Silvitra
Buy silvitra 120mg fast delivery
For rence of these conditions under different treatment the final recommendations impotence and high blood pressure 120 mg silvitra overnight delivery, other literature (basic literaregimens. Conclusions from scientific literature and reported in various ways on serum calcium levels. In directions for further research general, calcium levels within the target range can be achieved with different treatment (combinations), and the 4. Summary and interpretation of the main findings risk of severe hypoor hypercalcaemia is low. Data on QoL and the risk of complications have had a sample size of O100 patients. Also no studies are available that relate target calcium levels to clinically relevant endpoints. Study endpoints Thus, we do not know what the optimal calcium target Mortality " Only one study reported data on mortality is. No deaths were reported in this randomized study to formulate recommendations based on strict evidence. Measurements of whether relatively high normal serum calcium levels are of ionized or total calcium mostly refiect local traditions, specific harm to patients. It is generally assumed that this is exists on long-term benefits (or harms) of achieving these related to high serum phosphate levels and an increased therapeutic goals. Thus, we consider it inappropriate management, if therapeutic efforts have immediate R. Moreover, low magnesium levels may monitoring of patients at regular time intervals. Accordingly, calcium levels may, however, change and complications it seems reasonable to aim at keeping serum magnesium may emerge at any time, with or without any apparent levels within the reference range. Thus, we find it of importance to empower patients with knowledge of symptoms and co-morbidities and drugs R. If a patient is diagnosed with one of the have neuromuscular complaints (4, 38, 53). To ensure that diseases or initiates treatment with one of the drugs, this symptoms are not caused by low vitamin D levels, it seems may necessitate changes in the medical treatment of reasonable to ensure an adequate vitamin D status (55). As calciferol itself may be of and/or an albumin adjusted serum calcium level importance to a number of cellular processes and may 2C! No limit of that patients are without symptoms of hypocalcaemia and serum calcium levels have been defined below which serum calcium levels are maintained within the target treatment is unquestionably needed. On the other hand, no apparent symptoms may of activated vitamin D analogues, calciferol (ergocalciferol be present, despite low calcium levels, if the hypocalcae(vitamin D2) or cholecalciferol (vitamin D3)) was used in mia has developed slowly. Neuropsychiatric Neuropsychiatric diseases Seizures However, vitamin D levels should be optimised. If so, patients may have symptoms despite (apparently) normal calcium levels and Ca2C levels at actual pH should be requested. Today, dose of activated vitamin D analogue may be gradually activated vitamin D analogues are preferred due to a shorter changed (Fig. Larger changes in dose may be in case of intoxication, serum calcium levels will normalize neededincaseofseverehypo-orhypercalcaemia. Inorderto faster if patients are treated with activated vitamin D allow for a new steady-state, dose adjustments should (if analogues (69, 70). Effects of the different disturbancesaretobeadjusted,weeksmaybeallowedtopass analogues have not been compared head-to-head in between dose adjustments. It is Calcium intake " An adequate daily intake of calcium unknown whether a relatively high intake of calcium from diet and supplements is advisable. Intake of from supplements (O1000 mg/day) is of advantage, as calcium from dietary sources (mainly dairy products) is it may cause hypercalciuria. Thus, in selected cases high use calcium supplements in a total daily dose of doses of calcium supplement may be needed. Calcium carbonate is most considering a reduction in calcium intake, a sodiumoften used and less expensive than other calcium restricted diet, and/or treatment with a thiazide diuretic. Accordingly, it may be helpful to reduce the risk of extra-skeletal calcifications, interventions aiming at intake of sodium (Fig. If patients are on treatment with normalizing these biochemical indices may be considered a high daily dose of calcium supplements, daily dose of (88) (Fig. As calcium binds phosphate in the If dietary recommendations or changes in the daily intestine and calcitriol increases intestinal absorption of dose of calcium supplements and/or activated vitamin D phosphorous, it may be considered to titrate therapy so analogue do not reduce urinary calcium, treatment with that the daily dose of calcium supplements is increased, a thiazide diuretic may be considered (Fig. Thiazide which may allow for a decrease in daily dose of activated diuretics have been shown to reduce urinary calcium in vitamin D analogue. By lowering calcium should be measured in order to ensure that renal calcium excretion, thiazides may exert a calciumpatients have not developed severe hypercalciuria. Addition of amiloride to treatment with a Of notice, however, recent studies in patients with chronic thiazide may further lower urinary calcium losses and kidney diseases (mostly not on dialysis) have suggested decrease the risk of hypokalemia. Moreover, amiloride an increased mortality and risk of vascular calcifications may lower renal magnesium excretion (19, 84). However, in those on treatment with calcium-containing vs no data are available on whether thiazides reduce risk of calcium-free phosphate binders (89). A relatively high dose administered twice a day is often needed in order to lower 24 h urinary R. In order to including blood electrolyte disturbances and blood normalize magnesium levels, treatment with magnesium pressure. If magnesium levels are chronically low, a patients with renal stones should receive a full evaluation magnesium infusion test (0. If assessed at regular time intervals, in order to assure that renal function is severely impaired, this test should not be the treatment provides relief of symptoms, without done. In case of " severe hypoor hypercalcaemia, more frequent moniReasoning Normocalcaemia can be achieved in toring (several times a week) may be needed. The gain of function breastfeeding with levels to be kept at the lower end of the mutation causes a lowering of the calcium set-point in normal range (serum albumin adjusted total calcium is the parathyroid glands. Levels of serum calcium are recommended to be kept at the lower end of the normal R. During with activated vitamin D analogues and calcium supplelactation, there are high rates of bone resorption due to ments as in non-pregnant women. Gradually after weaning, the range and avoid symptoms of hypocalcaemia (97, 98, 99). The epidemiology consequences, if the mother has been hypocalcaemic of non-surgical hypoparathyroidism in Denmark: a nationwide case significantly during pregnancy. Prevalence and incidence of hypoparathyroidism in the United States using a large claims Supplementary data database. The rest of the working group has nothing serum calcium levels after thyroid surgeryfi Importance of insitu preservation of parathyroid glands during total thyroidectomy. Parathyroid hormone therapy potassium and magnesium-sparing properties of amiloride and for hypoparathyroidism. Endocrine Practice 2011 17 (Suppl 1) 20 Sikjaer T, Rejnmark L, Rolighed L, Heickendorff L & Mosekilde L. Therapy of hypoparathyroidism parathyroidism: a randomized,placebo-controlled study.
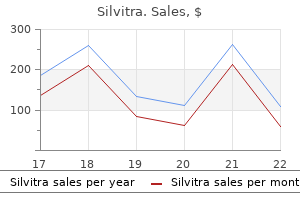
Order cheap silvitra
Unstable angina Unstable angina is characterised by a sudden change in the pattern of exertional angina erectile dysfunction treatment medscape buy silvitra 120 mg amex. Minor degrees of myocardial damage can be detected by specific serum protein markers (troponins, p306). Urgency Urgency of micturition denotes a strong desire to void and the patient often has to rush to the toilet because of an acute call to micturate. Urgency forms part of a cluster of symptoms which include frequency of micturition (p71), nocturia and hesitancy of micturition. Vasculitis Definition Disease caused by inflammatory destructive changes of blood vessel walls. Presentation Wide variety of clinical presentations affecting one or more organ systems. Skin: splinter haemorrhages, nail fold infarcts, petechiae, purpura, livedo reticularis. Respiratory: cough, haemoptysis, breathlessness, pulmonary infiltration, sinusitis. Neurological: mononeuritis multiplex, sensorimotor polyneuropathy, confusion, fits, hemiplegia, meningoencephalitis. Unilateral blindness is due to a lesion either of the eye itself or between the eye and the optic chiasm. Investigations will be determined by history and examination findings; a specialist opinion should be sought without delay. Screen for risk factors and causes of cerebrovascular thromboembolic disease 2 Venous plasma glucose. If found in isolation this suggests a spinal lesion at the level of C8/T1 or distally in the brachial plexus, or upper limb motor nerves. Unilateral wasting of the small muscles of the hand may occur in association with 2 Cervical rib. Bilateral wasting of the small muscles of the hand occurs in 2 Carpal tunnel syndrome (common). Wheeze Wheezes (rhonchi) are continuous high-, mediumor low-pitched added sounds audible during respiration. Typically they are loudest on expiration in asthma and may on occasion be heard without a stethoscope. If wheeze is audible only during inspiration this is termed stridor, implying upper respiratory obstruction. An important distinction must be made between monophonic and polyphonic wheezes and whether wheeze is localised to a single area or is heard throughout the thorax. Implies local bronchial obstruction, usually due to: 2 Bronchogenic carcinoma 2 Foreign body. Note: Stridor is a harsh form of monophonic wheeze arising from upper airway obstruction (Stridor (p81)). Tests have come and gone over the years and have been adopted with varying degrees of enthusiasm by specialist centres. In particular, there is often confusion over which tests to do, what procedures to follow and how to interpret the results. Interpretation of the absolute levels of hormones in isolation may be highly misleading. Some individuals have a heterophile interfering antibody that affects the results 2 Endocrinology & metabolism of many radioimmunoassays. Always ask patient for a full medication list (including herbal remedies and other self-medication). Endocrine tests are generally expensive and should not be performed unnecessarily or outside of standard protocols. Dynamic tests may have cautions and contraindications and can be hazardous if used inappropriately. A high degree of organisation and close liaison with the lab is required to perform these tests in a way that can be clearly interpreted. Hypopituitarism Definition 2 Failure of one or more pituitary hormones (usually multiple). Other clues, loss of body hair (especially axilliary), reduced shaving, hyponatraemia, growth failure in children. Also signs of space-occupying lesion: bitemporal hemianopia (rarely optic nerve compression, homonymous hemianopia), headache (esp. Note that the short synacthen test (Protocols (p162)) is only suitable for testing the hypothalmo-pituitary adrenal axis if pituitary failure is of long standing (>6 weeks) allowing time for adrenal atrophy to occur. Prostatism and urge incontinence resulting in urinary frequency should be distinguished by history taking as the patients do not have thirst. Then the first step is to identify straightforward causes such as drugs (diuretics), diabetes mellitus, hypercalcaemia, hypokalaemia and chronic renal failure. A glucose tolerance test should not be required to diagnose diabetes mellitus as the renal threshold for glucose needs to be exceeded (~10mmol/L) to cause polyuria and there should be glucose in the urine. Causes of polyuria/polydipsia 2 Diabetes mellitus 2 Diabetes insipidus (cranial or nephrogenic) 2 High Ca2+ 2 Low K+ 2 Chronic renal failure 2 Primary polydipsia (including dry mouth. A carefully supervised water derpivation test should be performed (Protocols (p159)). Serum sodium levels are helpful as diabetes insipidus is unlikely if Na+ <140mmol/L. Morning spot urine osmolality after overnight water restriction (not shown on chart) is occasionally useful: values >600mOsmol/L make significant degrees of dia106 betes insipidus unlikely. Measuring 24h urine volume is also useful as volumes over 3L are likely to be pathological. However, obligate urine volumes as low as 2L could still cause the patient to complain of polyuria. In such borderline cases, the distinction between partial diabetes insipidus, normality and primary polydipsia can be very difficult. Guidance on interpretation of the second line tests including the water deprivation test is given in the table. Note that primary polydipisa may be a psychiatric condition but can also occur in patients with a dry mouth.
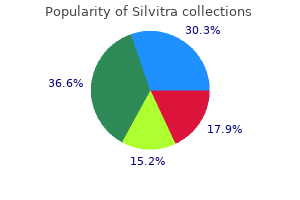
Buy silvitra master card
A geography index might list the names of localities subindexed by country erectile dysfunction drug types generic silvitra 120mg amex, with countries subindexed by continent. In 19th century books, it was not unusual to publish indexes as stand-alone volumes. You may be thinking that all this fuss over indexes is quaint, but it cannot apply to Big Data resources. Actually, Big Data resources that lack a proper index cannot be utilized to their full potential. Remember, in a Big Data resource, it is the relationship among data objects that are the keys to knowledge. The most useful Big Data resource has electronic indexes that map concepts, classes, and terms to specific locations in the resource where data items are stored. Without an index, Big Data resources can easily devolve into vast collections of disorganized information. Indexes should be accepted as another device for driving down the complexity of Big Data resources. An index can be read, like a book, to acquire a quick understanding of the contents and general organization of the data resource. This can be very frustrating if you know that the text covers the topic entered into the query box. By browsing the index you can find the term you need, without foreknowledge of its exact wording within the text. Indexes are constructed to contain the results of the search of every included term, obviating the need to repeat the computational task of searching on indexed entries. This permits the analyst to know the relationships among different topics within the index and within the text. Many indexes are cross-indexed, providing relationships among index terms that might be extremely helpful to the data analyst. When the location entries for index terms are annotated with the name of the resource, then merging indexes is trivial, and index searches will yield unambiguously identified locators in any of the Big Data resources included in the merge. Indexes can be created to satisfy a particular goal, and the process of creating a made-toorder index can be repeated again and again. For example, if you have a Big Data resource devoted to ornithology, and you have an interest in the geographic location of species, you might want to create an index specifically keyed to localities, or you might want to add a locality subentry for every indexed bird name in your original index. If terminology or classifications change, there is nothing stopping you from rebuilding the index with an updated specification. In the specific context of Big Data, you can update the index without modifying your data (see Chapter 6). In some cases, the data manager does not envision the full potential of the Big Data resource until after it is created. The index can be designed to facilitate the use of the resource, in line with the observed practices of users. A telephone book is an example of an index that serves its purpose without being attached to a related data source. Sherlock, preoccupied with his own ridiculous pursuits, dispatches Watson to the Baskerville family manse, in Dartmoor, to undertake urgent sleuth-related activities. The hapless Watson (Dudley Moore), standing in the great Baskerville Hall, has no idea how to proceed with the investigation. Text is composed of words and phrases that represent specific concepts that are connected together into a sequence, known as a sentence. These uncommon word sequences are bounded by sequences of common words or of sentence delimiters. The concept terms would consist of all sequences of uncommon words that are uninterrupted by common words. If it is a common word, delete it and place the saved word (from the prior step, if the prior step saved a word) into our list of terms found in the text. If it is an uncommon word, append it to the word we saved in step one and save the two-word term. If it is a sentence delimiter, place any saved term into our list of terms and stop the program. This simple algorithm, or something much like it, is a fast and efficient method to build a collection of index terms. To use the algorithm, you must prepare or find a list of common words appropriate to the information domain of your Big Data resource. This is a somewhat awkward method for a computer to follow, as most programming languages automatically cut text from a file line by line. A computer program has no way of knowing where a sentence begins or ends, unless the programmer finds sentences, as a program subroutine. There are many strategies for determining where one sentence stops and another begins. The easiest method looks for the occurrence of a sentence delimiter immediately following a lowercase alphabetic letter, that precedes one or two space characters, that precede an uppercase alphabetic character. This general pattern (lowercase, period, one or two spaces, uppercase) usually signifies a sentence break. The routine fails with sentences that break at the end of a line or at the last sentence of a paragraph. It might falsely demarcate a sentence in an outline, where a lowercase letter is followed by a period, indicating a new subtopic. Nonetheless, with a few tweaks providing for exceptional types of sentences, a programmer can whip up a satisfactory subroutine that divides unstructured text into a set of sentences. Basically, as you collect each term (as described above), you attach the term to the location at which it was found. This is ordinarily done by building an associative array, also called a hash or a dictionary depending on the programming language used. When a term is encountered at subsequent locations in the Big Data resource, these additional locations are simply appended to the list of locations associated with the term. After the entire Big Data resource has been parsed by your indexing program, a large associative array will contain two items for each term in the index: the name of the term and the list of locations at which the term occurs within the Big Data resource. However, in most cases, the data manger and the data analyst will not be happy with the results. The index will contain a huge number of terms that are of little or no relevance to the data analyst. The terms in the index will be arranged alphabetically, but an alphabetic representation of the concepts in a Big Data resource does not associate like terms with like terms. You will see that the indexer has taken pains to unite related terms under a single subtopic. Individual terms will be linked (cross-referenced) to related terms elsewhere in the index. A good index, whether it is created by a human or by a computer, will be built to serve the needs of the data manager and of the data analyst. The programmer who creates the index must exercise a considerable degree of creativity, insight, and elegance. Here are just a few of the questions that should be considered when an index is created for unstructured textual information in a Big Data resource.
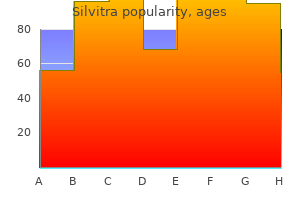
Generic 120 mg silvitra with visa
A real estate property with a known address is matched against crime statistics collected for its listed zip code erectile dysfunction ayurvedic drugs in india purchase silvitra 120 mg without prescription. A planting chart based on a list of popular flowers and vegetables within a locality is matched against a climate zone data set matched to geographic region. In both cases, the comparisons are made for data values held in heterogeneous data sets. In the Big Data era, standards serve to find the data relationships in heterogeneous data sources. Specifications do not force you to include specific types of information and do not impose a specific order on the data contained in the document. The strength of a standard is that it imposes uniformity; the weakness of a standard is that it has no flexibility and impedes innovation. An engineer might want to manufacture a cup with a very wide bottom rim and a narrow top rim, with no handle, with three handles, or with an attached computer chip. If the standard prohibits the bottom rim diameter to exceed the top rim diameter, requires exactly one handle, or has no method for describing ancillary attachments, then the innovator cannot comply with the standard. The strength of the specification is that it is highly flexible; the weakness of the specification is that its flexibility allows designers to omit some of the information required to fully specify the object. In practice, proper implementation of specifications is ensured by usability tests. If everyone seems to understand your implementation of a specification and if your implementation functions adequately and operates with other systems without problems, then the specification has served its intended purpose. New versions may appear, without much notice, and the new versions may not be fully compatible with older versions. Because the glitch is caused by a language incompatibility, not a programming error, you may find the debugging process exasperating. It is easy for a standards committee to create a complex standard or for an organization to develop a specification language that contains thousands of metadata tags. Data managers may be hesitant to stake their resource on tools that they cannot understand. The problem is that Big Data serves many different purposes and must comply with many different standards, all at the same time. After a standard has been created, there follows a Darwinian struggle for supremacy. Standards committees sometimes display group behavior that can be described as antisocial or even sociopathic. If there are other standards in the data domain, they sometimes use coercive methods to force everyone to use their standard. The proponents of a standard may suggest that those who fail to adopt the standard will be ostracized and marginalized by their colleagues. Vendors and Big Data managers select a standard in the full knowledge that a poor choice may bring financial ruin. If the vendor builds a data model to fit a standard, and the standard is not adopted by their market, then they will not be able to sell their software. If a Big Data manager annotates terabytes of data in conformance with an ontology that is soon to be abandoned by its user community, then the value of the resource will plummet. Nevertheless, there can be no excuses for bad behavior; coercion should not be tolerated. Learn how to decompose the standard document into an organized collection of data objects that can be merged with other data object collections or inserted into a preferred data model. It is often best to model your own data in a simple but flexible format that can be ported into any selected standard, as needed. Try your best to use standards that are open source or that belong to the public domain (see Glossary item, Public domain). Brent Scowcroft In 2000, I attended a workshop in San Diego whose purpose was to introduce pathologists to new, standardized protocols for describing different types of cancer specimens. Over the past decade, several groups had been pushing for standards that would ensure that pathology reports prepared in any U. Having a reporting standard seemed like a good idea, but as I looked at the protocols I saw lots of problems. Lists of required items seemed incomplete, and many of the descriptors were poorly defined. The final reports would not be highly reproducible between laboratories or within a single laboratory. I asked the chairman how she planned to deal with producing and controlling new versions of the standard. She replied that because the protocols had been prepared by experts and thoroughly tested by a panel of implementers, there would be no need to develop new versions. More than a decade has passed, during which the standards have been subjected to unceasing modifications. Nomenclatures in every area of science and technology are constantly being updated. Aside from the addition of new terms, old terms must be retired and new coding sequences are sometimes created. Changes in a nomenclature may have a ripple effect, changing the meaning of terms that are not included in the nomenclature. People infected with this organism were said to suffer from the disease known as allescheriasis. When the fungal name was changed, once more, to Pseudallescheria boydii, the 52 disease name was changed to pseudallescheriasis. In this case, changes in the fungal nomenclature necessitate reciprocal changes in every disease nomenclature. Such changes may require months, years, or even decades to adjudicate and finalize in the newer versions of the nomenclatures. Within this period, the term may change again, and the corrected versions of the disease nomenclatures may be obsolete on their release date. The horticultural nomenclature is riddled with naming conventions that date back to specific eras. After 1959, Latin forms were forbidden for cultivar names, but any modern language would suffice. For example, Enterobius vermicularis is called a pinworm in the United States and a threadworm in the United Kingdom, while Strongyloides stercoralis is just the opposite, a threadworm in the United States and a pinworm in the United Kingdom. The only way to escape this transatlantic confusion is to translate the common name of an organism back to its standard Latin binomial. The essay is a must-read for anyone seriously interested in terminologies, but we can examine a few of the points raised by Duncan. Version 2 of the terminology might accommodate the two subtypes: blue teapot and white teapot. The white and the blue teapots, implicitly considered to be made of porcelain, like all china teapots, stand divided across the subtypes. If the teapot is ornamental, then it has no tea-making functionality, and if it cannot be used to make tea, how can it be a teapotfi Must we change our concept of the teapot to include anything that looks like a teapotfi
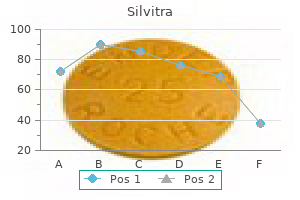
Order 120mg silvitra with visa
Intensive nursing with antibiotics impotence natural remedies buy silvitra 120 mg without prescription, fluid, and electrolyte replacement can prevent early death from this syndrome in human victims of radiation accidents, but these patients may die later 98 due to damage to other organs. The hematopoietic syndrome occurs at doses in the range of 2 to 8 Gy in humans (3 to 10 Gy in rodents) and is caused by severe depletion of blood elements due to killing of precursor cells in the bone marrow. There are substantial differences in the doses required to induce death from the hematopoietic syndrome. Following doses greater than about 2 Gy, humans will develop early nausea and vomiting within hours of irradiation (prodromal syndrome), which may be controlled with 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists. Retreatment tolerance Although tissues may repair damage and regenerate after irradiation, previously irradiated tissues may have a reduced tolerance for subsequent radiation treatments, indicating the presence of residual injury. For early responding tissues there is almost complete recovery in a few months so that a second high dose of radiation can be tolerated. For late-responding tissues the extent of residual injury depends on the level of the initial damage and is tissue dependent. There is substantial recovery in skin, mucosa, spinal cord, and lung over a period of 3 to 6 months, but kidney, heart, and bladder show little evidence of recovery. Clinical studies have demonstrated that retreatment to high doses with curative intent is possible depending on the tissues involved but usually entails increased risk of normal tissue damage. Volume effects As discussed above, the volume of a normal organ that is irradiated often plays a significant role in its sensitivity to irradiation. The effect of volume can be considered in the context of the functional subunits of an organ. Thus tolerance doses change markedly for lung, liver or kidney, if different volumes are irradiated but if a relative small length (~ 20 cm) of the whole cross section of the spinal cord is irradiated to 50-55 Gy (2 Gy fractions) myelopathy may be observed and the tolerance dose changes little as the volume is reduced until it gets below about 5 cm. Recent animal studies suggest that irradiation of part of the cross section of the cord can result in an increase in the tolerance dose. For skin or mucosa, volume is important because depletion of basal stem cells over a larger area of the surface results in a greater requirement for the surviving basal cells to proliferate and migrate to effectively repopulate the whole area prior to desquamation of the outer layers of the organ. If ulceration occurs this may predispose to infection and the development of consequential late effects. The impact of this increased volume receiving a lower dose is currently unknown but has raised concerns about possible second malignancies. Therapeutic ratio (or index) the therapeutic ratio is ill-defined numerically but the concept is that of a comparison between tumour control and normal tissue complications (Figure 3. Tumour-control curves tend to be shallower than those for normal tissue response because of heterogeneity. The therapeutic ratio is often defined as the percentage of tumour cures that are obtained at a given level of normal tissue complications. It remains imprecise, however, because it depends on the shape of the dose-response curves for tumour control and normal tissue complications. The curves shown in the figure depict a situation in which the therapeutic ratio is favorable (A) because the tumour-control curve is displaced to the left of that for normal tissue damage. Because the tumour control curve is shallower than that for normal tissue damage, the therapeutic ratio tends to be favorable only for low and intermediate tumour-control levels. If the two curves are close together (B) or the curve for tumour control is displaced to the right of that for complications, the therapeutic ratio is unfavorable because a high level of complications must be accepted to achieve even a minimal level of tumour control. Time-dose-fractionation It is generally accepted that for conventional radiation therapy the overall patient outcome is improved by fractionating radiation treatments. Many of the underlying biological effects occurring during fractionated radiation treatment have been identified, and the improvement may be explained in terms of the biological response of tissue. Repair the shoulder on a survival curve after single radiation doses is indicative of the capacity of the cells to accumulate and repair radiation damage. If multiple doses are given with sufficient time between the fractions for repair to occur (4 to 24 hrs depending on the cells or tissue involved) the effective survival curves is straight on a semilogarithmic plot and has a shallower slope than the curve for big single doses. The effective slope depends on the size of the individual dose fractions, becoming shallower as the fraction size is reduced (Figure 3. The single dose survival curve for most cells has a finite initial slope apparently due to a (single-hit) non-repairable damage component (Figure 3. At this limit, essentially all the repairable damage is being repaired between each fraction so that the cell killing is due almost entirely to non-repairable events. The fraction size at which this limit is reached is different for different cell populations depending on their repair capacity. When the size of the individual dose fractions is such that the survival is represented by the curvilinear shoulder region of the survival curve, as for most dose fractions used clinically, then repair will be maximal when equal-sized dose fractions are given. Repair kinetics have been estimated in a number of normal (rodent) tissues, and half-times for repair ranged from 0. Thus, repair will be complete in most normal tissues after an interfraction interval of 6 to 8 hours. In the rodent spinal cord, it has been found that the effective repair halftime is greater than 2 hours (it appears to have two components with one component having a halftime of as much as 4 hrs), so repair is not complete even with an interfraction interval of 8 hours. Repopulation In both tumours and normal tissues, proliferation of surviving cells may occur during the course of fractionated treatment. Furthermore, as cellular damage and cell death occur during the course of the treatment, the tissue may respond with an increased rate of cell proliferation. The effect of this cell proliferation during treatment, known as repopulation or regeneration, will be to increase the number of cells during the course of the treatment and reduce the overall response to irradiation. Repopulation is important in reducing acute responses during prolonged treatments, such as those involving a period without irradiation (split-course treatment). Repopulation is likely to be more important toward the end of a course of treatment, when sufficient damage has accumulated (and cell death occurred) to induce a regenerative response. There is evidence that accelerated repopulation can occur in human tumours during the later part of a course of fractionated therapy. The data are consistent with an (accelerated) doubling time of about 4 days for the clonogenic tumour cells, compared to a median volume doubling time of about 2 to 4 months for unperturbed tumour growth. Repopulation of tumour cells during a conventional course of radiotherapy is believed to be an important factor influencing local tumour control in patients with head and neck or cervical cancer. Repopulation provides the biological 101 rationale for accelerating fractionated radiation therapy. Overall treatment time would be expected to be less important for slower-growing tumours such as prostate or breast cancer. When repair occurs between the fractions, the shoulder of the survival curve is repeated for every fraction. Redistribution/recruitment Variation in the radiosensitivity of cells in different phases of the cell cycle results in the cells in the more resistant phases being more likely to survive a dose of radiation. Two effects can make the cell population more sensitive to a subsequent dose of radiation. Some of the cells will be blocked in the G2 phase of the cycle, which is usually a sensitive phase. Some of the surviving cells will redistribute into more sensitive parts of the cell cycle. Both effects will tend to make the whole population more sensitive to fractionated treatment as compared with a single dose. Because redistribution inevitably involves cell proliferation, the survival will also be influenced by repopulation, which reduces the effect of redistribution. Both redistribution and repopulation are important primarily in proliferating cell populations. Also, not all cell lines show large differences in radiosensitivity between cells in different cell cycle phases, and the effect of redistribution will be correspondingly less for these types of cells. In many normal tissues (and probably in some tumours), stem cells can be in a resting phase (G0) but can be recruited into the cell cycle to repopulate the tissue. There is some evidence that cells in cycle are slightly more sensitive to radiation than G0 cells, possibly because G0 cells may repair more potentially lethal damage.
Buy generic silvitra 120 mg online
This type of infection is considered bladder epithelium and prevents colonization impotence kidney order 120mg silvitra mastercard. Tamm-Horsfall protein, adheres to P fimbriae of the micro-organism and prevents colonization. Urine flow and bladder contraction serve to prevent involving parenchyma (pyelonephritis or prostatitis) and statis and colonization. Localisation of infection with segmented cultures of the Pathogenesis lower urinary tract in men. Bacteria in the enteric flora periodically gain access to Positive culture obtained from the first 10 ml of the genitourinary tract. A patient who develops bacteriuria as a result of urine obtained after a prostatic massage, indicates catheterisation should have treatment to re-estabprostatic infection. Antimicrobials used for treatment should be the prostatic massage is then performed per rectally. The safest and least expensive agents to which the patient is then asked to void urine, which is cultured. Relief of clinical symptoms does not always Causes for sterile pyuria indicate bacteriological cure. Biochemical tests for bacteriuria: Two metabolic the ascent is uninhibited as flow of urine occurs within capabilities shared by most bacterial pathogens of the the catheter only. Urinary catheters should be aseptically inserted correctable lesions that obstruct urine flow and cause using proper sterile techniques. Once or twice daily perineal care for catheterised Infants, boys, and men with first episode and girls patients should be done. Nonobstructed gravity flow must be maintained at junction, bladder, and urethra, a voiding cystourethroall times. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (2 tablets of Glom erulopathies 80 mg/400 mg each) every 12 hours. IgA nephropathy dose of specific antibiotics which can penetrate the Secondary glomerulopathies prostate. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis one of the following antibiotics given parenterally F. Asymptomatic bacteriuria: the following special situations warrant drug therapy irrespective of Classification of Nephritic Syndrom e colony count. Selective presence of low molecular weight protein in urine indicates a good prognosis (Fig. Foot process fusion is seen under amyloidosis (90% in children and electron microscope. Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical features include proteinuria, hypertension, M esangial Proliferative Glom erulonephritis azotemia and bacteriuria. They present with microscopic to gross haematuria Pathology and selective or non-selective proteinuria depending on 1. Intercapillary glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelsteilnonresponsive have a poor prognosis, developing renal Wilson disease) is pathognomic. Bacterial (infective endocarditis, sepsis, pneumococcal pneumonia, typhoid fever, second1. Overzealous use of diuretics schistosomiosis) should be avoided as the patients are often intraB. In most cases, the disease is self-limited, although the prognosis is less favourable and urinary abnormalities are more likely to persist in adults. Acute left ventricular failure and pulmonary glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine oedema. Functionally, they may result in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus with polyuria, nocturia, non-anion gap acidosis, salt wasting, and hypo or hyperkalaemia. Hypersensitivity nephropathy this is characterised by persistent urinary abnormalities, 2. Acute loin pain or renal colic due to haemorrhage a combination of analgesics, usually of phenacetin into the cysts. Nocturia, haematuria and urinary infection appear necrosis, sterile pyuria, or renal calculi. Control of hypertension (as hypertension accelerates development of renal failure) Two modes of inheritance are seen: 2. Sodium chloride replacement in patients with polycystic kidney disease and is usually fatal in the inability to conserve sodium. Intrarenal (crystals, calculi, papillary necrosis) this condition comprises of a rapidly rising serum b. Extrarenal (prostate enlargement, pelvic or urea, creatinine and K+, usually (but not invariably) with bladder neoplasm, retroperitoneal neoplasm or anuria or oliguria (< 15 ml/hr). A preserved urine Fractional excreted sodium = output implies a mild disorder and a better prognosis [Urine Na/Serum Na] (Fig. Interstitial pattern dominant recessive nephritis may cause fever, skin eruption and pyuria with 2. It is the initial infection of failure to thrive period of renal hypo-perfusion during which renal cysts ischaemic injury is evolving. Recurrent upper Common May be present urinary tract phase in which renal injury is established with low infection urine output resulting in uraemic complications. Indices Pre-renal Renal (acute tubular necrosis) Com plications Urine osmolality (mOsm/kg) > 500 < 350 Urine sodium (mEq/L) < 20 > 40 1. Hyperphosphataemia (due to decreased excretion) Endogenous nephrotoxins include: 7. Diagnosis is confirmed when renal perfusion improves with volume repletion, improvement in cardiac funcRecovery tion or repair of renal artery stenosis. Postrenal failure may be evident from a distended During the recovery phase, urine volume increases probladder, large prostate, pelvic mass or hydronephrosis. Daily rise in level of blood urea more than 30 mg/dL or a total rise of blood urea more than 1.

Buy 120 mg silvitra fast delivery
However diabetes and erectile dysfunction health buy genuine silvitra on-line, some qualitative differences in the adverse event29 profiles have been identified in indirect comparisons. Aldesleukin (first line) showed a higher rate of headache, dizziness, confusion, hypotension, erythema, thrombocytopenia, pyrexia and pruritus (C0008b)7,26 compared (indirectly) with pazopanib. Interferon alfa (first line) and combined therapy with interferon alfa plus bevacizumab (first line) showed higher rates of nausea and asthenia compared (indirectly) with pazopanib; the combination therapy had a discontinuation rate of 1 out of 4 patients because of proteinuria, headache, haemorrhage and dyspnoea (C0008b)7,26,27. In some of the countries where it is not reimbursed specials arrangements, such as approval on a case by case basis, can lead to reimbursement in exceptional cases. In addition, in many of the countries in which it is reimbursed restrictions (such as indication restrictions) are applicable (A0021). No C0008b C0008b significant differences in two quantitative indirect comparisons. At the time of the clinical cut-off (15 March 2010) 64% of the treatment-naive patients in the best supportive care arm and 34% of those in the pazopanib arm had received further anti-cancer therapies. However, a robust comparison of survival and progression free survival is difficult, and opinions differed among the authoring organisations of this pilot regarding the validity of progression free survival as a surrogate for overall survival in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. There are no studies directly comparing pazopanib with its comparators (except for best supportive care). If the trials included in the evidence synthesis differ, however, and the differences are modifiers of relative treatment effect, the results of the indirect comparison are biased. If the performance status modifies the relative effect, the assumption of similarity is not valid. However clinical trials often differ in design but these differences do not always imply effect modification. The indirect comparisons of safety data need to be treated with particular caution due to the lack of primary safety endpoints in studies, associated multiplicity issues (risk of Type I error), the difficulty of valuing different adverse effects against each other and the differences in followup duration between the different trials. Because the applicability of the body of evidence might differ in different clinical settings (due to differences in the distribution of the effect modifiers), judgements about major limitations of the applicability of individual studies should be made on a national level. It extends progression free survival compared with best supportive care, both in treatment-naive patients (median 8 months longer) and in cytokine pre-treated patients (median 3 months longer). Progression free survival may be considered to be an important intermediate endpoint if it predicts overall survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma or if it is substantiated that healthrelated quality of life in progression free patients is significantly higher than in patients with progression. Compared with sorafenib (second line) there is no evidence of differences in either benefits or harms. Based on these preferences a shortlist of four suitable pharmaceuticals was generated. Exclusion criteria for pharmaceuticals to be selected as the topic of this pilot: 1. A submission file compiled by the market authorisation holder is important basic information for most national rapid assessments of pharmaceuticals. The availability of such a file would, therefore, increase the resemblance of this pilot to daily practice in most countries. There was an additional team for developing the summary of relative effectiveness of pazopanib. The authors of the effectiveness and safety domain were not included in this team because it was considered beneficial for the members have a fresh view on the data. Overview of project phases Identifying Scoping Selecting Planning Assessment Consultations basic relevant domain and reporting documents research methods 1. There was a project manual and the project coordinators provided the domain teams with guidance and tools on how to proceed in each phase of the pilot. Most domain teams complemented the basic search with their own domain-specific searches during the assessment phase (see details in the methods sections of each domain report). Documentation by marketing authorisation holder and European Medicines Agency the submission file for pazopanib (Votrient) was provided by the marketing authorisation holder GlaxoSmithKline to be used specifically in this project. There was no need to create strict inclusion criteria in this phase, in which the requirements related to the type of information and research methodologies were different in all domains. Instead of restricting the search to specific outcomes, comparisons, or methodologies only, any article or document that was considered likely to be helpful for any of the domains was included. Coordinators prepared the first version of the scoping table, which was circulated for comments to all team members, both authors and reviewers, and was discussed in an emeeting. A brief justification was provided for those elements that were regarded as not relevant for this assessment (see Appendix 6 excluded generic questions). The domain teams translated the generic questions they had selected as relevant into answerable research questions. Plan of domain-specific methods the domain teams planned and reported the methodologies they intended to use in the assessment phase, within their particular domain. Instead, the methods sections of each domain report describe the methods actually used in the assessment. Assessment and reporting Preparing the domain reports the domain authors shared the research questions among them and did the assessment and reporting. The results were to be reported in a structured format represented by the result card. One result card contains one research question, the methods for finding the answer to it, and the answer to the question, with references (see Box 3). Additionally, each domain team provided a summary of main findings and a section discussing the work done in their domain. Additionally, coordinators abbreviated the individual domain summaries into even shorter paragraphs and compiled them as part of the report summary. Health problem and current use of the technology Authors: Agnese Cangini, Chris de Laet, Alexander Eisenmann 3. A0003 What are the known risk factors for acquiring advanced and/or metastatic renal carcinomafi A0020 What is the market authorisation status of the technology in different countries, or international authoritiesfi Summary of main results In 2008 kidney cancer was the tenth most common cancer in Europe, and the yearly increase in incidence is about 2%. Renal biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the type1 and grade of malignancy (A0024). In patients with resectable tumours and a good performance status the4 resection of metastases is recommended. In some of the countries where it is not reimbursed special arrangements, such as reimbursement on a case by case basis, can lead to reimbursement in exceptional cases. Moreover the results of the ongoing trials could have an impact on the future penetration of pazopanib. Because of the recent approval and the different time of coverage decisions it was not possible to analyse the variations in use across countries/regions/settings but this could be done when more data on consumption become available. B0010 What kind of data and records (patient level) are needed to monitor the use of the technologyfi If yes, data needs to be synthesised and discrepancies resolved o List of publications of corresponding author (which serves as an indicator of the level of involvement/expertise of the author) o Independently financed studies were preferred. As pazopanib is administered orally44 at a fixed dose it can be given in an outpatient setting. C0002 Was there any relationship between the adverse event rate and the daily dose of pazopanibfi C0005 What safety issues can be suspected in elderly patients or other vulnerable groupsfi C0008a What are the adverse events of pazopanib in renal cancer in comparison with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinibfi Particular attention was paid to head-tohead comparative safety, but placebo-controlled trials were included, as well as observational studies (especially cohorts and case reports) of pazopanib safety to retrieve rare and long-term adverse drug reactions of pazopanib.
Discount silvitra online visa
Common Medications Used in Advanced Cardiac Life Support: EpinephrineAtropine sulfate-Lidocaine-Procainamide hydrochloride-Bretylium tosylatemagnesium sulfate-adenosine-Diltiazem or verapamil-Isoproterenol-Sodium bicarbonate-Calcium 2 erectile dysfunction topical treatment quality 120 mg silvitra. Oxygen therapy: Nasal prongs-venturi masks-Nonrebreathing masks-A continuous positive airway pressure mask-Bilevel positive airway pressure c. Airway Management and Tracheal Intubation: Airway Management-Endotracheal intubation-Surgical airways d. Mechanical Ventilation: Indications-Initiation of mechanical ventilationManagement of problems and complications-Weaning from mechanical ventilationDrugs commonly used during endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation. Recognition and Management: Clinical diagnosis of arrhythmiasElectrocardiographic data-Bradyarrhythmias-premature complexes-Tachycardiab. Evaluation of nutritional assessment indices fi Reference distribution fi Reference limits fi Cutoff points 2. Subjective global assessment the prognostic value of nutritional assessment indices Nephro-Radiological and imaging sciences 1. Psychosocial problems related to dialysis in pediatric patients: Introduction, Adjustment, compliance, neuropsychological development, and rehabilitation. Autonomic Function and hemodynamic stability in EndStage Renal Disease Patients. Donor specific immune tolerance/ Tolerance induction by blockade of co stimulation 11. Treatment of psychiatric problemspreventive therapy-group therapies-environmental Manipulations-psychotherapy-pharmacotherapy-behavioral sexual techniques 3. Behavioral syndromes associated with psychological disturbances and physiological factors m. The dissertation will be guided by one or two members of the faculty of the department. Demonstrate ability to prepare and monitor the patient for Renal Transplantation 4. Assists the hemodialysis assistant in the use of new or modified techniques, dialysis equipment. Educating and training patients on peritoneal dialysis procedures and sterile techniques. Under supervision of the treating nephrologist is responsible to coordinate the care of potential renal transplant patients and donor by facilitating testing, maintaining documents and communicating with transplant coordinators, surgical or anesthesia teams under nephrologist supervision. Coordinates activities of the hemodialysis unit with the other departments/facilities of the organization. Hence, it is imperative to adequately compensate these professionals based on their qualifications and specialties. Despite a huge demand for services from this sector, allied and healthcare sciences is highly fragmented. Although it is estimated that there may be many more courses which are yet to be identified. Considering the lack of regulatory mechanism following 15 core professional groups (accounting for around 44 professions) has been enlisted below (The list is illustrative of the allied and healthcare professions. In future there may be addition or removal of certain professions based on the state of their regulation and standardization). It also needs a mention that most of these professions are not restricted to the professional groups under which they have been categorized, their role may extend to other professional services too. Similarly, the categorization is an indicative categorization, however this may evolve over time based on deeper understanding of the roles and responsibilities of each professional group: 1. Trauma Care Services the above mentioned groups account for over 44 job profiles in the allied and healthcare space, which are as followsA. The split up between theory and practical (bachelor level) proposed is as follows and accordingly the time available during the year could be allocated: st a. Student intake was recommended as one student for each 3-dialysis hemodialysis machines in the unit with a patient load of two shifts of dialysis per day. An in-house preceptor is to be allocated for each of 5 students for supervision of clinical practical, clarifications, counseling and guidance. As far as possible the theory knowledge is to be backed with practical clinical scenarios to develop the needed workforce oriented or job ready knowledge, learning and therapeutic management. Such a skilled pool with also enhance the clinical care of patients due their training background and contribute to improve the clinical skills within a dialysis unit. During internship the allocation of night duties under supervision should be mandatory. Logbook is mandatory and all procedures witnessed or performed under supervision as student needs to be documented in a logbook. A research project is mandatory for the degree candidates and all research projects, thesis and publications to be archived and available online for use by anybody. Standardized online theory session repository is to be developed for access to all candidates across the country once registered with an institution. Dialysis Therapy Technology course such as Transplant coordinator, Vascular Access Coordinator and Nephrology Physician Assistant etc. Thoughts on Self-Directed Learning in Medical Schools: Making Students More Responsible 2005. The impact of treatment transitions between dialysis and transplantation on illness cognitions and quality of life: a prospective study. Prevalence and Demographic and Clinical Associations of Health Literacy in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Mr Anirooddha Mukherjee, Research Assistant For additional details or queries, please contact: 1. To maximize the effectiveness of these Notes, annotate them as you listen to lectures. Many students find that previewing the Notes prior to the lecture is a very effective way to prepare for class. It also affords you the opportunity to map out how the information is going to be presented and what sort of study aids (charts, diagrams, etc. The study of the essential nature of disease, disease processes, and the structural and functional changes in organs and tissues that cause or are caused by disease 3. Tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin are used for routine light microscopic examination. A 27-year-old homeless man comes to the clinic because of a 3-week history of a fever, weight loss, night sweats,shortness of breath, and a cough with blood-tinged sputum. Which of the following is the most appropriate histochemical stain to use for these specimensfi

