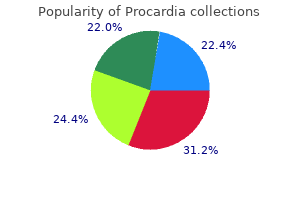
Procardia
Order procardia 30 mg on line
If a foster child receiving unearned income is placed in 5783 another region cardiovascular system in early sepsis generic 30 mg procardia, but jurisdiction remains with the original region, no change is made in 5784 the representative payee process. However, if jurisdiction is transferred, the 5785 representative payee responsibilities are also transferred. The entire 5792 representative payee account record will also be sent to the new region along with the 5793 family file. If the child is leaving Child and Family Services care, any funds 5799 remaining in the account when the case is closed will be returned to the applicable 5800 funding agency. Child and Family Services will remain the 5807 representative payee as long as the child remains in Child and Family Services custody. The parent or guardian must apply 5810 directly to the Social Security Administration to become representative payee after Child 5811 and Family Services custody is terminated. After any outstanding cost of care payments have been made, the remaining 5816 funds should be given to the legal representative of the estate or otherwise handled 5817 according to state law. Return any check received 5823 for the month of death or later to Social Security. The caseworker is responsible to notify 5833 the regional account custodian in advance when custody termination is being requested 5834 from the court for a foster child. A copy of the court order terminating custody must be 5835 provided to the account custodian. The remaining funds may not be sent to a parent or guardian to whom 5846 custody has been granted by the courts. Child and 5850 Family Services will require the child to show picture verification and sign a receipt 5851 when claiming the check from the agency. These children have a greater 5867 likelihood of emancipating from the system and not achieving legal permanency or permanent 5868 connections. Emancipation is the least preferred outcome but in the 5872 event that it becomes inevitable, youth aging out of care should have an array of informal 5873 permanent connections, healthy relationships, and access to formal resources. The caseworker is 5898 responsible to be prepared with the oral case presentation and answer questions 5899 from the group. Master practitioner: the master practitioner is an expert in permanency work 5903 and/or an expert in navigating unique challenges that may exist in specific types 5904 of cases. The facilitator will not lead the discussion in a 5907 particular direction but will take an active role in establishing an environment 5908 that stimulates and promotes the free exchange of ideas. The facilitator is 5909 responsible to make sure that all parties are focused on looking for solutions 5910 rather than getting caught up in the past. External permanency consultant: A person who is outside of the administrative 5915 chain of command for the case selected. It is preferred that the consultant be 5916 outside of the region where the case management is conducted. The consultant 5917 is primarily responsible to provide suggestions during brainstorming and action 5918 planning. Others: On rare occasions, the situation may require a specialist from outside of 5922 the agency to provide specific knowledge, skills, and expertise, which will assist 5923 the work of permanency. In these situations, the participant should have 5924 completed the Values training. Some rules that should be considered include no electronics 5930 and maintain permanency focus. Case Presentation (20 Minutes): Caseworker presents the case using the Oral 5932 Case Presentation outline. At 5933 the conclusion, the supervisor may also be given an opportunity to add 5934 information to the presentation. Debrief (5 Minutes): Check-in with the caseworker and supervisor regarding the 5945 implementation of the Action Plan, lessons learned, etc. Accessing Casey Grant dollars for barrier busting: Casey Family Programs has provided 5948 money to assist caseworkers in overcoming barriers to achieving permanency. All requests must include a rationale for how this will promote legal permanency 5953 or permanent connections for the youth. These services will be designed to maintain and 5961 enhance parental functioning, care, and familial connections. The out-of-home caseworker will also 5971 explain to the parents the role of the agency, the caseworker, the out-of-home caregiver, the 5972 team, and the court process. The caseworker will contact the parents within five working days of receiving the case. The importance of parental involvement and contact with the child and Child and Family 5987 Services. Expectations and time lines associated with participation or non-participation in service. Parental rights and responsibilities while the child is in care, including financial support. This collection of information should 6007 form a big picture understanding of the child and family and how to provide effective services 6008 for them. A functional assessment also identifies critical underlying issues that must be 6009 resolved for the child to live safely with his/her family independent of agency supervision or to 6010 obtain an independent and enduring home. A permanency plan assembles supports, services, and 6014 interventions into a holistic and coherent service process that provides a mix of elements 6015 uniquely matched to the child and family situation and preferences. Transitions are internal processes that a family experiences and must manage in order 6020 to be successful as they move through the process of change. Examples of typical transitions 6021 include: removal, change in placement, change in school, change in caseworker, change in 6022 therapist, reunification, case closure, graduation, independent living, agency transfers, loss of 6023 family, and adoption. It includes considering how the current picture 6035 needs to be changed or altered to achieve the future circumstances that are needed or desired. This will include efforts to 6044 engage the parents in appropriate parenting tasks such as attending school meetings, etc. Child 6045 and Family Services staff will recognize child and family contact as a right for both the parent 6046 and the child. However, engagement of the parents is 6061 to occur whenever possible and may still occur in some cases where the parents 6062 are in declining health or when rights have been terminated. Child support obligation when custody of a minor is vested in an 6109 individual or institution. Utah law mandates that all parents are responsible for the support of their minor 6114 children. The parent or guardian is to meet with the Office of Recovery Services within 10 days of 6117 the shelter hearing to begin the process of providing financial support while their child is 6118 in out-of-home care. Office procedures for income withholding for orders issued or 6136 modified on or after October 13, 1990. Individuals approved and selected to 6146 provide out-of-home care will have the experience, personal characteristics, and temperament 6147 necessary to work with children and their biological families. For all types of placement, to provide for the 6156 health, well-being, and safety of children in their home, out-of-home caregivers will: 6157 1. Integrate children into their household as equal members by providing a 6158 pleasant, safe, and nurturing family atmosphere.

Purchase cheap procardia line
This debate continues in all aspects of human development carotid arteries 100 blocked order procardia once a day, and most scholars agree that there is a constant interplay between the two forces. It is difficult to isolate the root of any single behavior as a result solely of nature or nurture. The answer to that question often depends on which developmental theorist you ask and what topic is being studied. Stage theories or discontinuous development assume that Source developmental change often occurs in distinct stages that are qualitatively different from each other, and in a set, universal sequence. At each stage of development, children and adults have different qualities and characteristics. Others, such as the behaviorists, Vygotsky, and information processing theorists, assume development is a more slow and gradual process known as continuous development. For instance, they would see the adult as not possessing new skills, but more advanced skills that were already present in some form in the child. Brain development and environmental experiences contribute to the acquisition of more developed skills. Active versus Passive: How much do you play a role in your own developmental path Are you at the whim of your genetic inheritance or the environment that surrounds you Some theorists see humans as playing a much more active role in their own development. Piaget, for instance believed that children actively explore their world and construct new ways of thinking to explain the things they experience. In contrast, many behaviorists view humans as being more passive in the developmental process. Some theorists argue that the personality traits of adults are rooted in the behavioral and emotional tendencies of the infant and young child. Others disagree, and believe that these initial tendencies are modified by social and cultural forces over time. Historical Theories on Development th Preformationist View: Well into the 18 century, children Figure 1. Preformationism, or the belief that a tiny, fully formed human is implanted in the sperm or egg at conception and then grows in size until birth, was the predominant early theory. Children were believed to possess all their sensory capabilities, emotions, and mental aptitude at birth, and as they developed these abilities unfolded on a predetermined schedule (Thomas, 1979). John Locke (1632-1704): Locke, a British philosopher, refuted the idea of innate knowledge and instead proposed that children are largely shaped by their social environments, especially their Source: A tiny person inside a sperm. He believed that through education a child learns socialization, or what is needed to be an appropriate member of society. Locke indicated that the environment exerts its effects through associations between thoughts and feelings, behavioral repetition, imitation, and rewards and punishments (Crain, 2005). Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778): Like Locke, Rousseau also believed that children were not just little adults. However, he did not believe they were blank slates, but instead developed according to a natural plan which unfolded in different stages (Crain, 2005). He did not believe in teaching them the correct way to think, but believed children should be allowed to think by themselves according to their own ways and an inner, biological timetable. This focus on biological maturation resulted in Rousseau being considered the father of developmental psychology. Arnold Gesell (1880-1961): Gesell spent 50 years at the Yale Clinic of Child Development, and with his colleagues he studied the neuromotor development of children. Further, he believed that development unfolded in fixed sequences, and he opposed efforts to teach children ahead of schedule as he believed they will engage in behaviors when their nervous systems had sufficiently matured. Freud emphasized the importance of early childhood experiences in shaping our personality and behavior. In our natural state, we are biological beings and are driven primarily by instincts. During childhood, however, we begin to become social beings as we learn how to manage our instincts and transform them into socially acceptable behaviors. His beliefs formed the psychodynamic perspective and his theories of psychosexual development and psychopathology Sigmund Freud from Wikimedia dominated the field of psychiatry until the growth of behaviorism in the 1950s. Freud suggested that much of what determines our actions were unknown to us, and as scientists we cannot measure these unconscious concepts. Erikson (1950) proposed a model of lifespan development that provides a useful guideline for thinking about the changes we experience throughout life. Erikson proposed that each period of life has a unique challenge or crisis that the person who reaches it must face, referred to as psychosocial crises. According to Erikson, successful development Erik Erikson involves dealing with and resolving the goals and demands of each of these psychosocial crises in a positive way. These crises are usually called stages, although that is not the term Erikson used. If a person does not resolve a stage successfully, it may hinder their ability to deal with later stages. His theory also focused on the social expectations that are found in certain cultures, but not in all. For instance, the idea that adolescence is a time of searching for identity might translate well in the middle class culture of the United States, but not as well in cultures where the transition into adulthood coincides with puberty through rites of passage and where adult roles offer fewer choices. Learning Theory: Also known as Behaviorism, is based on the premise that it is not possible to objectively study the mind, and therefore psychologists should limit their attention to the study of behavior itself. Skinner used the ideas of stimulus and response, along with the application of rewards or reinforcements, to train pigeons and other animals. In addition, he used the general principles of behaviorism to develop theories about how best to teach children and how to create societies that were peaceful and productive (Skinner, 1957, 1968, 1972). The behaviorists made substantial contributions to psychology by identifying the principles of learning. Although the behaviorists were incorrect in their beliefs that it was not possible to measure thoughts and feelings, their ideas provided new insights that helped further our understanding regarding the nature-nurture debate as well as the question of free will. The ideas of behaviorism are fundamental to psychology and have been developed to help us better understand the role of prior experiences in a variety of areas of psychology. His theory calls our attention to the ways in which many of our actions are not learned through conditioning, as suggested by Skinner.
Syndromes
- Confusion
- Weakness of muscles in one or both of your legs
- What other symptoms do you have?
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Bleeding from wound
- Avoid using alcohol and drugs during pregnancy.
- Do not try to neutralize the poison with lemon juice or vinegar, or any other substance, unless you are told to do so by the Poison Control Center or a doctor.
- Thyroid disease
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Purchase 30 mg procardia with mastercard
Even a child who exhibits no current symptoms of the abusive experience benefits from help in answering these questions capillaries large cross sectional area purchase discount procardia online. Facilitating resolution of the abuse includes clarifying insights, correcting distortions, placing responsibility for the abuse more objectively, acknowledging attempts to manage the abuse experience(s), and supporting positive and productive behavior. In order to accomplish this objective, the therapist needs to help the child access the memories of abuse or neglect; identify the sensations, thoughts, feelings, and beliefs that were generated by the abuse or neglect; and develop productive responses and behavior that enhances a positive self-image. Accessing the Abuse Memories Discussing the details of the abuse helps the child think about his/her experience. As the child articulates his/her unexpressed feelings and hidden thoughts, the child shares his/her personal experience of the abuse. Sensations Physical and/or sexual abuse assaults the body with stimuli and creates sensations that can be fearful, painful, or overwhelming. These sensory memories are stored and may become stimuli for flashbacks, nightmares, phobic behavior, or panic attacks. Various factors such as lighting, location, temperature, presence of other people during the abuse, as well as physical sensations need to be noted. Pleasurable sensations (sexual abuse) can be overwhelming for the child and can become frightening, especially when the child understands that the occurring behavior is wrong. These stimuli need to 55 identified, assessed, and explained to the child so that he/she understands that his/her reactions are often related to actual experience. Thoughts and Feelings the ability to think about the harmful experience and recognize feelings and behavior generated by those thoughts allows children to make distinctions, decisions, and choices. Thinking about their experience means gathering information that explains why the abuse occurred. Thinking about the experience, discriminating between feeling safe or unsafe and recognizing abusive behavior enables the child to identify problematic situations and make choices that can help him/her remain safe from harm. As the child recognizes that he/she has the ability to think and choose, he/she begins to feel better about him/herself and feel more powerful and in control. Discharging feelings generated by the abuse is an important component of the treatment process. Identifying, acknowledging, and sharing feelings about the experience can help the child recognize the relationship between feelings and self-esteem, self-worth, and behavior. A child benefits from therapeutic experiences that allow him/her to act out his/her feelings, exaggerating his/her responses until those responses are intense enough that the child feels they represent how he/she felt at the time of the abuse. Techniques, such as hitting a pillow or punching bag, using batakas or encounter bats, or writing down all their feelings and throwing them in the wastebasket can help the child discharge some of his/her pent up emotions and begin to let go of those emotions. It is also important to teach the child socially acceptable means of expressing him/herself. A child needs to know that hitting something, such as a pillow, may be an acceptable release for his/her feelings. Haaken and Schlaps note that the patient is not simply a vessel that has been filled up 152 with bad experiences, and consequently, can be emptied out and refilled with remedial messages. These researchers emphasize that the manner in which the therapist listens and reacts to the child in the process is more central to sustained therapeutic change than only abreacting traumatic experiences and reassurances. If the perpetrator used threats or violence, the decisions a child made at the time of the abuse may have been critical to his/her physical or emotional survival. A child may benefit from exploring the choices he/she made during the abuse incidents and may need to determine that he/she made the best choices possible given the nature of the situation. A child may also need to acknowledge that the behavior necessary during the abusive incidents or before disclosure may 153 no longer be useful to him/her. Beliefs When a child is overwhelmed by sensory stimuli, he/she attempts to make sense of or find order and meaning for the experience. For a young child, or a child whose understanding is limited by his/her cognitive and emotional experience, these explanations are often primitive or inaccurate. Attribution theory suggests that, when negative events occur, blaming oneself for the event (internalizing responsibility) results in depressed feelings whereas blaming others (externalizing responsibility) results in 154 anger. When a child believes that the cause of the abuse was something to do with him/her, rather than something to do with the perpetrator, the child blames him/herself for the abuse. A child who internalizes the cause of the abuse and believes the abuse was his/her fault has a difficult time feeling good about him/herself. However, this child may feel angry and experience a sense of emptiness and wonder about his/her worth and value. A child who feels that the abuse has changed his/her value may also think the abuse has changed his/her prospects and opportunities for the future. A child who thinks that the abuse has marred him/her or made him/her different from other children feels differently about him/herself and his/her body. A change in beliefs about the self can generate changes in behavior, which in cyclical fashion, reinforce new more positive, beliefs about oneself and others. These more positive and productive beliefs or expectations about the self, other, and the world are a self-confirming prophecy. What one expects and believes to be true is often what one recognizes and also determines how one responds. As a child begins to evaluate his/her beliefs about him/herself and begins to think of his/her reactions to the abuse or neglect in more sympathetic and favorable terms, the child often feels more hopeful and is more willing to try to make changes in his/her behavior. This, in turn, confirms a more positive sense of self and elicits more positive responses from other people. At this point, the child has experienced most of the acute pain and grief generated by the abuse. A child can be encouraged to think about what he/she wants and make decisions about how he/she wants to accomplish that goal. A child can be encouraged to think about how he/she wants to behave and evaluate the outcome of his/her behavior and, if necessary, make changes. During the consolidation/termination phase, the child needs to practice that skill in other areas of his/her life. A child needs to identify those adults and peers who can be helpful and responsive to his/her needs. They need to know that this is perfectly normal; what matters is how they resolve their problems. A child needs to know how to define the problem, generate options, attempt solutions, and continue until the problem is solved. The child must be able to seek out rewarding exchanges and avoid situations that he/she knows are dangerous or repetitive of abusive interactions. The child needs to feel worthy of positive interactions, believe that he/she is desirable, and that he/she deserves rewarding interactions with adults and peers. It is important to encourage the child to participate in social and community activities, develop hobbies and interests that help him/her connect with other children, and join teams and clubs that are of interest to them. The child needs to practice developing relationships with viable adults who will carry on the nurturing, interest, and attention that has been provided in therapy. In this way, the child learns to distinguish between helpful and hurtful behaviors, and he/she develops a support system and role models for relationships. In this final phase, the child transfers the knowledge and skills he/she has acquired in therapy to other areas of his/her life.
Purchase genuine procardia line
They found53 namic variables it is impossible to provide fixed cut-off that the sensitivity and specificity of symptoms sugges values on a clear scientific basis cardiovascular biotherapeutics news 30 mg procardia for sale, so as to define any tive of either of 3 final urodynamic findings (Urodyna specific pathologic feature. If contraction is observed without leakage, it may be only suggestive of detrusor overactivity incontinence. The current terminology does not distinguish overactivity accompanied by the sensation of urgency from sensation-free overactivity. More recent value of overactive bladder syndrome (frequency, studies on this subject have given similar results [33,33 urgency and/or urge incontinence) for detrusor overac 54 5954-59]. It is felt, however, that Using voiding frequency and voided volume retrieved stress incontinence as the dominant symptom with from frequency-volume charts, one study gave a nomo auxiliary evidence is specific to and predictive of uro gram for the probability of detrusor overactivity [60]. The62 provide objective pathophysiological explanations symptom score for leakage associated with physical of symptoms and/or dysfunction activity was higher for stress incontinence but other symptom scores addressing nocturia, frequency, urgen Urodynamic investigations should be conducted cy, urge incontinence or incomplete voiding did not dif safely in a scientific and respectful manner. Accurate des nence as the dominant symptom has a positive predicti cription of study conditions and methods is essential. In the context of this chapter, an impor Development of formal qualifications for investiga tant aim of cystometry is to reproduce the symptom of tors through certification of courses in the practice of incontinence. The bladder can be catheterized supra pubically or it can be filled solely via (forced) renal Determination of physiological, technical and inter excretion [65]. Bladder filling may be carried out with65 pretational variability for urodynamic study results. If catheters are tions underlying the types of incontinence and the introduced using an anesthetic agent, the effect must be corresponding urodynamic observations, and further taken into account in the interpretation. It is important refinement of the recommended terminology to to keep in mind that any variations in technique may reflect this. Gas (carbon dioxide) is usually infused overactivity or urge or stress incontinence, include cou at a high rate (> 100 ml/min), allowing rapid and inex ghing (Figure 3), change of position from supine or sit pensive performance of a study. However, it is unphy ting to standing, filling in the standing position, running siologic and compressible, and easily provokes detrusor water, handwashing, and waiting with a full bladder overactivity (see below) [66]. In women lead to erroneous diagnosis of reduced bladder com with incontinence, filling cystometry in the supine posi pliance. It is not suitable for studying voiding, and lea tion without provocation demonstrates Odetrusor insta kage is very difficult to detect due to invisibility of the bilityO in only 38% of bladders shown ultimately to be gas. The physical properties Handwashing is another potent provocation of Odetru of the liquid, its acidity, the type of contrast medium sor instabilityO [82]. In women with symptoms of urge82 and the concentration of ions such as K+ and Ca++ may incontinence, sitting on a commode with a full bladder affect detrusor overactivity [68-70]. The temperature of68 70 for 1 minute was the most provocative maneuver for the liquid is usually either room temperature or body Odetrusor instabilityO, being about 27 times more pro temperature. Traditionally, the filling rate is referred to vocative than remaining supine [83]; the second most83 as OfastO (> 100 ml/min), OmediumO or OslowO (< 10 provocative maneuver was handwashing for 1 minute. Natural bladder filling is on average 1-2 ml However, these two results were based on carbon dioxi per minute, although diuresis at up to 15 ml/min is pos de cystometry, a non-recommended method. Therefore, even OslowO urodyna dren, OslowO bladder filling while distracting their mic filling is already non-physiologic filling rates. For attention should help to evoke Odetrusor instabilityO children a rate above 10% of predicted or known blad [84]. Since over-provocation may reveal overactive84 der capacity per minute might be considered a OfastO detrusor function of no clinical significance, as obser filling rate. Stepwise cystometry, Bladder sensation during cystometry is judged on the with OfastO intermittent volume increments, has been basis of the volume in the bladder at patientOs Ofirst sen used in research settings to determine the viscoelastic sation of bladder fillingO, Ofirst desire to voidO and properties of the detrusor [71-73]. Urgency is a compelling desire filling is used, the volume of liquid in the bladder may to void. A strong desire to void or urgency N depen be considerably larger than the measured volume. Methods of questioning the patient regarding these sensation para Some authors advise that OfastO filling rates should be meters are only vaguely defined. Their reproducibility used if no detrusor contractions can be elicited in the is not well documented. This74 repeated bladder filling increased sensation intensity, may conflict with the aim to reproduce the symptoms which was more consistently related to intravesical experienced in daily life (see over-provocation, below). Provi-85 Ice water testing can be used to demonstrate the exis ding the patient with a push-button system to record tence of a temperature-sensitive reflex detrusor contrac sensations appears a promising way of standardizing tion mediated by afferent C-fibers, the reflex is inter the testing of sensation and increasing reproducibility preted as evidence for a neurogenic abnormality [75-75 [86]. Instructing patients not to voluntarily inhibit the79 urge to void, but merely to communicate sensations, When no equipment is available or referral is not fea increases the efficacy for identifying detrusor contrac sible, Osimple cystometryO (Figure 4) is an option [87,87 tions. For the detection of detrusor overactivity, taking irritative symptoms, a randomized double blind proto multichannel cystometry as the standard, simple cysto col asking patients to either inhibit or not inhibit mictu metry is reported to have specificity and sensitivity of rition during cystometry showed a statistically signifi over 80% in elderly patients [89-91]. In both geriatric89 91 cant increase in the presence of involuntary contrac and female populations, the rate of detection of detru tions when patients were instructed not to inhibit mic sor overactivity was not substantially different in turition [80]. Cys tometric capacity is determined differently in different Screening of urine for bacteriuria at the time of the test types of dysfunction. In the normal case it is the volu is important to rule out unrecognized infection. Anti me at which the patient states that he/she can no longer biotics administered at or just after the study, are at the delay micturition because of strong desire to void or discretion of the investigator. In urge incontinence it is the volume at which the main risks of cystometry are those associated with involuntary voiding occurs. Dysuria (painful voiding) cystometric capacity is the volume at which the inves occurs in some patients after urodynamic testing, but tigator decides to terminate filling. The used for catheterization, and for handling of transducers event that determines cessation of filling should be and connecting tubes, varies in different centers from reported. It is not known whether these variations per detrusor pressure increment (ml/cm H2O). In any case, that all volumes should refer to the volume actually pre appropriate aseptic techniques should be used. Detrusor overactivity the amplitude and the duration of the contraction and is defined as an involuntary detrusor contraction during the intravesical volume at which the contraction occurs the filling phase. Sub-classification that no method of monitoring attempted suppression or 330 inhibition has been standardized. If flow or leakage Bladder compliance is influenced by infusion rates, occurs, the pressure attained does not fully represent position of the patient, the volume of fluid in the blad the strength of the contraction or its clinical significan der and the part of cystometrogram used for complian ce. There is insufficient data to precisely define cut-off values between normal or abnormal com Observation of detrusor overactivity by itself is sugges pliance, but values in the range 12. Detrusor overactivity needs to taking into account the multiple phases of bladder be interpreted in the light of symptoms and signs. In children, the101 Observation of involuntary detrusor contraction that compliance determined by urodynamic investigation is an important outcome parameter [102-104]. If abnor-102 104 leads to leakage (detrusor overactivity incontinence) is mally low compliance is observed, cystometry at a more conclusive because it is clearly abnormal. Despite the differences of opinion mentioned above about the interpretation of the cystometrogram, the Traditionally, detrusor overactivity has been subdivided OarchetypalO cystometric patterns of a normal detrusor, into Odetrusor hyperreflexiaO (overactivity with a rela detrusor overactivity, and low compliance are straight vant neurological condition) and Odetrusor instabilityO forward and simple to understand. These terms65 a cystometrogram according to these landmarks [105],105 have been replaced by nerogenic detrusor overactivity even though only approximate normal values are and idiopathic detrusor overactivity, respectively. Borderline (cut-off) values of volume or pressure for the various sensation are at present undetermined. Similarly, exact reference values for normal96 urodynamic capacity are not available, because they depend on the technique of the investigator. The actual capacity is the total volume of fluid a patient will hold before voiding and is somewhat dependent on the rate of infusion, but changes also with repeated filling [41]. As another97 approximate guide, 60 ml + 60 ml x age (in years) for Figures 4: Schematic diagram of simple cystometry. The children less than 2 years old and 180 ml+15 x age (in height above the symphysis of the fluid meniscus in a syrin years) for children over 2 years old have been recently ge indicates intravesical pressure. However, cost-effective-106 To demonstrate incontinence, provocative maneu ness, defined in terms of treatment outcome, was not vers designed to elicit leakage should be performed considered in this study. A107 recent paper failed to show any difference in outcome in a If catheter-mounted transducers are used, the initial value of p may differ from zero by up to a few cm group receiving full urodynamics as opposed to simpler det H O. Such investigations have usually inclu-108 2 ded women both with and without symptoms of urgen pves and pabd should respond equally to coughs; cy and urge incontinence. In order to maintain continence the urethral112 113 (cure rate 39%) [109] or those with high-amplitude109 lumen should seal completely; this hermetic effect is 110 dependent upon the softness and compressibility of the overactivity (cure rate 28%) or low compliance [110]. Together, these properties determi-114 these observations suggest an important place for ne the intraluminal urethral pressure.
30mg procardia with amex
Both the provider and as a basis for termination of treatment services or as the basis patient should be aware that drug testing is intended to help for arrest blood vessels in brain procardia 30mg cheap, incarceration, or as a prima faciae basis for reflexive both the woman and her family and does not serve a punitive revocation of probation or parole, particularly in this vulner purpose (see Clinical Use of Drug Testing, p. Therefore, urine is an Continuing Care appropriate matrix for drug testing of pregnant women. Providers a drug-testing component is appropriate for most patients in should inform patients that there is no known safe level of stable recovery, although this rarely occurs in practice. If the provider suspects Alcohol with addiction treatment, there is evidence that any approach Use Disorder or the patient displays known risk factors, a to drug testing people in recovery should be individualized laboratory test for alcohol use is warranted. Including them in the test discussion of desired behavior change using a Motivational panel can provide important information that impacts clinical Interviewing approach, and referral to additional services as decision making. Testing is random, meaning that typically every day of the work week the physician participants call a phone number to see if that day they need to submit a sample for testing. Information should be recorded about the relapse (ie, relapse severity, substance type, content/setting, temporal relationship to patient care, whether impairment was suspected, etc) All positive screening results must be confirmed prior to reporting. This model has been highly effective among physicians and Summary of Recommendations other healthcare professionals [70]. A positive definitive test result triggers an immedi When to Test Adolescents ate re-evaluation of the patient to consider the benefits of a Use drug testing to assist in early identification of sub different treatment approach or a more intensive level of stance use in high-risk populations of adolescents including care. This model, including regular drug testing, may have but not limited to those with known past substance use and applications for other populations who would benefit from those in treatment for mental health disorders. For a pregnant patient with a history of addiction, providers Adolescents and Home Testing Kits should be aware that the postpartum period is a time of Because of a variety of limitations with home drug testing increased vulnerability. Therefore, assessment for relapse, process and interpretation, providers should not encourage which may include drug testing, should be part of the the use of home drug testing for adolescents. Providers should keep drug test results and associated Adolescent Consent diagnoses confidential to the extent permitted by law. Before beginning the drug testing process with an adoles cent, providers should explain drug-testing protocols Patient-Provider Relationship in full. When speakingwith patients,providersshouldemphasizethe Drug testing an adolescent without his or her consent is not therapeutic reasons for drug testing to avoid stigmatization. Test Considerations Providers should acquire consent before drug testing an In a prenatal care setting, routine Screening and Brief adolescent with symptoms such as school failure, fatigue, Intervention for alcohol use should be conducted. Because these are not emergency tory testing for alcohol use is not recommended except in situations, they are not hazardous enough to warrant skip cases of suspected or known risk factors for Alcohol ping this step. Adolescent Confidentiality Before beginning the drug testing process, providers Test Results should ask the adolescent for permission to share the As a follow up to a presumptive positive test result, results with parents/guardians and discuss confidentiality providers should use definitive tests to clearly identify with parents/guardians in order to encourage parental individual drugs. Responses to positive drug test results can include: patient If an adolescent declines to share drug test results, the education, referral to treatment, and the creation of a provider should not share them unless there is an acute risk treatment plan. Providers should be familiar with local treatment resources and programs for pregnant women. Choosing a Test Panel for Adolescent Patients Drug test panels for adolescents should include the sub People in Recovery stances most used by the demographic. It is appropriate to conduct drug testing for a minimum of 5 years in healthcare settings for most patients in stable Responding to Positive Test Results recovery. Immediate evaluation for treatment or treatment intensi fication as a response to a positive drug test result is Pregnant Patients appropriate for most patients in stable recovery. Consequences and Confidentiality Health and Other Professionals Providers should be aware of the adverse legal and social Drug testing is especially useful in supporting recovery of consequences of detecting substance use among pregnant individuals who have increased access to psychoactive women. They should familiarize themselves with local and substances, including healthcare professionals and pro state reporting requirements before conducting a drug test fessionals in safety sensitive positions. Additional testing and relay this information to their patient before conduct should be considered for those in recovery who have ing a drug test. Part 1: Principles of Drug Testing in Addiction Additional study is required to determine the detectability of Treatment cannabis use in multiple matrices, namely oral fluid and hair. Further research should include clinically useful in ascertaining substance use patterns and mediators and moderators of the relationship. Part 2: Process of Drug Testing in Addiction Further research on tobacco testing in the context of Treatment addiction treatment would be useful. Significantly more research is needed on optimal testing frequency as well as the relationship between specific Part 5: Settings frequency and duration of drug testing and treatment Further research is needed on the role of drug testing for monitoring and outcomes. Before making any specific recommendations of frequency While evidence suggests that random testing schedules are or duration specific to level of care, further research more effective than testing on a predictable timeline, should occur. Further and ongoing research is needed on which drugs the same applies to the role of drug testing in determining should be included in drug test panels. Further research is needed to determine whether testing Additionally, more research is needed on the benefits of frequency should vary between full agonists, partial ago forgoing presumptive testing and beginning with definitive nists, and antagonists when treating addiction involving testing, and on discerning the roles of different kinds of opioid use. Part 6: Special Populations While it is agreed that instances exist where an adolescent Part 3: Additional Considerations for Drug ought to be drug tested regardless of their own desires, the Testing in Addiction Treatment exact circumstances would benefit from further refinement. More research on effective personnel training to increase Further research is needed to determine what, if any, the reliability of drug testing conducted at the point of care clinical benefit there is to routinely utilizing drug testing is needed. Though manufacturer recommended cut utilized to test for identification of alcohol use during offs are generally more appropriate for workplace rather pregnancy. Drug Testing as a Component of Addiction Treatment and Monitoring Programs and in Other Clinical Settings. Detection times of drugs of abuse in blood, urine, and auditor/docs/audits/2013/201213743c. Available at: Dispelling the myths and designing strategies: California Academy of Resolving Erroneous Reports in Toxicology and Thera in outpatient methadone treatment: a meta-analysis. Embarrassing, degrading, or beneficial: patient and Health Services Administration, Published 2006; Updated 2013. Testing for drugs of abuse in definitive drug testing results in their work with substance-use patients: children and adolescents. Urine testing in methadone maintenance treat systematic review of tampering methods in urine drug screening and ment: applications and limitations. Focus on alcohol and drug abuse: from day hospitaltreatment in lower socio-economic cocaine-dependent ensuring validity in urine drug testing. Advances in drug testing for substance abuse alternative incentives: interaction with intake stimulant test results. False-positive interferences of another potential strategy to reduce illicit drug-related harm. Manda and other substance use disorders: ethical issues in obstetric and gyneco tory Guidelines for Federal Workplace Drug Testing Programs [Notice]. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Federal Register; May 2008, Vol. Language, substance use disorders, and and drugs in sampled oral fluid is related to sample volume. Confronting inadvertent testing for drug use monitoring in outpatient treatment for opiate stigma and pejorative language in addiction scholarship: a recognition dependence. Influence of chemical straightening on the drug testing in substance use treatment contexts. Anoverviewoftheuseofurine,hair,sweat of both abstinence and chronic excessive alcohol consumption.
Best purchase for procardia
The challenge to find appropriate measures and to use them wisely has direct consequences in measuring response to treatment capillaries and alveoli buy cheap procardia line. For ex ample, there is predictable variation in how children perform on different tests (Lord and Schopler, 1989a). Children with autism tend to have the greatest difficulty on tests in which both social and language components are heavily weighted and least difficulty with nonverbal tests that have minimum demands for speed and motor skills. Even within a single test that spans infant to school-age abilities, there is still variation in tasks across age that may differentially affect children with autism; this variation is exemplified in many standard instruments such as the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (Thorndike et al. In one study (Lord and Schopler, 1989a), mean differences between test scores at 3 years or younger and 8 years and older were greater than 23 points. There are diffi culties analyzing age equivalents across different tests because of lack of equality in intervals (Mervis and Robinson, 1999). Indeed, adaptive behavior may be a more robust pre dictor of some aspects of later outcomes (Lord and Schopler, 1989b; Spar row, 1997). Similar to findings with typically developing children, tests of intel lectual ability yield more stable scores as children with autistic spectrum disorders become older and more varied areas of intellectual develop ment can be evaluated. Although the process of assessment can be diffi cult (Sparrow, 1997), various studies have reported on the reliability and validity of appropriately obtained intelligence test scores (Lord and Schopler, 1989a). Clinicians should be aware that the larger the sampling of intellectual skills. As a result, overall indices of intellectual functioning may be misleading (Ozonoff and Miller, 1995). Second, correlations re ported in test manuals between various assessment batteries may not readily apply, although scores often become more stable and predictive over time (Lord and Schopler, 1989a; Sparrow, 1997). Third, for some older children with autism standard scores may fall over time, reflecting the fact that while gains are made, they tend to be at a slower rate than expected given the increase in chronological age. This drop may be par ticularly obvious in tests of intelligence that emphasize aspects of reason ing, conceptualization, and generalization. Approximately 10 percent of children with autism show unusual is lets of ability or splinter skills. The kinds of talents observed include drawing, block design tasks, musical skill, and other abilities, such as calendar calculation (Treffert, 1989; Shah and Frith, 1993; Prior and Ozonoff, 1998). Such abilities do not seem to be based just on memory skills; they may reflect other aspects of information processing (Pring et al. Specific cognitive goals, often including social, communicative, and adaptive do mains, are necessary to evaluate progress effectively. Direct evaluations of academic skills are also important if children are learning to read or are participating in other academic activities. Various experimental tasks and proce dures used to investigate this capacity generally indicate that many some what more able. While not all children with autistic spectrum disorders entirely lack a theory of mind (Klin et al. There appear to be strong relationships between verbal ability and theory of mind capacities in autism. The theory of mind hypothesis has been a highly productive one in terms of generation of research, and in focusing increased attention on the social aspects of autism, including deficits in joint attention, communication, and pretense play (see Happe, 1995, for a summary). However, specific behaviors that evidence a deficit in theory of mind are not by themselves sufficient to yield a diagnosis of autism, which can be associated with other cognitive deficits. In addition, research in which theory of mind concepts were taught to individuals with autism did not result in general changes in social behavior, suggest ing that links between theory of mind and sociability are not simple (Hadwin et al. A second body of work has focused on deficits in executive function ing, that is, in forward planning and cognitive flexibility. Such deficits are reflected in difficulties with perseveration and lack of use of strategies (see Prior and Ozonoff, 1998). Tests such as the Wisconsin Card Sort (Heaton, 1981) and the Tower of Hanoi (Simon, 1975) have been used to document these difficulties. In preschool children, the data on executive functioning deficits are more limited. McEvoy and colleagues (1993) used tasks that required flexibility and response set shifting, and noted that younger children with autism tended to exhibit more errors in persev eration than either mentally or chronologically age-matched control chil dren. More recently, others did not find that the executive functioning in preschoolers with autistic spectrum disorders differed from that in other children (Griffith et al. A third area of theoretical interest has centered on central coherence theory, in which the core difficulties in autism are viewed as arising from a basic impairment in observing meaning in whole arrays or contexts (Frith, 1996; Jarrold et al. As Frith (1996) has noted, it is likely that a number of separate cognitive deficits will be ultimately identified and related to the basic neurobiological abnormalities in autism. Neuropsychological assessments are sometimes of help in document ing sensory-perceptual, psychomotor, memory, and other skills. Exten sive neuropsychological assessments may not provide enough useful in formation to be cost-effective. However, selected instruments may be helpful in answering specific questions, particularly in more able chil dren. Academic performance, for this discussion, refers to tasks related to traditional reading and mathematics skills. This literature consists primarily of single-subject design, quasi-experimental design, and descriptive observational research, rather than randomized clinical trials. The studies have usually included children with autism at the top of the age range covered in this report. Notwithstanding these caveats, there is evidence that some young children with autistic spectrum disorders can acquire read ing skills as a result of participation in instructional activities. There is very limited research on instructional approaches to promoting math ematics skills. A range of instructional strategies have involved children with autis tic spectrum disorders. In early research, Koegel and Rincover (1974) and Rincover and Koegel (1977) demonstrated that young children with au tism could engage in academic tasks and respond to academic instruction as well in small-group instructional settings as they did in one-to-one instruction with an adult. Kamps and colleagues replicated and extended these findings on small-group instruction of academic tasks to a wider range of children within the autism spectrum and other developmental disabilities (Kamps et al. In another study, Kamps and colleagues (1991) first performed de scriptive observational assessment of children with autism in a range of classroom settings. They used these data to identify the following com monly used instructional approaches: 1. Incorporate naturally occurring procedures into intervention groups across classrooms. This combination of instructional strategies (choral responding, student-to-student responding, rotation of materials, random student re sponding) was also found to be effective in teaching language concepts to elementary-aged children with autism in a later study (Kamps et al. In their subsequent research, Kamps and colleagues (1994b) have examined the use of classwide peer tutoring. In a single-subject design study, these research ers found increased reading fluency and comprehension for children who received peer tutoring, as compared with those who received traditional reading instruction. Using an inci dental teaching technique, McGee and colleagues (1986) embedded sight word recognition tasks in toy play activities and found that two children with autism acquired sight-word recognition skills and generalized those skills to other settings.
Balm (Lemon Balm). Procardia.
- Improving the quality of sleep, when taken with valerian.
- How does Lemon Balm work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Cold sores.
- What other names is Lemon Balm known by?
- What is Lemon Balm?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96446
Buy procardia 30mg mastercard
These laxatives draw toilet capillaries with an incomplete lining are called cheap procardia 30 mg mastercard, 2-3 times a day for 5-10 minutes after meals (within water into the stool thereby making the stools softer and 30 minutes of meal intake), (b) make the defecation easy to pass. However in children <1 year of age, the only drug motivating the child and avoiding child-parent conflict. Adequate intake of fiber Combinations therapy with two classes of laxatives is not rich diet (cereals, whole pulses with bran, vegetables, recommended for children [5]. High fiber diet chart should be given to parents (as per Stimulant Laxatives: Stimulant laxatives are used only as local practice). Stimulants are when constipation is associated with behavioral co usually required as rescue therapy (an acute or sudden morbidity or pelvic floor dysfunction in older children and episode of constipation while being on regular compliant adolescents. While on follow-up, the maintenance training advice should continue even after stoppage of dose may be increased or decreased to achieve daily laxatives. Triggers and precipitating factors of functional passage of stools, keeping in view the features of constipation should have been adequately addressed. Parents should have the knowledge about the management and also risk of relapse of symptoms on Successful outcome of treatment should be defined as stoppage of medication. Normalcy of stools should defined as daily, not constipation should be investigated for hypothyroidism, hard, nor loose watery stools, with absence of pain, celiac disease, Hirschprung disease, Cow milk protein straining, bleeding, posturing or incontinence. These children also need evaluation for In Western countries, 50% of children with functional presence of slow colonic transit, pelvic dyssynergia and constipation recover and are taken off medication within 6 pseudo-obstruction, in centers with expertise. Emphasis should be laid on toilet-training and When to stop laxatives: No clear guidelines exist and only importantly in counselling particularly related to long expert opinions are available. Evaluation and Normal bowel pattern in children and dietary and other Treatment of Functional Constipation in Infants and precipitating factors in functional constipation. Separation from the best friend, failure in an examination, severe illness of a family member, loss of job by a parent, frequent punishment by parents and living in an area affected by separatist war remained independently associated with constipation (p < 0. In conclusion, constipation was significantly higher in children exposed to stressful life events. Key words: emotional stress, functional gastrointestinal disorder, constipation, child, adolescent, war. Introduction irritable bowel syndrome in children [7] and adults Childhood constipation is a common cosmopolitan [8]. Up to now there are no systematic studies to problem which accounts for $3% of visits to general assess the association between day-to-day stresses paediatric clinics [1] and 25% visits to gastroenter and childhood constipation. Materials and Methods the definite cause of constipation is unclear in those with functional constipation and psychological this was a cross-sectional survey conducted in Sri abnormalities are considered as contributory factors. Three provinces of the country were ran Previous studies reported significant physical or domly selected to represent the island. Two rural and psychological trauma and history of personal health three urban schools were also randomly selected from problems in children with constipation [4], while these provinces and two of these schools were from others have demonstrated clinical range of scores government controlled areas in the Eastern province in the Child Behaviour Check List in one-third of affected by the separatist war. However, tration and the parents were informed before other studies failed to demonstrate such distribution of questionnaires and their consent was association [6]. We associated with other functional gastrointestinal used the setting of a typical examination in the school diseases such as functional abdominal pain and to make certain that children would not see ques tionnaires of the others. The questionnaire was in the native language (Sinhalese) and questions were simple and easy to understand. Research assistants were Correspondence: Dr Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana, present with students throughout while they filled the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Talagolla Road, Ragama, Sri Lanka. The data collection started in January 2007 these two authors contributed equally to this work. Since this is an epidemiological study, we did Age distribution not use the diagnostic criterion of palpable faecal Mean age 12. Bowel habits and stressful life events Figure 1 shows the relationship between defecation Results frequency and stressful life events. Mean bowel frequency has a negative correlation with the A total of 2770 questionnaires were distributed and number of stressful life events exposed both in 2699 (97. Table 1 events and bowel habits in patients with constipation compares the demographic data of children with is demonstrated in Table 3. Stressful life events and constipation Patients with constipation have been exposed to significantly more stressful life events (mean 2. Table 2 demonstrates the association symptoms and exposure to stressful life events in between different stressful life events and constipa patients with constipation. Even though, previous studies have demonstrated a strong association between functional constipation and psychological symptoms such as anxiety and depression in adults [11, 12], the exact relationship between emotional stress and childhood functional constipation has not been assessed sufficiently. The few studies performed in relation to this, have assessed this effect indirectly. However, this study did not assess the impact of common family and school related stressful events. Correlation between defecation frequency abnormal oral habits as an indirect measurement of and number of stressful life events. This probably underestimates the Discussion actual relationship between constipation and stress, In this study, constipation was significantly higher in since only severe emotional stress would cause such those exposed to family and school-related stressful abnormal oral habits [4]. Similarly, we between constipation and difficulties in the school also found a higher prevalence of constipation in [13]. Similarly, we found an association between those who undergo frequent parental punishment. The separatist war in the eastern province of the country has been going on for nearly 30 years. We found a significantly higher prevalence of constipation in children living in war Stressful events Stressful events affected areas compared with rest of the country. Therefore, these data confirm the Painful bowel motions important role of war-related psychological stresses No 101 (29. Further gastrointestinal disorders: psychological, social and studies are required to assess the exact relationship somatic features. Stool form scale as a useful Abdominal pain and weight loss were more guide to intestinal transit time. Childhood association between emotional stress and gastroin functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. These findings show that effects of stress on mechanisms, stress level and anorectal physiology in gastrointestinal function are wider in children with patients with functional constipation. Coping effects of profound stress in the biologically predis stratergies, illness perception, anxiety and depression posed individual may lead to a reduced ability of the of patients with idiopathic constipation: a population central nervous system to filter visceral and somatic based study. Modulation of gut motility through brain Gastroenterology 2008;134(4 Suppl 1):A112. Bowel gut axis probably impairs colonic transit and ano disorders in gulf war veterans. Influence of dietary, psychological, and its impact during the treatment of affected children. Physiologic and psychologic characteristics of an elderly population References with chronic constipation. Relationship between psychological state and level of Epidemiology of childhood constipation: a systematic activity of extrinsic gut innervation in patients with a review.
Buy discount procardia line
Benefits may also be used for 5463 clothing coronary artery location and function generic 30 mg procardia overnight delivery, medical care not covered by Medicaid or personal insurance (such as 5464 eyeglasses and hearing aids), recreation, personal incidentals, and comfort items. In 5465 addition, funds may be used for training programs, school tuition, or daily school 5466 expenses if other needs have been met. The caseworker is responsible to 5470 request and authorize payments each month using the following precedence: 5471 (1) Payment for spenddown for Medicaid, when determined appropriate. Medicaid requires that any case requiring a spenddown be th 5494 closed if the spenddown has not been cleared by the 10 of the following month. If the 5495 case is closed, a new Medicaid application is required to reopen Medicaid. The state office revenue team is 5506 responsible to identify which services and what portion of costs is included in the 5507 calculation of cost of care. The cost of care amount should be calculated and paid as 5512 soon as possible after costs have been incurred for a given month. Cost of care 5516 that was estimated must be reconciled and any adjustments made within 30 5517 days after receipt of actual billing from provider. Regional finance staff must 5518 review and approve all estimated costs of care prior to payment and verify 5519 accuracy of reconciliations and payment adjustments. Compare cost of care total to unearned income received (or available 5526 after spenddown) and document. If total cost of care is greater than unearned income received, authorize 5528 preparation of check(s) to Child and Family Services for total unearned 5529 income amount, minus personal needs allowance. If cost of care is less than unearned income amount, authorize 5531 preparation of check(s) to Child and Family Services for cost of care, 5532 leaving personal needs allotment and any additional remaining unearned 5533 income in account to be used for current and future needs of the child. When applicable, adjust cost of care for prior months when there is 5535 retroactive unearned income or when additional costs are incurred for 5536 prior months that may not have already been included in cost of care 5537 calculation. The following procedures apply 5539 when depositing cost of care reimbursements and other funds from foster child 5540 representative payee accounts. Deposit funds from client trust accounts (including special needs and cost 5549 of care reimbursements) as a refund of expenditures. When appropriate, the Child and Family Team 5559 will be consulted about use of personal needs funds. The region director or designee 5560 will approve in advance any expense from a representative payee account that is $500 5561 or over, other than payment for a medical bill, Medicaid spenddown, cost of care 5562 payment, or reimbursement check to the funding agency when the account is being 5563 closed. Child and Family Services should request approval to 5570 apply the funds to cost of care for the months for which the funding was granted. These dedicated funds may only be used for 5578 costs authorized by the Social Security Administration and may only be used for past 5579 cost of care when approval is specifically granted by the Social Security Administration. Any funds 5585 remaining in the representative payee account carried over into the following month must be 5586 counted as an asset. Consult with eligibility caseworker for questions regarding lump sum payments and 5590 impact on eligibility. When a foster child receiving unearned income is placed at 5621 home on a trial home placement, Child and Family Services will remain the 5622 representative payee as long and the child remains in Child and Family Services custody. The parent may apply to become representative payee 5629 after the court has returned custody to them. The transition to adult living plan should include plans for the child to 5652 become recipient of the funds after age 18 or transfer to an appropriate representative 5653 payee after leaving Child and Family Services custody if funding will continue. When a foster child receiving unearned income is placed for adoption, Child 5673 and Family Services will remain the representative payee as long and the child remains 5674 in Child and Family Services custody. When Child and Family Services is requesting the court to grant custody 5700 of a foster child receiving unearned income to a guardian, Child and Family Services will 5701 remain the representative payee until custody is terminated. In many cases, the availability of unearned income 5707 may make a guardianship subsidy unnecessary or inappropriate. The regional account custodian must keep a 5726 record of all actions taken with the representative payee account, including income 5727 received, authorization for payments, checks issued, cost of care monthly records, 5728 correspondence, reports, internal audits, and monthly and final account reconciliation. The representative payee is responsible to 5731 provide expenditure reports to the responsible funding agency, as required by the 5732 funding agency. Child and Family Services will report funds received and 5736 expenditures as requested by the Social Security Administration, traditionally in the 5737 following three categories: 5738 (1) Food and housing. Clothing, education, medical/dental not covered by Medicaid, personal 5740 items, recreation, and miscellaneous 5741 (3) Savings. Notification may be made by telephone, mail, or in 5753 person, as allowed by the funding agency. Provide activities that enhance physical, cognitive, social, and emotional 6160 development; teach problem solving skills; and act as positive role models. Commit to keep the child without disruption until permanency has been 6162 accomplished by using available supports to prevent disruption.
Discount procardia 30mg visa
The encephalopathies caused by isolated lost wages because of a higher rate of unemployment [14]; poor defects of liver metabolism heart disease icd 9 30 mg procardia for sale. Finally, the cost extends to with severe liver disease may suffer from other types of delirium families and caregivers, considering the need of continuous care, or coma that are not related to hepatic failure or portal-systemic with absence to work and lost wages for family members, and shunting. Pathophysiology most relevant questions to answer, considering relevance, urgency and completeness of the topics to be covered. Several organs contribute to the development of hyperammonaemia and the increase in inammatory cytokines. In addition, other toxic substances are produced by an altered gut microbiota (left panel). Peripheral cytokines and ammonia activate the brain microglia, which, in turn, amplies the inammatoryreaction. In addition, ammonia impinges on neurotransmission and oxidative metabolism directly, by promoting the production of inhibitoryneurosteroids(rightpanel). Sites/conditions Mechanisms Kidneys Ammoniogenic properties and regulation of serum levels of urea (a substrate used by the gut microbiota urease for the production of ammonia) Urinary tract Release of ammonia from urea by the action of urease-containing bacteria Muscle Utilization of ammonia for glutamine synthesis Fasting Protein breakdown and consequent amino acid oxidation Increase of pro-inammatory cytokines Sensitization to the action of ammonia Hyponatremia Sensitization to the action of ammonia Alkalaemia Sensitization to the action of ammonia Further, encephalopathy can be induced by the administration dysfunction. This process is favoured by the activation of pro of ammonia salts in patients with cirrhosis [18], the administra inammatory cytokines and low sodium levels. It is therefore reasonable to qualify this inhibitory neurosteroids synthesis [51]. Hyperintense globus pallidus and, to a lesser extent, globus example, the levels of ammonia and indole are correlated, because striatum and substantia nigra reticulata on T1-weighted Magnetic the origin of these substances is similar. Manganese is neurotoxic and can the production of ammonia [34], the urinary tract, where ammo impair dopaminergic neurotransmission, as well as cause astro nia can be released from urea by the action of urease-containing cyte oxidative stress [57]. The time-course of mental alteration; tates the entrance of ammonia in the brain with rst order kinetics 4. The precipitating and facilitating events (the latter being spon andcanexplain,atleastinpart,theneurologicalndings. This can lead to death because of cerebellar tonsils her ity transition, mitochondrial dysfunction leading to astrocyte niation [61]. The severity of mental impairment has prognostic [63] and infection,whichresolvedaftertwodaysoftreatmentwithlactulose management implications. Presence of precipitating and facilitating events [yes (and if so, which does not have a universally accepted diagnosing tool. Comput causes of neurological and psychiatric dysfunction, which may erized tests assessing attention [70,71], working memory [72] or explain the entire set of abnormalities. This process is not necessar Please cite this article in press as: Montagnese S, et al. By contrast, as false positives are common in ammonia mea Electrolyte-related encephalopathy. Differential diagnosis to be considered are severe eitherinthecompleteabsenceofliverdiseaseorinassociationwith hypercapnia, hypoglycaemia, hyponatremia, acidosis, bacterial or portal hypertension not due to cirrhosis. Glucose, electrolytes, arterial blood gases, unsuspected or misdiagnosed, because of the absence of signicant including pH, and C reactive protein are helpful in this respect. Finally, arterial angiography can help identify normal range have a high negative predictive value and virtually severe cerebral damage/death. Although the large majority of cirrhotic patients who criterion to qualify transplantation as futile. They are relatively easy to administer, have good exter Adapted from Strauss et al. FormsandpertinentItaliannormsareavail reported in Table 4, which is based on a combination of the West able [93], also for purposes of on-line scoring. Tested in Italy [70] but not in app form; no Italian norms because of its sound (opposite to overt) rather than its meaning available. Neuropsychological tests have the advantage of and improvement after therapy [99,100]. It requires specialized being closer to the disability one is attempting to measure but equipment. For example, the risk of intracerebral haemorrhage whilewaitingforlivertransplantation. Arterial angiography can help identify and the Prometheus system (which combines fractionated plasma severe cerebral damage/death. This is Any bacterial or fungal infection should be rapidly recognized not standard practice in Italy but the option should at least be con andtreated. Antiepileptic drugs are used to administer drugs which are only available/known to work utilized in the presence of seizures. Glucose and sodium levels need as by mouth formulations in patients who are unable to swallow or to be tightly controlled [105]. Anyhow,neitherofitsavailableformulations(ivandoral has been administered at various doses across studies. Lowerdoses(5g)may Probiotics are live bacteria that, when ingested, may confer a also have benecial effects via their prebiotic properties [130]. It is a poorly absorbed compound and has a very low, (a combination of pre and pro-biotics) with placebo or no inter if any, potential for drug-to-drug interactions [133]. According to a Cochrane review [161], countries, rifaximin is currently approved for the treatment of the majority of trials suffered from a high risk of systematic error Please cite this article in press as: Montagnese S, et al. It should be noted that probiotics, just like antibi fast, and should be encouraged. There is very limited evidence for the benets of the to draw reliable conclusions. Thisther apy is based on the capacity of ornithine to stimulate glutamine synthetase activity in peripheral organs, hence incorporating 6. Despite promising, these are preliminary experiences on Please cite this article in press as: Montagnese S, et al. Therefore, their routine treatment has not been gener Patrizia Burra: none to report. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: patients who are perceived to be at particular risk of the con 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Physiopathology and surgical treatment of hepatic marginally slowed, inadequate or irritable (grade I according to the encephalopathy after porto-caval anastomosis. Conclusions and future research atic encephalopathy is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis independent of other extrahepatic organ failures. In several liver disease in liver transplant setting: evidence by means of 2 independent instances, Italian research has been at the forefront of these efforts. In-hospital mortal [40] Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Petteno E, Mapelli D, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, et al. Considerations for the cost-effective management of hepatic pressureofammoniaversusammoniainhepaticencephalopathy.
Buy procardia with a mastercard
Behaviorally cardiovascular disease updates buy procardia 30mg online, anger is frequently seen in tantrum behaviors, yelling, hitting, and kicking. Children with anger control problems fall into two different categories: (a) those with a behavioral excess (anger is too intense, too frequent, or both), or (b) those with a behavioral deficit (an inability to express anger). Because anger can serve as a constructive force in relationships, children who are unable to express their anger in ways that facilitate conflict resolution are considered to have anger problems (Bowers, 1987). Aggressive youths anger is expressed is learned by watching, generate fewer effective solutions and fewer listening to , or interacting with others and varies potential consequences in hypothetical across and within cultures (Bowers, 1987). Aggressive behavior, defined as the set of interpersonal actions that consist of verbal and What Should I Do as a Parent/Teacher The following areas of investigation most children (Bandura, 1973; Lochman, 1984). Children (frequency, intensity, duration, who display a wide range of different kinds of pervasiveness) An observation of specific behaviors used by the child and his/her peer group in the setting in (b) Behavior modification strategies such as which the problem behavior occurs is an response cost, mediated essay, behavioral important component of the assessment contracting, and direct reinforcement of process. Finally, normative arousal reduction, (2) cognitive change, (3) measures (Feindler & Fremouw,1983), behavioral skills development, (4) moral interviews (students, parents, and teachers), reasoning development, and (5) appropriate and an examination of self-monitoring and self anger expression. For example, Feindler and her following approaches are recommended: colleagues. Incorporating strategies to enhance self-management (3) Praise children when they are not angry (self-observation, self-recording, self (Bowers, 1987); reinforcement, and self-punishment) and self efficacy (belief that the treatment will be (4) Suggest that the explosive child temporarily effective and that the child can actually leave the room to regain composure (Bowers, implement the skills) also seem to be 1987); imperative. Cognitive-behavioral assessment and peer adjustment problems: Social cognitive treatment with aggressive children. Stress of adult antisocial behavior: Replications from inoculation training for adolescent anger longitudinal studies. For disorders" and students who are referred to as having both behavior "emotional disabilities," "behavioral disorders," patterns, we have "serious emotional disturbances," or "emotional and identified what we behavioral disorders" have two common elements want them to do that are instructionally relevant: (1) they demonstrate instead of the current problem behavior. Using effective teaching strategies will promote student academic and social behavioral success. Focusing behavior approach a student with a "conduct disorder" and a management systems on positive, prosocial student with a "behavioral disorder" is to replacement responses will provide students with the operationally define exactly what it is that each opportunity to practice and be reinforced for student does that is discrepant with the expected appropriate behaviors. Humor in the classroom lets students view behaviors that can be directly observed, the task of school and learning as fun. If all a student does is perform as a Two questions need to be addressed in developing passive participant in the classroom, then little growth any behavior change procedure regardless of the in social skill acquisition can be expected. We It is necessary to target specific prosocial behaviors may want the student to play with peers on the for appropriate instruction and assessment to occur. It is important (3) an explanation of what is expected of each student to base all social skill instructional decisions on during the group. It is also the teacher must determine whether the social skill important to reinforce the students when they use new problem is due to a skill deficit or a performance skills. These books are part of a nine-book series, "Working with =-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-= Behavioral Disorders. This publication w as prepared w ith funding from "Teaching students with behavioral disorders: the O ffice of Educational Research and Basic questions and answers. The behavior encompasses physical deaths in school, 51 casualties were the result of aggression, threats, teasing, and harassment. Bullying is often a factor it can lead to violence, bullying typically is not in school related deaths. It is, however, an unacceptable anti-social psychosocial adjustment, criminal activity and behavior that is learned through influences in the other negative long-term consequences. Verbal abuse, on the other hand, psychological aggression or harassment toward remains constant. Department of Justice others, with the goal of gaining power over or reports that younger students are more likely to dominating another individual. They generally do not have many, if any, Why Do Some Children and Adolescents Become good friends and may display poor social skills and Bullies When 76 children receive negative messages or physical hiring police to patrol the halls have no tangible punishment at home, they tend to develop positive results. Bullying also thrives in an programs that promote a positive school and environment where students are more likely to community climate. Existing programs can effectively receive negative feedback and negative attention reduce the occurrence of bullying; in fact, one than in a positive school climate that fosters program decreased peer victimization by 50%. Such respect and sets high standards for interpersonal programs require the participation and commitment of behavior. Researchers advocate advocates, supports, or promotes bullying intervening in elementary or middle school, or as behavior. Support services personnel human rights; they are more likely to resort to working with administrators can help design violence to solve problems without worry of the effective teacher training modules. School frustration with bullying can turn into vengeful personnel should never ignore bullying violence. However, A positive school climate will reduce bullying installing metal detectors or surveillance cameras or and victimization. School-associated violent deaths in the Safe and Responsive Schools Project United States, 1994-1999. Retrieved June 15, 2004 from National Resource Center for Safe Schools ecap. Journal of the American Medical Psychologists, 4340 East West Highway, Suite 402, Association, 285, 2094-2100. Surveys indicate that as many as half of all anger management training, and increased adult children are bullied at some time during their school supervision. Boys suggest that he or she try walking away to avoid the tend to use physical intimidation or threats, regardless of bully, or that they seek help from a teacher, coach, or the gender of their victims. The simple Children who are bullied experience real suffering act of insisting that the bully leave him alone may that can interfere with their social and emotional have a surprising effect. Bullies may also be depressed, angry or upset about If your child becomes withdrawn, depressed or reluctant events at school or at home. Children targeted by bullies to go to school, or if you see a decline in school also tend to fit a particular profile. Bullies often choose performance, additional consultation or intervention may children who are passive, easily intimidated, or have few be required.

