Indocin
Buy indocin discount
More recent analyses of Totiviridae genomes have identified a frameshift signal in the penaeid shrimp infectious myonecrosis virus (Nibert arthritis in knee of horse order 75mg indocin with mastercard, 2007), Armigeres subalbatus totivirus (Zhai et al. This frameshift also regulates the ratio of the putative polymerase protein to the structural protein. These findings suggest that a common viral problem, that of regulating the abundance of structural and enzymatic viral proteins, is solved in the Totiviridae family by manipulating translation fidelity, albeit by slightly different mechanisms. Like the Totiviridae, retroviruses use frameshift signals to modulate the ratio of gag protein to gag-pol fusion protein. The ratio of gag to pol proteins has been shown to be important for viral replication and infectivity in several retroviral systems. The authors postulated that a recoding event was responsible for the production of the polymerase. The first characterization of a viral frameshift signal was of the Alpharetrovirus Rous sarcoma virus (Jacks & Varmus, 1985). The region of the genome containing the frameshift signal was cloned into an expression vector, transcribed and translated. The result clearly showed that a gag-pol polyprotein was produced from the same transcript as the gag protein (Jacks & Varmus, 1985). Frameshift signals have since been identified in Alpharetroviruses, Betaretroviruses, Deltaretroviruses and Lentiviruses. The frameshift signal from the Mason-Pfizer monkey Betaretrovirus, (simian retrovirus 1), has also been characterized (ten Dam et al. Additional Lentivirus frameshift signals from equine infectious anemia virus, feline immunodeficiency virus and simian immunodeficiency virus have been characterized (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; Chen & Montelaro, 2003; Morikawa & Bishop, 1992). Putative signals in bovine immunodeficiency virus, caprine arthritis virus, ovine lentivirus, Jembrana disease virus and Visna virus have been described (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; Bekaert et al. Additional frameshift signals in an Alpharetrovirus genome (avian leukosis virus), and a Deltavirus genome (bovine leukemia virus) have also been identified (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; Bekaert et al. A putative signal from a Betaretrovirus, the cancer causing Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus, has also been been described (Bekaert et al. In several retrovirus genomes, the gag and pol genes are separated by a stop codon. It has been shown that readthrough of the stop codon can produce a fusion protein. A pseudoknot facilitates the readthrough of murine leukemia virus and pseudoknots are predicted to be present at the gag-pol junction of several retroviruses (Wills et al. Interestingly, two competing structures, a stem-loop structure and a pseudoknot, were described for the murine leukemia virus (Alam et al. This suggests that secondary structures are important for modulating ribsome fidelity during retroviral protein production in both readthrough and frameshifting, although exactly how they stimulate the ribosome remains a mystery. The replicase proteins are translated as two polyproteins that are processed by self-encoded proteases. The smaller polyprotein has several domains including papainlike cysteine protease, chymotrypsin-like cysteine protease, metal binding and transmembrane motifs. Altering frameshifting efficiency has been shown to be detrimental for coronavirus replication (Ahn et al. Additionally there is an example of a kissing stem-loop that promotes coronavirus frameshifting (Herold and Siddell, 1993). Functional frameshift signals have been identified in some Arteriviridae including equine arteritis virus, lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; den Boon et al. A frameshift signal has been identified in the simian hemorrhagic fever virus (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005). A frameshift signal in the Gill-associated Okavirus has been shown to be functional (Cowley et al. More recently frameshift signals have been identified in the Chicken, Mink, Ovine and Turkey astroviruses (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; Bekaert et al. Recently a frameshift signal was identified and characterized in the West Nile virus. Potential frameshift signals have been identified in three other flaviviruses; Japanese encephalitis virus, Murray Valley encephalitis virus and Usutu virus (Firth & Atkins, 2009). Frameshift signals have been found in Enamoviruses, Luteoviruses and Poleroviruses. A similar genome arrangement and frameshift signal has been found for the rose spring dwarf-associated virus (Salem et al. Other luteoviruses with putative frameshift signals include the Bean leafroll virus and Soybean dwarf virus (Domier et al. A frameshift signal has been identified in the Enamovirus pea enation mosaic virus (Demler & de Zoeten, 1991). The structure of the pseudoknot from the pea enation mosaic virus-1 frameshift signal has been characterized (Giedroc et al. The frameshift signals for beet chlorosis virus, beet western yellows virus, cucurbit aphid-borne yellows virus, potato leafroll virus have all been shown to be functional (Bekaert & Rousset, 2005; Kim et al. The discovery of a functional frameshift signal in the Semliki Forest virus 6K gene is expected to have wide ranging effects on the understanding of alphavirus lifecycle (Firth et al. The 6K protein is involved in envelope processing, membrane permeabilization, virus budding and virus assembly. Sequence comparisons indicated that frameshift signals are present in other alphaviruses including Seal louse virus, Middleburg virus, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, Ndumu virus, Sinbis virus, Barmah Forest virus, Sleeping disease virus and Eastern equine encephalitis virus. Some of these viruses are transmitted by fungal species, but either the virion or genetic material are infective. Thus there appears to be some link between control of translation and replication of the virus. The stimulatory element has a dual function, it causes the translating ribosome to pause on the message when the slippery site is positioned within the ribosome and it stimulates ribosomal error. Nucleotides involved in the codon:anticodon interaction are shown with dots indicating base pairing. The efficiency of frameshifting promoted by each heptameric slippery site varies depending on the system used to assay frameshifting. The stimulatory sequences were predicted to fold into stem loops until Brierley et al. Sequence comparisons indicated that some structures downstream from slippery sites in other viruses could also be pseudoknots (for example: Bredenbeek et al. It has also been shown that the stimulatory structure could involve long range interactions (Herold & Siddell, 1993; Paul et al. It has also been postulated that stop codons stimulate frameshift events, presumably by pausing translation (Castano & Hernandez, 2005; Horsfield et al. Molecular modeling has been useful in elucidating some of these structures (Ahn et al. This difference in frameshifting efficiency was recapitulated in both mouse fibroblasts and human lymphoid cells (Cassan et al. References are listed that describe different methods used to characterize viral stimulatory elements. This spacer region needs to be un-paired to fit within the ribosome entry tunnel when the slippery site is correctly positioned inside the ribosome. This variation suggested that different aspects of ribosome fidelity were affected during frameshifting. Different groups spent the next two decades analyzing several frameshift signals from a variety of virus families with the goal of understanding frameshift mechanisms. The availability of error-inducing frameshift-stimulating sequences from viruses has facilitated the study of ribosome function.
Purchase genuine indocin on-line
Lalas arthritis knee injections purchase indocin with paypal, 2007:Modeling framework for estimating impacts of climate change Masera, O. Omicron Consulting, Vancouver, of modern methods of construction in housing: a case study using a lifecycle Canada, December, 2004. Energy Efficiency Instrument: Comparative Analyses of Regulation and Market McMakin, A. Environment, fying ex post estimates of utility conservation impacts at the regional level. Sherwin, 2002: Comparative Evaluation of the National Action Plan for Energy Efficiency, 2009: Customer Incentives for Energy Impact of Roofing Systems on Residential Cooling Energy Demand in Florida. Krouk 2010: the State of the Efficiency Program the Implementation of Tradable White Certificates. Draft reports as of July 2008, Directorate-General for Energy, Assessment of Standard and Green Roofs. Volume 1: Energy mental performance of an experimental green roof system installed in a nursery Consumption Baseline. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy, 27(5): the household energy and health project. Tonn, 2002: Nonenergy benefits from the weatherization Wide Energy Savings from Improved Energy Efficiency. Selection, state of the art and energy potential investigation of a system installed 74. Rainer, 2000: Non-compressor cooling alternatives Ireland: Extent, Affected Groups and Policy Issues. Feustel, 1999: Energy and peak power savings potential of mercial and institutional buildings. Oreszczyn, 2010: Two models for benchship: control, trust and confidence in co-operative behaviour. Butcher, 2010: Employment Impacts of a Large-Scale Deep Building Energy Energy Efficiency: Lessons from Brazil, China, India, and Beyond. Environmental Programme, the Sustainable Buildings and Climate Initiative, Thiers, S. A first aration: Employment Impacts of a Large Scale Deep Building Energy Retrofit assessment. Prepared by the Center for Climate Change and Central European University, Budapest, Hungary. Center for Climate Change European Climate Foundation, the Hague, the Netherlands. A review of 10 countries within Impacts of Energy Efficiency Investment Programmes. Norford, 2007: Tale of two low-energy ing on the Least Developing Countries and Sub-Saharan Africa. Gong, 2008: Quantifying air pollution removal by green roofs tural analysis of household energy use behaviour in Japan and Norway. Hestnes, 1999: Solar versus green: the analysis of a Journal of Public Health, 32(4). Clair, 2005: Easing the Natural Gas Crisis: use in China building sector: current status, existing problems and solutions. Reducing Natural Gas Prices through Increased Deployment of Renewable Frontiers of Energy and Power Engineering in China, 4 (1). Weifeng, 2005: Energy efficient techniques and simulaGeneration Resource Inventive & Diversity Standards, Senate Committee tion of energy consumption for the Shanghai ecological building. In Proceedings on Energy and Natural Resources, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2005 World Sustainable Building Conference. Rymkevich, 1998: Comparison of heating and cooling energy of uncontrolled airfiow in a light commercial building. Levine, 2007: Energy Use in China: Sectoral Trends and domestic appliances: environment, behaviour and design. Itismandatory fordentiststo have athorough scientific knowledgesoastoidentifyanddifferentiateulcersaffectingthe oralandperioralstructures. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the Publisher. This book and the individual contributions contained in it are protected under copyright by the Publisher (other than as may be noted herein). In using such information or methods they should be mindful of their own safety and the safety of others, including parties for whom they have a professional responsibility. To the fullest extent of the law, neither the Publisher nor the authors, contributors, or editors assume any liability for any injury and/or damage to persons or property as a matter of products liability, negligence or otherwise, or from any use or operation of any methods, products, instructions, or ideas contained in the material herein. Preceded by Pediatric decision-making strategies to accompany Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 16th ed. The purpose and basic algorithalgorithms have been discussed with the appropriate specialists. As with the original text, the purpose is to assist the stuto any given problem, and not all diagnoses can ft neatly into dent, house ofcer, and clinician in the evaluation of common an algorithm. Even though the algorithms cannot be considered pediatric signs and symptoms and abnormal laboratory all-inclusive, the goal is to facilitate a logical and efcient stepfndings. The algorithmic format provides a rapid and concise wise approach to reasonable diferential diagnoses for the comstepwise approach to a diagnosis. They have all been Greenbaum of Emory School of Medicine for Fluids and extremely helpful and patient. Amanda Brandow for Hematology; Anoop Singh and Shanelle Special thanks to Kelsie Birschbach for her invaluable assisClark for Cardiology; Scott Van Why and Cynthia Pan for tance in the manuscript preparation. With periostitis, infection within the mastoid air cells has 5 spread to the periosteum that covers the mastoid process. Ear tugging middle ear and should be suspected if retraction or is not a specifc sign. The main clue to the diagnosis of a furuncle in the canal, 7 A swollen red auricle may be due to a contusion from although uncommon, is the severe pain elicited when the 2 blunt trauma. The canal appears generally recognize development of a hematoma with subperichondrial normal, except for the erythematous papule or pustule.

Purchase generic indocin from india
What are the major Decrease cytokine production mechanisms of action of (cyclosporine A juvenile arthritis diet treatment order discount indocin, tacrolimus), decrease cell immunosuppressive drugs proliferation (azathioprine, mycophenolate administered after mofetil, rapamycin), inhibit action of transplantationfi Myelosuppression and hepatotoxicity (especially in combination with allopurinol) Mycophenolate mofetilfi Nausea, diarrhea, and myelosuppression General effects (all Opportunistic infections and malignancies agents)fi Hyperacute: Caused by preformed rejection, and how is each recipient antibodies against the donor; type mediatedfi Acute: Occurs in the first week to several months after transplantation; may be humoral or cell-mediated, resulting in mobilization of lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells, and in production of cytokines to produce intense infiltration, edema, and destruction of the graft. Chronic rejection: Occurs years after transplantation; characterized by slow fibrosis and irreversible destruction of the graft. What are the later Opportunistic infections, cardiovascular complications of renal disease, increased incidence of malignancy transplantationfi What is the half-life of a Allografts from living donors have a halftransplanted kidneyfi N Engl J Med 50% reduction in the combined end 1993;329:1456 points of death, need for dialysis, or transplantation in insulin-dependent diabetics with nephropathy and macroalbuminuria compared with a similar group of patients treated with other antihypertensives. Dietary modification: No significant renoprotection associated with the lowprotein diet. A sustained benefit was shown in the group that was maintained with tight control 8 years earlier, despite their subsequent return to glycemic levels comparable to the conventional treatment group. While combination therapy slowed proteinuria compared with ramipril or telmesartan alone, it did not confer significant renal protection and was demonstrated to have increased risk of hypotension. There was no significant difference in mortality, recovery of renal function, or failure of nonrenal organs between the 2 groups. This demonstrates that over a wide variety of patients, even a small rise in Cr can have serious consequences. J Am Soc vasculitis and evidence of severe renal Nephrol 2007;18:2180 involvement as demonstrated by renal biopsy and elevated Cr were given oral prednisolone and cyclophosphamide and randomized to adjunctive treatment with either 7 plasma exchange treatments or infusion of methylprednisolone 3,000 mg. Increased urinary albumin, however, was associated with longer time since donation. The potential risk of morbidity and mortality associated with screening procedures the need for unnecessary evaluation of false-positive tests False-negative results What factors contribute to 1. For which tumors do Cancers of the cervix, breast, prostate, effective screening tests colon, and rectum. Men should be aware that any testicular swelling or aching should be examined by a physician without delay. Should be offered annually to men with at least a 10-year life expectancy beginning age 50 Stool hemoccultfi Men and women aged 50 years and older on a yearly basis Papanicolaou smear and Women starting 3 years after beginning pelvic examinationfi Men and women aged 50 years and older, sigmoidoscopy every 5 years or colonoscopy every 10 years Mammogramfi In bed 50% of the day 3: Confined to bed 50% of the day, but able to care for self 4: Unable to care for self. What are the symptoms of More than 90% of patients complain of spinal cord compressionfi Patients with a history of cancer must be advised that back pain should be promptly evaluated by their physician. Other symptoms of neurologic compromise include numbness, paresthesias, muscular weakness, and urinary and fecal incontinence. What is the character of Pain is localized to the spine and exacerspinal cord compression bated by movement, recumbency, cough, painfi The pain can be radicular in nature (sharp and electric shocklike, radiating in the distribution of a spinal nerve root). What are the physical Tenderness to percussion at the involved findings in patients with spine. Neurologic findings are decreased sensation and motor strength, positive Babinski sign, and hyperrefiexia. How does metastatic cancer the tumor restricts the vascular supply to cause loss of neurologic the spinal cord with resultant spinal cord function in the spinal cordfi What is the treatment High-dose dexamethasone, followed by of acute spinal cord radiation therapy or surgical decomprescompressionfi What are the symptoms Headache, nausea and vomiting, altered and signs of intracranial mental status, seizures, visual loss, focal metastatic diseasefi Chapter 9 / Oncology 547 What is the treatment for High-dose steroids acutely symptomatic Anticonvulsants intracranial metastasesfi Mannitol Hyperventilation (if the patient is intubated) Surgery (for isolated masses) versus radiation therapy (for multiple lesions) What are the symptoms of Headache, nausea and vomiting, carcinomatous meningitisfi In malignant cases, both chemotherapy and radiation may be used depending on the type of cancer. Medications that lead to an elevated serum uric acid or that acidify urine are discontinued. Chapter 9 / OncologyChapter 9 / Oncology 549549 What causes renal failure in Precipitation of urate crystals in the patients with tumor lysis tubules syndromefi The dose often needs to be should be used in patients adjusted for renal insufficiency in this with a large tumor burden setting. What is the management Panculture and broad-spectrum antibiotics of patients with significant. The choice of antibiotic depends on the fiora and sensitivities at the hospital (consider additional coverage for gram-positive organisms for severe mucositis). What other treatment options Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor are considered for patients with neutropenic feverfi How do you manage hemorRed blood cell and platelet transfusion to rhage in acute leukemiafi Immunohistochemical stains, fiow cytometry, and cytogenetics are useful in subtyping leukemias and determining treatment options. What congenital disorders Down syndrome, Bloom syndrome, are associated with an Fanconi anemia, and ataxia telangiectasia increased incidence of leukemiafi Chapter 9 / Oncology 551 What acquired disorders are Myeloproliferative diseases, associated with an increased myelodysplastic syndromes, and aplastic incidence of leukemiafi What treatments/therapies Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are associated with an increased risk of leukemiafi What molecular genetic the heavy chain promoter region is event occurs with the juxtaposed next to the c-myc oncogene. Promyelocytic leukemia is A translocation between chromosomes 15 associated with what and 17, commonly abbreviated as t(15;17) chromosomal translocationfi What molecular genetic the promyelocytic leukemia gene is event occurs in this translojuxtaposed next to the retinoic acid cation, which is thought to receptor alpha gene, yielding a fusion play a role in the pathogeneprotein. Generalized lymphadenopathy, fever, night sweats, weight loss, easy fatigability, weakness, and increased bleeding are common complaints. Frequent infections and exaggerated responses to insect bites are occasionally noted. What ethnic group has a More common in Ashkenazi Jewish males higher preponderance of hairy cellfi What are the presenting Weakness, weight loss, recent pyogenic symptoms of hairy cell infection, or symptoms attributable to leukemiafi Do patients with hairy cell Not usually; 80% of patients have leukemia have an elevated leukopenia. What is unusual about the the bone marrow is often difficult to bone marrow aspiratefi What is the treatment for the nucleoside analogs cladribine and hairy cell leukemiafi Interestingly, 25% of cases are associated with rheumatoid arthritis, making it difficult to distinguish from Felty syndrome. Lymphomas can present with symptoms attributable to enlarged lymph nodes anywhere in the body.
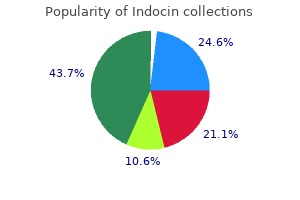
| Comparative prices of Indocin | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | A&P | 242 |
| 2 | Lowe's | 362 |
| 3 | SUPERVALU | 962 |
| 4 | Burlington Coat Factory | 417 |
| 5 | Winn-Dixie Stores | 473 |
| 6 | Ace Hardware | 218 |
| 7 | Giant Eagle | 795 |
| 8 | Verizon Wireless | 361 |
| 9 | Best Buy | 768 |
Buy 25mg indocin with amex
When a human eats insufficiently Diphyllobothrium latum cooked pork muscle arthritis diet margaret hills purchase cheapest indocin, the larval cysticercus converts to (Fish Tapeworm) the adult tapeworm in the intestine, and the cycle continues (see Fig. Infected individuals usually have minimal sympIt is acquired by ingesting larvae in raw freshwater toms. The Cysticercosis occurs when humans play the role of adult tapeworms in the human intestine drop off their the pig and ingest eggs rather than encysted largravid proglottids loaded with eggs. These eggs hatch within the small intestine, and end up in water, they convert to a motile larval form, the larvae migrate throughout the body, where they which is then ingested by a crustacean, which is then penetrate into tissue and encyst, forming cysticerci in i ngested by a freshwater fish (trout, salmon, pike, etc. If vitamin B,2 these eggs hatch in the intestine and develop into lardeficiency develops, anemia will occur. Most larvae are concentrated in the liver, but larvae may also infect Hymenolepis nana the lungs, kidney and brain. Only 10% of hydatid Infection) cysts cause symptoms, and treatment of these is difficult. Tissue Nematodes (Trichinosis, Dracunculiasis, Fi(although this alone is rarely curative). Saline, iodophors, or ethanol is next instilled York: Churchill Livingstone 1995;2531-2537. New York: Churchill Livingstone cation or a poor surgical candidate, therapy with alber1995;2544-2553. This trophozoite can convert including 1 or 2 nuclei, mitochondria, food vacuoles, and to a precyst form, with two nuclei, that matures into a endoplasmic reticulum. The protozoa ingest solid pieces of food through a Sometimes (10% of infected individuals) the trophosmall mouth called the cytostome. Here the ature changes, transit down the intestinal tract, or trophozoite infection causes pulmonary abscesses and chemical agents), the protozoa can secrete a protective often death (worldwide: 100,000 deaths annually). It moves by extending creeping projecAdverse effects of metronidazole tions of cytoplasm, called pseudopodia (false feet). There is no drinking allowed on the train because it About 10% of the world population and 1-5% of the U. If you eat the train, as King Kong once attempted, bas live in peace inside their host carriers. The motile feeding form of the amoeba is and as a mature, motile trophozoite that looks like a the trophozoite, which cruises along the intestinal wall kite. The organcontaminated municipal water sources and in infants ism is also harbored by many rodents and beavers; in day care centers. Cryptosporidium is ingested as a round oocyst that After ingestion of the cyst, Giardia lamblia converts contains 4 motile sporozoites. Its life cycle occurs to the trophozoite form and cruises down and adheres within the intestinal epithelial cells, and it causes dito the small intestinal wall. These symptoms are selfsmall intestine, interfering with intestinal fat absorpli miting in immunocompetent individuals. The patient will have a greasy, frothy cer patients, or organ transplant recipients who are diarrhea, along with abdominal gassy distension and receiving immunosuppressive therapy), this organism cramps. These patients may have 3-17 liters of For diagnosis and control of Giardia: stool per day. Diagnosis of Trichomonas: Trichomonas vaginalis 1) Microscopic examination of vaginal discharge on a Fig. Two patients who survived were treated with intrathecal amphotericin B, an antifungal agent. Both amoeba can cause an infection of the multiple antifungal drugs with pentamidine. Naegleria this organism may also infect the cornea (in imfowleri munocompetent persons), often when contact lenses are will cause a sudden deadly infection in immunocompetent persons, while Acanthamoeba will cause a not properly cleaned. Treatment is with antimicrobial slow granulomatous infection, usually in immunocompromised persons. We have already discussed 2 parand high protein, exactly like a bacterial meningitis!!! In fact, Toxoplasma encephalitis zoan but now has been shown to be more closely related is the most common central nervous system infection to fungi. Examination of the retina reveals yellowism will live comfortably within the lung without causwhite, fluffy (like cotton) patches that stand out from ing symptoms. Chest X-ray may show diffuse bilateral interstitial inLike rubella (see Chapter 28), congenital toxoplasmofiltrates, or it can be normal. If the infection is acNo Helpers quired early during gestation, the disease is severe, often resulting in stillbirth. She says she has no reactivation results most commonly in retinal inflammedical problems but has lost weight. You order an absolute T4-cell count and find that she has 150 T-helper cells (Normal is greater than 1000). Symptomatic patients can be treated with zero) and so zero hours was called one, 24 hours high dose trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or intracalled two, and 48 hours called three. They infect to either fall within this period or be continuous, with about 300-500 million persons worldwide each year, reless pronounced chills and sweats. The anopheles mosquito carries the organisms within its salivary glands and inPlasmodia Life Cycle jects them into humans while it feeds. The different species of Plasmodium Imagine yourself in Kenya with a patient who has inburst the red cells at different time intervals. What are those life cycle stages are asked if you have ever had malaria when you donate and what do they look likefi They may find their way into the mosquito to the liver and burrow into a liver cell. These episodes commonly mic membrane then forms around each nucleus, creatlast about 6 hours and are associated with the rupture i ng thousands of small bodies called merozoites. These sticky cells plug up post-capillary venules in Other merozoites will enter the bloodstream and organs such as the kidney, lung, and even brain, resultenter red blood cells, starting the erythrocytic cycle. In the red cells the trophozoite is shaped often develop cerebral malaria characterized by like a ring with the nuclear material looking like the seizures and impaired consciousness, leading to coma. Nuclear division then occurs with Even with treatment, 20% of children with cerebral formation of a large multinucleated schizont. The released merozoites stimuphagocytic cells (of the reticuloendothelial system) pick late an immune response, manifested as fevers, chills, up large amounts of debris from the destroyed red blood and sweats. The merozoites can continue to invade other red cells Many African-American and African blacks are resisand then grow for another 2-3 day cycle followed by ruptant to P. Endemic infection with malaria in the African continent is thought to have led to a Darwinian selection process, resulting in high levels of sickle trait and absence of Duffy a and b in many African and African-American blacks. United States and just as effective), artemether 2) Chemical Prophylaxis for travelers: When traveling (see below), pyrimethamine/sulfadoxine, or to an area without chloroquine resistance, chloroquine mefloquine. A new drug named artemether (or its ica south of the Panama Canal, South America, India, brother artesunate) is derived from a traditional Chiand South East Asia (see map). Unfortunately, even with therapy, 20% of children with cerebral malaria still die. To treat malaria you must understand two concepts: 1) the geographic pattern of susceptibility of P. It is pyrimethamine are safe in all trimesters of transmitted by the bite of a blood sucker (tick in this case) pregnancy. They can ex1) There are more than 100 species of Babesia, mostly amastigotes, ist as rounded cells without flagella, called causing disease in cattle and other domestic or wild or as flagellated motile forms called promastigotes, epianimals. Leishmania is zoonotic, carried by rodents, dogs, and the sporozoites invade erythrocytes and differentiate foxes, and is transmitted to humans by the bite of the into pear or ring-shaped trophozoites. The disease leishmaniasis is found in South asexually bud and divide into 4 merozoites that stick toand Central America, Africa, and the Middle East. Red cell infection results in only mild hemolysis, mastigote invades phagocytic cells (macrophages) and so infection is usually asymptomatic and sub-clinical. The amastigAsplenic patients are unable to clear the organisms as ote multiplies within the phagocytic cells in the lymph well and may have severe infection similar to falcinodes, spleen, liver, and bone marrow (the reticuloenparum malaria. It appears that some patients have genetically deficient defenses against Leishmania and will be afflicted with more severe disease. Leishmaniasis presents in a spectrum of disease severity: from a single ulcer that will heal without treatment; to widely disseminated ulcerations of the skin and mucous membranes; to the very severe infection striking deep into the reticuloendothelial organs, the spleen and liver. There are 3 clinical forms of this disease: 1) Cutaneous leishmaniasis a) Simple cutaneous lesions b) Diffuse cutaneous lesions Fig. At the site of the sandfly (Leishmania and Trypanosoma) bite, a skin ulcer develops, called an "oriental sore.
Cheap indocin 50 mg with amex
In girls arthritis in neck causing shoulder pain buy 50mg indocin free shipping, excesgonadal failure may be associated with galactosemia, myotonic sive androgens may lead to acne, hirsutism, or clitoromegaly. Anorchia is the Estrogen efects include vaginal cornifcation/discharge, breast absence of testes and must be distinguished from bilateral cryptdevelopment, uterine size, and onset of menarche 2 to 2. The testes are usually clude identifcation of midline facial defects and tests for olfacundescended or retractile, but rarely no testes are found even tion. Skin examination includes cafe au lait spots cryptorchidism, owing to compromised Leydig cell function, (neurofbromatosis), tanning (adrenal insufciency), and ichnormal testosterone levels may only be achieved with elevated thyosis (congenital ichthyosis, Kallmann syndrome). Irradiation or chemotherapy may also cause of specifc syndromes may be identifed on initial exam. Bone age implicated in testicular dysgenesis syndrome include environassessment, estradiol or testosterone levels, and prolactin and mental chemicals that may act as endocrine disruptors (bisphethyroid studies may be considered. Tere is a family history of delayed puberty, a consistent heart murmurs, nail changes, and deformed ears. The 45,X karyotype is most age equals height age, which is less than the chronological age. Chapter 174 262 Part X u Endocrine System Specifc stigmata may be indicative of certain syndromes. Isolated gonadotropin defciency is associshort stature, and mild mental retardation. The hypogonadism ated with a number of genetic disorders, including a subset with is hypothalamic. Multiple lentigines syndrome includes cardiac defects, urologic Endocrinopathies include hypothyroidism, diabetes in14 abnormalities, short stature, and deafness. Hyperprolactinemia is more common in girls; it may be primary (idiopathic, pituitary adenoma) or Clinical evidence that may suggest hypopituitarism include 12 secondary to disruption of the pituitary stalk or to hypothyroidsymptoms like growth failure, anosmia, midline facial deism. T us, infection in one part usually attacks the adjacent structures and may spread to the tracheobronchial tree and lungs. Bacterial pathogens can also be the primary causative agents of acute upper respiratory infections, but more frequently, they cause chronic infections. These includes intracranial spreading of suppurative infection, sudden airway obstruction due to epiglottitis and diphtheria, rheumatic fever after streptococcal tonsillitis, etc. In this chapter, we will describe clinical settings, diagnostic work-up, and treatment of upper respiratory infections, with special consideration to complications and life-threatening diseases occurring as a result of these infections. In the normal circumstances, air enters the infections include rhinitis (infammation of the nasal respiratory system through nostrils where it is fltered, mucosa), rhinosinusitis or sinusitis (infammation of humidifed, and warmed inside the nasal cavity. They are the leading cause laryngitis (infammation of the larynx), laryngotracheitis for people missing work or school and, thus, have (infammation of the larynx, trachea, and subglottic important social implications. They range from mild, area), and tracheitis (infammation of the trachea and self-limiting disease like common cold, syndrome of the subglottic area). In general, progress to a systemic illness in immunocompromised symptomatic therapy is sufcient (analgesics, antipyretics, patients. In most immunocompromised persons, or during epidemics, cases, the infection spreads from person-to-person, when medical attention is necessary. The aim is to recognize touching the secretions by hand or directly by inhaling the or detect the causative agent and, thus, enable efcient respiratory droplets. In some instances, visualization and imaging cause of upper respiratory tract infection, but they may techniques help in the management of these patients. The armamentarium of investigations to reach the risk factors for the development of upper respiratory fnal diagnosis is huge. Most frequent flter and trap some pathogens and mucus coats are very is a group a Streptococcal infection, especially with efcient. Group help transport all kinds of particles up to the pharynx; a b-hemolytic streptococcus is the etiologic agent in from there, they are swallowed into the stomach. Special If clinical suspicion is high, no further testing is attention is recommended in those with suboptimal necessary and empirical antibiotic is given. When the immune defenses like those for instance, without a diagnosis is inconclusive, further testing is recommended. Many nonspecifc Ct fndings, including personnel in rare occasions like in a persistent disease, thickened turbinates and difusely thickened sinus suppurative spread, and in immunocompromised mucosa may be detected (Figure 2). The search for Ct fndings suggestive of chronic sinusitis include causative agent in rhinosinusitis may be necessary if mucosal thickening, opacifed air cells, bony remodeling, the disease has an extended duration, or if infuenza, and bony thickening due to infammatory osteitis of the mononucleosis, or herpes simplex is suspected. Bony erosion can occur in severe rare occasions of laryngitis, the suspicion of diphtheria cases especially, if associated with massive polyps or warrants specifc tests. The materials for microbiology analysis are collected If symptoms of rhinosinusitis extend despite therapy or by several procedures: throat swab, nasal wash, swabs, or if propagation of disease into adjacent tissue is suspected, aspirates for sinus puncture, and aspiration, or by the aid sinus imaging is indicated. Sinus ultrasonography may also be useful in the radiological studies, plain radiographic flms, computed intensive care or if radiation exposure is to be avoided. Classifcation and etiology of Rhinitis Type of rhinitis Etiology Nasal endoscopy and laryngoscopy Infectious rhinitis Viruses, bacteria, fungi Nasal endoscopy has a defnite role in the identifcation Vasomotor rhinitis Disbalance of the parasympathetic and sympathetic system of sinonasal disease. But it has to be underlined that it does not apply to most of the patients with acute diseases Occupational Inhaled irritants rhinitis who seek medical attention for the frst time but only to those with prolonged course, severe symptoms, or when Hormonal rhinitis Estrogen imbalance a suspicion of serious complications exists. The instrumentation can provoke airway altered sense of smell, postnasal drip with cough, and spasms and induce respiratory insufciency. Tese properties do not diferentiate viral from duration of symptoms and changes of nasal mucosa, bacterial infection. Terapy should be directed to symptomatic care, which includes analgesics, antiAcute Viral Rhinitis (Common Cold) pyretics, and saline irrigation. The use of topical or oral decongestants leads to rebound symptoms and should acute infectious rhinitis and rhinosinusitis are usually be avoided. Fluid intake should be encouraged to replace the part of an upper respiratory infection, which involves insensible losses and reduced oral intake. In plain radiograph of the sinuses may reveal complete sinus children, the most common symptoms of bacterial opacity, air-fuid level, or marked mucosal thickening. While nasopharyngeal discharge is purulent and minimal, not responding to swab is unreliable, microbiological cultures should be symptomatic medication and, occasionally, accompanied obtained by direct sinus aspiration. Usually, guided cultures of the middle meatus may be considered especially in adults, the pain is restricted to diseased sinus. Due to lack of precision and practicality of usually it is most striking in the morning, after waking current diagnostic methods, the clinical diagnosis of up, as a reaction to the accumulated secretions in the acute bacterial rhinosinusitis is made primarily on the posterior pharynx during the night. Notice the leakage of purulent secretion from nasopharynx more consecutive days to oropharynx and larynx. Children with non-type I penicillin allergy may be treated with combination of a third-generation oral cephalosporin and clindamycin. Intranasal corticosteroids are recommended as an adjunct therapy in individuals with a history of allergic rhinitis. Endoscopy reveals chronic rhinitis with multiple which probiotics are associated with the greatest efcacy mucosal erosions and almost completely destroyed nasal septum. Chronic Rhinitis Chronic rhinitis is usually a prolongation of subacute infammatory or infectious viral rhinitis.
Purchase 25mg indocin with mastercard
Conduction aphasia was traditionally explained as due to a disconnection between sensory (Wernicke) and motor (Broca) areas for language gouty arthritis diet order 50mg indocin with amex, involving the arcuate fasciculus in the supramarginal gyrus. Certainly the brain damage (usually infarction) associated with conduction aphasia most commonly involves the left parietal lobe (lower postcentral and supramarginal gyri) and the insula, but it is variable, and the cortical injury may be responsible for the clinical picture. This phenomenon suggests that an acoustic image of the target word is preserved in this condition. A similar phenomenon may be observed in patients with optic aphasia attempting to name a visual stimulus. A similar behaviour is seen in so-called speech apraxia, in which patients repeatedly approximate to the desired output before reaching it. The term may also be used to refer to a parapraxis in which patients attempt to perform a movement several times before achieving the correct movement. Cross References Aphasia; Conduction aphasia; Optic aphasia; Parapraxia, Parapraxis; Speech apraxia 90 Congenital Nystagmus C Confabulation the old definition of confabulation as the falsification of episodic memory occurring in clear consciousness, often in association with amnesia (in other words, paramnesias related as true events), has proven increasingly deficient, not least because most amnesic patients, suffering from medial temporal lobe/hippocampal lesions, do not confabulate, and poor memory alone cannot explain confabulation. Schnider has developed a fourfold schema of intrusions, momentary confabulations, fantastic confabulations, and behaviourally spontaneous confabulations, of which the latter are clinically the most challenging. Anterior limbic structures are thought culpable, and the pathogenesis includes a wide variety of diseases, which may include associated phenomena such as amnesia, disorientation, false recognition syndromes including the Capgras delusion, and anosognosia. Moreover, as there is a lack of correlation of meaning when this term is used by different health professionals, it is regarded by some as an unhelpful term. This may be due to a variety of factors, including prolonged muscle spasticity with or without muscle fibrosis. This often occurs in the context of limb immobilization or inactivity, for example, in a fiexed posture. Injections of botulinum toxin to abolish muscle spasticity may be required to assess whether there is concurrent ligamentous restriction, and thus to plan optimum treatment, which may involve surgery. The former is a complex vocal tic most characteristically seen in Tourette syndrome although it actually occurs in less than half of affected individuals. The pathophysiology of coprolalia is unknown but may be related to frontal (cingulate and orbitofrontal) dysfunction, for which there is some evidence in Tourette syndrome. Cross Reference Tic Copropraxia Copropraxia is a complex motor tic comprising obscene gesturing, sometimes seen in Tourette syndrome. Cross References Coprolalia; Tic Corectopia Corectopia is pupillary displacement, which may be seen with midbrain lesions, including transtentorial herniation and top-of-the-basilar syndrome, peripheral oculomotor nerve palsies, and focal pathology in the iris. Corneal Refiex the corneal refiex consists of a bilateral blink response elicited by touching the cornea lightly, for example, with a piece of cotton wool. As well as observing whether the patient blinks, the examiner should also ask whether the stimulus was felt: a difference in corneal sensitivity may be the earliest abnormality in this refiex. The fibres subserving -93 C Corneomandibular Refiex the corneal refiex seem to be the most sensitive to trigeminal nerve compression or distortion: an intact corneal refiex with a complaint of facial numbness leads to suspicion of a non-organic cause. Trigeminal nerve lesions cause both ipsilateral and contralateral corneal refiex loss. Cerebral hemisphere (but not thalamic) lesions causing hemiparesis and hemisensory loss may also be associated with a decreased corneal refiex. The corneal refiex has a high threshold in comatose patients and is usually preserved until late (unless coma is due to drug overdose), in which case its loss is a poor prognostic sign. The patient may assert that they are dead and able to smell rotten fiesh or feel worms crawling over their skin. Although this may occur in the context of psychiatric disease, especially depression and schizophrenia, it may also occur in association with organic brain abnormalities, specifically lesions of the non-dominant temporoparietal cortex, or migraine. Cross References Capgras syndrome; Delusion; Disconnection syndromes Coup de Poignard Coup de poignard, or dagger thrust, refers to a sudden precordial pain, as may occur in myocardial infarction or aortic dissection, also described with spinal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Subarachnoid haemorrhage presenting as acute chest pain: a variant of le coup de poignard. Coup de Sabre Coup de sabre is a localized form of scleroderma manifest as a linear, atrophic lesion on the forehead which may be mistaken for a scar. This lesion may be associated with hemifacial atrophy and epilepsy, and neuroimaging may -95 C Cover Tests show hemiatrophy and intracranial calcification. Whether these changes refiect infiammation or a neurocutaneous syndrome is not known. The cover test demonstrates tropias: the uncovered eye is forced to adopt fixation; any movement therefore represents a manifest strabismus (heterotropia). The alternate cover or cross-cover test, in which the hand or occluder moves back and forth between the eyes, repeatedly breaking and re-establishing fixation, is more dissociating, preventing binocular viewing, and therefore helpful in demonstrating whether or not there is strabismus. It should be performed in the nine cardinal positions of gaze to determine the direction that elicits maximal deviation. Cross References Heterophoria; Heterotropia Cramp Cramps are defined as involuntary contractions of a number of muscle units which results in a hardening of the muscle with pain due to a local lactic acidosis. Cramps are not uncommon in normal individuals but in a minority of cases they are associated with an underlying neurological or metabolic disorder. Symptomatic treatment of cramps may include use of quinine sulphate, vitamin B, naftidrofuryl, and calcium channel antagonists such as diltiazem; carbamazepine, phenytoin, and procainamide have also been tried. Assessment: symptomatic treatment for muscle cramps (an evidence-based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Cross References Fasciculation; Myokymia; Neuromyotonia; Spasm; Stiffness Cremasteric Refiex the cremasteric refiex is a superficial or cutaneous refiex consisting of contraction of the cremaster muscle causing elevation of the testicle, following stimulation of the skin of the upper inner aspect of the thigh from above downwards. The cremasteric refiex is lost when the corticospinal pathways are damaged above T12 or following lesions of the genitofemoral nerve. It may also be absent in elderly men or with local pathology such as hydrocele, varicocele, orchitis, or epididymitis.
Generic indocin 25 mg visa
These include crescents rheumatoid arthritis diet meal plan generic 50mg indocin free shipping, situs inversus, congenital pigmentation, coloboma, drusen and hypoplasia of the optic disc. Anomalies of vascular elements, such as persistent hyaloid artery and congenital tortuosity of retinal vessels. These include albinism, congenital night blindness, congenital day blindness, Oguchifis disease, congenital retinal cyst, congenital retinal detachment and coloboma of the fundus. Coloboma of the optic disc It results from the failure in closure of the embryonic fissure. Drusen of the optic disc Drusens are intrapapillary refractile bodies, which usually lie deep beneath the surface of the disc tissue in childhood and emerge out in the early teenagehood. Thus, in children they present as pseudo-papilledema and by teens they can be recognised ophthalmoscopically as waxy pea-like irregular refractile bodies. Hypoplasia of the optic disc Hypoplasia of the optic nerve may occur as an isolated anomaly or in association with other anomalies of the central nervous system. It is associated with maternal alcohol use, diabetes and intake of 302 certain drugs in pregnancy. Inflammatory Disorders of the Retina these may present as retinitis (pure retinal inflammation), chorioretinitis (inflammation of retina and choroid), neuroretinitis (inflammation of optic disc and surrounding retina), or retinal vasculitis (inflammation of the retinal vessels). The infection usually involves the surrounding structures and soon converts into metastatic endophthalmitis or even panophthalmitis. It is characterised by multiple superficial retinal haemorrhages, involving posterior part of the fundus. Vision may be blurred due to involvement of the macular region or due to associated papillitis. It may be bacterial (tuberculosis, leprosy, syphilis and actinomycosis), viral (cytomegalic inclusion disease, rubella, herpes zoster), mycotic, rickettsia or parasitic in origin. It is characterised by recurrent vitreous haemorrhage, so it is also referred to as primary vitreous haemorrhage. Clinical features It is a bilateral disease, typically affecting young adult males. The common presenting symptoms are sudden appearance of floaters (black spots) in front of the eye or painless loss of vision due to vitreous haemorrhage. Medical treatment: a course of oral corticosteroids for extended periods is the main course of treatment during active inflammation. Laser photocoagulation of the retina is indicated at the stage of neovascularization. Vitreoretinal surgery is required for non-resolving vitreous haemorrhage and tractional retinal detachment. Vascular Disorders of Retina Common vascular disorders of retina include: retinal artery occlusions, retinal vein occlusions, diabetic retinopathy, hypertensive retinopathy, sickle cell retinopathy, retinopathy of prematurity and retinal telangiectasia. Clinical features Clinically retinal artery occlusion may present as central retinal artery occlusion or branch artery occlusion. On ophthalmoscopy examination retinal arteries are markedly narrowed but retinal veins look almost normal. Central part of the macular area shows cherry-red spot due to vascular choroid shining through the thin retina of this region. After a few weeks the edema subsides, and atrophic changes occur which include grossly attenuated thread-like arteries and consecutive optic atrophy. Treatment of the central retinal artery occlusion is unsatisfactory, as retinal tissue cannot survive ischemia for more than a few hours. Immediate lowering of intraocular pressure by intravenous mannitol and intermittent ocular massage. Vasodilators and inhalation of a mixture of 5 percent carbon dioxide and 95 percent oxygen (practically patient should be asked to breathe in a polythene bag) may help by relieving element of angiospasm. Later on the involved area is atrophied leading to permanent sectoral visual field defect. Pressure on the vein by a sclerotic retinal artery where the two share a common adventitia. Central retinal vein occlusion is more common in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Local causes are orbital cellulitis, facial erysipelas and cavernous sinus thrombosis. Fundus examination in early cases reveals mild venous congestion and tortuosity, a few superficial flame-shaped hemorrhages more in the peripheral than the posterior retina, mild papilledema and mild or no macular edema. Macula may show chronic cystoid edema in moderate cases or may be normal in mild cases. Visual loss in rest of the cases is due to chronic cystoid macular edema, for which no treatment is effective. In late stages, marked sheathing around veins and collaterals is seen around the disc. In branch vein occlusion edema and hemorrhages are limited to the area drained by the affected vein. Treatment Grid photocoagulation may be required in patients with chronic macular edema. In patients with neovascularization, scatter photocoagulation should be carried out. Hypertensive Retinopathy It refers to fundus changes occurring in patients suffering from systemic hypertension. Pathogenesis Three factors which play role in the pathogenesis of hypertensive retinopathy are vasoconstriction, arteriosclerosis and increased vascular permeability. Primary response of the retinal arterioles to the raised blood pressure is narrowing (vasoconstriction) and is related to the severity of hypertension. It occurs in pure form in young individuals, but is affected by the pre-existing involutional sclerosis in older patients. In older patients arteriosclerotic changes may preexist due to involutional sclerosis. Increased vascular permeability results from hypoxia and is responsible for haemorrhages, exudates and focal retinal edema. Grading of hypertensive retinopathy Keith and Wegner (1939) have classified hypertensive retinopathy changes into the following four grades: Grade I. It consists of mild generalized arteriolar attenuation, particularly of small branches, with broadening of the arteriolar light reflex and vein concealment. It comprises marked generalized narrowing and focal attenuation of arterioles associated with deflection of veins at arteriovenous crossings (Salusfis sign). Clinical types Clinically, hypertensive retinopathy may occur in four circumstances: 310 1. When hypertension occurs in elderly patients (after the age of 50 years) in the presence of involutionary sclerosis the fundus changes comprise augmented arteriosclerotic retinopathy. It occurs in young people, where elastic retinal arterioles are exposed to the raised blood pressure for a short duration. This condition is seen in young patients with prolonged benign hypertension usually associated with benign nephrosclerosis. The young arterioles respond by proliferative and fibrous changes in the media (compensatory arteriolar sclerosis).
Cheap indocin 75mg overnight delivery
A control test conducted after 2 weeks usually gives an initial indication of a seroconversion arthritis gout relief generic indocin 25mg fast delivery. It should be noted that the antibodies of patients with various autoimmune diseases can cross-react with Trichinella antigens [127]. It can be exported to other countries by migrants who are subclinically infected and can also pose a risk to local populations in connection with blood transfusions. Intestinal changes (megacolon, megaesophagus) can also develop which are caused by the destruction of autonomic ganglia or myositis. Because it is difficult to detect parasites during the acute and the latent phase of the infection, antibody detection plays a significant role in laboratory diagnostic testing. There are several different test formats with various antigen preparations from different developmental stages of T. The new developments, which sometimes represent up to 14 different antigen regions and, thus, portions of all developmental stages of T. A lower specificity of these assays is expected in countries with endemic Leishmania infections since there is a pronounced cross reaction between Trypanosomatidae. When the infection is chronic 213 and as the patient ages, antibodies increase which react with non-parasitic epitopes in the sense of an autoimmune reaction. There is currently no serological marker for successful treatment for this patient group. Developers of Chagas tests also have serum panels at their disposal which reproduce both a seroconversion and regionally different immune responses. A specific diagnostic reliability is required by serological tests that are used to screen blood or organ donors in affected regions. For donors, weakly positive reactions in asymptomatic adults without parasitemia should be verified using a confirmatory test. In Germany, unlike in Spain, the screening of blood donors for Chagas disease is currently not recommended. In non-endemic regions, diagnostic reliability can be improved by combining at least two different tests. A cross reaction with Leishmania is possible when there is a corresponding travel history or origin. When an acute infection is suspected, diagnostic reliability is improved by combining serological monitoring of disease progression (at an interval of around 4 weeks) with molecular pathogen detection. The disease occurs focally and predominantly in poor rural regions (around 20,000 to 30,000 cases per year). Antibody detection plays a significant role in laboratory diagnostic testing for chronic T. A positive reaction in a serum dilution > 1:4 is an indication of an infection and is occasion for follow-up testing [301]. However, the test is not considered to be the gold standard for a definitive diagnosis since there are obvious country and population-specific differences in the formation of the antibody profile. When antibody detection is positive, an infection is probable and parasite detection is subsequently required. In residential areas, Aspergillus species are 215 found on moist walls, on potted plants and in organic waste. The single-cell, hydrophobic Aspergillus conidia are absorbed from the environment. The point of entry is usually the lungs, in rarer cases it can be the skin or digestive tract. Unlike infections caused by Candida albicans, which mostly occur endogenously, this etiology is rare for aspergillosis. However, Aspergillus species can be chronic colonizers, for example, of the paranasal sinus. Despite immunocompetency, infections of the ear canal, associated with the Aspergillus species, are possible. Symptoms are uncharacteristic and determined by location and scale of the infection. However obtaining this sample is an invasive process that can be difficult for patients. Since Aspergillus species can only be detected in blood cultures in exceptional cases, a negative result does not rule out a hematogenous spread. Depending on the study population, the test has a sensitivity and specificity of between 40 and 100% when testing serum. It is also known that false-positive results frequently occur in pediatric patients and patients with graft versus host disease. This means the plurifungal test is not specific for infections caused by the Aspergillus species. The commercially available assays (limulus assays) are not suitable since single tests for an emergency diagnosis cannot be processed economically. However, the diagnostic significance of the test cannot be conclusively assessed based on the currently available data. Because of the possibility of false-positive results as described above, single antigen tests should always be confirmed by subsequent tests. An assessment of Aspergillus serology in the context of other diagnostic measures can also be found in MiQ 15 [348]. These fungi develop yeast cells in their anamorphic (asexual) form which reproduce through budding (yeast). Candida species, particularly Candida albicans, can regularly be found in the mouth or digestive tract of a majority of healthy populations as commensal organisms. Candida yeasts can cause both superficial skin and mucous membrane mycoses, as well as invasive, disseminated organ mycosis in risk patients. The incidence rate of invasive candidiasis is around 22 to 29 per 100,000 inhabitants. The oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract and invasive catheters are the main entry points for deep infections. Typically no bacterial pathogens can be detected and empirical antibiotic treatment is not successful. When patients have a high degree of immunosuppression, disseminated candidiasis frequently runs a lethal course even under adequate antimycotic chemotherapy. Indirect detection methods can provide valuable additional diagnostic information since blood cultures are less sensitive and because pertinent, invasive diagnostic testing in culture of the organ candidiasis is often not possible when there is severe immunosuppression. Both antigen and antibody detection methods are available to serologically diagnose invasive fungal infections. However, it should be noted that the clinical interpretation of serological test results can be problematic [348]. An acute infection is indicated by the positive detection of antigens as well as high or rising (whole) antibody titers. The literature has indicated that Candida-IgA and IgM antibody titers are especially elevated during an acute infection [243]. An infection is suspected in agglutination tests when titers are between 16 and 32 and there is a normal peripheral neutrophil count. False positive results occur, for example, when there are existing rheumatoid factors or limited kidney function. The amount of detectable mannan is, however, not the same for individual Candida species due to the antibodies used in the test. The results of mannan antigen detection are inadequate, particularly for infections with C. The disadvantages of the different test systems for detecting antigens are the low sensitivity, particularly with the agglutination methods, and the often false-positive results.

