Mobic
Discount mobic 7.5 mg with amex
An excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time arthritis workouts buy line mobic. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. Code First/Use Additional Code notes (etiology/manifestation paired codes) Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation. They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition. Code Also A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter. The 7th character must always be the 7th character of a code Chapter 1 Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) Includes: diseases generally recognized as communicable or transmissible Use additional code to identify resistance to antimicrobial drugs (Z16. B04 Monkeypox B05 Measles Includes: morbilli Excludes1: subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (A81. Code first condition resulting from (sequela) the infectious or parasitic disease B90 Sequelae of tuberculosis B90. B95 Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere B95. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, etc. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned. Malignant neoplasms (C00-C96) Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary (of specified sites), and certain specified histologies, except neuroendocrine, and of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue (C00-C75) Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx (C00-C14) C00 Malignant neoplasm of lip Use additional code to identify: alcohol abuse and dependence (F10. A-) C15 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus Use additional code to identify: alcohol abuse and dependence (F10. A1 Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, unspecified lymph nodes of head, face, and neck C84. A4 Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, unspecified, lymph nodes of axilla and upper limb C84. A5 Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, unspecified, lymph nodes of inguinal region and lower limb C84. Z Other lymphoid leukemia T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (associated with rheumatoid arthritis) C91. A Acute myeloid leukemia with multilineage dysplasia Acute myeloid leukemia with dysplasia of remaining hematopoesis and/or myelodysplastic disease in its history C92. Z Other specified malignant neoplasms of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue C96. Z Other myelodysplastic syndromes Excludes1: chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (C93. Z Other specified neoplasms of uncertain behavior of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue D47. Z9 Other specified neoplasms of uncertain behavior of lymphoid, hematopoietic and related tissue Histiocytic tumors of uncertain behavior D47. Excludes1: transitory endocrine and metabolic disorders specific to newborn (P70-P74) this chapter contains the following blocks: E00-E07 Disorders of thyroid gland E08-E13 Diabetes mellitus E15-E16 Other disorders of glucose regulation and pancreatic internal secretion E20-E35 Disorders of other endocrine glands E36 Intraoperative complications of endocrine system E40-E46 Malnutrition E50-E64 Other nutritional deficiencies E65-E68 Overweight, obesity and other hyperalimentation E70-E88 Metabolic disorders E89 Postprocedural endocrine and metabolic complications and disorders, not elsewhere classified Disorders of thyroid gland (E00-E07) E00 Congenital iodine-deficiency syndrome Use additional code (F70-F79) to identify associated intellectual disabilities. The dysfunction may be primary, as in diseases, injuries, and insults that affect the brain directly and selectively; or secondary, as in systemic diseases and disorders that attack the brain only as one of the multiple organs or systems of the body that are involved. F01 Vascular dementia Vascular dementia as a result of infarction of the brain due to vascular disease, including hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Includes: arteriosclerotic dementia Code first the underlying physiological condition or sequelae of cerebrovascular disease. These disorders generally have onset within the childhood or adolescent years, but may continue throughout life or not be diagnosed until adulthood F90 Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorders Includes: attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity attention deficit syndrome with hyperactivity Excludes2: anxiety disorders (F40. A0 Cyclical vomiting, not intractable Cyclical vomiting, without refractory migraine G43. A1 Cyclical vomiting, intractable Cyclical vomiting, with refractory migraine G43. B0 Ophthalmoplegic migraine, not intractable Ophthalmoplegic migraine, without refractory migraine G43. B1 Ophthalmoplegic migraine, intractable Ophthalmoplegic migraine, with refractory migraine G43. C0 Periodic headache syndromes in child or adult, not intractable Periodic headache syndromes in child or adult, without refractory migraine G43. C1 Periodic headache syndromes in child or adult, intractable Periodic headache syndromes in child or adult, with refractory migraine G43. D0 Abdominal migraine, not intractable Abdominal migraine, without refractory migraine G43. D1 Abdominal migraine, intractable Abdominal migraine, with refractory migraine G43. The category is also for use in multiple coding to identify these types of hemiplegia resulting from any cause. The category is also for use in multiple coding to identify these conditions resulting from any cause Excludes1: congenital cerebral palsy (G80. The category is also for use in multiple coding to identify these conditions resulting from any cause. If the extent of the visual field is taken into account, patients with a field no greater than 10 but greater than 5 around central fixation should be placed in category 3 and patients with a field no greater than 5 around central fixation should be placed in category 4, even if the central acuity is not impaired. A Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A1 Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A11 Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, right ear with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A12 Conductive hearing loss, unilateral, left ear with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A2 Sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A21 Sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, right ear, with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A22 Sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, left ear, with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A3 Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A31 Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, right ear with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H90. A32 Mixed conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, left ear with restricted hearing on the contralateral side H91 Other and unspecified hearing loss Excludes1: abnormal auditory perception (H93. A1 Myocardial infarction type 2 Myocardial infarction due to demand ischemia Myocardial infarction secondary to ischemic imbalance Code also the underlying cause, if known and applicable, such as: anemia (D50. A9 Other myocardial infarction type Myocardial infarction associated with revascularization procedure Myocardial infarction type 3 Myocardial infarction type 4a Myocardial infarction type 4b Myocardial infarction type 4c Myocardial infarction type 5 Code first, if applicable, postprocedural myocardial infarction following cardiac surgery (I97. A1) subsequent myocardial infarction of other type (type 3) (type 4) (type 5) (I21. Use additional code, where applicable, to identify: exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (Z77. X Influenza due to identified novel influenza A virus Avian influenza Bird influenza Influenza A/H5N1 Influenza of other animal origin, not bird or swine Swine influenza virus (viruses that normally cause infections in pigs) J09.
Syndromes
- Breathing in irritating substances
- Avoid asthma triggers
- Stroke
- Loss of a toe, foot or leg
- Learning problems
- Are allergic to shellfish or iodine substances
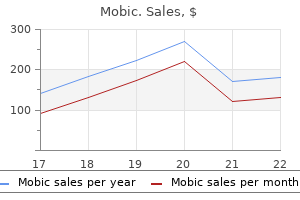
Buy mobic without prescription
There is a growing understanding of opioid-induced hyperalgesia (24); a situation in which patients taking opioids arthritis in neck tingling buy mobic american express, paradoxically, become more sensitive to painful stimuli. This is another reason for these drugs to be used in a controlled fashion for long-term management of non-malignant pain. Failure to comply with the above may result in the patient being referred to a drug dependency agency and the use of therapeutic, analgesic opioids being stopped. The aim is to use a slow or sustained release preparation starting with a low dose and titrating the dose every 3 days to 1 week against improvement in both function and pain. It may also be beneficial when there are intolerable side effects from other opioids. Oxycodone may have greater efficacy than morphine in some situations, such as hyperalgesic states including visceral pain (26). Analgesics with a dual mode of action may have a role in the management of chronic pain. Tramadol is an established analgesic with dual effects on opioid receptors and serotonin release. It is too early to assess its real value in the armamentarium for pain management. It is clear that further more rigorous trials should be undertaken to provide some clarity for a commonly used intervention. These techniques are only used as part of a broader management plan and require regular follow-up. These are expensive interventions and thus many of the patients involved are refractory to other therapies. Many are aimed at management of neuropathic pain or conditions in which central mechanisms are implicated. At this stage in management, the involvement of trained clinicians with expertise in chronic pain management should be considered. This information is kept on file in the European Association of Urology Central Office database. This guidelines document was developed with the financial support of the European Association of Urology. Some successful examples of turning the recommendations into reality at country level already exist, and should be highlighted and used as models. Many of these fatalities are in children, particularly in low and middle income countries. Sepsis claims more lives than breast, bowel and prostate cancer put together, but until recently, few had heard of it. In the context of the rising threat of antimicrobial resistance, however, we must do so responsibly. We have come a long way since I, and others around the world, started this fght a number of years ago. Coders stick to strict rules, and cannot make a diagnosis someone has missed or written incorrectly. In turn, coding afects, for example, how much a hospital gets paid; and more importantly our broader societal understanding of clinical and public health issues. The increase in recorded incidence of sepsis will be in part due to heightened awareness and more reliable recording, but our ageing populations and increasing tendency to perform a greater number of invasive interventions will have a signifcant efect. Over recent years, studies among wider populations have placed this incidence progressively higher as recording and coding has improved. The group also estimated indirect costs, primarily due to lost productivity but also in litigation. Clearly, if a patient has died because of sepsis, they are unable to return to productive life, and they will not be able to pay taxes. We know, for example, that 22% of survivors of sepsis who have needed Intensive Care have post-traumatic stress disorder; and that 17% of survivors have moderate-to-severe cognitive decline. These changes have, at times, created confusion, but it is hoped that from the time of writing there will be a period of stability for some years while we continue to advance improvements in clinical systems. No defnition is currently perfect, and we do not yet enjoy the routine adoption of any one set of crtieria to prompt either a screen for sepsis or treatment for sepsis. Where it is felt it will add clarity, make reference to now historic aspects of sepsis defnitions. That same study also found that patients organ dysfunction, we need to know in which patients we should start looking for sepsis. But in a resource-constrained, busy healthcare system, this is not always 100% reliable. This is helpful in order for us and our patients to understand that antibiotics alone will not fx the problem. People with evidence of a systemic infammatory cellular and metabolic abnormalities substantially increase mortality. The frst version was a highly validated tool in the identifcation of deterioration from any cause. All that is needed is a reasonable clinical suspicion of infection, so a chesty cough with green sputum, or i. Ask a senior, make sure someone orders tests such as a chest X-ray, and revisit the diagnosis once you Measurement Score Measurement Score have more information. The risk here is the ready availability of clinical staf with sufcient eperience and gestalt. Whilst most General Practitioners If you identify one or more Red Flags, assume the patient has sepsis. Amber Flags, bloods should be sent in addition to ensuring review by a senior clinician. If care in the community is considered suitable, then verbal and written lactate, Full Blood Count, urea and electrolytes, C-reactive Protein, liver function tests and enzymes and safety netting instructions should be provided where appropriate. This can make early diagnosis challenging, as early signs can often be missed by healthcare providers. Few doctors can describe the defnition of sepsis accurately, so it is no surprise that sepsis can be difcult to identify and therefore that delays in initiating treatment are common. Regular screening of patients at risk of sepsis and early, and judicious treatment of those presenting with likely sepsis, are key to improving patient outcomes. An understanding of the potential and common sources of infection and their modes of presentation will help you to identify those at risk of sepsis and choose an appropriate treatment regime.
Mobic 15 mg sale
Because these signs also4 may indicate other diseases arthritis medication for back pain cheap mobic 15 mg on-line, a person must consult a healthcare provider to determine their cause. In other words, resistance spreads with the infection itself; it therefore tends to concentrate in geographically identifable areas. The decrease in the number of cases and the case rate between 1992 and 2006 was notably greater among men than women. Figure 2 shows the tuberculosis rates in 2007 by race/ethnicity in the United States. Preliminary data show that tuberculosis cases among persons born interna tionally (foreign-born persons) but now living in the United States accounted for 58. Four countries of origin (Mexico, the Philippines, India and Vietnam) accounted for over half (51. One type of skin test, the Mantoux test, is preferred and should be used for screening and diagnosis. In this test, a small amount of testing material is injected under the very top layers of skin on the forearm. It is extremely important that these screening programs undergo regular evaluation of their usefulness. Please visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention fact sheet at. Results have been inexplicably con ficting, with some studies seemingly showing that it works, others that it is worthless. Generally, vaccines approved for use in the United States are at least 70 percent effective. Ethambutol (or streptomycin in young children) also should be included in the initial regimen until the results of drug-resistance tests are available. They include recommenda tions for rapid identifcation of persons with active disease, relying not only on skin testing (which may give false-negative results) but also on chest x-rays and sputum analysis; and screening of high-risk populations. Other recommenda tions address the need for comprehensive contact investigation and follow-up; preferred treatment regimens, including management of noncompliance with therapy; environmental control of infection in hospitals and other institutions; and prevention of recurrent infection and protection of health care personnel. Costing $11 per patient for a six-month drug supply in some coun tries, the World Bank has ranked the strategy as one of the most cost-effective of all health interventions. The targets were missed on a global scale as only 60 percent and 84 percent of cases were detected and treated, respectively. The National Association for the Study and Prevention of Tuberculosis, as it was known then, was the frst nationwide voluntary health organization aimed at conquering a specifc disease. Joseph Wales realized that the small sanatorium on the Brandy wine River in Delaware where he worked was down to its last dollar. In response, Emily Bissell designed the frst American Christmas Seal and borrowed $40 to have 50, 000 of them printed. The National Association embarked on a research program that was to become truly signifcant in its scope and infuence. Representative of the myriad of scientifc refnements and improvements were those affecting the x-ray and tuberculin test. The research committee of the National Association began supporting investigations into improved x-ray machines and techniques. Public Health Service, bought and took these tools to locations where people were in order to conduct testing. The National Association launched a medical research and teaching fellow ships award program in 1948, targeting young physicians or students in related felds. As more strains of tuberculosis emerge and become resistant to frst-line anti biotics, there is an increased reliance on second-line drugs to successfully treat multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis infections. Researchers, funded by the Ameri can Lung Association, aim to develop new antibiotic derivatives that regain antibacterial activity against resistant strains with fewer side effects. Other research is exploring why only some people infected with tuberculosis actually develop the active, infectious disease. The American Lung Association also supports the Healthy People 2010 goal of less than one new case per 100, 000 persons in the United States by 2010. Estimates for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, pneumonia/infuenza and other lung diseases are from Chart Book, 2007, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, 2007. Race and Gender Differences in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Deaths in the United States: An Analysis of Multiple-Cause Mortality Data (1979-1996). Ventilation with Lower Tidal Volumes as Compared with Traditional Tidal Volumes for Acute Lung Injury and the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Pathogenic and Prognostic Signifcance of Altered Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Acute Lung Injury/Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. A Meta-Analysis of Time-Series Studies of Ozone and Mortality with Comparison to the National Morbidity, Mortality and Air Pollution Study. Association of Low-Level Ozone and Fine Particles with Respiratory Symptoms in Children with Asthma. Short-Term Effects of Low-Level Air Pollution on Respiratory Health of Adults Suffering from Moderate to Severe Asthma. Association Between Ozone and Hospitalization for Respiratory Diseases in 16 Canadian Cities. Increased Risk of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Episodes Associated with Acute Increases in Ambient Air Pollution. Power Plant Emissions: Particulate Matter-related Health Damages and the Benefts of Alternative Reduction Scenarios. State of the Air: Health Effects of Outdoor Air Pollution, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Report on the National Survey of Lead-Based Paint in Housing, Base Report: Executive Summary. Improving the Health of Workers in Indoor Environments: Priority Research Needs for a National Occupational Research Agenda. Effect of Exposure to Traffc on Lung Development from 10 to 18 Years of Age: A Cohort Study. Pediatric Patient Asthma-Related Emergency Department Visits and Admissions in Washington, D. Indoor Air Quality in Homes of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Diabetes Enhances Vulnerability to Particulate Air Pollution-Associated Impairment in Vascular Reactivity and Endothelial Function. Environmental Equity: Reducing Risk for All Communities, Volume 1: Workgroup Report to the Administrator. Traffc Density in California: Socioeconomic and Ethnic Differences Among Potentially Exposed Children. Power Plant Emissions: Particulate-Related Health Damages and the Benefts of Alternative Emissions Reductions Scenarios. Home Indoor Pollutant Exposures Among Inner-City Children with and without Asthma. Indoor Exposures to Air Pollutants and Allergens in the Homes of Asthmatic Children in Inner City Baltimore.
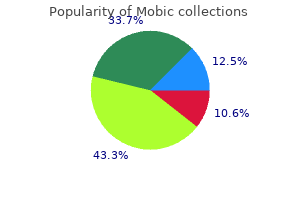
Mobic 15 mg without prescription
The lipids coat the cells rheumatoid arthritis reddit buy 7.5 mg mobic with visa, cells are pushed toward the limit of the stratum spinosum. The cells are kera of the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum and stratum tinized and have completed their programmed cell death granulosum. Although the cells are of the spiny appearance of the cells in microscope slide no longer living, chemical activity continues inside the cells preparations. During the process of making the slide, the as the fnal modifcations are made to the keratin. The spines are where the desmosomes are still viable, terminally differentiated keratinocytes, the stratum holding the cells together. Keratinocytes entering the stratum granulo flled cells (bricks) are surrounded by the lipids (mortar) sum contain characteristic keratohyalin granules (Figure secreted while the cells were in the stratum granulosum 2-12). The keratinocytes are programmed to fll with keratin; (Freinkel and Woodley, 2001, p 25). Although they are dead, the keratohyalin granules contain proteins (proflaggrin, the cells of the stratum corneum continue to undergo keratin, and loricrin) that facilitate the process (Freinkel and modifcation as they are pushed from the deeper portion of Woodley, 2001, p 23). The lamellar granules become active the stratum corneum to the surface of the skin. The cells as the cells reach the upper portion of the stratum granu in the deeper portion of the stratum corneum are thicker losum. The outer papillary lay surface, the cell membrane becomes more rigid and the er is a loose connective tissue containing anchoring fbrils desmosomes are degraded. Dermal papillae are malleable, Communication of the keratinocytes with the melanocytes, peglike projections of the papillary dermis between the Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells is necessary for the skin primary and secondary ridges. During the genetic material of the keratinocytes from ultraviolet dam remodeling, the epidermis forms sheets of tissue that age (Junqueira and Carneiro, 2003, p 374). These reside in the basal layer of the epidermis and, in addition sheets of tissue are called anastomoses. As the epidermal to providing the surrounding keratinocytes with melanin, anastamoses form, the dermal papillae are molded into produce vitamin D. The formation of dermal papillae and epider Langerhans cells initiate an alert that causes the body to mal anastomoses increases the surface area of attachment recruit more aggressive immune cells (T cells) to attack the between the epidermis and dermis, thereby increasing the invaders (Freinkel and Woodley, 2001, p 30). Merkel cells oc dermis with strength and resilience (Freinkel and Woodley, cur sporadically in the basal layer of the epidermis and are 2001, p 38). The reticular dermis is connected to the hypo associated with free nerve endings from the dermis. Cross section of friction ridge skin with detail of the epidermis separated from the dermis to display the dermal papillae and complementary epidermal anastomoses. Free nerve endings from the arterial plexus and into the dermal papillae to and Meissner corpuscles are found in the dermal papillae. Meissner corpuscles (Figure 2-16) are found Blood passes from the arterial capillaries in the dermal in about every fourth papilla and function as touch recep papillae to the venous capillaries. Pacinian and three plexuses: one associated with each arterial plexus Ruffni corpuscles are located throughout the dermis and and a third plexus in the middle of the reticular dermis also function in the transmission of pressure (Freinkel and (Junqueira and Carneiro, 2003, p 376). The autonomic nerve network is responsible for Although the skin produces several appendages. Eccrine sweat touch, temperature, pain, and itch (Freinkel and Woodley, glands are found all over the body surface and function 2001, p 153). Beneath the fbrous reticular dermis there is an abrupt Eccrine sweat glands are classifed as simple tubular transition to the adipose tissue of the hypodermis. Adipose glands whose ducts open at the skin surface (Junqueira (fat) tissue serves as an energy reserve, cushions the and Carneiro, 2003, p 380). The fuid secreted by the eccrine sweat through interlocking fbers and share blood vessel and glands is predominantly water (99. The remaining constituents of sweat primary cell of the hypodermis is the adipocyte. Adipocytes include sodium chloride, potassium, ammonia, urea, lac are organized in lobules by fbrous connective tissue and tate, uric acid, creatinine and creatine, amino acids, sugars, store the subcutaneous fat. The basement the concept of keeping things the same despite constant membrane is a fbrous sheet that attaches the basal input and output of materials and energy is referred to as keratinocytes of the epidermis to the underlying dermis. Homeostasis is critical to the functioning of attachment plaques, termed hemidesmosomes, which all organisms. The dermis projects physical attachments and the careful regulation of cell pro anchoring fbers back up toward the epidermis. The hemidesmosomes There are structural features of the overall skin and of the and interlocking fbers prevent the basal cells from migrat skin cells that maintain the structure of the epidermis (even ing. The basal keratinocytes are locked down to their posi though skin cells are always sloughing at the surface). The third level of primary/secondary ridge attachment with anastomoses, the attachment consists of the cell-to-cell attachments of basement membrane zone, and cell-to-cell attachments. The frst level Desmosomes and focal tight junctions attach the kerati of attachment is the topography at the junction of the nocytes to one another. The alternating system of primary the cells move from the basal layer to the surface. Upon and secondary ridges on the bottom of the epidermis pro reaching the outer portion of the stratum corneum, the vides general structural support for the surface ridges and desmosomes and focal tight junctions are broken down to furrows. The sweat glands of the primary ridges are frmly release the cells from the surface. G1 is Skin must maintain the protective barrier while existing in the resting period between mitoses. The rate at which basal cells divide in the basal to its duration greatly infuence the number of basal cells layer must coincide with the rate at which cells are leav produced (Freinkel and Woodley, 2001, p 202). There must be a mechanism in place to the cell reaches a critical restriction point and monitors con control the rate of cell division of the basal keratinocytes and ditions to determine whether it will enter the next phase of to monitor the thickness of the skin. The keratinocytes are also in communication with the rest of the body via the dermis. Rapid communication between the G2 phase, the cell reaches a second critical restriction cells is achieved via gap junctions. The that permit the direct exchange of small molecules, ions, M phase, mitotic phase, is the physical division of the cell and hormones. Rapid communication via gap junctions results in the keratino Upon completion of mitosis, the basal cells may enter cytes acting in a coordinated manner rather than as inde into G1 and continue the cell cycle or they may enter G0. Basal cells entering G0 are no longer cycling but may re enter the cell cycle upon receipt of the appropriate signal 2. The new cells cre cell-to-cell communication through gap junctions, cells ated by the basal cells will either withdraw from the cell also have modifed proteins embedded in the outer mem cycle and begin differentiation or cycle a few more times brane that can respond to signals sent through the blood (transient amplifying cells) before differentiating. When a signal mol that have started to differentiate are the cells entering the ecule binds to the outer surface of the membrane protein, stratum spinosum. There are many opportuni ties throughout the cell cycle to regulate the rate at which 2. Cell communication is necessary for include hormones, proteins, ions (particularly calcium), and monitoring and adjusting the rate at which the basal cells vitamins A and D. The fve phases of the cell cycle are cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Freinkel and Woodley, represented as G0, G1, S, G2, and M.
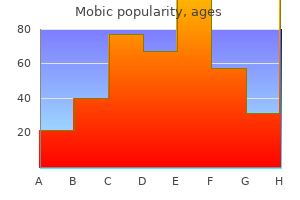
15mg mobic for sale
Recently arthritis relief drink cheap 15mg mobic fast delivery, changes in the sympathetic nerve firing pattern were observed with sympatho inhibition during weight loss [Lambert, et al. These observations provide the evidence of a strong linkage between the activity of the sympathetic nervous system and insulin levels. Fasting insulin levels were greater in hypertensive-type 2 diabetic patients and type 2 diabetic patients compared to hypertensive patients or healthy normotensive subjects. These findings, although obtained in patients still under medication, provided evidence that type 2 diabetic patients had elevated sympathetic nerve activity regardless of the prevailing blood pressure levels, and that the combination of hypertension and type 2 diabetes resulted in an augmentation in sympathetic nerve activity and levels of plasma insulin. Several investigations on the contributions of 2 and 3-adrenoceptor polymorphisms to type 2 diabetes also support a strong relationship between sympathetic nerve hyperactivity and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes [Masuo, et al. Figure 1 summarizes the relationships between sympathetic nerve activity and insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (Figure 1). Obesity causes both insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia and sympathetic nervous activation, and both link closely each other. Many investigations have shown that insulin resistance, sympathetic nervous activation, and adrenoceptor polymorphisms play important roles in the onset and maintenance of obesity, type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Insulin resistance in obesity, hypertension and type 2 diabetes Insulin resistance [Ferrannini, et al. The clinical evaluation of insulin resistance is growing interest because it is a strong predictor and plays an important role in the development of the metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Table 1 shows the criteria for metabolic syndrome characterisation, as can be seen insulin resistance is prominent [Alberti, et al. Table 2 summarizes the methods usually used in clinical and epidemiological studies (Table 2). Hyperinsulinemia as a marker of insulin resistance Insulin is an exceptional hormone in that its action is regulated not only by changes in concentration but also by changes in the sensitivity of target tissues. Inadequate insulin action can be the consequence of: (i) insufficient insulin concentration at the site of action, (ii) decreased tissue (effectors) responses to insulin, or (iii) a combination of low concentration and a decreased response. Regulation of circulating insulin levels is mainly (but not exclusively) achieved by changes in secretory rates. Nevertheless, the major determinant of insulin secretion, and therefore of plasma insulin concentration, is glucose. Any change in glucose concentration from the narrow normal range results in an insulin response appropriate to restore homeostasis. Thus, changes in insulin sensitivity occur in various physiological states and pathological conditions. For any amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas, the biological response of a given effector is dependent on its insulin sensitivity. Any decrease in insulin sensitivity (insulin resistance) is immediately translated into minute increases in blood glucose concentrations that will in turn act on the cell to produce a compensatory stimulus of insulin secretion, leading to a degree of hyperinsulinemia that is approximately proportional to the degree of effector resistance. In steady state conditions, this compensatory hyperinsulinemia prevents a more exaggerated hyperglycaemia. The inability of cells to enhance insulin secretion means that blood glucose will keep increasing until the level of hyperglycaemia produces an adequate cell stimulus to attain the required insulin response. When the cell is unable to compensate for the prevalent insulin resistant state by further augmenting insulin secretion, hyperglycaemia continues to increase, producing impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance and diabetes mellitus development. Relationships between sympathetic nervous activity and insulin resistance in obesity, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes It is widely recognized that insulin resistance or hyperinsulinemia relates to obesity [Ferrannini, et al. Many epidemiological and clinical studies have shown a close relationship between sympathetic nervous system activity and insulin levels in obesity [Anderson, et al. Elevations of sympathetic nervous system activity and insulin levels during weight gain [Masuo, et al. These longitudinal studies have shown that heightened sympathetic nerve activity and insulin resistance are closely linked to obesity (weight gain), the onset of obesity and the maintenance of obesity. In addition, a calorie restricted diet and exercise may have different mechanism on weight loss-induced blood pressure reduction. Figure 2 shows changes in neurohormonal parameters over a 24-week period weight loss regimens with a mild calorie restricted diet alone, mild exercise alone, or a combination with a mild calorie restricted diet and mild exercise. This study showed that a calorie restricted diet contributed strongly to normalization/suppression of sympathetic activation, and exercise related to insulin resistance. In addition, calorie restricted diet and exercise may have different mechanisms on weight loss-induced blood pressure reduction [Masuo, et al. Reduced energy expenditure and resting metabolic rate are predictive of weight gain and obesity development. The sympathetic nervous system participates in regulating energy balance through thermogenesis (Figure 1). Landsberg and other investigators hypothesized that energy intake stimulates hyperinsulinemia and sympathetic nerve activity resulting in blood pressure elevations in a cycle in order to inhibit thermogenesis. Insulin-mediated sympathetic nerve stimulation in obese subjects is therefore considered part of a compensatory mechanism aimed at restoring the energy balance by increasing the metabolic rate [Landsberg. Hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in obese subjects are all part of a response to limit further weight gain via stimulating sympathetic nerve activity and thermogenesis [Landsberg, 2001]. On the other hand, Julius and Masuo generated a hypothesis based on data from their longitudinal studies that increased sympathetic nerve activity in skeletal muscle causes neurogenic vasoconstriction, thereby reducing blood flow to muscle and consequently inducing a state of insulin resistance by lowering glucose delivery and uptake in hypertension and obesity. Both blood pressure elevations and weight gain may reflect a primary increase in sympathetic nervous tone. Heightened sympathetic nerve activity might play a major role in blood pressure elevations, and insulin resistance might play an ancillary mechanism for blood pressure elevation and genesis of hypertension. In hypertensive patients who already have heightened sympathetic nerve activity and insulin resistance, both heightened sympathetic nerve activity and insulin resistance are related to further blood pressure elevations. On the other hand, in exercise alone group, normalization of insulin resistance was observed, and then weight loss and suppression of sympathetic activation. When significant changes were observed comparisons between a calorie restricted diet vs. A calorie restricted diet caused Sympathetic Nervous Activation and Insulin Resistance as Renal and Cardiac Risk 169 suppression/normalization of sympathetic activation measured with plasma norepinephrine levels followed by improvements of insulin resistance, whereas exercise improved insulin resistance followed by normalization of norepinephrine levels. Their investigations may help to explain why discordant results have been observed. However, at least their hypotheses showed a strong linkage between sympathetic activation, insulin resistance, obesity and hypertension. Their findings that a generalized decrease of adrenergic responsiveness in hypertension supports the hypothesis that heightened sympathetic nerve activity through down-regulation of adrenoceptor-mediated thermogenesis, may facilitate the development of obesity in hypertension. Their results suggested that sympathetic nerve activity-induced hypertension may subsequently lead to the development of obesity. Moreover, both acute and chronic hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia may enhance adrenergic vasoconstriction and decrease vasodilation in animal models (pithed rats) [Takatori, et al. Insulin causes forearm vasoconstriction in obese, insulin resistant hypertensive humans [Gudbjornsdotti, et al. Sympathetic nervous activity and leptin in obesity and the metabolic syndrome Interactions between the sympathetic nervous system and leptin are widely acknowledged with each being able to influence the other. Indeed, the leptin system mediates some of its action through the sympathetic nervous system [Haynes, et al. These studies, together with others, indicate that both insulin resistance and leptin may be regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. In subjects with the metabolic syndrome, weight loss with a low caloric diet diminished the whole-body and regional sympathetic nerve activity, as indicated by determinants of the whole-body norepinephrine spillover to plasma and muscle sympathetic nerve activity. Of interest, the decrease in norepinephrine spillover to plasma after weight loss was positively and independently associated with the decrease in plasma leptin, but not with insulin sensitivity in overweight insulin resistant subjects, while in overweight subjects without insulin resistance, the decrease in plasma norepinephrine after weight loss correlated with the improvement of insulin sensitivity. Sympathetic nervous activity and insulin resistance in the metabolic syndrome the metabolic syndrome is a cluster of abnormalities with basic characteristics being insulin resistance and visceral obesity. Importantly, obesity and the metabolic syndrome are associated with significant co morbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and certain types of cancers. Sympathetic activation occurred in not only subjects with the metabolic syndrome, diabetic patients, but also in normotensive non-diabetic offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes with the degree of activation being in proportion to their plasma insulin levels. This series of studies indicates the presence of a mechanistic link between hyperinsulinemia and sympathetic activation, both of which could play a role in the subsequent development of cardiovascular risk factors.
Scotch Mercury (Digitalis). Mobic.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Digitalis?
- Irregular heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation or flutter.
- How does Digitalis work?
- Congestive heart failure (CHF).
- Asthma, promoting vomiting, epilepsy, tuberculosis, constipation, headache, spasm, wound and burn healing, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What other names is Digitalis known by?
- Dosing considerations for Digitalis.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96310
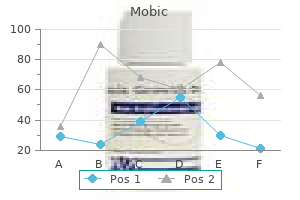
Generic mobic 15mg with mastercard
Techniques such as angiography and transcranial Doppler imaging can be utilized to identify vasospasm arthritis pain medication cream buy mobic 15mg amex. Calcium channel blockers and neurointerventional techniques are not well studied in children and not commonly used. Figure 3: Subarachnoid hemorrhage Skull fractures are commonly associated with head trauma in 2-21% of 9 children. The four major types of skull fractures are linear, depressed, diastatic and those at the skull base. Linear skull fractures are the most common and should be followed for epidural hematoma. Skull fractures depressed deeper than surrounding inner table (> 1cm) may require operative management. Deeper depressions are associated with greater risk of dural tear as well as cortical laceration and therefore worse prognosis [10]. The Monro-Kellie doctrine states that given that the cranium is a rigid, nonexpansile container, the total volume of the intracranial contents must remain constant and any increase in the volume of one component must be at the expense of the others, assuming the intracranial volume remains constant (Figure 5). This exam should be performed, preferably before the administration of sedation and neuromuscular blockade. Attention should be paid to scalp lacerations, which may be the source of shock in pediatric patients. Although pediatric patients are prone to hypoglycemia, this is rare in the first phases of trauma. As hypoxia and hypotension can cause secondary brain injury, this should be avoided in the suspected head trauma. There is an approximately 10% association of cervical spine fractures associated with intracranial injuries [18]. Moreover, patients with hyperglycemia in the first 48 hrs after admission are also associated with a worse prognosis [21]. Cerebral edema peaks at 72-96 hours after injury and will slowly resorb over a 7 day time period. Intensive Care Management the patient should be positioned with the head of the bed elevated to 15-30 degrees. Sedation and analgesia should therefore be implemented when clinically possible and safely at the 8 discretion of the treating physician. Current recommendations are to begin therapy in patients with documented intracranial hypertension and/or impending signs of herniation. Mannitol usage has fallen out of favor due to several side effects including the rebound effect of secondary cerebral ischemia, serum 285 electrolyte imbalance and hypovolemia. Recent data suggests that 3% hypertonic saline should be used as the mainstay therapy to maintain serum Na concentrations of 150-170 mEq/L and serum osmolarity of 360 mOsm/L. Serum osmolarity of 360 mOsm/L has been reported to be well tolerated in the pediatric patient with a head injury [27]. Hypertonic saline has also been reported to have several other potentially beneficial effects which include vasoregulatory, hemodynamic, neurochemical, and immunologic properties. Myelinolysis is more likely to occur with a rapid transition from hyponatremia to hypernatremia. Young age and non-accidental trauma are independent predictors for the development of seizures. Treatment includes a loading dose of phenobarbital 15-20 mg/kg as a single dose with maintenance dose given 12-24 hours later at 5 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hrs and subsequently titrated for therapeutic levels at 15-40 mcg/mL. These studies have also noted trends of increased pneumonia and suppression of endogenous cortisol levels. Decompressive craniectomy, high-dose barbiturate therapy, hyperventilation, lumbar drain placement, and the use of moderate hypothermia should be considered in these patients. Early decompressive craniectomies has been shown to provide improved outcomes in several small single-center studies [32 33]. Their side effects limit their current use to those patients with injuries refractory to first-line therapies as evidence has been limited to several small case series [34, 35]. Their use is associated with hemodynamic instability therefore close monitoring is imperative. Finally, therapeutic hypothermia may be considered as a second line therapy as the benefits seen in animal models remains unproven in humans. Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations and Deaths. Mild traumatic brain injuries in children between 0-16 years of age: a survey of activities and places when an accident occurs. Guidelines for the acute medical management of severe traumatic brain injury in infants, children, and adolescents-second edition. Pediatric critical care medicine: a journal of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and the World Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care Societies. Antibiotic prophylaxis for preventing meningitis in patients with basilar skull fractures. Guidelines for the acute medical management of severe traumatic brain injury in infants, children and adolescents. Cervical spine trauma associated with moderate and severe head injury: incidence, risk factors, and injury characteristics. Acute hyperglycemia is a reliable outcome predictor in children with severe traumatic brain injury. Effect of endotracheal suctioning on cerebral oxygenation in traumatic brain-injured patients. Role of hypertonic saline and mannitol in the management of raised intracranial pressure in children: A randomized comparative study. Use of hypertonic saline in the treatment of severe refractory posttraumatic intracranial hypertension in pediatric traumatic brain injury. Decompressive craniectomy in children: single-center series and systematic review. Fanconi S, Kloti J, Meuli M, et al: Dexamethasone therapy and endogenous cortisol production in severe pediatric head injury. Kloti J, Fanconi S, Zachmann M, et al: Dexamethasone therapy and coristol excretion in severe pediatric head injury. Comparison of outcomes following decompressive craniectomy in children with accidental and nonaccidental blunt cranial trauma. Decompressive craniectomy in 14 children with severe head injury: clinical results with long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Aggressive physiologic monitoring of pediatric head trauma patients with elevated intracranial pressure. Efficacy of barbiturates in the treatment of resistant intracranial hypertension in severely head injured children. Measuring the burden of secondary insults in head-injured patients during intensive care. Treatment of acute traumatic brain injury in children with moderate 290 hypothermia improves intracranial hypertension. In 2012, according to the National Trauma Database Registry, 12% of pediatric trauma patients suffered injury to the chest. Although chest trauma is less common in children, it remains an area of concern because it is associated with increased mortality. In fact, chest trauma accounts for up to 14% of trauma-related deaths in the pediatric population, making it second only to blunt head injuries. However, in cases where there is multi-system involvement concomitant with thoracic injuries, such as abdominal or brain injury, mortality drastically increases to nearly 40% to 70%. This makes motor vehicle crashes the number one mechanism of traumatic chest injury in the pediatric population overall. Children are either passengers in traffic accidents or pedestrians struck by motor vehicles.
Order mobic 7.5mg fast delivery
Dysregulation of the synthesis and secretion of these peptides has been associated with rheumatoid arthritis medication orencia purchase mobic 15mg with visa, and implicated in, the aetiology of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes. A possible role for adipokines in the regulation of myocardial metabolism only emerged recently [143-145]. Myocardial Insulin Resistance: An Overview of Its Causes, Effects, and Potential Therapy 201 Leptin is synthesised by white adipose tissue and is involved in appetite control and energy expenditure. Although the absence of leptin leads to obesity and insulin resistance, most obese patients have elevated leptin levels but do not respond to the appetite suppressing and other effects of the peptide [146, 147]. Mutations of the leptin receptor (Ob-R) are associated with obesity in the db/db mouse [148] and the Zucker (fa/fa) rat [149] and leptin deficiency occurs in obese (ob/ob) mice [150] while the treatment of patients [151, 152] and animals [150] with recombinant leptin reduces body weight and improves serum lipid levels. Serum triglyceride levels and blood glucose handling also improved in women with lipodystrophy and leptin deficiency indicating that leptin may alter lipid metabolism and prevent lipotoxicity [153]. This reduction in serum fatty acid levels will also counter the effect of insulin on lipogenesis [74, 154]. A simplified illustration to demonstrate the effects of adipocytokines on tissue insulin sensitivity and inflammation. The lipid lowering effects of leptin in heart muscle was demonstrated in a study where 24 hour high fat feeding of mice was associated with cardiac lipid accumulation in animals with low leptin levels but not those with high plasma leptin levels [156]. Leptin administration decreases cardiac muscle lipotoxicity in a subsequent study by this group [157]. Leptin administration to the perfusate of isolated rat hearts perfused with palmitate and glucose significantly increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced intramyocardial triglyceride content without increasing cardiac work. This was accompanied by increased myocardial oxygen consumption and reduced cardiac efficiency [143]. The significance of leptin in metabolism is further highlighted in genetic models such as the leptin deficient ob/ob mouse and the leptin resistant db/db mouse that has a loss-of-function mutation on the leptin receptor. These animals are obese, insulin resistant and display excess intramyocardial lipid accumulation. They are also more prone to increased cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction than their control littermates [158-162]. Circulating adiponectin levels are reduced in obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes and correlate with the extent of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia [163-165]. It is synthesised by adipocytes, skeletal muscle, heart muscle and endothelial cells [166] and is a key adipocytokine in the regulation of metabolism. It is considered to be an anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic agent with adiponectin deficient animals becoming glucose intolerant, insulin resistance and hyperleptinaemic [167, 168]. Studies utilising adiponectin replacement therapy have demonstrated its ability to decrease dyslipidaemia [169] and improve insulin sensitivity (Figure 6) [170-172]. Its action is mediated through the AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 receptors [170] that are both expressed in cardiac tissue [174]. Resistin is secreted from white adipose tissue but is also expressed in other tissues [178]. It was given its name because it was originally shown to counter the effects of insulin by suppressing insulin signalling [179]. Over-expression of resistin is associated with dyslipidaemia and insulin resistance [180, 181] and inhibition of glucose uptake in cardiomyocytes [182]. In humans plasma resistin levels are closely correlated to insulin resistance irrespective of body weight [183]. In both high fat diet and genetic mutation induced obesity, resistin levels were closely associated with body weight with obese animals having significantly elevated resistin levels [179]. The exact role of resistin in insulin resistance is however poorly understood and unresolved. Myocardial Insulin Resistance: An Overview of Its Causes, Effects, and Potential Therapy 203 8. Cardiac metabolism is under the control of several hormones with insulin being a key regulator of glucose, fatty acid and lactate metabolism. This is achieved through a constant supply of oxidizable substrates from the circulation. The most important substrates utilized by the heart are: fatty acids, glucose and lactate. The concentration of fatty acids present in blood greatly dictates their uptake and metabolism by the heart [190]. During anaerobic conditions as occurs during myocardial ischaemia, pyruvate may be converted to lactate. There is a delicate interplay in the utilisation of these two myocardial substrates which is intricately related to their circulating levels. Impact of myocardial insulin resistance on myocardial metabolism the early onset of insulin resistance in obesity may be a physiological response to increased lipid availability leading to increased lipid utilisation and a reciprocal reduction in glucose metabolism. Chronic dysregulation of glucose uptake and metabolism by dyslipidaemia and inflammation may however induce pathological changes in cardiac metabolism that compromise cardiac morphology and mechanical function. With myocardial insulin resistance, fatty acid oxidation rates are normal or elevated, while glucose oxidation rates are normally reduced both in the presence or absence of insulin stimulation [5, 44, 45, 203-205]. Although a limited number of studies have reported similar myocardial fatty acid and glucose oxidation rates in obese, insulin resistant animals when compared to lean controls, they have all found that insulin stimulated myocardial glycolytic flux rates remain suppressed with insulin resistance [89, 206]. In humans similar increases in myocardial fatty acid metabolism were reported in obese men and women. Gender however also played and important role in determining the impact of obesity of glucose and fatty acid uptake and utilization [207]. Women were less prone to obesity induced dysregulation of myocardial metabolism than their obese male counterparts. These gender based differences in myocardial metabolism in response to obesity may translate to differences in the development of obesity-related cardiovascular diseases. These observations were corroborated in obese insulin resistant mice (ob/ob and db/db) that had increased myocardial lipid oxidation rates, decreased glucose oxidation rates and decreased cardiac efficiency. These changes were also associated with systolic dysfunction when compared to lean insulin sensitive littermates [45]. Although genetic models of obesity do not accurately resemble the phenotype of human obesity, the recent development of a number of models of diet-induced obesity have contributed to a better understanding of the impact of obesity and insulin resistance on myocardial function. The authors and other research groups have however also shown that rodent models of diet-induced obesity with insulin resistance have either normal [90, 203, 205, 209, 210] or compromised [110, 203, 204, 211, 212] cardiac mechanical function. It is currently not possible to conclusively attribute the cardiac dysfunction reported in these studies to myocardial insulin resistance since there are several studies that have reported normal cardiac function in animal models with insulin resistance [90, 203, 205, 209, 210]. Reduced cardiac efficiency possibly contributes to cardiac dysfunction in obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes [44, 45, 213]. Animals [44, 45, 162, 213] and humans [95] that are obese and insulin resistant or diabetic have increased myocardial oxygen consumption which reflects a decreased cardiac efficiency as determined by the myocardial work to myocardial oxygen consumption ratio [214]. This data from human and rodent studies also implicate impaired mitochondrial energetics in the cardiac dysfunction associated with obesity and insulin resistance. Recent epidemiological evidence points to an important mediatory role for insulin resistance in the development of obesity related congestive heart failure [215]. Effect of dyslipidaemia and insulin resistance on myocardial tolerance to ischaemia/reperfusion A key feature of myocardial ischaemia is the reduced oxygen and substrate availability that results in lower mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation rates. Although oxidative metabolism is reduced during ischaemia, reperfusion after ischaemia is associated with an initial increase in glycolytic flux rate which quickly declines to normal levels [217]. Despite myocardial ischaemia decreasing mitochondrial substrate oxidation, fatty acid oxidation predominates during ischaemia and subsequent early reperfusion [221]. During early ischaemia there is a transient increase in anaerobic glycolysis while glucose oxidation decreases [199, 221-224]. Hearts from animal models of obesity and insulin resistance [211], isolated insulin resistance [225] and diabetes [226] have a reduced tolerance to ischaemia and reperfusion and suffer more severe ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Although fatty acids are predominantly oxidized by the ischaemic heart, the preference for fatty acid oxidation as occurs under dyslipidaemic conditions also has adverse effects on the ischaemic and reperfused heart. Increased fatty acid oxidation consequently reduces cardiac efficiency during ischaemia and subsequent reperfusion.
Order 7.5mg mobic overnight delivery
In many instances arthritis knee exercises elderly discount 15 mg mobic otc, a patient will have little to no pain and will not show signs of the injury externally; however, this can be misleading as the patient may be suffering from a life-threatening injury. It is especially common for a patient with multiple lower rib fractures to have severe intra abdominal injuries while experiencing no significant pain. Causes of Blunt Trauma Blunt trauma can be caused by any incident that causes a blunt impact to the abdomen. Common causes of blunt abdominal trauma include seat belt impact during a motor vehicle accident, impact from a fall, sports-related injuries, abuse, and any other incident that causes blunt trauma to the abdominal region. In many instances, the injury will not be immediately apparent, even if a patient has a confirmed blunt trauma. Therefore, it is important to assess any patient that has experienced trauma to the abdominal region for possible blunt abdominal injuries. While any type of incident that causes blunt trauma can produce blunt abdominal trauma, the three most common causes of blunt abdominal trauma are seat belts, sports, and physical abuse. Due to the blunt force produced during a motor vehicle accident, an individual often sustains injuries from the compression of the seat belt across the lap and chest. To protect an individual from crashing into parts of the vehicle during impact, the seat belt diverts energy from the head to the chest and 1313 nursece4less. During motor vehicle accidents, the risk of an abdominal injury when an individual is not wearing a seat belt is less than 10%. However, when an individual is wearing a seat belt, the risk of abdominal injury increases to 20%. While any area of the abdominal region can suffer damage from a motor vehicle accident, seat belt injuries typically affect a specific set of organs. Patients typically experience injuries in the stomach, small bowel, colon, rectum, liver and spleen. The abdominal injuries caused by seat belts differ from those sustained by an individual who is not wearing a seat belt. Therefore, the evaluating physician must be aware of the seat belt specific injuries so that the patient receives the proper assessment and treatment. Sports Abdominal injuries are common sports-related injuries, especially in high contact sports such as football, rugby and hockey. Sports-related abdominal injuries can range in severity, with the most minor injuries being abdominal strains and the most severe injuries being internal bleeding and organ damage. Sports-related abdominal injuries are some of the most serious injuries sustained during athletic events, and proper assessment and treatment is crucial to a successful outcome. While athletes can experience a variety of different abdominal injuries as the result of sports-related accidents, there are a number of injuries that are 1414 nursece4less. Solar Plexus Injury Many athletes experience a blow to their solar plexus, which can result in temporary paralysis of the diaphragm. Solar plexus injury can also occur as the result of falling on an object such as a ball or piece of equipment. Common symptoms include substantial pain, acute shortness of breath, and feelings of panic. Typically, a solar plexus injury is relatively insignificant; however, in some instances, it can cause extreme discomfort in the patient and will require some amount of treatment to minimize discomfort. When a hernia occurs in the femoral ring, the intestines will protrude below the inguinal ligament and then come out through the femoral canal. When a hernia occurs in the inguinal region where the spermatic cord passes through, the intestines will protrude through the inguinal canal alongside the spermatic cord. Both types of hernia produce an increase in abdominal pressure, which occurs as the result of a muscle contraction or applied external pressure. Typical symptoms include tenderness and/or a palpable mass at the site of herniation. Immediate treatment is necessary to prevent significant damage to the intestine, which may occur as the result of strangulation of the 1515 nursece4less. Muscle Injury Since the abdominal muscles are the primary support of the abdominal region, they are especially prone to injury. Most injuries to the abdominal muscles are mild and only cause insignificant damage to the area. Mild trauma includes muscle strains and overuse injuries, which are easily treatable. Therefore, patients must be examined and assessed to ensure that there is not severe damage to the abdominal muscles. Organ Damage Organ damage is considered to be the most severe and dangerous sports related abdominal injury. Organ damage poses the risk of internal bleeding and organ failure, so it is crucial that the patient receive immediate care. Many patients only experience mild tenderness and present with typical muscle guarding. When this occurs, the patient may be treated using an abdominal splint, which can further hide the severity of the injury. In many patients, organ damage, especially hemorrhage, will not become apparent for days or weeks. After this time, the patient may experience systematic dysfunction or organ failure. Therefore, it is crucial that patients who present with significant abdominal trauma be examined thoroughly, even when they do not present with any signs of organ damage. The following is a description of the different organ injuries a patient may experience as part of sports-related abdominal trauma. However, this is not common, as most athletes do not participate in athletic events with a full bladder. If an athlete does sustain a ruptured bladder, the following symptoms may be present: o Hematuria o Difficulty with urination o Abdominal rigidity Lower Back A direct blow to the lower back can cause significant damage. Athletes who experience this type of trauma are likely to present with kidney or intestinal damage. Some athletes will experience a contused or ruptured kidney, which can cause the following symptoms: o Hematuria o Muscle guarding o Back and flank pain o Nausea o Vomiting o Shock When a significant force causes a trauma, the patient may suffer severe intestinal damage or a bowel perforation. When this occurs, the patient will experience the following symptoms: o tenderness to the area o changes in bowel function o bloating 1717 nursece4less. The symptoms of liver damage include: o rapid heart rate o low blood pressure o abdominal pain o nausea o blood in vomit, feces or urine Spleen Damage to the spleen is common in athletes and is the leading cause of death in athletic injuries. Abuse in other vulnerable populations, such as women and elderly, is 1818 nursece4less. Therefore, it is important to identify the cause when a child presents with abdominal injuries. Abdominal trauma that occurs from abuse has a higher rate of mortality and morbidity in children than trauma that occurs from accidents. The majority of abuse-related abdominal injuries occur in the liver, spleen and bowels. In many children, external bruising will be present; however, approximately 40% of children with abuse-related abdominal trauma show no outward signs. In many instances, children who present with abuse-related abdominal injuries also have injuries in other areas of the body, especially the head. Penetrating Abdominal Trauma Penetrating abdominal trauma occurs any time an object penetrates the abdomen, which can occur in a variety of incidents including motor vehicle accidents, falls, industrial accidents, military combat, stabbings, and gunshots. In some instances, the patient will experience full evisceration, while other incidents will produce a small wound, as further described in this section. Penetrating trauma causes injuries to patients in different ways: 1) the object physically damages organ tissues as it penetrates, 2) object penetration forces pressure in all directions, stretching the organs and injuring adjacent organs/tissue. Due to the elastic nature organs they stretch, which can cause a cavity to develop that may become permanent. A penetrating object at high speed and more kinetic energy is transmitted to the organs with potential of ricocheting off bony objects and causing fragmentation. It is important for healthcare providers to understand the complexity and severity of penetrating abdominal trauma to adequately assess and treat the patient. Abdominal trauma is especially dangerous due to the number of organs located within the abdominal cavity.
Order generic mobic
This will help them to decide if your child is best cared for at the home or needs to see a healthcare professional face to face vitamin c arthritis pain mobic 7.5mg line. Your healthcare professional may decide that your child needs a follow up appointment. They will give you information on how to look for symptoms that may suggest more serious illness and how to get further help if they occur. Any information that is shared in this way will not identify your child unless we have your consent. For the frst 10kg of weight 4ml/kg/hour, for the second 10kg 2ml/kg/hr, for all remaining kg 1ml/kg/hr. Parents can use this guideline aiming for 75-100% of the fuid volumes listed below per hour when awake, given gradually over the hour via syringe. You need to tick the boxes below each time your child has a drink, and also mark down if your child vomits or has diarrhoea. It can lead to dehydration when the body does not have enough water or the right balance of salts to carry out normal functions. Gastroenteritis is usually caused by a virus and requires no treatment other than plenty of fuids. Ibuprofen should not be given if your child has not passed urine or has blood in their stools. Provide verbal/written information about care of child with abdominal pain, warning signs and when to seek further advice. Jaundice Hepatitis may present with pain due to liver swelling Urinary Tract Infection Routine urine analysis for children presenting with abdominal pain Bites and stings Ask about possibly bites and stings. La malabsorcion intestinal puede comprometer la absorcion de vitamina D, aunque macro y micronutrientes. Experiencias su aporte dietario es responsable solo del 20% clinicas en paises desarrollados y de las concentraciones sericas, por lo que lo en Latinoamerica muestran un importante es la exposicion dermica al sol. La deciencia con diarrea grave y compromiso de Cu se ha descrito de preferencia en celiacos nutricional hasta formas atipicas con adultos. Carlos the small bowel compromise may affect activity enfermedad si el nacimiento fue por Castillo-Duran: and vitamin D absorption. No hay hasta ahora claridad Debido al dano intestinal proximal, se han respecto a la fisiopatologia que explique por que descrito deficiencias de micronutrientes Fe, Zn en algunos casos se puede afectar la nutricion y Ca. Si se afecta el intestino mas difusamente, de un solo micronutriente y en otros de varios se puede producir malabsorcion de vitaminas micronutrientes. Algunas hipotesis sugieren liposolubles (A, D, E y K) y tambien de vitaminas que puede estar dado por el efecto deletereo del B12 y B6, Se y Cu. En las formas con presentacion atipica, los sintomas digestivos son minimos o Deciencia de hierro no aparentes; en algunos casos, la anemia o talla La absorcion de hierro esta asociada a las baja sugieren una malabsorcion prolongada. Se observo deficiencia de estado en el enterocito (Tabla 1); a ellas, se agrega la nutricional de estos micronutrientes, pero sin ferroportina, proteina responsable de la salida diferencias entre ambas formas. Deciencia de micronutrientes y enfermedad celiaca en pediatria / 459 encargada de la regulacion de la ferroportina. Los paises estas, el interferon gamma y la interleucina 6 son con buen desarrollo socioeconomico tienen baja mediadores de hipoferremia en la inflamacion, prevalencia de anemia por deficiencia de Fe, que induce la sintesis de la hormona hepcidina minima desnutricion proteico-energetica, baja reguladora de la exportacion de Fe. Un aumento prevalencia de bajo peso al nacer, alimentaciones en la sintesis de hepcidina produce un incremento con buen contenido de Fe (carnes y pescados) en la degradacion de ferroportina y la inhibicion y uso generalizado de formulas fortificadas de la liberacion de Fe por parte del enterocito, lo u otros alimentos fortificados. La anemia nutricional es mas los depositos de Fe hayan sido restablecidos, comun en celiacos; se manifiesta como anemia aproximadamente 6 meses despues de comenzar microcitica, hipocromica, con concentraciones la dieta sin gluten. Cada uno de estos anemia por deficit de Fe se ha comunicado transportadores, a su vez, puede tener varios como mas alta que en otros grupos de riesgo, y polimorfismos. En la acrodermatitis enteropatica, se encontro una relacion de mujeres:varones de enfermedad con alteracion congenita en la 2:1. La absorcion para fuentes 460 / Arch Argent Pediatr 2014; 112(5):457-463 / Actualizacion alimentarias de origen animal esta en torno al 30% La malabsorcion intestinal juega un rol en de lo ingerido. En un indicador sensible de estado nutricional de estudio con isotopos estables de Zn en ninos Zn. Las concentraciones esta claro como se puede dar esta asociacion y plasmaticas siguen siendo las mas utilizadas sus implicancias. El nivel socioeconomico alterar la confiabilidad de las mediciones; un bajo y las practicas alimentarias en una estres metabolico dentro de cuadros infecciosos comunidad pueden ser un factor de riesgo de o de dano tisular puede disminuir un 10-20% deficiencia nutricional de Zn, por ejemplo, las concentraciones sericas de Zn. Hay consenso dietas con bajo consumo de alimentos carneos, de que concentraciones < 70-80 ug/dL son pescados y mariscos, y alto en vegetales con gran sugerentes de deficiencia de Zn. Las Los signos de deficiencia mas importantes recomendaciones de Zn incluyen un aumento comunicados son retraso del crecimiento, mayor para poblaciones con esas alimentaciones, en riesgo de infecciones (principalmente, digestivas, especial ante dietas con una relacion molar respiratorias y dermicas), alteraciones de piel y fitatos/Zn > 15:1. Las poblaciones que viven en latitudes En la decada de los 60, se describio la extremas (> 40-45 latitud norte o sur) son un deficiencia nutricional de Cu por actividad grupo de riesgo de deficiencia de vitamina D, enzimatica disminuida de cuproenzimas, como en parte, por menor radiacion solar de rayos superoxidodismutasa, lisil oxidasa y catalasas. Se ultravioleta B y, en parte, por menor exposicion encontro en la desnutricion energetico-proteinica al aire libre ante temperaturas ambientales muy la enfermedad de Menkes, en las alimentaciones bajas. Actualmente, hay consenso por neutropenia, leucopenia, anemia ferropriva en que la deficiencia se define por concentraciones que no responde a Fe y si a la terapia con Cu, < 20 ng/mL e insuficiencia, por concentraciones infecciones respiratorias agudas bajas, retraso de entre 20 y 30 ng/mL. La vitamina E esta conformada por diversas El diagnostico de deficiencia se comprueba con variantes de tocoferoles, con participacion en el Cu plasmatico < 70-80 ug/dL y de ceruloplasmina proceso de regulacion de la lipoperoxidacion. Las concentraciones en pelo pueden Esta ampliamente distribuida entre los alimentos contribuir tambien al diagnostico. Se requiere la suplementacion para En el adulto mayor, la deficiencia de vitamina tratar estas deficiencias y prevenir especialmente B12 es frecuente y causada principalmente consecuencias irreversibles, como el potencial por malabsorcion de vitamina B12 (deficit de dano neurologico periferico de algunas factor intrinseco), que ocurre en un 60-70% deficiencias. Ages of celiac disease: deficiencias dietarias (< 5%), malabsorcion (< 5%) from changing environment to improved diagnostics. Nutritional deciencies in children on gastrica, sobrecrecimiento bacteriano, gastritis restricted diets. A guide to diagnosis of iron A l i g u a l q u e a l g u n o s d e l o s o t r o s deciency and iron deciency anemia in digestive diseases. High de folato, que puede llegar hasta un 20-30% prevalence of asymptomatic coeliac disease in Norway: de los recien diagnosticados. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol informacion en pacientes pediatricos, por lo 1999; 11(2):185-7. A short que no conocemos si esta deficiencia se debe review of malabsorption and anemia. World J Gastroenterol a condiciones de los adultos o bien requiere 2009; 15(37):4611-52. Gastrointestinal factors inuencing zinc Neurologic impairment due to vitamin E and copper absorption and homeostasis. Copper concentrations of prepubertal children: a meta-analysis deciency myeloneuropathy due to occult celiac disease. Estimation of optimal serum concentrations of homeostasis and gut function in children with celiac disease. Controlled trial of copper supplementation during the Cognitive impairment and celiac disease. Luis Domingo Garcia Azzarini, a 10 anos de su fallecimiento, se otorgara un premio a la mejor Comunicacion sobre las practicas profesionales de un equipo interdisciplinario para ninos/as y jovenes.
Cheap mobic 15 mg on line
However arthritis relief back pain buy cheap mobic on line, the largest proportion of patients that have discomfort are Inguinal and femoral hernias are two hernias that occur in the groin (Figure 1). Inguinal hernias account for 96% of all groin hernias, while femoral hernias make up the other 4%. You may need to be seen by a cardiologist to get often happen in children and young adults and become evident when intestines or other approved for surgery if you have significant heart problems. In other situations, the area of an anesthesiologist who will discuss your health history with you. The lifetime risk of developing a groin hernia is 4 C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K 5 around 25% for males and 3% for females. Femoral hernias are much less common than inguinal care or surgery may be needed after a thorough work-up by a physician. Some believe that femoral hernias may Anatomy carry more risk than inguinal hernias and should be repaired in all patients. In males, the combination of the vessels to the testicles and the vas often appears as a distinct bulge or lump in the groin or going down to the scrotum. As a man develops as fetus in the womb, there is these hernias can also create a sensation of heaviness, pulling, vague discomfort, and a canal that connects the abdomen to the scrotum which begins at the internal ring. If a hernia contains Sometimes, this canal does not close fully during pre-natal development. When this incarcerated bowel, patients may complain of pain, nausea or vomiting, abdominal happens, organs that are normally inside the abdomen can later protrude through this bloating, and pain. If bowel becomes strangulated, severe abdominal pain will develop, canal and form a hernia. They tend to be perhaps more prone to occur when there is increased pressure in the abdomen, such as when patients frequently strain in the bathroom or gain extra weight. Direct hernias come directly through the abdominal wall and occur within an area Figure 2. They form due to the weakness of the abdominal wall musculature, and often occur in older males. However, they can occur in younger men and patients may be genetically predisposed to these types of hernias. While some hernias can be chronically incarcerated and the patients can live normally, strangulation of a hernia contents is a life-threatening problem and requires immediate surgical attention. The strangulated portion of the intestines may die and make the patient extremely sick or challenge their life. In order to repair a hernia, the contents of the hernia are pushed back into the Surgery is the only way to fix hernias, but not all hernias need to be treated. When only sutures are used, it inguinal hernia that does not cause any major symptoms can be observed. There are several ways to close the defect with be less than 1% per year3, but in this study many patients whose hernias became sutures only, and surgeons often have their own preference. Both inguinal and femoral symptomatic were no longer observed and underwent surgery. The major problem with primary causing bowel obstruction and strangulated hernias should be addressed surgically on repair is a high (up to 15%) recurrence rate, which is when the repair fails and the hernia an emergent basis. Mesh repair and if, indeed, tissue or organs are pushing through the hernia, these organs can become can be used to treat inguinal and femoral hernias. Indeed, as hernias increase in size, they Open vs laparoscopic repair can become more difficult to repair, lead to a greater chance of complications, and may An open inguinal hernia repair is the traditional approach, where a small (2-3 inch) yield a higher chance of recurrence of the hernia after repair. The hernia contents are reduced into the to develop symptoms or until their symptoms become worse have a greater chance of abdomen, and the floor of the inguinal canal is reinforced with a mesh to reduce the risk chronic discomfort, even after the hernia is fixed. The Lichtenstein repair (Figure 3) or a variation of this technique, known be assessed by and discussed with your doctor or surgeon. Most involve a soft, flexible, plastic-like substance called mesh, while a few repair, but these techniques are uncommon, usually result in more post-operative pain others only use sutures. The meshes used for repair of groin hernias are most often and have a higher recurrence rate. There are several synthetic, slowly absorbable where 3 small (inch to inch) incisions are spaced across the middle of the abdomen. Laparoscopic hernia repair requires a used in groin hernia repair except in the presence of a higher than normal risk of mesh to be placed. It is secured to the abdominal wall with small permanent or infection or by physician preference. The laparoscopic 8 C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K C A R O L I N A S H E R N I A H A N D B O O K 9 Figure 3. Lichtenstein Mesh Repair Preparation for Surgery A health history and physical exam is performed by the surgeon and sometimes an anesthesiologist prior to surgery. An evaluation by a heart specialist may be required if there is a significant history of heart disease. Aspirin and Plavix slow down blood clotting and, in general, are stopped 7 days prior to the procedure to decrease the risk of bleeding. Coumadin also slows down blood clotting and should be stopped 3-7 days prior to the surgery. It is extremely important to discuss these medications with doctors, as stopping these medications without substituting other medicines may be dangerous in certain situations. Fasting is required overnight prior to morning surgeries, or at least 6 hours prior to afternoon or evening procedures. Recovery In the absence of complications, patients frequently go home the same day as their surgery and medications for pain are prescribed. Some post-operative pain is expected, repair is often quoted to result in a reduction in early post-operative discomfort and offer and the recovery time varies from patient to patient. Patients may return to work a few days after the surgery if There are situations where open or laparoscopic technique is preferred. Patients are often advised to limit needs a second operation for a failed open repair, a surgeon is more likely to choose a heavy lifting or strenuous physical activity for 2-6 weeks after the procedure. The open technique is often employed during emergency situations, such as There is a risk of side-effects from anesthesia, which are the medications used to with strangulated bowel, but surgeons can consider a laparoscopic approach in certain induce a sleep-like state during surgery. Occasionally, patients with heart these include: patients with a high risk of bleeding from illness or medicines, patients problems may need approval from a Cardiologist before surgery. Other risks involved with liver failure, and patients with heart conditions that cannot tolerate the anesthetic with surgery, in general, include bleeding, infection of the skin, deeper tissues, or medications needed for complete sedation in laparoscopic surgery. Patients often receive previous pelvic surgery may also be less than ideal candidates for laparoscopic surgery antibiotics prior to surgery to attempt to prevent infection. This catheter may be placed and immediately removed or be allowed to stay in 24 or Intraoperative death is extremely rare during hernia surgery. Death can also occur after more hours according to the discretion of the physician. These issues during standard inguinal hernia Chronic groin discomfort (pain lasting for months after hernia repair) affects from surgery are extremely rare. The Recurrence actual rate of chronic discomfort often depends on how an investigator defines its Recurrence rates for inguinal hernia repair with mesh are generally low. Most presence post-operatively and how sensitive the quality of life tool is that the investigator studies with long-term follow-up (5 years in some cases) report recurrence rates to be uses.

