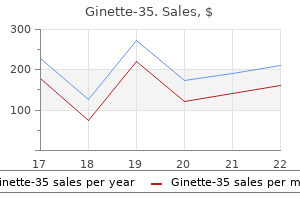
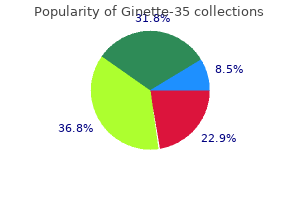
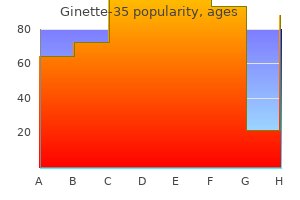
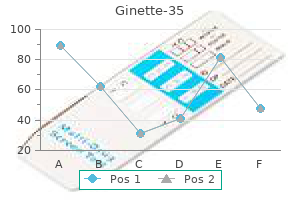
Ginette-35
Generic ginette-35 2mg with amex
Cosmetic repairs requests without physiological disability or severe deformities may not meet certain payers policies 2 womens health 40 discount 2mg ginette-35 free shipping. Chest X-ray after the current episode of symptoms started or changed should be performed initially in all cases since it can identify bone abnormalities or other causes of right upper extremity pain. Costochondritis can be readily diagnosed with palpation tenderness and/or hooking maneuver and imaging is non-specific. Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases full text, the Task Force on the Diagnosis and Management of Pericardial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology. Current use of imaging in the evaluation of primary mediastinal masses, Chest, 1990; 98:466-473. Brachial plexus injury: clinical manifestations, conventional imaging findings and the latest imaging techniques, RadioGraphics, 2006; 26:S133 S143. Page 224 of 794 13. Natural history of thoracic aortic aneurysms: indications for surgery, and surgical versus nonsurgical risks, Ann Thorac Surg, 2002; 74:S1877-S1880. Prognosis of aortic intramural hematoma with and without penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer: a clinical and radiological analysis. Page 227 of 794 2. Chest X-ray should be performed initially in all cases, after the onset of symptoms or if there has been a change in symptoms, since it can identify 1,2 boney abnormalities or other causes of right upper extremity pain. Trauma with altered mental status Page 230 of 794 H. Suspected epidural abscess or disc space infection [All of the following] Page 233 of 794 1. No red flags and failure to respond to conservative medical management [One of the following] a. Page 235 of 794 21. Annual follow-up with no change in signs or symptoms Page 238 of 794 5-8 V. History of diabetes, dialysis or peripheral vascular disease Page 239 of 794 4. No red flags and failure to respond to conservative medical management Page 240 of 794 a. Page 241 of 794 17. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or a course of oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Atrophy Page 244 of 794 3. Straight-leg raising reproduces the pain between 30 and 70 degrees of leg elevation 13. Radiculopathy Page 245 of 794 l. Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: A joint clinical practice guideline form the American College of physicians and the American Pain Society, Ann Intern Med. Evidence-based clinical guidelines for multidisciplinary spine care: diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis, North American Spine Society. Page 248 of 794 17. No red flags and incomplete resolution with conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids B. Primary or metastatic bone tumor (Gadolinium not required if there are no neurological signs or symptoms) [One of the following] 1. Weakness or stiffness of the legs (objective weakness on exam that is 3/5 or less) 8. Paresthesias (tingling) Page 251 of 794 5. For the Clinical Efficacy Assessment Subcommittee of the American College of Physicians and the American College of Physicians/American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guidelines Panel*, Diagnosis and Treatment of Low Back Pain: A Joint Clinical Practice Guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society, Ann Intern Med. Guidelines for the Management of Acute Cervical Spine and Spinal Cord Injuries, Section on Disorder of the Spine and Peripheral Nerves of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and the Congress of Neurologic Surgeons. Page 253 of 794 11. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis and long-term management of multiple sclerosis, Neurology, 2004; 63(Suppl 5):S3-S11. Page 254 of 794 37. Pain increased with straining Page 256 of 794 n. Clumsiness of the hands Page 257 of 794 2. Infection (including osteomyelitis and discitis and epidural 11-16 abscess) [One of the following] A. Follow-up during or after therapy for osteomyelitis, epidural abscess or disc space infection [One of the following] Page 258 of 794 1. Pain and paresthesia along the ulna aspect of the forearm, hand and 4th and 5th fingers b. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; failure to respond to conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or a course of oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Clinical findings and/or symptoms with no red flags; incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks; or oral steroids [One of the following] 1. Objective weakness in a nerve root distribution on examination which is 3/5 or less B. Neck pain lasting at least 6 weeks and with a history of prior 9,19-27 surgery with a posterior approach [One of the following] A. No red flags and failure to respond to conservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids B. Repeat advanced diagnostic imaging is appropriate when evidence of neurologic deterioration. Neck pain, cervical radiculopathy, and cervical myelopathy, the J Bone & Joint Surg, 2002; 84:1872-1881. Diagnostic and therapeutic radiology of the spine: an overview, Imaging, 2002; 14:355-373. Page 263 of 794 20. Evaluation of magnetic resonance myelography in the investigation of cervical spondylotic radiculopathy, the British Journal of Radiology, 2003; 76:525 531. No red flags and incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids B. Primary or metastatic bone tumor (contrast not required if there are no neurological signs or symptoms) [One of the following] 1. Known malignancy with thoracic spine pain Page 265 of 794 2. Periodic assessment during chemotherapy, radiation Rx, or surgery for bone tumor 5. Clinical findings and symptoms with no red flags incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or a course of oral steroids injections [One of the following] Page 266 of 794 1. Clinical findings and symptoms with no red flags incomplete resolution withconservative medical management consisting of either treatment with anti-inflammatory medication or muscle relaxants for at least 6 weeks or oral steroids [One of the following] 1.
Syndromes
- Argininosuccinic aciduria
- X-ray of the bone
- Is there irritability?
- Do you have any allergies?
- Plant foods
- Adults over age 45, repeated every 3 years
- Muscles are very tense, then very relaxed
- Croup
- X-rays of the abdomen
Generic 2mg ginette-35 mastercard
X-5 with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and oppositional symptoms: A randomized women's health center waldorf purchase genuine ginette-35 on-line, double-blind, 172. X-4 families of preschoolers at risk for disruptive behaviour disorders: utilization, cost effectiveness, 163. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 1995 Effectiveness of an intensive outpatient program for Oct;36(7):1141-59. X-11 parents as therapists to evaluate appropriate behavior of their children: application to a tertiary diagnostic 174. X-11 adolescent delinquency and substance abuse: understanding within-session processes. Dating violence: outcomes following a brief on emotion-potentiated startle in healthy humans: motivational interviewing intervention among at-risk H-10 adolescents in an urban emergency department. Acad patients: a double-blind, placebo and baseline Emerg Med 2013 Jun;20(6):562-9. X-1 controlled, crossover trial of fish oil treatment for impulsive aggression in children and adolescents 177. J Child Adolesc Dissemination and effectiveness of multisystemic Psychopharmacol 2014 Apr;24(3):140-8. Parent Sci increase academic performance in children with Pract 2007 Nov;7(4):331-55. X-7, X-8 How do outcomes in a specified parent training intervention maintain or wane over time X-4 Outcomes, moderators, and mediators of empathic emotion recognition training for complex conduct 189. Comparison commands presented to boys with oppositional and of behavioral intervention and sensory-integration hyperactive behavior. X-4 effects of a weighted vest on aggressive and self injurious behavior in a child with autism. X-4, X-5, X-6, X-7, X-8 Family Check-Ups in Early Childhood: Intervention Effects From Home to Early Elementary School. X-4 disruptive behaviour problems in children: community based randomised controlled trial. X-4 Prevention of problem behavior through annual family check-ups in early childhood: intervention 185. J Eltoprazine in aggressive mentally handicapped H-11 Abnorm Child Psychol 2014;42(3):343-54. Predicting success in an online parenting Sequential evaluation of reinforced compliance and intervention: the role of child, parent, and family graduated request delivery for the treatment of factors. Errorless compliance training: building a cooperative Psychol Sci 2013 Apr;24(4):456-65. A study of X-7, X-8 psychological intervention of children with aggressive conduct disorder. X-4 Improving initial session attendance of substance abusing and conduct disordered adolescents: A 208. Journal of Child & Adolescent Parental Emotion Coaching and Child Emotion Substance Abuse 1998;8(1):1-13. X-2, X-7 Regulation as Protective Factors for Children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder. X-2, X-5, X-6, X-7, X-8 effects of annoyance and retaliation on aggressive behavior. X-11 Mental health problems of young refugees: duration of settlement, risk factors and community-based 200. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 2013 possible antisocial effects of viewing television Oct;18(4):604-23. Influence acquisition of key parenting skills during parent of treatment for disruptive behavior disorders on training. Social isolation as a School-Based Preventive Intervention for Conduct punishment procedure: a controlled study. J Exp Problems: Follow-Up Results From a Randomized Child Psychol 1973 Oct;16(2):236-49. X based, noncoercive treatment of oppositional 11 behavior in children from violent homes. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 1973 Sep;7(3):169 Combined Treatment on Turkish Children Diagnosed 73. Aripiprazole treatment in the adolescent patients with inhalants use disorders 216. Treating boys with low school achievement and Yeni Symposium: psikiyatri, noroloji ve davranis behavior problems: comparison of two kinds of bilimleri dergisi 2010;48(3):229-33. Mental Health Services Research preventive intervention for youth experiencing 2001;3(1):35-44. Parent-child interaction therapy with X-4, X-5, X-6, X-7, X-8 behavior problem children: One and two year maintenance of treatment effects in the family. X Stimulant medication in pre-school children in New 2, X-5, X-6, X-8 South Wales. Aripiprazole Development and Pilot Testing of an Internet-based in children and adolescents with conduct disorder: A Parenting Education Program for Teens and Pre single-center, open-label study. X-2, X-4 African American families in parent-child interaction therapy: A pilot study. X-2, X-6, X-7, X-8 Facilitating tolerance of delayed reinforcement during functional communication training. Treatment with paliperidone X-5, X-6, X-7 in children with behavior disorders previously treated with risperidone: An open-label trial. X-11 modification of the token economy for nonresponsive youth in family-style residential care. X-5, X-6, Antisocial behavior, school performance, and X-8 reactions to loss: the value of group counseling and communication skills training. X-11 examination of a Group Curriculum for parents of young children with disruptive behavior. X-4 Prolactin levels during long-term risperidone treatment in children and adolescents. An analysis of the Incredible Years aggressive behaviors in hypogonadal adolescents. Pediatr Ann 1977 school bullying in Hong Kong: a longitudinal mixed Oct;6(10):637-45. Aggressive children in a day treatment program: Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 2008 Oct;13(4):593 changed outcome and possible explanations. Helping parents solve effects on children with and without attention-deficit stressful life problems enhances the effectiveness of hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc interventions for child aggression and antisocial Psychiatry 1997 Aug;36(8):1056-64. The effect of orally administered midazolam on Risperidone added to parent training and stimulant children of three age groups during restorative dental medication: effects on attention-deficit/hyperactivity care. Behandlungseffekte kombinierter kognitiver Effects on peer aggression in public school settings. J Verhaltenstherapie mit Elterntraining bei Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1990 hyperkinetischen Kindern. Randomized prevention trial for early conduct Stability and change in types of behavioral problems: effects on proactive parenting and links to disturbance of children and adolescents. Paternal mothers and conduct-problem children: is there involvement in Multisystemic Therapy: effects on training for harmony as well as fighting Effects of an explanation and brief psychosocial interventions on children with parent training on child and parent behaviors. J disruptive and emotional disorders treated in a health Abnorm Child Psychol 1976;4(3):277-88. Recreation for the conduct study evaluating the effect of massage therapy on disorder child. Except Child 1969 stress, anxiety and aggression in a young adult Summer;35(10):787-91.
Cheap ginette-35 2mg amex
The population figures for a given sector always include the interim workers employed in this sector enterprise menstrual extraction procedure discount ginette-35 2 mg otc. Some sectors of activity like the wood industries, the building and the metal industries are more at risk to cause back injury accidents than others, with the incidence rate respectively of 12. In other sectors like finance and insurance, hotels and restaurants, distribution of electricity and gas, the risk of having an accident with a back injury is much lower (2. However, any control strategy should also take into account the absolute number of accidents observed within a given sector: building sector, trade workers, health and social workers had the highest number of accidents, and those three sectors provided 46 % of the back injury accidents recorded during the three years studied. It is worth underlining that some high risk sectors for back injury occurrence like metal or steel industries exhibit much lower risk for permanent disability. On the contrary, the health sector which th ranks at the 11 place for back injury occurrence is the second high risk sector for permanent disability due to back pain. Yearly incidence rate of back injury accidents per 1000 workers at risk and outcomes according to the sector of activity in 2001-2003 (n = 34. On this basis the top ten list of the most risky sectors is presented in table 29. The results obtained in this way are in several respects different from those presented in table 28. They would be more valid as the proportions given in table 28 are influenced by the declaration rate of minor accidents (no day off). An example is high proportion of no sick leave accidents found in the steel industries (Nace 27), a sector that can hardly be considered as a low risk sector. In the table 29, the risk of getting a permanent incapacity is clearly the highest in two sectors: health and social sector (18. Figure 13 shows the distribution of the three outcomes analyzed for back injuries resulting from overexertion, from falls and from other circumstances. The other important type of back injury is the commotions/internal traumatism (18. The comparison between back injuries following overexertion, falls and other circumstances shows that Sprains (74. On the other hand, fractures are mostly observed in injuries following Falls (64. Even if the accuracy of the nature of injury codes selected by the enterprise administrative staff is not guaranteed, these data suggest that falls result in more serious trauma than the other type of accident circumstances. Distribution of nature of injury codes in the whole sample of back injury accidents and in the three subgroups of precipitating circumstances (n= 36,905) Total Overexertion Falls Others N % n % n % N % 10 Fractures 693 1. Comparison of back injuries outcome severity according to the accident circumstances the figure 14 shows the comparison of sick leave durations between workers with back injury from overexertion, from falls and from other circumstances. The figure shows that in the group with a back injury following an overexertion and those following other circumstances, the grade of permanent incapacity was less than 10 % in respectively 84. Back injuries were mostly recorded in young, male, blue-collar workers, working with little seniority in small enterprises located mainly in Flanders. Wallonia appears to be at higher risk both for the incidence of back injuries and for the incidence of a partial disability outcome. However, no further analysis could be performed for adjusting for potential confounding factors. In absolute terms, trading, building, health and transport sectors had the highest number of back injuries. However, in terms of incidence rate, wood, building and metal industries were identified as more susceptible to cause back injuries, while in terms of permanent incapacity, building, health, agriculture and forest sectors are at high risk to lead to a partial disability. A new and more accurate coding system is now applied in Belgium based on a European coding system. This is likely to result in an underestimation of the number of back pain episodes occurring during work activities. N re je cte d N Rejected back N N Rejected back accidents reject injuries/tota accepted declared injuries/tot (all types ed l rejected back back al declared of injury) back accidents injuries injuries back injurie injuries s n1 n2 % n3 n4 % 2 001 14,054 3,588 25. In work accident compensation systems, the relationship between a sudden generally unexpected event or work disruption and a bodily injury is the key element that the insurance is assessing when examining a worker claim for a work accident. Such a causal relationship cannot by definition be applied easily to the sudden appearance of a painful sensation in the low back when carrying out a given work task. There is still much debate as to whether an acute back pain is the final stage of a long process of disc degeneration, a given movement or effort prior to the pain being only an accessory revealing phenomenon, or could also be caused in a more direct way by some excessive mechanical stress. That question cannot be solved by the medical advisor of the insurer who relies instead on the legal definition of a work accident: when a sudden event cannot be established before the pain occurrence, most insurers are thus prone to reject the claim; rejection is more likely also when the worker is injured while doing a physically non-demanding task. As shown in the table above, more than one fifth of back pain claims in a work accident context are rejected. In addition, spontaneous claim rates are likely to be influenced among the workers by the likelihood of their claim being susceptible to be accepted. The data presented cannot thus be considered as representative of the true incidence of acute low back pain episodes occurring during work. The reasons why some claims are rejected may conversely be considered as possible confounding factors for the interpretation of the risk factors of the accepted claims. In that context, it must be noticed that the overexertion category of accident is by far based on the assumption that the movement or effort having preceded the back pain appearance had exceeded the normal physiological limits of the vertebral anatomical structures; such assumption is almost never based on force measurements or biomechanical calculations but inferred from the accident circumstances description. Similarity between back injuries and all types injuries Before commenting the factors that seem to influence the incidence rate of back injuries in the working population, it must be checked whether their distribution differs from the one of the occupational accidents as a whole. An identical pattern is observed for gender (77% of all accidents occurring in males), and professional status (75. This pattern reflects the gender distribution in the sectors most exposed to accidents: for instance the workforce in the building sector is essentially male. Moreover, it is well known that white collar jobs are less exposed to various hazardous factors. Slight differences are observed for age: back injuries are more frequent between 30 and 49 years than all other accidents (58. Whereas many work accidents are attributed to a lack of experience in young workers, it is likely that back injuries are related more to the spine aging process and to the cumulative effect with time of biomechanical stresses associated with working activities. For the regional factor, trends are similar but far more marked for back injuries. When accident outcomes are taken into consideration, permanent (partial) incapacity prevalence figures are higher for back injuries than the corresponding figures for all types of accident (8. In summary, back injury accidents seem to have specific age and regional distributions. Those injuries have also on average a worse outcome than other types of accidents. The regional factor in back injuries incidence the results showed that the regional differences in incidence cannot be ascribed to variations in the distribution of accident prone sectors between regions. Similarly large differences in back injury incidence between regions have indeed been observed in two sectors of activity, the building and the health sectors known to have an homogeneous distribution of employed people across the whole country. For back complaints of long duration (3 months or more during the last 12 months), this survey shows trends in the same direction but with smaller differences. Such regional differences may tentatively be ascribed to cultural differences (between Flemish and French-speaking citizens) in 337, 338 complaints rate as previously shown in a Belgian epidemiological study. This allowed us to compare our results with those found by Prevent in their 383 report because they used the same criterion. In this analysis, the building sector and the metal industries were at high risk to cause occupational accidents in general and back injury accidents in particular; similar findings have been described in the Prevent report. One explanation put forward refers to the fact that the building industry employs a lot of workers (180. However, it is likely that the kind of work typically observed on building works plays a major role. When considering prevention policies, a particular attention should be paid also to the Health and Social sector, which contributes to a large number of back accidents, but also ranks at the second place for a permanent disability outcome. Natural history of back injuries the Belgian data summarized in figure 10 allow a comparison with the data published in other countries for similar compensated cases of back injuries. This figure is slightly higher than the average 75 % described in the literature 99 387, 388 but slightly lower than the figures observed in general patient populations. Factors influencing the outcome of back injuries Caution is needed when analyzing the outcome of work accidents. Depending on the social environment they are working in, people may be more or less prone to file in an accident claim even if there is no day off needed. In some industrial sectors, trade unions have been successful in informing the workers that an accident claim, even for a minor injury, offers a legal protection against an unexpected and delayed health effect. The high claim rate with no sick leave recorded in these sectors cannot necessarily be interpreted as a proof of a high risk situation.
Order ginette-35 no prescription
Also menstruation girls purchase ginette-35 mastercard, in the weight loss or hepatomegaly), requiring dietary event that chronic renal disease has restriction or continuous medication, or; inca pacitating episodes (with symptoms such as progressed to the point where regular fatigue, malaise, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, dialysis is required, any coexisting hy arthralgia, and right upper quadrant pain) hav pertension or heart disease will be sep ing a total duration of at least two weeks, but less than four weeks, during the past 12 arately rated. Urinary frequency: 7501 Kidney, abscess of: Daytime voiding interval less than one hour, or; Rate as urinary tract infection. Marked obstructive symptomatology (hesitancy, slow or weak stream, decreased force of 7507 Nephrosclerosis, arteriolar: stream) with any one or combination of the fol Rate according to predominant symp lowing: toms as renal dysfunction, hyper 1. Testis, underscended, or con recurrent stone formation requiring genitally undeveloped is not a rat one or more of the following: able disability. Thereafter: Complete removal of both ovaries 130 7541 Renal involvement in diabetes Removal of one with or without mellitus, sickle cell anemia, systemic partial removal of the other. Any change in evalua wearing of absorbent materials which tion based upon that or any subsequent must be changed more than four times examination shall be subject to the provi per day. If there has been no local recurrence or Requiring the wearing of absorbent mate metastasis, rate on residuals. Hemoglobin 7gm/100ml or less, with find (4) Wide local excision (including ings such as dyspnea on mild exertion, partial mastectomy, cardiomegaly, tachycardia (100 to 120 lumpectomy, tylectomy, beats per minute) or syncope (three epi segmentectomy, and sodes in the last six months). If there has been no local recur myelosuppressants and for three months rence or metastasis, rate on residuals. With visible or palpable tissue loss and ei Note (2): If multiple qualifying scars are ther gross distortion or asymmetry of one present, or if a single qualifying scar af feature or paired set of features (nose, fects more than one extremity, or a single chin, forehead, eyes (including eyelids), qualifying scar affects one or more ex ears (auricles), cheeks, lips), or; with two tremities and either the anterior portion or or three characteristics of disfigurement. The midaxillary line on each Skin hypo-or hyper-pigmented in an area side separates the anterior and posterior exceeding six square inches (39 sq. The midaxillary line on each 7808 Old World leishmaniasis (cutaneous, Oriental side separates the anterior and posterior sore): portions of the trunk. If treatment is con 7802, 7803, 7804, or 7805), depending fined to the skin, the provisions for a 100 upon the predominant disability. If treatment is confined to the vascular involvement, mental disturbance (de skin, the provisions for a 100-percent mentia, slowing of thought, depression), evaluation do not apply. Noncompensable complications are con four episodes during the past year, or; weak sidered part of the diabetic process under diag ness and fatigability, or; corticosteroid therapy nostic code 7913. Automatic Disability in this field is ordinarily states or automatisms are character to be rated in proportion to the impair ized by episodes of irrational, irrele ment of motor, sensory or mental func vant, disjointed, unconventional, aso tion. Consider especially psychotic cial, purposeless though seemingly co manifestations, complete or partial ordinated and purposeful, confused or loss of use of one or more extremities, inappropriate activity of one to several speech disturbances, impairment of vi minutes (or, infrequently, hours) dura sion, disturbances of gait, tremors, vis tion with subsequent amnesia for the ceral manifestations, injury to the seizure. In rating disability from the cial standing remained seated, mut conditions in the preceding sentence tered angrily, and rubbed the arms of refer to the appropriate schedule. When there is doubt as to the true the seizure manifestations of psycho nature of epileptiform attacks, neuro motor epilepsy vary from patient to logical observation in a hospital ade patient and in the same patient from quate to make such a study is nec seizure to seizure. The guished from developmental) or almost frequency of seizures should be complete personality disintegration ascertained under the ordinary condi (psychosis). Consider espe 8020 Brain, abscess of: cially psychotic manifestations, complete As active disease. Deter tal disorders) when there is a diagnosis of minations as to the presence of residuals not a mental disorder. Ex here that are reported on an examination, ecutive functions are goal setting, speed evaluate under the most appropriate diag of information processing, planning, orga nostic code. This 10 percent rating will not be of two or more conditions cannot be clear combined with any other rating for a disability ly separated, assign a single evaluation due to cerebral or generalized arteriosclerosis. However, if the manifestations are nosis of multi-infarct dementia with cerebral clearly separable, assign a separate eval arteriosclerosis. This classification does not affect the rating assigned under diagnostic code 8045. For having difficulty fol even routine and famil lowing a conversation, iar decisions, occa recalling recent con sionally unable to iden versations, remem tify, understand, and bering names of new weigh the alternatives, acquaintances, or find understand the con ing words, or often sequences of choices, misplacing items), at and make a reason tention, concentration, able decision. For ex 3 Objective evidence on ample, unable to de testing of moderate im termine appropriate pairment of memory, clothing for current attention, concentra weather conditions or tion, or executive func judge when to avoid tions resulting in mod dangerous situations erate functional impair or activities. Examples are: ity to perform pre mild or occasional viously learned motor headaches, mild anx activities, despite nor iety. May be unable to touch or name own body parts when asked by the ex aminer, identify the rel ative position in space of two different ob jects, or find the way from one room to an other in a familiar envi ronment. The ratings for the cranial nerves Schedule of ratings are for unilateral involvement; when bilateral, Major Minor combine but without the bilateral factor. All radicular groups the ulnar nerve 8513 Paralysis of: 8516 Paralysis of: Complete. Complete; the foot dangles and drops, Posterior tibial nerve no active movement possible of mus cles below the knee, flexion of knee 8525 Paralysis of: weakened or (very rarely) lost. At this point, if there has and/or generalized convulsions with un consciousness. The personality disorder will be rated as a Rate under the general rating formula for minor dementia. All Diagnostic Codes under Mental Disorders October 1, 1961; except as to eval uation for Diagnostic Codes 9500 through 9511 September 9, 1975. Lungs and Pleura Tuberculosis Ratings for Pulmonary Tuberculosis (Chronic) Entitled on August 19, 1968: 6701. Ratings for Pulmonary Tuberculosis Initially Evaluated After August 19, 1968: 6730. Burn scar(s) of the head, face, or neck; scar(s) of the head, face, or neck due to other causes; or other disfigurement of the head, face, or neck. The content of this Orphanet Report Series represents the views of the author only and is his/her sole responsibility; it can not be considered to reflect the views of the European Commission and/or the Consumers, Health, Agriculture and Food Executive Agency or any other body of the European Union. The European Commission and the Agency do not accept any responsibility for use that may be made of the information it contains. Lichen planus is believed to represent an abnormal immune response in which epithelial cells are recognized as foreign, secondary to changes in the antigenicity of the cell surface. Recalcitrant lesions can be treated with systemic steroids or other systemic medications. However, there is only weak evidence that these treatments are superior to placebo. The nail beds may also be important for clinicians to be aware of its clinical presenta affected, with resultant ridging, thinning and subungual hyperkeratosis. Figure 3: Plaque-type variant of reticular oral lichen planus with Figure 4: Erosive oral lichen planus involving the buccal mucosa. In the bullous form, intraoral presentation from smooth, at areas to irregular, elevated bullae are present on the buccal mucosa and the lateral areas.
Order 2 mg ginette-35 overnight delivery
Being an effective communicator will help on the Ultimate field and serve students well into adulthood menstruation through the ages generic ginette-35 2 mg fast delivery. The state of New York has even put a relationship management section into their state standards in which students are supposed to: "Demonstrate positive interpersonal and intra-personal behaviors when working with others. Integrating Fitness Education Like many sports and activities that require a lot of movement and energy to be successful, the sport of Ultimate can be used as a vehicle for integrating technology and educating individuals about their fitness needs. Pedometers the rules of Ultimate and the designated boundaries make it so that there is a lot of movement up and down the field. Here are some ideas on how to use pedometers during Ultimate: Every 10,000 steps (players add their steps together) = 1 point for their team Players use their pedometer log to calculate calories burned/day or unit Each player that records 25 minutes or more of activity = 1 point for their team Every 10 minutes of activity (players add their time together) = 1 point for their team All points recorded from fitness equipment add up. Using monitors that can store data is much different than using monitors that only take a real time measurement. Data Recorders the telemetry strap can sometimes shift during throwing, catching, laying out, or reaching for the disc. Every 10 minutes in the heart rate zone (players add their time together) = 1 point for their team All points recorded from fitness equipment add up. Single Readings these are much harder to use and typically require the whole field to stop play in order to allow students to check their heart rate. However, because play is supposed to stop for violations calls and in between points, you can find time to have students do a check. The teacher can also call a time out to get everybody to stop which will allows students to check their heart rate. A pass not necessarily intended to gain yards, but to move the disc to a better position on the field, or reset the stall count. Generally, it occurs when the offensive player runs so close to another player on either team that the defensive player must stop, slow down, or alter her/his course in order to avoid a collision, thus leaving the offensive player open to receive a pass. Although legal in basketball, it is a dangerous play in Ultimate because of the speed at which players are running. The disc is brought back to the thrower for a replay, except in the case where the throw resulted in a turnover. The rules to Ultimate can be changed to accommodate students on crutches, in wheelchairs, or those that have motor control impairments. Just like every other unit in physical education, participation is the most important thing. Any student (even those without impairments) might learn or benefit from having any of the following accommodations. Wheel Chair Accommodations Playing the game inside or on tennis courts will make the game much more wheel chair friendly. Also allowing the student in the wheel chair two feet of space at all times on offense will help increase their involvement in the game. Gait Accommodations the easiest way to change the game for students who cannot travel as quickly as other students is to make running against the rules. Similarly, allowing the defense to move (or run) only when the disc is in the air will give students who have a slower gait or are limited by crutches a chance to keep up and get into position on offense. Limiting the defense to the same number of steps as the offense can help ensure that students who require crutches or cannot walk as quickly have a chance to get open on offense. Coordination Accommodations Teaching students who have coordination deficits or impairments with smooth motor control to throw and catch can take a lot of time. Using a softer disc or a ball will allow them to play the game with other students and keep them from getting injured by the hard plastic. Allowing the students who need accommodations more time to throw the disc and more distance from the defender will provide more opportunity for success. Another adaptation could be allowing students a chance to pick up one drop per point, or allowing each team to play the disc where it lands (even if it is not caught). Mental Disability Accommodations Ultimate moves very quickly and some of the rules can be confusing. For example, allowing students to run with the disc until they are tagged might help students adapt because they are familiar with football. Removing the end zones and asking students to count the number of throws they can complete in a row can substitute as a scoring system. Students with mental disabilities are generally more productive, have more fun, and learn more from cooperative games. Thus, instead of forming two separate teams, having everybody on one team and timing how quickly they can score may be a good adaptation to standard Ultimate. If you initiate or contribute to the unraveling of spirit, the concept falls apart quickly. If you act to mend things (or at least not worsen the situation) by following (1) above, the game heals itself. Time and again, great teams and star players have shown that you can bring all your competitive and athletic zeal to a game without sacrificing fair play or respect for your opponent. In the extreme case where you were severely mistreated, you may bring the issue up with a captain, tournament director, or even lodge a complaint with the governing body. We recall point (1): treat others as you would have them treat you, not as they have treated you. After a hard foul, close call, or disputed play, take a step back, pause, and take a deep breath. By giving yourself just a bit of time and space, you will gain enough perspective to compose yourself and concentrate on the facts involved in the dispute (was she in or out; did you hit his hand or the disc; did that pick affect the play). Remark to a teammate that you admire his honesty in calling himself out of bounds. Look players in the eye and congratulate them when you shake their hands after a game. Not only does the realization that your actions will be remembered for a long time serve to curb poor behavior, it can also inspire better conduct.
Teucrium chamaepitys (Ground Pine). Ginette-35.
- Dosing considerations for Ground Pine.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Stimulating menstrual (or "period") flow, gout, rheumatism, malaria, fluid retention (edema), causing sweating, wound healing, use as a tonic, and other uses.
- What is Ground Pine?
- How does Ground Pine work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96667
Ginette-35 2mg low cost
Clumsiness and painful tightness in the hand and forearm occur during writing or playing women's health clinic ne calgary purchase 2mg ginette-35 with visa, and abnormal tension Kamath V, Stothard J. Erratum to: A clinical questionnaire for the diagnosis and strange posturing develop. Endoscopic versus open surgical of local anaesthetic (or topical anaesthetic) is followed by treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Corticosteroid injection for the Methylprednisolone is about ve times as powerful as hydrocorti treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. High-quality evidence for the the neck moves almost constantly during waking hours through effectiveness of many treatment modalities is limited and often exion, extension and rotation at the intervertebral and facet joints contradictory. Treatment aims to control pain and Instability, caused by laxity (congenital or acquired) or lack of restore movement and function of the shoulder. Patients present with pain and tenderness over the lateral the elbow is a compound synovial joint composed of a complex epicondyle and pain with resisted movements. Prognosis is of two closely related articulations between the humerus and both generally favourable, with 80% recovery within a year. Management is directed towards controlling pain, avoiding aggravating activities and maintaining movement. It is some the neck and shoulder are two of the most common sources of times hard to distinguish between pain arising from the neck or musculoskeletal pain. The majority of neck pain is acute shoulder girdle or over the scapula indicates referred pain from and self-limiting and can be attributed to a mechanical or postural the neck. Shoulder pain has a self-reported point prevalence of between Details of hand dominance, any injury, hobbies, sporting activities 14 and 26% in the general population. The incidence of shoulder and treatments for this or any other similar previous musculoskel pain increases with age, as does its functional impact. The history should elicit the presence of any clinical features that indicate potentially serious pathology. This includes the scapulotho racic articulation, where the scapula slides on the ribcage. Nevertheless, nocturnal pain should raise suspicion of nerve root pain, bony pathology or underlying malignancy, particularly if there is a history of cancer It includes careful inspection, palpation, movement, special and/or systemic symptoms. Neurological symptoms should be sought and their Neck pain distribution ascertained (Figure 3. Other notable symptoms include stiffness, clicking, clunking or Pain in the neck usually arises because of poorly dened mechani locking. Joint swelling around the shoulder or elbow can occur in cal inuences, although it can occur because of pathology within relation to arthropathy, infection or trauma. A list of differential diag such as fevers, night sweats, weight loss, generalized joint pains, noses of neck pain is shown in Box 3. Restricted cervical movements and local and the degree of functional decit and coexisting pathologies. These symptoms ischaemia, referred diaphragmatic pain, warrant urgent referral for specialist assessment. Symptoms may be persistent, although 50% of patients recover within 3 months and 80% within 12 months. Risk factors for chronicity after whiplash include the severity of the initial symptoms and psychological disturbance. It usually responds to con high prevalence of asymptomatic degenerative changes in the cervi servative treatment, although patients should be instructed to cal spine, plain radiographs are rarely diagnostic, and pain severity return for further assessment if symptoms persist or change in correlates poorly with radiographic abnormalities. Radicular pain, due to compression of a nerve root from hernia tion of a cervical disc, or due to non-compressive causes such as Treatment of neck pain local infection or tumour, refers to neck pain that radiates into the Patients should be informed of the generally favourable prognosis shoulder girdle and/or arm with paraesthesia or numbness in a root of neck pain and the fact that serious underlying conditions are distribution. Pertinent psychosocial and occupational issues may may not reveal the nerve root level because of the extensive overlap need to be explored. Motor involvement and/or objective Neck pain usually responds to simple analgesia and advice about sensory loss warrant urgent referral for specialist assessment. There is no evidence that collars reduce pain or of difculty walking, lower limb symptoms or bladder and bowel improve function, nor is there evidence about special pillows. Motor signs of myelopathy below the level of spinal general patients are advised to sleep on their side with a single Pain in the Neck, Shoulder and Arm 15 pillow supporting the neck. Surgery may also be indicated in people with myelopa asthma, past history of peptic ulcer, renal impairment). If there is signicant nocturnal pain, a tricyclic Shoulder pain antidepressant. The best type and mix of exercise has not been dened, but includes stretching, strengthening and proprioceptive retraining exercises (usually prescribed by Box 3. Exercise therapy is contraindicated in the presence of Pain arising from the shoulder myelopathy. Cognitive behavioural therapy has been Instability and dislocation shown to decrease time off work and other behavioural manifesta Traumatic labral tears tions of pain but not to change the degree of pain.
Order discount ginette-35 line
Imagine my surprise when he invited me to participate in the renewed ar chaeological excavations at Tel Halif women's health clinic yakima wa cheap ginette-35 2mg line, Israel. Our mutual interests in the daily activities of the average ancient Judahite would be our focus at Tel Halif, utilizing the methodology of household archaeology. As a result of the Halif excavations, Oded has become a mentor and a friend, and it is my privilege to contribute to this volume in his honor. The study of diet, cooking, and eating practices is an effective way to understand daily life of ancient societies not only because food was essential to their physical sur vival, but also because meals are much more than just food. Meals contain a diverse collection of cultural practices embedded within them, such as dietary preferences and taboos, culinary practices, household economics, religious ritual, gender roles, power relations, and accepted social norms, just to name a few. This chapter begins with a brief survey of past and present scholarship on food studies within the research of ancient/biblical Israel and Judah, followed by 279 280 Cynthia Shafer-Elliott a description of the interdisciplinary methodology used for this present study. Focusing on one aspect of daily life, namely daily food preparation (and its assumed con sumption), will allow us to learn more about the cultural context of eighth-century Judah. Within biblical scholarship the topic of food was a concern mostly in the form of dietary laws and the sacrificial system. Within archaeology of the southern Levant and the Mediterranean world, food in the form of elite feasting and drinking was the popular topic. Neither of these historical foci illuminates the daily food preparation and consumption for the average ancient Israelite and Ju dahite very well, but there are some that paved the way for the present interest in cultural context. One of the most influential contributors into the daily life of ancient Israel is Oded Borowski. A second forerunner of food studies in ancient Israel is Carol Meyers, whose research on food preparation stems from her interest in the roles of women in the biblical world. Her numerous articles on the subject of Israelite women as preparers of food and their subsequent power and authority within the household are important contributions to both feminist and food stud 2 ies. The third publication worth noting here is the 1999 volume of Semeia Studies edited by Athalya Brenner and J. Brenner and van Henten acknowledge the lack of scholarship on food and drink within biblical studies and hoped their volume would provide the motivation for scholars to look more deeply into the subject; however, excluding further work by Borowski and Meyers, the interest into food preparation and consumption was somewhat long in coming (Brenner and van Henten 1999). Present scholarship includes broad encyclopedias to various areas of detailed specialization ranging 4 from the study of diet, plant and animal remains, baking, and feasts. The incorporation of studying plant and animal remains allows archaeologists an opportunity to investigate the actual physical remains of meals. A natural result of the interest in food in ancient Israel is the organization of groups dedicated to its study in various scholarly institutions, such as the Ameri can Schools of Oriental Research and the Society of Biblical Literature. Both currently have a session dedicated to the research of various aspects of food in cluding production, preparation, and consumption through archaeological, textual, and iconographic materials. Accordingly, a volume concentrating on feasts in ancient Israel and the ancient Near East was recently published and is one of the few volumes that are specifically on an aspect of food studies, namely feasting (Altmann and Fu, 2014). The current interest in researching food in an cient and biblical Israel/Judah will surely provide us with more publications on the subject. Fuller summaries of scholarship can be found in Nathan MacDonald 2008; Alt mann and Fu 2014. For a current encyclopedia on food studies within in archaeology, see Bescherer Metheny and Beaudry 2015. Primary resources include archaeological material cul 5 ture and textual sources. Indeed, the present study must be interdisciplinary in nature simply because the primary textual resource for ancient Israel and Judah, the Hebrew Bible, does not provide a detailed record of food preparation, daily or otherwise. Archae ological evidence provides us with the physical reality of ancient cultures, including food and feasting in ancient Judah. With that said, there are a few things that must be kept in mind when utilizing ancient texts. The majority of the average population in ancient Judah would have been mostly illiterate (Mandell 2013, 81). The Hebrew Bible, along with other ancient liter ature of the ancient Near East, were written and edited by the literate elite and not the average man or woman; consequently, the Hebrew Bible rarely reflects the daily lives of the average person. When an ancient text does make reference to aspects of daily life, it must be discerned if they reflect actual or ide alized practices of daily life. This does not mean we discard this biblical text altogether; rather, the inclusion of the law of Jubilee into biblical law reveals specific aspects of the economy of ancient Israel and Judah. For instance, that while the land itself was considered sacred and inalienable, there were various economic circumstances that led to the loss of household land. Archaeological excavations uncover the material culture of ancient societies; archaeologists base their interpretations on the mate rial culture of their site and other sites that are parallel to it in time and space. There are many types of archaeologies, but the type that best suits our pur poses here is household archaeology. The discipline of household archaeology concentrates on the lived environment and daily activities of the home and its members. The first floor consisted of a back-broad room with one to three (most often three) rooms running perpen dicular to it. The first floor had wood or stone pillars supporting the second floor; these pillars often had short boundary walls between them to help segregate space. Houses were small but still ranged in size depending if the house was in an urban or rural environment (Shafer-Elliott 2013, 109). For this reason, it is best to think of the houses in Iron Age Israel and Judah as being multi-functional with several household activities taking place in the limited space available. The first floor was used for a variety of domestic activities including storage, production (such as pottery making), food preparation and consumption, and religious ritual. The social aspect includes the members of the household and their relation ship to each other. In other words, a household is a group of people who typically live and/or work together but may or may not be related. A family is a group of people who are related to each other either biologically or through marriage, but they may or may 6. For instance, an ancient Judahite household could include immediate and extended family members, such as par ents, unmarried daughters and sons, married sons and their families, and any unmarried or widowed women, but also non-related members such as slaves, guests, concubines, or hired workers. The evidence from the material aspect of the household is applied to determine what activities or functions the artifact was used for.
Purchase ginette-35 2 mg on-line
A smoothly G-equivariant prefactorization algebra on M is an G algebra F over Disjg and an action of the Lie algebra g of G on the under M lying prefactorization algebra of F such that for every X g pregnancy zumba dvd purchase generic ginette-35, every operation G (g. G Remark: In some cases, an algebra A over Disjg should possess a natural action of M g. Suppose V is an open such that gU V for every g in some neighborhood of the identity in G. Then we can dierentiate the structure maps mg: A(U) > A(V) to obtain a map X: A(U) > A(V) for every X g. Example: Let F be a locally constant, smoothly translation invariant factorization algebra on R, valued in vector spaces. Being locally constant means that for any two intervals (0, 1) and (t, t + 1), there is an isomorphism F ((0, 1)) F ((t, t + 1)) coming from the isomorphism F ((a, b)) > F (R) associated to inclusion of an interval into R. As F is trans lation invariant, there is another isomorphism F ((0, 1)) > F ((t, t + 1)) for any t R. Composing these two isomorphism yields an action of the group R on A = F ((0, 1)). One can check that this is an action on associative algebras, not just vector spaces. The fact that F is both smoothly translation-invariant and locally constant means that the action of R on A is smooth, and thus it dierentiates to an inn itesimal action of the Lie algebra R on A by derivations. In the case that F is the cohomology of the factorization algebra of observables of the free scalar eld theory on R with mass m, we will see in Section 3 that the algebra A is the Weyl algebra, generated by p, q, ~ with commutation relation 1 2 2 2 [p, q] = ~. The divergence complex of a measure In this section, we will revisit the ideas and constructions from Chapter 2. Re call that in that chapter, we studied the divergence operator associated to a Gaussian measure on a nite-dimensional vector space and then generalized this construc tion to the innite-dimensional vector spaces that occur in eld theory. We will q 0 q nd a cochain complex Obs such that H (Obs) is the vector space we constructed in Chapter 2. To make the narrative as clear as possible, we will recapitulate our approach there. One way to describe the divergence operator is to contract with the volume form ef/~ to identify Vect(M) with n1(M) and C(M) with n(M). Explicitly, 0 the contraction of a function with ef/~ is the volume form ef/~, and the 0 0 contraction of a vector eld X with ef/~ is the n 1-form ef/~. Under 0 X 0 this identication, the divergence operator is simply the de Rham operator from n1(M) to n(M). Here we use ef/~ to denote the contraction map; it is the natural ex 0 tension to polyvector elds of the contractions we dened for functions and vector elds. In summary, after contracting with the volume ef/~, the divergence complex 0 i becomes the de Rham complex. Note that this second cochain complex is a dierential graded algebra, which is not the case for the divergence complex. Indeed, this whole complex is the Koszul complex for the equations cutting out the critical locus. Remark: We will call a manifold with a nice sheaf of dg commutative algebras a dg manifold. Since the purpose of this section is motivational, we will not develop a theory of such dg manifolds. We are using the concrete object here as a way to think about the derived geometry of this situation. The ordinary critical locus of f is the intersection of (d f) with the zero-section M TM. In short, we nd that the ~ > 0 limit of the divergence complex is the dg commutative algebra of functions on the derived critical locus of f. The derived critical locus for a general function f can be viewed as a deformation of T[1]M obtained by introducing a dierential d f. We will dene the prefactorization algebra of observables of a free scalar eld theory as a divergence complex, just like we de ned H0 of observables to be given by functions modulo divergences in Chapter 2. It turns out that there is a slick way to write this prefactorization algebra as a twisted factorization envelope of a certain sheaf of Heisenberg Lie algebras. We will explain this point in a nite-dimensional toy model, and then we will use the factorization envelope picture to dene the prefactorization algebra of observables of the eld theory in the next section. The construction is quite general: we do not need to assume 0 that q is non-degenerate. The derived critical locus of q is described by the cochain complex W given by /q V > V [1], where the dierential sends v V to the linear functional qv = q(v, ). Note that W is equipped with a graded anti-symmetric pairing h, i of co homological degree 1, dened by pairing V and V. In what follows, we will dene the prefactorization algebra of observables of a free eld theory as a Chevalley-Eilenberg chain complex of a certain Heisenberg Lie algebra, constructed as in this lemma. The prefactorization algebra of a free eld theory In this section, we will construct the prefactorization algebra associated to any free eld theory. We will concentrate, however, on the free scalar eld theory on a Riemannian manifold. We will show that, for one-dimensional manifolds, this prefactorization algebra recovers the familiar Weyl algebra, the algebra of observ ables for quantum mechanics. In general, we will show how to construct correla tion functions of observables of a free eld theory and check that these agree with how physicists dene correlation functions. Let M be a Riemannian manifold with metric g, so M is equipped with a natural density. We will use this natural density both to integrate functions and also to provide an isomorphism between functions and densities, and we will use this isomorphism implicitly from hereon. The scalar eld theory has smooth functions as elds, and we use the notation C(M) for an arbitrary eld. The action can be viewed here as a device for producing these partial dierential equations. If U M is an open subset, then the space of solutions to the equation of motion on U is the space of harmonic functions on U. In this book, we will always consider the derived space of solutions of the equation of motion. As this derived space is a cochain complex (and hence linear in nature), it is natural to work with the polyno mial functions. The space E (M) has the structure of dierentiable cochain complex (essentially, it is a sheaf of vector spaces on the site of smooth manifolds). In other words, we consider smooth multilinear maps from n copies of E (M), and then we take the S n-coinvariants. The algebra of all polynomial functions on E (M) is the space P(E (M)) = nPn(E (M)). For example, the space P (E (M)) = E (M) of smooth linear functionals on 1 E (M) is the space 1 4 0 E (M) = Dc(M) > Dc(M), where Dc(M) indicates the space of compactly supported distributions on M. The classical observables with support in U M are then the symmetric algebra of 4 E (U) = Dc(U)[1] > Dc(U), where Dc(U) indicates the space of compactly supported distributions on U. The complex E (U) is thus the graded, smooth linear dual to the two-term complex E (U) above. Note that, as the graded dual to E, this complex is concentrated in cohomological degrees 0 and 1. These are precisely the observables that only depend on the behavior of the eld on the open set U. Thus, as a rst pass, one would want to dene the classical observables as the symmetric algebra on E (U). When we work with an interacting theory, these di culties can only be surmounted using the techniques of renormalization. For a free eld theory, though, there is a much simpler solution, as we now explain.
Buy generic ginette-35 line
The shallower anterior include high myopia menopause constipation generic 2mg ginette-35 with visa, cataracts, vitreoretinal degeneration, chambers and larger crystalline lenses in these patients and retinal detachment. Open-angle, anterior segment probably account for their myopia and proclivity to dysgenesis and neovascular forms of glaucoma have all 120,121 develop phacomorphic pupillary block. Pupillary block angle cotton-like amyloid vitreous opacities, eyelid abnor closure by forward displacement of a small spherical lens malities, extraocular muscle weakness, proptosis, con from loose zonules or subluxation is the most common junctival microaneurysms, internal ophthalmoplegia, mechanism of glaucoma, and this may be exacerbated by 124 irregular pupillary margin, anisocoria, and retinal miotics, which reduce zonule tone on the lens equator. Some patients may develop an open deposition and degenerative changes in the trabecular 127,128 meshwork may obstruct aqueous outflow. Systemic administration of certain nonsteroidal drugs Approximately 29 to 36% of eyes treated with may precipitate angle-closure glaucoma. Medications charged-particle external beam radiation can develop with anticholinergic or sympathomimetic effects can neovascular glaucoma. In eyes with heavy irradiation, cataract surgery may accelerate the development of neovascular glaucoma,162 Selective serotonin Fluoxetine (Prozac) and perioperative photoablation of the ischemic retina reuptake inhibitors Atypical agents Paroxetine (Paxil)175,176 may be indicated. Even prolonged administration of Hydroxyamphetamine inhaled glucocorticoids and chronic facial application Cocaine of potent corticosteroids can increase the risk of ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. Diseases of the lens and vit Mydriatics Cyclopentolate, Tropicamide, reous, glaucoma and hypotony. Systemic blood pressure cause angle closure by encouraging swelling or for in glaucoma. A case from nonsteroidal drugs lies in identifying patients at control study of risk factors in open angle glaucoma. Hypertension perfusion pressure and primary medications with anticholinergic or sympathomimetic effects may require open-angle glaucoma: a population-based assess prophylactic iridotomy to prevent acute angle-closure glaucoma. Shock induced optic neuropathy: a cause of nonprogres Mydriatic agents that act through anticholinergic sive glaucoma. Presum tory blood pressure monitoring in glaucoma: the ably, these agents diminish ciliary muscle tone and fur nocturnal dip. Because of this, hour blood pressure monitoring in normal tension practitioners should defer using these agents to dilate glaucoma. Diurnal and optic nerve damage until after the pressure is better nocturnal blood pressure drops in patients with controlled. Open-angle chamber angle structures, resulting in a congenital form glaucoma and diabetes: the Blue Mountain Eye of glaucoma. Increased plasma non and primary open-angle glaucoma in the Baltimore cortisol glucocorticoids activity in open-angle glau Eye Survey. Poikilodermatomyositis Prevalence of increased intraocular pressure in with retina hemorrhages and secondary glaucoma. Reversal of osteogenesis imperfecta: a new autosomal recessive poorly controlled glaucoma on diagnosis and treat syndrome. Blood and cutaneous melanosis and encephalofacial plasma viscosity measurements in patients with angiomatosis. Neovascular bocythemia and central vein occlusion with neovas glaucoma as a complication of the Wyburn-Mason cular glaucoma. Glaucoma in Sturge notype with ocular involvement: clinical and ultra Weber syndrome. Glaucoma in sive hemorrhage mechanisms in the Sturge-Weber in the Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome. Ocular Opitz syndrome, Hallermann-Streiff-Francois syn findings in partial trisomy 3q: a case report and drome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Ocular anomalies in Trisomy istence of Prader-Willi syndrome, congenital ectro 13-15: an analysis of 13 eyes with two new findings. Medical treatment of glaucoma after helium-ion irradiation for uveal glaucoma associated with cicatricial retinopathy of melanoma. Anterior for malignant melanomas of the choroid: with fol segment abnormalities in cicatricial retinopathy of low-up results more than 5 years. Long-term agement of late-onset angle-closure glaucoma results of 125I irradiation of uveal melanoma. Primary familial amyloidosis enucleation after plaque radiotherapy for posterior (ocular manifestations with histopathologic obser uveal melanoma. Secondary glaucoma tive factors for the development of rubeosis follow accompanied with primary familial amyloidosis. The vast majority of glaucoma is treated with eyedrops, Other drug properties include receptor selectivity, and successful glaucoma management requires a com corneal penetration, and protein/melanin binding. The selectivity of action compares the potency at different recep conjunctival cul-de-sac is a unique pharmacokinetic envi tors. For example, timolol maleate has a similar potency at ronment and provides many challenges to effective topi both beta1 and beta2-adrenoceptors. The principles reviewed here can be applied to is 100 times more potent at the beta1-adrenoceptor than at subsequent chapters dealing with each specific drug class. The physician should also confirm that the patient receives education about the proper instillation of Pharmacokinetics is the study of the rate of processes that medications, and the importance of adhering to the pre govern absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excre tion of a medication. Finally, with continuing changes in health care management and pharmaceutical developments, these processes in the eye. Blinking the properties of drugs include efficacy, potency, and causes the majority of the drop to spill out onto the cheek therapeutic index. However, the 1 not surprising that only 1 to 7% of an instilled dose pen two agents are similar in ocular hypotensive efficacy. Therapeutic index is the ratio of drug efficacy to the magnitude of adverse side effects. The stroma is 78% water and is passed most and may explain why timolol remains active long after the treatment is stopped. Because the lipophilic endothe lium is only one cell layer thick, it is a much weaker barrier Esterases are common in the eye and are known to than the epithelium. Medication entering the anterior chamber is immediately Although ocular cytochrome p450 levels are highest in diluted as it mixes with aqueous from the anterior and the ciliary epithelium and retinal pigment epithelium, they posterior chambers. Elimination of the drug occurs are still severalfold lower than in tissues such as liver and lung. Medications also may be in the metabolism of drugs taken by oral and intravenous bound to aqueous proteins and melanin in the iris and routes, does not significantly affect the bioavailability of ciliary body.
Buy ginette-35 2 mg on-line
The granny had 930 genes that were found to be statistically significant having p-values < 0 menstrual flow results in the discharge of order ginette-35 without a prescription. The mom, twin, and cousin had 343 genes that were found to be statistically significant with p-values < 0. A comparative analysis between these two gene lists showed a gene overlap of 118 genes. An individual human genome consists of 3-4 million variants, or locations that vary from the human reference genome. This can be done by means of various heuristics such as allele frequencies and their effects on protein functions (Cooper and Shendure, 2011; Goldstein et al. There is a need in the biomedical research community for a tool that is capable of filtering these millions of variants based on the most up-to-date annotations and utilizes the growing arsenal of genome analysis methods. Nonetheless, a majority of these tools focus on processing raw sequence data to detect high confidence genomic variants rather than focusing on downstream analyses such as annotation-based variant filtering and statistical analysis (Lam et al. Furthermore, it has been well documented that every individual or pedigree will carry numerous so-called private mutations 65 etd. It is hypothesized that rare variants are likely to cause disease and for this reason, variants with very low or no available frequency data are prioritized. Rare, possible disease-causing variants are likely to be at an extremely low frequency in this database and any variant with a frequency that is higher than 1% is removed from the list of interest. Highly conserved genes are believed to be more likely to have deleterious phenotype effects if they are dysregulated or structurally altered (Kumar et al. If any of the disorders are related or similar to the disease of interest, then that gene and variant will become the leading candidate for further analysis. Variant coordinates were manually entered and searched against three 68 etd. So the above analysis may not sufficiently illustrate that causal mutation(s) for a complex disease can be easily detected by processing the sequenced data of only a small sample size. Nevertheless, these results suggest that the filtration and prioritization procedure utilized above can help dramatically downsize the number of candidate variants to a very small subset that is human-manageable; and is unlikely to filter out good candidates. However, there remains an uncertainty as to whether these variants are in actual fact deleterious, because some algorithms use common source data to make predictions and a poor call by one algorithm may then be replicated by other algorithms accordingly. Primary data for pathway analysis is frequently sourced from genotyping or gene expression arrays, though in theory any data elements that could be mapped to genes or gene products could be used. As such, pathway analysis represents a potentially powerful and biologically-oriented bridge between genotypes and phenotypes. Information derived from pathway analysis includes in depth and contextualized findings to help understand the mechanisms of the disease in question, discovery of genes and proteins associated with the etiology of a specific disease, prediction of drug targets, as well as understanding how to intervene therapeutically in disease processes and conduct targeted literature searches. Furthermore, data integration such as integrating diverse biological information from the scientific literature, knowledge databases, genome sequences, protein sequences, motifs and structures. Functional discovery by assigning functions to genes can also be retrieved from pathway analysis bioinformatics. To identify and prioritize these alleged relations, a wide range of enrichment analysis tools have been developed in recent years. One such tool is EnrichNet, and is described here as an example that illustrates the principles and steps of pathway analysis clearly. EnrichNet generates a novel graph-based statistic, developed to manipulate information from molecular network structures linking two gene/protein sets, with a new interactive visualization of network sub-structures. This united network analysis and visualization allows direct molecular interpretation of how a user-defined set of genes/proteins is related to a gene/protein set of known function. Based on previous work that entails the merging of network and pathway analysis methods (Glaab et al. A general workflow for EnrichNet involves the following: (1) Input a list of 10 or more human gene or protein identifiers and the selection of a database of interest (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (Kanehisa et al. Next, a network analysis procedure is applied, this procedure entails two basic steps: a procedure to score the distances between the mapped target gene set and reference datasets in the network using a random walk with restart algorithm and the comparison of these scores against a background model and (3) Output a ranking table of the reference datasets. For every pathway, a hyperlink allows the user to create an interactive graph-based visualization of the sub-network representing the analysed datasets in the molecular interaction network. The user can explore this network by zooming into it, searching and highlighting specific genes/proteins and retrieving additional annotations and topological information by clicking on a node of interest. This disadvantage has been overcome in this study by modelling only the direct gene-gene interactions defined by the software. Under the build tool, trim was selected and under interactions (Default: Indirect), was highlighted for the removal of all indirect interactions. Parameters for the grow tool were set to include both direct and indirect interactions, and adding 10 molecules at a time. Parameters were set to include direct interactions only, and adding all molecules. Numerous transcript variants encoding various isoforms have been found for this gene. Conjugates of this protein have been found to be noncovalently attached to intermediate filaments. It is believed to have evolved as a result of an ancient cell lines, ovarian cancer organismal death, Kvasnicka et al. Two transcript variants encoding various isoforms and one non-coding transcript have been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene may be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. The genes in green contain rare variants, the genes in red contain novel variants and the blue genes contain rare and novel variants identified in my study. Acute Phase Response Signaling is a coordinated response to tissue injury, infection or inflammation. A remarkable feature of this response is the selection of acute phase proteins, which are involved in the restoration of homeostasis (Moshage, 1997). Tec Kinase Signaling or Tyrosine kinases have roles in the control of cell survival, activation, and differentiation. There is ample to be learnt from the genetics of sub-Saharan African populations regarding the origin and nature of human complex disease. Presently, we have little understanding of the genetic structure of sub-Saharan populations and the genetic basis of complex disease in African populations because very few studies have been conducted in African ethnic groups. Our lack of knowledge about the involvement of genetics to disease in 90 etd. However, the finding of a missense mutation on its own cannot be assumed to be causal. The variant selection tool used in the analysis incorporated robust models of cross species sequence conservation, which further improve the accuracy in differentiating between benign and disease-causing variation. Therefore, if a variant causes changes that are not good for the species then they are more likely to be selected against. Therefore, additional basic research needs to be performed on the role each transcript plays and the effect a variant has on each of them. Whilst the Mendelian inheritance model was also considered (Asymptomatic Model) in this analysis, it is clear that there is insufficient background information and too few family members in order to conduct a meaningful investigation of Mendelian inheritance in the family. For a relatively low price, all known protein-coding regions of the genome are included, and each region is sequenced in often 50-100 fold redundancy. Considering the fact that an average individual has approximately 10,000 protein-coding non-reference variants (Ng et al. Therefore, the above mentioned variants could contribute to a plausible explanation for disease susceptibility amongst the affected members and a lack thereof amongst unaffected members of this family. It is also plausible that the susceptibility variants proposed from the analysis of the Susceptibility Model, the Tipping Point variants identified in the Tipping Point model, and the Protective variants identified in the Protective mutation model could work together in a dynamic process that drives the presentation of the disease phenotype or suppresses it. Figure 6 is a proposed model for how these variants might work individually, or together, at different levels in the continuum from unaffected phenotype to susceptible phenotype, and from susceptible phenotype to disease phenotype. In many complex diseases there is also a strong role for environmental factors that may also affect the progression to the disease state.

