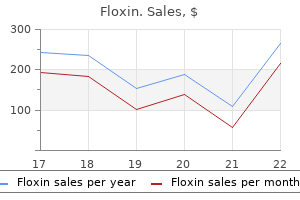
Floxin
Proven 200 mg floxin
For the young girl in the vignette who has disclosed no history of sexual abuse antibiotics for uti and breastfeeding order cheap floxin line, who is displaying developmentally-appropriate behavior, and who has no findings concerning for sexual abuse on history or physical examination, a forensic examination for sexual abuse is not indicated. The timing and nature of the reported or suspected abuse are important factors to consider when determining whether forensic evidence collection is indicated. In most states, forensic evidence collection is required if sexual abuse involving the exchange of bodily fluids occurred within the past 72 hours. Studies have demonstrated that forensic evidence is rarely obtained from prepubertal children after 24 hours following the occurrence of abuse. As with physical examination findings, confirmatory forensic evidence is certainly not required to make a diagnosis of child sexual abuse. Whenever a reasonable suspicion for sexual abuse exists, all providers are obligated to report the suspicion to child protective services, in addition to local law enforcement agencies (if the identity of the perpetrator is known). In some cases, children may present for evaluation when one parent accuses another parent (or his/her contacts) of sexually abusing the child. These cases can be extremely challenging, especially if the pediatrician believes that allegations of sexual abuse may be related to a custody dispute or other parental conflict. If the evaluation does not support a history of sexual abuse but a parent continues to express concern, the family may need referral to a mental health expert or to a pediatric child abuse specialist. The statement that sexual abuse is unlikely because the girl has a normal physical examination is incorrect. In fact, most sexual abuse victims have normal anogenital examinations and multiple studies have found that definitive physical findings are not commonly present in sexual abuse victims. It is important for pediatricians to educate caregivers that a physical examination alone cannot determine whether their child has been sexually abused. This particular behavior does not indicate that the girl has been a victim of sexual abuse. However, forensic evidence is rarely obtained from the bodies of prepubertal children after 24 hours following the occurrence of abuse. The evaluation of children in the primary care setting when sexual abuse is suspected. The most likely pathogen in this vignette is Enterococcus, therefore ampicillin is the preferred choice. Enterococci are normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract of humans and other animals. They are widely recognized as a cause of urinary tract infections, as well as bacteremia, endocarditis, and wound infections. Since they reside in the human gastrointestinal tract, they must be considered in the presence of intra-abdominal infections. Enterococci are opportunists and their rise to prominence has been attributed to a growing population of patients that are immunocompromised or severely ill and necessitate medical devices such as central venous or urinary catheters. Enterococci should be considered in any child who requires chronic bladder catheterization and develops an urinary tract infection. Enterococci are intrinsically resistant to cephalosporins, therefore cefixime and cephalexin would not be correct choices. Cephalosporins are appropriate antimicrobials to use for urinary tract infections caused by gram-negative enteric bacteria. The vignette, however, reveals that the etiology of the infection is due to a gram-positive organism. Nitrofurantoin can be used for the treatment of cystitis caused by a susceptible gram-negative or gram-positive organism or for prophylaxis of urinary tract infections. Nitrfurantoin has activity against susceptible enterococci, but either penicillin or ampicillin are preferred agents for uncomplicated urinary tract infections. The use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for enterococcal urinary tract infections is controversial. While there are some in vitro data to suggest susceptibility, this may not correlate with clinical outcomes and thus is not the best treatment for this patient. She also eats pureed food twice daily and teething crackers several times per day. The dietician reviewed the formula mixing instructions at the last visit and found that the mother was mixing correctly. Her physical examination is only remarkable for bilateral lower extremities with 2+ pitting edema. Laboratory results are shown: Laboratory Test Laboratory Test Result Complete blood cell count Normal Hepatic transaminases Normal Albumin 2. Her low serum protein including low immunoglobulins, poor weight gain, edema, and diarrhea support this diagnosis. The presentation of protein or calorie malnutrition varies based on the underlying etiology. The differential diagnosis includes inadequate intake, increased demand because of a medical condition (ie, cardiac or liver disease), and malabsorption. The presentation and characteristic laboratory findings will vary depending on the underlying cause of the malnutrition (Item C59). Finally, infantile inflammatory bowel disease typically presents with large volumes of bloody diarrhea, severe failure to thrive, anemia, and elevated serum inflammatory markers. The most common mechanisms of this injury include landing from a jump, twisting with the foot planted, and sudden deceleration. Neuromuscular training programs that emphasize control of knee position during sports have been shown to decrease the risk of knee injuries. Successful programs incorporate strengthening, balance, and plyometric (jump) training and cues for athletes that encourage proper technique. Athletes who participate in sports with a high risk of ankle sprains, such as football and basketball, should be counseled about the protective effect of strengthening programs and ankle braces. On physical examination, you find a 5 mm, painless, rubbery lesion located on the left lower eyelid. A chalazion results from an inflammatory process involving the meibomian glands of the upper or lower eyelid. It typically presents as a firm, slow growing, nontender, rubbery nodule in the lower or upper eyelid, which varies between 3 to 10 mm. As recommended for the boy in this vignette, the treatment for a chalazion consists of warm compresses to the eyelid multiple times a day. The chalazion is not the result of an infectious process, so antibiotics (either topical or oral) are not indicated unless there is also a secondary infection present. A secondary infection of a chalazion will typically present with the onset of pain and tenderness. Most chalazia will resolve on their own with the warm compresses; however, excision may be necessary if the chalazion distorts vision or leads to a cosmetic issue. A referral to an ophthalmologist is not indicated until routine treatment has been tried. Incision and drainage of the chalazion is not helpful, as there is no infection to drain. In contrast to a chalazion, a hordoleum represents a more acute infectious process of the glands of the eyelid (the meibomian glands or the glands of Zeis or Moll). An external hordoleum, also known as a common stye, involves an infection of the glands of Zeis or Moll that are associated with the hair follicles of the eyelid. The lid margin can be mildly red and swollen and the infection points to the lid margin. Treatment of choice for an external hordoleum consists of warm compresses to help relieve the obstruction and promote drainage. An internal hordoleum results from an infection of the meibomian gland, the large sebaceous gland that has its opening at the lid margin. The swelling tends to be more diffuse and the infection will point to either the lid margin or the conjunctival surface of the eye.
Buy 200 mg floxin fast delivery
N} Maximum character length: 2 Permissible values: Value Meaning 1 Patient and provider in the same physical location 1 antibiotics for uti and drinking purchase floxin toronto. Patient and provider not in the same physical location refers to service events delivered via a telephone call or video link (telemedicine). Clinical services that are not specifically identified in this Guide for use should be classified as one of the groups in the data domain on the basis of the type of clinical professional staff involved in providing the service event. That is, paediatric medical should be reported as medical and paediatric surgical should be reported as surgical. Intersex or indeterminate, should be confirmed if reported for people aged 90 days or greater. Legislation (Gay, Lesbian and Transgender) Amendment Act 2003 1465 Reference documents: Legislation (Gay, Lesbian and Transgender) Amendment Act 2003. Data element attributes Collection and usage attributes Collection methods: Operationally, sex is the distinction between male and female, as reported by a person or as determined by an interviewer. When collecting data on sex by personal interview, asking the sex of the respondent is usually unnecessary and may be inappropriate, or even offensive. It is usually a simple matter to infer the sex of the respondent through observation, or from other cues such as the relationship of the person(s) accompanying the respondent, or first name. The interviewer may ask whether persons not present at the interview are male or female. This code(s) would also be applicable after the person has completed such a process, if they have a procedure involving an organ(s) specific to their previous sex. Should not generally be used on data collection forms completed by the respondent. Should only be used if the person or respondent volunteers that the person is intersex or where it otherwise becomes clear during the collection process that the individual is neither male nor female. Revenue received from the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing under the Australian Health Care Agreements to assist in the cost of providing public patients with free access to public hospital services within a clinically appropriate time irrespective of where patients live. Includes revenue received for services listed in the Medical Benefits Schedule that are provided by registered medical practitioners. Many medical services in Australia are provided on a fee-for-service basis and attract benefits or revenue from the Australian Government under Medicare. Includes revenue received for medical services provided to private admitted patients in hospitals as well as some revenue that is not based on fee-for-service. Excludes Medicare payments from Medicare Australia (part of Department of Human Services) reported under code 103. State and territory health authorities may report revenues for admitted patients, from private health insurance funds and private households, as a combined total if these revenues are not able to be reported separately. Excludes benefits paid under workers compensation insurance, public liability, common law or medical negligence. This item is not currently required to be reported by state or territory health authorities. If a common law claim is not successful, the worker will continue to receive workers compensation under the statutory scheme. Cost-sharing is a provision of health insurance or third party payment that requires the individual who is covered to pay part of the cost of health care received. This is distinct from the payment of a health insurance premium, contribution or tax which is paid whether health care is received or not. Cost-sharing can be in the form of co-payments, co-insurance or deductibles: co-payment: cost-sharing in the form of a fixed amount to be paid for a service; co-insurance: cost-sharing in the form of a set proportion of the cost of a service; and deductibles: cost-sharing in the form of a fixed amount which must be paid for a service before any payment of benefits can take place. These include organisations such as the National Heart Foundation, Diabetes Australia or the Cancer Council etc. Include revenues received from all corporations or quasi corporations, whose principal activity is the production of market goods or services (other than health insurance). Included are all resident non-profit institutions that are market producers of goods or non-financial services. These include health or health-related organisations such as hospitals, pharmacies, medical and diagnostic laboratories, residential aged care facilities and providers of medical specialist services, and non-health organisations such as research organisations. Includes funds provided from overseas countries for areas of health care such as research. Funds may be channelled through 1477 government or non-government organisations or private institutions. Also includes overseas visitors receiving health care for whom travel insurance is the major funding source. Source and reference attributes Submitting organisation: Health Expenditure Advisory Committee Reference documents: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2007. The expected revenue source should be reported if the fee has not been paid but is not to be waived. Excludes psychiatric hospitals, psychiatric units and drug and alcohol units located within or operating from hospitals, and outpatient clinics (see codes 05-07). Includes psychiatric hospitals and psychiatric units within and outside of hospitals. Data element attributes Collection and usage attributes Comments: Source of referral is important in assisting in the analyses of inter sectoral patient/client flow and for health care planning. Context: To assist in analyses of intersectoral patient flow and health care planning. These episodes are characterised by recent onset of severe clinical symptoms of mental disorder that have potential for prolonged dysfunction or risk to self and/or others. The key characteristic of acute services is that this treatment effort is focused on short-term treatment. Acute services may be focused on assisting people who have had no prior contact or previous psychiatric history, or individuals with a continuing mental disorder for whom there has been an acute exacerbation of symptoms. This category applies only to services with a mental health service setting of overnight admitted patient care or residential care. Includes programs providing rehabilitation services that have a primary focus on intervention to reduce functional impairments 1484 that limit the independence of patients. Rehabilitation services are focused on disability and the promotion of personal recovery. They are characterised by an expectation of substantial improvement over the short to mid-term. Patients treated by rehabilitation services usually have a relatively stable pattern of clinical symptoms. Also includes programs providing extended care services that primarily provide care over an indefinite period for patients who have a stable but severe level of functional impairment and an inability to function independently, thus requiring extensive care and support. Patients of extended care services present a stable pattern of clinical symptoms, which may include high levels of severe unremitting symptoms of mental disorder. Treatment is focused on preventing deterioration and reducing impairment; improvement is expected to occur slowly. These are specialised psychiatric hospitals and specialist psychiatric units located within hospitals that are not specialised psychiatric hospitals.
Order 400 mg floxin with visa
They are also a good source of Avoid adding salt to your food in cooking or at the table length of antibiotics for sinus infection buy floxin cheap online. Aim to eat at least five portions of Use herbs, spices and pepper instead of salt. Eating less fat Some tips: can also help reduce the level of cholesterol in your blood. Information and support Some tips: Ask for copies of our patient information sheets: Avoid butter, lard and ghee. This is one of the British Heart Foundation the chemicals which effects blood pressure Tel: 0300 330 3322 and circulation. Pint of normal strength beer Reducing your alcohol intake is important to help lower your blood = 2. It will also reduce the risk of developing other vascular diabetic complications such as Information and support stroke, heart attack, foot ulcers, and eye problems. However, you should know the name of your Tel: 0300 123 1110 key contact person who you are likely to see most often. There are many types Men and women should not regularly drink more than 14 units of of medications available and your doctor will discuss with you which type alcohol a week. HbA1c (which indicates your blood glucose levels for the previous two to three months) should be below 50 mmol/mol. The medication you are taking find you tire more easily and this may be might also affect your sex drive. Men may experience difficulties getting and difficult for people with jobs that are very keeping an erection and in women orgasms may be less frequent. Before stopping work or reducing your monitoring during pregnancy to prevent high hours it is important for you to get financial advice. If you have problems getting insurance still possible for women to become pregnant. This causes tiredness and loss of energy but can be successfully treated Can I use over the counter with medications. Kidney function your heart and may also hasten the deterioration in your kidney function. If you are attending the kidney clinic regularly you may wish to register with PatientView which enables you to view your latest blood test results online: It is Where a tiny piece of tissue is this is a procedure that creates an the body. This may be done Urethra A form of dialysis that takes place Where urine is stored before at home or in a dialysis unit. Urine exerts against the walls of your Abbreviation for estimated the liquid produced by your Supportive care arteries as it flows through them. The main blood vessels are the A hormone, made by your kidneys, Veins Toxins (poisons) arteries and the veins. A measure of your weight relative to your height, which is A form of dialysis where your Transplant kidney associated with your body fat and blood is cleaned outside your body, A kidney transplant operation is health risk. This is person is placed in the body of Cholesterol done either in a dialysis unit or at another person with kidney disease. A kidney can either be donated by body, can cause narrowing of the someone who has died or from a blood vessels. Tel: 020 7188 7924 Mykidney website A website to help people understand more about kidney disease Psychologists and how to live with it. If you register at Can help you by providing support, advice and information on finances, the kidney clinic you will receive a username and password that will work and practical help at home. It also provides Tel: 020 7188 5684 / 4023 information about kidney conditions and treatments. This booklet is meant for information purposes only and does not replace the detailed discussions you have with your consultant and other healthcare professionals. This document is a comprehensive update of the 2009 Renal Transplantation Guidelines. Additional chapters will be added in the coming year to address ethical issues surrounding kidney transplantation as well as the issue of prior malignancy in kidney transplantation. A broad and comprehensive literature search, covering all sections of the Renal Transplantation Guidelines was performed. A total of 2,601 unique records were identified, retrieved and screened for relevance. The next update of the Renal Transplantation Guidelines will be published in 2019. For each recommendation within the guidelines there is an accompanying online strength rating form which addresses a number of key elements namely: 1.
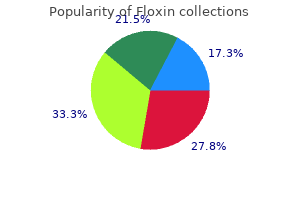
| Comparative prices of Floxin | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Brinker International | 614 |
| 2 | Delhaize America | 643 |
| 3 | Defense Commissary Agy. | 589 |
| 4 | Costco | 181 |
| 5 | Dell | 688 |
| 6 | Walgreen | 420 |
| 7 | Bon-Ton Stores | 389 |

Buy floxin 200 mg without prescription
Patients with significant cervical spine arthritis that results in C1-C2 instability or ankylosis of posterior vertebral processes are at risk for spinal cord injury (Figure 140-2) antibiotic resistance multiple choice questions order floxin 200 mg amex. Functional disabilities historically occurred in 15-30% of children; however, with early aggressive treatment and the availability of biologic medications, the prognosis has improved greatly. Cervical spine radiograph showing fusion of the spinous processes of C2-C4 and C5-C7 in a 9-year-old boy with systemic arthritis since 18 months of age. The symptoms are primarily those described in the name, as well as fatigue and occasional joint or stomach pain during the fever episode. A recent study showed that a significant proportion of children have improvement or resolution of fever after tonsillectomy. Hereditary periodic fever syndromes are characterized by recurrent episodes of fever and inflammation related to inborn errors of the innate immune system, with no evidence of autoimmune dysfunction. They have Mendelian patterns of inheritance, either autosomal recessive or dominant. Gene mutations for the 4 main hereditary periodic fevers have been identified over the last 15 years. The most common of these syndromes is familial Mediterranean fever, an autosomal recessive disorder most often occurring in individuals of eastern Mediterranean origin. It usually presents during young childhood with monthly fevers lasting up to 3 days, associated with polyserositis, arthritis of lower extremity joints, myalgias, and an erysipelas-like rash. Treatment with colchicine is usually effective in preventing the fevers and the long-term complication of amyloidosis. The differential can be divided into 5 main categories: rheumatologic, orthopedic, infectious, tumor, and miscellaneous entities. Rheumatologic diseases include oligoarticular arthritis (which involves 4 joints), psoriatic arthritis, juvenile ankylosing spondylitis (or enthesitis-related arthritis) and sarcoidosis, with the first 2 diagnoses more likely in this patient. Orthopedic problems affecting the knee include repetitive stress injuries, trauma, Osgood-Schlatter disease, osteochondritis desiccans, and patellofemoral syndrome, all of which, except trauma, are unlikely in a child this young. The main infectious cause to consider in a patient with a 3-month history of knee swelling is Lyme disease. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis are unlikely in this case, considering the long duration of symptoms and the relatively mild clinical findings. Possible tumors are osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, and pigmented villonodular synovitis. Concern for a malignant process increases if the child has pain that is out of proportion to findings on physical examination and/or has a history of frequent focal bone pain, especially pain that awakens the child from sleep. Rheumatoid factor is negative in more than 90% of patients with childhood arthritis. Furthermore, false-positive results can occur, making rheumatoid factor a very poor screening test for childhood arthritis. The main reason to perform a joint aspiration is to rule out an acute bacterial infection, which is not expected in this case based on the long duration of relatively mild symptoms. Synovial fluid cultures aimed at recovering Borrelia burgdorferi are usually unsuccessful. Polymerase chain reaction of synovial fluid, and especially synovial tissue, has a much higher yield for identifying the presence of the Lymecausing spirochete. Furthermore, if Lyme disease is suspected because the patient resides in, or has traveled to a Lyme-endemic region, serologic studies (Lyme titers/Western blot) are usually performed, rather than joint aspiration. This is the best examination to detect early uveitis, an insidious eye disease in which most young patients lack eye symptoms. Later complications, such as cataracts, band keratopathy, and synechiae, can be seen by examination with an ophthalmoscope. Children at high risk for uveitis should have a slit lamp examination every 3 months. Initial treatment for children with uveitis includes topical steroids and mydriatics. Tumor should always be included in the differential diagnosis of focal bone or joint pain. Orthopedic conditions involving the hip include Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (idiopathic avascular necrosis) in younger children and slipped capital femoral epiphysis in adolescents. The child with toxic synovitis is generally 3-10 years of age, may limp, complain of pain in the hip, thigh, or knee, and may have limited hip range of motion. If there is any clinical suspicion that the patient may have septic arthritis, the hip joint must be aspirated immediately. Enthesitis is inflammation at tendon insertion sites, for example, the Achilles insertion. Patients commonly have involvement of hip and axial joints, but they may also have arthritis of peripheral, especially lower extremity, joints. It is present in approximately 90% of whites but only 60% of African Americans with ankylosing spondylitis. These include answers B and D, as well as the ability to hyperextend the metacarpophalangeal joints when the wrist is in extension so that the fingers are parallel to the forearm, and the ability to touch the floor with the palms of the hands with the knees straight. Look for these physical findings in young children (especially between the ages of 3 and 10 years) who have increased pain after activity, as well as intermittent night pain. The incidence of benign hypermobility syndrome is increased in girls (female-to-male ratio is 2:1). Rarely, a small joint effusion in the ankles or knees may be observed; otherwise, there is absence of any clinical or laboratory signs of inflammation. Treatment includes parental and patient reassurance, education about this entity, avoidance of high-impact activities that increase joint symptoms, physical therapy to work on muscle strengthening, joint protection education, supportive footwear, and evening acetaminophen or ibuprofen on occasion. If night awakening occurs regularly, then bedtime treatment with acetaminophen or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, as well as a passive stretching program are helpful to decrease occurrence of symptoms. The child with this diagnosis should have no morning stiffness or other significant joint or bony pain during the day because these symptoms, in association with night awakening secondary to pain, could raise concern for an inflammatory process or malignancy. Revision of the proposed classification criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Durban 1997. On physical examination, she has cervical adenopathy and mild swelling of her finger joints. Approximately 4 weeks ago, a mother noticed that her 7-year-old son had a rash on his face and knuckles. Two weeks later, she noted he had decreased endurance and was having difficulty running and climbing at the playground. His teacher reported to his mother that he was having problems ascending 2 flights of stairs to go to music class. Which of the following would you not expect to find on initial physical examination of this child For the past few days, a 5-year-old child has been complaining of intermittent abdominal pain. She has palpable purpuric lesions, coalescing by the ankles, and ascending up to the buttocks. An 18-month-old boy was healthy until the acute onset of persistent fevers 4 days ago. His mother brings him to the emergency department and you note an exanthem on the trunk. You may expect to see all but which of the following findings on your admission physical A 15-year-old girl has had Raynaud symptoms for 1 year, and she occasionally develops sores on her fingertips. Over the past 6 months, she developed fullness of her fingers with skin tightening and decreased finger-joint range of motion. In the past 6-12 months, an 8-year-old boy developed an altered appearance of his lower right leg including tautness and shininess of the skin and decreased ankle range of motion. It is important to have a broad differential when first assessing this type of patient. Children with leukemia may present with musculoskeletal pain that is frequently out of proportion to the physical findings.
Buy cheap floxin on-line
Users typically experience alteration in perception virus estomacal order floxin 400mg visa, distortion of shapes and colors, visual hallucinations, distorted cognition and time sense, and alterations in mood (ranging from euphoria to extreme anxiety or fear). It involves recurrence of perceptual distortions that were previously experienced when the individual was acutely under the effects of the hallucinogenic substance ("flashbacks") in the absence of another disorder (such as schizophrenia) that would explain these symptoms. His past medical history includes recurrent otitis media and 2 hospitalizations for pneumonia. Anesthesia is called for airway management and, on intubation, they observe the image shown in Item Q253. The child in the vignette is fully immunized, but has an invasive infection, epiglottitis, and bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae type b. The humoral immune panel would allow one to measure antibody titers to several vaccine antigens, allowing for an assessment of vaccine response. Generally, immunity is divided into 2 components, the innate and adaptive immune system. The adaptive immune system is further divided into the cellular and humoral immune systems. The innate immune system is comprised of proteins and cells, including monocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer cells. The cellular and humoral immune systems is composed of T and B-lymphocytes, respectively. However, this is a simplistic approach to the immune system because there is cross talk between components of the various systems and defects can occur that affect several aspects of immunity simultaneously. Defects of the cellular immune system or T-lymphocyte function tend to present with failure-to thrive, chronic diarrhea, and recurrent opportunistic infections, including cytomegalovirus, Candida, and Pneumocystis jirovicii. Disorders of T-lymphocyte function include severe combined immunodeficiency, DiGeorge syndrome, and X-linked hyperimmunoglobulin M. A complete blood cell count is the first test for assessing a defect of the cellular immune system, as some disorders are characterized by lymphopenia. Absence of lymphopenia does not rule out a cellular defect, as qualitative or functional defects can be present. Delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity and the lymphocyte proliferation assay are 2 means of assessing T-lymphocyte function. Defects of the humoral immune system present as recurrent sinopulmonary infections with encapsulated bacteria. Disorders of the humoral immune system include X-linked aggamaglobulinemia and common variable immunodeficiency. Additionally, some disorders are characterized by low to absent B cells, detectable by flow cytometry. You review a recent clinical case with them of a 15-month-old boy followed in the well child clinic since 3 months of age. His mother described bulky and greasy stools, gassiness, and abdominal distention. Review of the growth chart demonstrated decreasing weight from the 38th percentile at birth to the 10th percentile. Malabsorption of fat and disaccharides are most commonly involved, and clinically present with diarrhea, failure to thrive, gassiness/bloating, and fat-soluble vitamin deficiency. Fecal fat testing measures the amount of fat in the stool, either in a spot evaluation or with a 72-hour test. Screening for infectious etiologies of malabsorption is performed with stool culture, ova and parasite testing, and occult blood testing. Disaccharide malabsorption can be identified with a low stool pH and positive stool-reducing substances. Upper endoscopy and colonoscopy can be used to identify bowel inflammation that may result in malabsorption, and small bowel biopsies can quantify disaccharidase levels. This is particularly helpful in the evaluation for lactase and sucrase deficiency. Biopsies may also help diagnose inflammatory bowel disease and eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease. It would be unusual for a child to develop cow milk protein intolerance after 1 year of age. Disaccharidase deficiency presents with gassiness and diarrhea, but without pulmonary symptoms. Endocrine pancreatic insufficiency is associated with diabetes and does not present with gastrointestinal symptoms. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth presents with gassiness and diarrhea after antibiotic exposure, or during an acute illness with associated dysbiosis. Developmental changes and fructose absorption in children: effect on malabsorption testing and dietary management. He feels pain behind his knees about once per week, generally at night as he is falling asleep. His parents have been treating the pain with acetaminophen and massage, which generally alleviates the pain within 20 to 30 minutes. The parents deny any history of limp, joint swelling, fevers, or skin changes in their son. The boy occasionally reports leg pain when walking more than 4 blocks, but his activity level is age appropriate. Given this history, lack of constitutional symptoms, and normal physical examination findings, he does not require additional evaluation. A French physician first described the clinical syndrome of growing pains in the 1800s. Affected children, typically between the ages of 3 and 10 years, report cramping limb pain generally in the evening or at night. Pain is typically bilateral and self-limited, involving the knees, shins, or calf muscles, and awakens some children from sleep. Despite the term growing pains, the peak age of incidence does not correspond with a time of rapid growth, and the etiology of this syndrome remains unclear. Massage and over-the-counter analgesics are often helpful for accelerating pain relief. The term benign nocturnal limb pains of childhood is now used to describe this syndrome. When taking a history for a child with limb pain, the practitioner should ask about associated symptoms, gait changes, history of travel, and family history of autoimmune conditions. Children who exhibit activity-related pain, increasing pain intensity, joint swelling, limp, or constitutional symptoms (eg, fever, malaise, or a decrease in activity) should be evaluated for other conditions such as idiopathic arthritis or infection. Leukemia should be considered in a child with limb pain and constitutional symptoms because 25% of children with leukemia have extremity pain as a presenting symptom. When the history or physical examination findings are inconsistent with benign nocturnal limb pains of childhood, an initial evaluation should include laboratory and radiographic testing. For young children, radiographs should be obtained of the site of reported pain, as well as the joint above and below the site to evaluate for sources of referred pain. A complete blood cell count and C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate should be obtained to evaluate for infection and other inflammatory conditions. Although some children with growing pains tend to have pain on days when they are especially active, a 4 week rest period is unlikely to significantly alter nighttime pain episodes. Five-year outcome of children with "growing pains": correlations with pain threshold. Her parents report that she is starting to climb the stairs by herself and ask for your advice on how to avoid stair climbing injuries. Stairway accidents are a frequent cause of injury in young patients, especially as their mobility increases. The most common injuries sustained in stairway accidents are soft tissue injuries, closed head injuries, and lacerations. The most common anatomic locations of injuries are the head and neck, upper extremities, and lower extremities. The most frequent mechanism of injury is the child falling down the stairs (without mention of another action or object), followed by the child being carried down the stairs by an adult who loses his or her balance.
Cheap floxin 400 mg fast delivery
An integral part of regarding their expectations in the process relies on constant virus 100 buy floxin with mastercard, regular staff feedback to residents, and this terms of both behaviors and requires staff to maintain strong observational and communication skills. This is intended to create an environment where Supervisors work closely with subordinate staff to encourage active, residents and staff work constructive dialogue and conflict resolution when problems occur. All Springfield Academy residents attend classes begin the process of learning to begin the process of learning their thinking patterns and linking their their thinking patterns and thoughts to problems in their lives and the lives of others. Residents are linking their thoughts to evaluated twice daily on their behaviors and thinking patterns, and they problems in their lives and the review their evaluations daily to receive immediate feedback on their lives of others. This process involves a Youth Rating System, and staff ratings are evaluated twice daily on their behaviors and thinking reviewed by supervisors at multiple levels of the agency to ensure patterns, and they review their consistency across raters. The rating system is immediate feedback on their combined with a structured staff intervention process designed to assist behavior. This seven level system helps youth a Youth Rating System, and learn a continuum of responses to problematic behaviors. The seven levels of staff ratings are reviewed by supervisors at multiple levels intervention are as follows: of the agency to ensure consistency across raters. Level 5 Group Support (Staff and Peers) Level 6 Staff Intervention Level 7 Physical Restraint or Removal Administrators report that this process is successful, and frequently residents thank staff members for providing meaningful feedback. In addition, the Springfield administrative team has a relatively constant presence in the facility to observe the interaction with staff and youth. Information is exchanged during shift change meetings to inform staff and supervisors of the milieu climate, and supervisors look for opportunities to use this time for staff development since specific problems are usually discussed. The presence of appropriately selected and trained staff is fundamental to the success of any correctional organization. Administrators interviewed for this study consistently described the need for excellent staff who can relate well to inmates. Staff are the most positive agents of change in corrections, and can either encourage or sabotage institutional treatment and programming Entry requirements were (Briscoe & Kuhrt, 1992; Fewell, 1988); their attitudes and behaviors can revised to ensure that define the institutional environment. As a Many current agencies have difficulty today recognizing what was result of this extensive screening process, only about understood a generation ago: Progressive correctional operations consider 4% of those who apply to work correctional officers to have roles and functions beyond traditional custody in the San Francisco County (Johnson, 1987: 142). This role has been succinctly articulated by correctional Jail are actually hired. They learn how to care for the physical health of a person, how to promote mental/emotional well-being, and how to lift the spirit by promoting self esteem. In each of the facilities we studied, administrators discussed the recruitment, hiring and selection of correctional staff as critical ingredients in creating and maintaining safety. Table 4 provides a comparison of the employee hiring, training and staff development among the study sites, including Jefferson County. Table 4 shows remarkable congruence in the practices employed by each of the agencies in recruiting and hiring staff. Each agency was actively engaged in recruiting and selecting a cadre of employees who met and sustained the vision and mission of the organization. Once hired, administrators ensured that staff training protocols focused on developing and refining the skills considered critical to creating a safe and secure environment where the institutional culture prioritizes treating offenders with and promoting individual dignity. The San Francisco County Sheriff hires staff who are interested in public service rather than law enforcement. He made a commitment to staff diversity at every level of the organization three decades ago. Entry requirements were revised to ensure that minorities are not screened out based on requirement for high levels of education or extensive job experience. Jail deputies must have a high school diploma or equivalent, be at least 21 years old, have no felony convictions, and at least one year of work experience. An active campaign exists to recruit from neighborhoods that house diverse cultural communities. Job announcements are translated into several languages (including Chinese, Spanish, Tagalog) and distributed in culturally diverse neighborhoods. Positions are advertised in community newspapers, radio and television stations, community meetings to discuss recruitment are conducted in churches, and job fairs to explain the application and selection process. A credit history check is also important because the 30 department wants to screen out individuals whose level of debt may make them susceptible to corruption. As a result of this extensive screening process, only about 4% of those who apply to work in the San Francisco County Jail are actually hired. Each then receives three weeks training on jail operations prior to working in the jail. Once a deputy receives his or her jail work assignment, formal on-the-job training begins with a senior deputy who has completed a 40-hour course to become a training officer. Each of the county jails has a facility training coordinator who works with the training deputy to ensure that all the elements in the training curriculum are addressed along with topics specific to that facility. More information on the operations of the San Francisco County Jail can be found in Appendix D, document 3, including a logic model that links objectives, activities and tasks with outcomes. Brief description of hiring, training and staff development San Francisco Orange County Mecosta Shelby Patrick J. Jail employee, allowing positions were elevated in payment status and given equal treatment both in supervisors time to evaluate training and recognition. During this initial At the Mecosta County Jail the jail chief hired staff who expected to work period, administrators and long-term in corrections rather than those who wanted to use the jail supervisors can assess the assignment as a stepping stone to patrol positions. A six-step process includes a written skills test, an oral interview, a polygraph examination, a psychological examination, a medical background check and a physical examination, and a comprehensive background examination. Unlike Mecosta County, all deputy staff begin by working in the jail, even those who are ultimately interested in patrol positions, and between 5 and 19% move to patrol positions each year. Administrators reported that this process ensures that an adequate number of trained individuals are available to provide supervision in the jail should it become necessary to temporarily assign jail positions to patrol deputies. Woodfield Cottage Detention Center administrators, like many other juvenile care agencies, face the dilemma of losing experienced staff to supervisory positions at other criminal justice agencies offering higher paying positions. To manage this problem, Woodfield staff are a combination of contract and full-time employees. Nearly everyone begins as a contract employee, allowing supervisors time to evaluate an individual prior to hiring them as a full time, permanent employee. The approach was developed by asking staff to form working groups to identify competencies and personal characteristics that were necessary for excellent performance. This resulted in the development of a questionnaire that is posted on the website to inform candidates that agency officials stay focused on these throughout the hiring process. Springfield Academy administrators faced challenges familiar to many juvenile child care agencies: its positions are paid at a lower rate than many other local employers. The agency engages in a broad recruitment effort focused on providing information at job fairs and colleges. Wherever possible, Springfield staff take residents to the presentations so they can be part of the hiring process.
Order cheapest floxin
There can be significant heterogeneity within the same family with this condition antibiotic powder for wounds purchase floxin online now. Associated anomalies may include renal agenesis, midline facial defects, cryptorchidism, microphallus, sensorineural deafness, and visual abnormalities. Onset of puberty typically depends more on the bone age than the chronological age. A boy with a bone age of 10 would not be expected to be in puberty; thus his gonadotropin levels would be in the prepubertal range in all conditions listed. Once the bone age advances to a pubertal age, gonadotropin levels in boys with hypergonadotropic hypogonadism will become elevated. Because puberty corresponds more closely with bone age than with chronological age, a girl with a bone age of 13 years should be in puberty, and lack of puberty at this bone age would suggest hypogonadism. The correlation between bone age and pubertal onset is less clear in obese children because overnutrition often causes an advancement in bone age. Gonadarche (maturation of the hypothalamic-pituitary gonadal axis) and adrenarche (maturation of the adrenal gland) are two separate processes. Therefore, adrenarche leading to the development of pubic hair can occur without gonadarche. Constitutional delay in puberty is the most common cause of delayed puberty in boys. Children with panhypopituitarism causing delayed puberty usually come to attention because of other hormonal deficiencies. The several accepted techniques of assessing bone maturation include the Tanner-Whitehouse method and the method of Greulich and Pyle. Delayed puberty is defined as the absence of signs of puberty in a child at a chronological age greater than 2 standard deviations above the mean of pubertal development for a given population. This is also the age at which most boys will be starting high school where communal showering is common; thus their concerns regarding lack of puberty increase. In very early puberty, levels of gonadotropins and sex steroids are first detectable at night. Gonadotropin levels and sex steroid levels should be checked in a laboratory with very sensitive assays appropriate for children. Turner syndrome in girls presents with primary ovarian failure because of atresia of the ovaries in fetal life. Many girls with Turner syndrome first present in early adolescence because of short stature and delayed puberty. Craniopharyngioma and the subsequent treatment can lead to panhypopituitarism, and anorexia nervosa can lead to hypothalamic hypogonadism. Secondary hypogonadism is a result of disorders that decrease gonadotropin secretion. Girls with Turner syndrome usually present with short stature and delayed puberty because of primary ovarian failure. Occasionally, girls are diagnosed at birth because of puffy hands and feet, and a webbed neck because of lymphedema. Associated features include webbed neck, low posterior hairline, cubitus valgus, spooned nails, renal anomalies, and left-sided cardiac defects including coarctation of the aorta. Right-sided cardiac defects are found in Noonan syndrome, which has similar phenotypic findings as Turner syndrome with a normal karyotype. Girls with Noonan syndrome have normal ovarian function, but boys typically have cryptorchidism and abnormal Leydig cell function. Klinefelter syndrome is the most frequent form of hypogonadism in males with an incidence of 1 in 500-1000 males. Patients have variable Leydig cell function and thus can have testosterone levels from low to normal. Patients often have the onset of puberty at a normal age, but secondary sexual changes do not progress to the adult stage. The typical phenotype includes tall stature with long arms and legs, small firm testes, small phallus, poor muscular development, language difficulties, and poor social adaptation. Bone age has been shown to be a better predictor of pubertal milestones than chronological age. Conditions that cause an advancement of bone maturation (such as undertreated congenital adrenal hyperplasia) can lead to precocious puberty. The goals of therapy for delayed puberty include inducing the development of age-appropriate secondary sex characteristics, a growth spurt, and psychosocial benefits. Psychosocial concerns tend to be more pronounced in boys than girls because of societal pressures and can lead to low self-esteem and poor body image. If the therapy advances the bone maturation too quickly, children can have premature epiphyseal fusion and end up short as an adult. On review of systems, the child has been complaining of fatigue but is doing well at school. There is a history of some type of thyroid problem in the maternal grandmother and paternal aunt. On physical examination you notice that the child has a goiter with no palpable nodules (see Figure 40-1). What other information would be most helpful to narrow your differential diagnosis The thyroid gland is tender to palpation, and the child reports that he/she has had an upper respiratory tract infection the last few days. Most circulating triiodothyronine is derived from (A) peripheral conversion from thyroxine (B) thyroid gland (C) pituitary gland (D) parathyroid glands (E) hypothalamus 12. Which of the following is true regarding newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism Which of the following is the leading cause of congenital hypothyroidism in iodine-sufficient areas All of the following are signs or symptoms of hyperthyroidism except (A) delayed deep tendon reflexes (B) nervousness (C) fatigue (D) palpitations (E) A and C 18. Which of the following statements is true regarding the treatment of Graves disease Children with hypothyroidism often manifest slowing of their growth, whereas children with hyperthyroidism eventually have accelerated growth if the disorder is not detected and treated appropriately. Free thyroxin index is a calculation that reflects bioavailable thyroid hormone because it takes into account the amount of binding protein. Several antibodies against thyroid antigens have been demonstrated in chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, and these levels should be determined in a child with a goiter. Subacute thyroiditis is a self-limited inflammation of the thyroid gland that usually follows an upper respiratory tract infection. There is often a pattern of hyperthyroidism secondary to inappropriate release of thyroid hormone. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism can persist for 1-4 weeks, after which transient hypothyroidism typically develops with recovery of the gland. Children with euthyroid sick syndrome do not present with a goiter, and the presentation usually does not follow a mild illness. The most common abnormality of thyroid function in children is hypothyroidism, usually caused by autoimmune (Hashimoto) thyroiditis. Hashimoto thyroiditis is characterized by circulating thyroid antibodies and varying degrees of thyroid dysfunction. It is more prevalent in girls, and many patients have a family history of autoimmune thyroid disease. Patients can present with a picture of hyperthyroidism (hashitoxicosis), euthyroidism, or hypothyroidism. The most common manifestation of hypothyroidism in children is subnormal growth velocity leading to short stature. Other manifestations of hypothyroidism specific to children include delayed bone maturation and sexual disorders, including both delayed and precocious puberty. Other symptoms of hypothyroidism include bradycardia, cold intolerance, fatigue, constipation, muscle aches, and dry skin.
Cheap floxin online amex
An understanding of these influences is and failure attributed to low ability antibiotics resistance 400 mg floxin otc, while feedback to necessary to maximize education and choices for all boys indicated failure was because of lack of effort or children. These messages of confidence/no con fidence are received and internalized by students. Male, economically has found smaller and fewer gender differences deprived, and minority students are more likely to fail and greater differences in ability within each gender and consequently be retained or diagnosed with learn than between genders. Students in special education, Gender role refers to social expectations regarding minority students, and males are more likely to leave how males and females should behave. Boys are school as white males and twice as likely as black encouraged to explore and take things apart, tasks that girls. Males may drop out to go to work; minority are prerequisites for science and spatial knowledge. While more Career development and vocational training opportu girls are now taking higher-level math courses, nities in schools are limited and may retain vestiges of females still obtain less than 25% of college degrees traditional gender stereotypes. Girls Females tend to do better in school, but drop out for exhibit desired school behavior. The dropout rate for minority females is two but without encouragement from teachers and parents to three times as high as for white females. Minority many talented young women are reticent to compete girls are likely to drop out of school because of limited in fields where they are a minority. Gender Gender-fair (or teaching that has no gender bias) and gaps: Where our schools still fail our children. The psychology of sex dif the school experience is further complicated and ferences. Males have higher rates of autism, psy Addressing gender equity in special education. Albany: choses, and schizophrenia, as well as attention deficit State University of New York Press. Females are more likely to be diagnosed with depression; however, teenage males are more likely to commit suicide. Russo and Wehmeyer report in their recent book, Generalization is the transfer of training effects Double Jeopardy: Addressing Gender Equity in from one situation to another. There are three types Special Education, that the ratio of males to females of student performance that may be considered evi in special education is 2:1. The first, stimulus general assessed, and eventually placed are those who are ization, occurs when skills taught in one situation noticed. In this example, the student uses a out hyperactivity and internalizing disorders such as new skill (saying please) with different individuals anxiety and depression, which are less likely to be (the family) in a new setting (the home) to make a detected. For example, a program and Herzog (1985) to describe how peers reinforce designed to reduce physical aggression in the school gender-associated behavior. However, parents begin may also result in a reduction in other problematic gender education at birth by their differential treat behaviors such as truancy and verbal assaults. Schools and society promote Finally, maintenance, a third form of generaliza innate differences by stereotyped curriculum and tion, occurs when trained responses continue to be expectations. Eliminating gender bias will maximize demonstrated across time after the completion of the potential of all boys and girls. Wilson continue to use the trained skills with peers long after the formal training is terminated. See also Aggression in Schools; Attention Deficit the goal of education is to teach students skills that Hyperactivity Disorder; Bullying and Victimization; Depression; Discipline; Dropouts; Eating Disorders; will benefit them in other educational environments, Gangs; Harassment; Puberty; Race, Ethnicity, Class, and in the community, and at home. One strategy for enhancing generalization is to this approach requires measurement of student make training conditions as similar as possible to nat behavior under a variety of relevant conditions and ural conditions. Results of this research will ultimately the value and exchange of money would benefit from assist in the development of procedures that increase classroom activities that simulate those under which the generalization of student behavior. Thompson to the grocery store) with supervised opportunities for money to be exchanged. A similar strategy involves See also Learning; Research; Single Case Experimental the inclusion of multiple examples in training. Applied behavior the likelihood that student performance will gene analysis for teachers. Generalization for students with that performance will be limited to the one or two severe handicaps. An implicit technology desired behavior will increase the probability that of generalization. To enhance ence of worry and anxiety far out of proportion to the generalization, training programs should be designed feared event. For example, concentrating, irritability, and muscle tension in addi a special education student with severely limited tion to the ever-present worry and anxiety. It should be noted that some forms of generali Children may feel an inability to control their worry zation are undesirable, such as the performance of ing, which at times interferes with their ability to pay a particular behavior only under certain conditions. Exposure to both examples and exceptions health, or the safety and well-being of others. They may not undertake tasks Given that transfer of training effects is a critical in which there is a risk of imperfect performance. The gains made by these about perfectionism, worry) that are associated with children were still present after one year. As part of this process, the school psychologist trained to become aware of self-statements they make may use behavior observations and personality and that exacerbate their feelings of anxiety and worry. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for anx team (including the parent) agree that the child: ious children: Therapist manual. Department of Education defines gifted program, which is frequently run in group settings, is students as those who demonstrate extraordinary designed to increase awareness of the causes of the performance or have the potential to demonstrate anxious reaction. Each child and parent explores the outstanding performance in the areas of general intel physiological symptoms and thoughts that trigger or lectual ability, specific academic areas, the fine and result from the anxious response. The defin playing and modeling, children are taught thought ition also stipulates that these are students who require stopping techniques as well as ways to inject alterna services beyond what is offered in the regular school tive coping cognitions. This definition is the most taught problem-solving techniques and are rewarded widely adopted definition at the state and local school for successful demonstration of coping thoughts and division levels. Finally, strategies for maintenance and procedures and program implementation limit the generalization of what they have learned are planned scope of the definition to exceptional intellectual abil and implemented. After treatment has been com based on the three characteristics of above-average pleted, the school psychologist would work with the intelligence, creativity, and task commitment in any mental health staff to plan for a smooth transition back specific area of performance (mathematics, verbal into school. Students who exhibit multiple sources of information, and include both tasking commitment are provided instruction that school and nonschool performance.

