, 220 cm high and 20 cm deep. We could identify the variable (numeric) parts of the messages, convert from digital to analog, perform addition or averaging operations, and then convert back to digital, a very complex procedure that requires a priori knowledge of the specific format of the messages. Another possibility for producing a composite would be to simply replace some characters in the first message with corresponding characters in the second message. For example if we used the first half of message 1 and the second half of message 2 the result would be: Build a red brick wall 910 cm wide, 320 cm high and 18 cm deep. If one of the messages had, for example, high as the first parameter, and wide as the second parameter, the result of the merge would not be meaningful. Suppose the messages were: Build a red brick wall 1000 cm wide, 220 cm high and 20 cm deep. Now the meaning of the merged message would be disturbed because the result would be: Build a red brick wall 1000 cm wie, 320 cm high and 18 cm deep. The reason for this detour is that the genetic communications system is in fact a serial digital system and bears an eerie resemblance to modern digital data systems. The genetic system has four symbols, synchronization patterns, formats, redundancy, error detection, merging, framing errors, language, and many other properties of digital systems. The genetic system is constrained by the digital data considerations described above. This has significant consequences for evolution theory and aging theory as will be explained in detail. We can use the term digital genetics to refer to these aspects of genetics that are driven by the digital nature of the genetic system. It was thought that characteristics of progeny tended to average out the characteristics of their parents. Variation is not only a fundamental property of an analog system but the occurrence frequency of a variation is inversely proportional to its size. This fits the bell shaped curve we would expect if we measured, for example, height variations in 18-year-old males. That is, there was a minimum unit of inheritance such that some characteristics were either inherited by a given individual, or not, with no averaging or intermediate possibility. Progeny could exhibit characteristics that were not Figure 15 Gregor Mendel displayed by either of their parents but were displayed by grandparents or other ancestors. Subsequent extensive research into inheritance disclosed the existence of chromosomes and other aspects of the digital inheritance system. Watson and Crick in 1953 published their famous paper[10] A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid describing the basic mechanism (the double helix) whereby genetic information is recorded, copied, and transmitted in all living organisms. Serial Digital Genetic Codes As determined by Watson and Crick, and extended by many subsequent investigators, the system used by nature to store, copy, and transmit genetic information is a digital system. These sequences then ultimately determine all the inherited characteristics of the organism. Because of the digital nature of the genetic code, some parts of genetic sequences have been faithfully reproduced. As we have previously seen, an analog system would never be capable of accommodating the very large number of consecutive duplications involved in the evolution of life on Earth. We could translate A to 00, G to 01, T to 10, and C to 11 and then represent any amount of genetic code as a binary number sequence. Complementing a sequence therefore does not remove any 69 the Evolution of Aging information. From an information viewpoint, a base, is the same as a base pair, is the same as a letter, is the same as a nucleotide. Approximately half of the genome consists of repeat sequences that are highly repetitive and therefore, according to information theory, contain very little information. Some of the repeats are tandem repeats that consist of sequential repetitions of a simple sequence. Although the sequence has been determined, the actual specific functions of most of the genetic code remain unknown. Chromosomes are visible under certain conditions using optical microscopy and were discovered by Walther Flemming in 1882. In 1907, Thomas Hunt Morgan associated chromosomes with inheritance using fruit fly experiments. Another special sequence more centrally located (position varies depending on the chromosome) is called the centromere. When a cell divides to form a second cell, the genetic information content is duplicated in a process called mitosis. During mitosis, chromosomes expand to a somewhat less compressed form in which they can be seen as the familiar microscopic rod-shaped objects. If completely unwrapped and extended, the chromosomes in a single human cell would total several cm in length. The telomeres, centromeres, and other structural aspects of chromosomes are known to be essential to the proper duplication of one (and only one) complete set of chromosomes during cell division. Almost every non-sex cell in more advanced organisms has two sets of genetic data, (two sets of chromosomes) one inherited from each parent. In this diploid configuration, the chromosomes are paired, that is, corresponding chromosomes are physically attached to each other to form the familiar conjoined rod shapes. To further illustrate the information content, the upper and lower case characters in the English alphabet (52 alphabetic characters, 10 numerical digits, and space) could be represented in binary form using 6 bits per character. The phrase Four score and seven would correspond to a binary string of 120 bits and could be expressed in genetic code using 60 bases. It would take a very, very, large number of monkeys and typewriters a very long time to randomly duplicate even this very short phrase! If you and any other living thing share a significant sequence of code that is approximately the same then you and the other organism must have had a common ancestor because the chances of a random duplication are impossibly low. Not only can they determine if you are related to your alleged children, they can determine if mice and men had a common ancestor (yes, of course) and can even determine from the number of errors that have crept into the genetic messages approximately how long ago humans and mice had a common ancestor (about 50 million years ago). Errors and Mutations Errors introduced in copying or storing genetic data are the source of the genetic changes that drive evolution. Some errors, such as in a sequence which controls basic cell design, or oxygen transport, or other crucial process, are almost always immediately fatal and so are immediately selected out and do not propagate into the genetic code of descendent organisms. Humans share some sequences with yeast that both humans and yeast must have received from a common ancestor. An error in such a sequence might only cause slight variation of a parameter and only very mildly affect fitness. Finally, some sequences (possibly more than 90 percent of the human genome) have no apparent biological purpose. Changes in such a sequence generally have no immediate effect on the organism and are putatively not selected against at all, thus apparently freely propagating to future generations. Since larger animals have trillions of cells, there are trillions of opportunities for mutations. However, for a mutation to be inherited it must occur in the sequence of cell division between the original egg cell and the subsequent egg or sperm cell. In modern electronic data systems, it is not unusual for errors to occur more or less frequently depending on the pattern of the data. Errors in both electronic and genetic systems can be caused by substitution of an incorrect letter in a sequence and can also be caused by deletion of a letter or insertion of an extra letter. In the genetic code, which is all about pattern and sequence, it is not surprising that it is also true that the chance for an error is pattern sensitive. Copying errors (insertion/deletion 71 the Evolution of Aging errors) which change the length of these repeats are thought to occur virtually every generation. Because of pattern sensitivity, the probability of particular errors varies enormously and is difficult to predict. Genes in the duplicated sections can have subsequent errors that sometimes result in new, useful genes. Presumably, this is the mechanism whereby a more complex and longer genome can evolve from a simpler one.
Order terramycin 250mg on line
Other signs of increased intracranial pressure include papillitis (which can be difficult to assess in a toddler) antibiotic xi purchase terramycin 250 mg with visa, head tilt, limb weakness, or gait abnormalities. In this case, computed tomography showed obstructive hydrocephalus and an intraventricular mass that was found to be a choroid plexus papilloma (Item C78). The boy in the vignette will require urgent imaging and neurosurgical consultation and intervention. A neurologist or ophthalmologist may be consulted in the hospital, but referral to an outpatient clinic or urgent care is not appropriate in this situation. On physical examination, the boy has a prominent fat pad on the back of his neck, central obesity, and stretch marks (striae) on his abdomen. The child in this vignette is rapidly gaining weight while his linear growth is decelerating, and has physical examination signs consistent with Cushing syndrome. Children with exogenous obesity will have normal linear growth, and should not undergo evaluation for Cushing syndrome. Evaluation for Cushing syndrome can be performed by measurement of 24-hour urine free cortisol, overnight dexamethasone suppression, late night salivary cortisol, and in some cases, assessment of diurnal variation in cortisol. Thus, of the choices offered, a 24-hour urine-free cortisol would be appropriate for this patient. Obtaining a prolactin level can help rule out prolactinoma as the cause of poor growth. Thyroid stimulating hormone and free thyroxine levels are used when evaluating for hypothyroidism. A 24 hour urine-free cortisol would be the best test to determine the cause of his poor growth. She has been increasingly intolerant of physical activity and now experiences shortness of breath when climbing 1 flight of stairs. Her heart rate is 152 beats/min, and her respiratory rate is 40 breaths/min and labored. Auscultation of the lungs reveals diffuse polyphonic wheezing in upper and mid lung fields with decreased breath sounds at both bases. The cardiac and abdominal examinations are unremarkable, with the exception of tachycardia. In this patient with rash, arthritis, fatigue, pallor, hematuria (suggested by the tea-colored urine), and syncope, evidence of a pulmonary renal syndrome and autoimmune or vasculitic condition should be sought. The most common etiology for focal pulmonary hemorrhage is chronic infection or inflammation; classic examples are tuberculosis and the endobronchial infections that cause bronchiectasis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Cardiovascular associations include arteriovenous malformations and pulmonary hypertension. Noncardiac etiologies include celiac disease, coagulation disorders, and acute idiopathic pulmonary hemorrhage of infancy. When an exhaustive search for an etiology of diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage is unrevealing, patients may be designated as having idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis. Patients may never expectorate blood and instead are likely to present with fatigue, pallor, tachycardia, or exercise intolerance. Radiographs are often nonspecific, but may demonstrate bilateral alveolar opacities with lower lobe predominance as in the patient in this critique. Therapy is dependent on underlying condition, but may include systemic steroids and immunosuppressive agents. The patient in this vignette is not in the age group classically associated with foreign body aspiration. In addition, there is no asymmetry or air trapping on chest radiograph to suggest an inhaled foreign body. Similarly, the radiograph does not reveal nodularity or lymphadenopathy suggestive of tuberculosis. Furthermore, the bleeding in both of these conditions would be expected to be more brisk with notable bright red hemoptysis. An adolescent may be diagnosed with cystic fibrosis if they have atypical or mild disease. Bleeding from the airways in patients with cystic fibrosis, however, occurs from bronchiectasis, which is a late manifestation of disease. However, the joint, skin, and urinary symptoms found in the patient in this vignette would not be expected. The parents have had difficulty finding the formula and ask if the baby could be fed a different type of milk while still maintaining the benefits of premature formula. Most mineral accumulation occurs during the third trimester, therefore premature newborns are at risk for developing deficiencies of calcium, phosphorus, iron, copper, and zinc; other mineral deficits (eg, iodine) are possible, but there have been few if any clinical reports of these deficiencies. The current recommendations are that premature newborns consume 150 to 200 mg/kg of calcium and 60 mg/kg to 75 mg/kg of phosphorus each day. Unfortified human milk, even preterm breast milk, and formulas produced for term infants do not provide sufficient calcium and phosphorus to meet these needs. Therefore, preterm babies less than 2,000 g in weight should receive human milk supplemented with fortifier or preterm formula in order to achieve sufficient intake of calcium and phosphorus (Item C81). Banked human milk is primarily term milk and does not provide enough calcium and phosphorus to prevent metabolic bone disease. There are currently no studies of the clinical impact of 25 hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in preterm newborns, so deficiency and sufficiency is based on extrapolation from adult and pediatric populations. Current recommendations are that low birth weight infants receive 2 to 3 mg/kg per day of iron beginning at 1 to 2 months of age. Although the iron concentrations in formula or human milk plus fortifier are quite variable, this route can supply at least part of this iron supplementation. For the infant in the vignette, she may be able to consume enough iron from term or preterm formula. As part of his pre operative evaluation, a metabolic panel was ordered that revealed an alkaline phosphatase of 325 U/L (upper limit of normal = 116 U/L). His past medical history is significant only for tonsillar hypertrophy and related obstructive sleep apnea. The development of secondary sexual characteristics is triggered by the increased secretion of pituitary gonadotropins. The typical age of the onset of puberty can vary by ethnicity, particularly among girls. A recent study by Susman and colleagues looked at the longitudinal development of secondary sexual development in a multiracial population and found the mean age for each stage of sexual development (see suggested reading 5). All of the sex hormones, including estradiol and testosterone, increase during puberty. Follicle-stimulating hormone increases, but can plateau when sexual maturity rating 3 is achieved. Her physical examination demonstrates an area of incomplete alopecia at the vertex. Within the affected area are hairs of differing lengths and 2 areas of hemorrhage (Item Q83). These physical findings suggest trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder), a form of traumatic alopecia in which individuals repetitively twist, twirl, or pull hair. The areas of hemorrhage observed in the adolescent in the vignette represent sites from which hairs were pulled (Item C83A). Item C83A the girl described in the vignette has an area of hair loss within which hairs of differing lengths may be seen. Trichotillomania usually involves the scalp, but any hair-bearing area can be affected (eg, eyebrows, eyelashes). In young children, trichotillomania often represents a habit similar to thumb sucking. In such cases, parents may be advised to offer a gentle reminder when the behavior is observed. In older children and adolescents, trichotillomania often represents a compulsion, and is considered among the obsessive-compulsive-related disorders. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are often employed, but evidence supporting their efficacy is lacking. The tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine has been shown to reduce hair-pulling urges and increase the ability to resist such urges. N-acetylcysteine has been investigated for use in trichotillomania, but data regarding its benefit are conflicting.

