Ketoconazole Cream
Cheap ketoconazole cream 15 gm overnight delivery
Preventive measures: Early detection and local treatment of any infection in the mouth antibiotics for uti not penicillin buy ketoconazole cream 15gm fast delivery, oesophagus or urinary bladder of those with predisposing systemic factors (see Susceptibility) to prevent systemic spread. Fluconazole chemoprophylaxis de creases the incidence of deep candidiasis during the rst 2 months following allogenic bone marrow transplantation. Anti fungal agents that are absorbed fully (uconazole, ketocon azole, itraconazole) or partially (miconazole, clotrimazole) from the gastrointestinal tract have been found to be effective in preventing oral candidiasis in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Topical nystatin or an azole (miconazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, ucon azole) is useful in many forms of supercial candidiasis. Oral clotrimazole troches or nystatin suspension are effec tive for treatment of oral thrush. Itraconazole suspension or uconazole is effective in oral and oesophageal candi diasis. Epidemic measures: Outbreaks are most frequently due to contaminated intravenous solutions and thrush in nurseries for newborns. Fatal cases are characterized by the presence of great numbers of parasites in the small intestine together with ascites and pleural transudate. Diagnosis is based on clinical ndings plus the identication of eggs or larval or adult parasites in the stool. Isolated cases have also been reported from Colombia, India, Indonesia, and the Islamic Republic of Iran. Experimentally, infective larvae develop in the intestines of freshwater sh that ingest eggs; monkeys, Mongolian gerbils and some birds fed these sh become infected, the parasite maturing within their intestines. Preventive measures: 1) Avoid eating uncooked sh or other aquatic animal life in known endemic areas. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: Case report by most practi cable means, Class 3 (see Reporting). Epidemic measures: Prompt investigation of cases and con tacts; treatment of cases as indicated. The picture is that of an acute or subacute hepatitis with marked eosinophilia resembling that of visceral larva migrans; the organism can disseminate to the lungs and other viscera. Diagnosis is made by demonstrating eggs or the parasite in a liver biopsy or at necropsy. When ingested by a suitable host, embryonated eggs hatch in the intestine; larvae migrate through the wall of the gut and are transported via the portal system to the liver, where they mature and produce eggs. Spurious infection in humans may be detected when eggs are found in stools after consumption of infected liver, raw or cooked; since these eggs are not embryonated, infection cannot be established. Preventive measures: 1) Avoid ingestion of dirt, directly (pica) or in contaminated food or water or on hands. In the soil, larvae develop in the eggs and remain infective for a year or longer. Infection is acquired mainly by children, through ingestion of infective eggs in soil or in soil-contaminated food or water. Human cases have been recorded from the Islamic Republic of Iran, Morocco and the former Soviet Union; animal infection has been reported in North and South America, Europe, Asia and Australia. Often preceded by a cat scratch, lick or bite that produces a red papular lesion with involvement of a regional lymph node, usually within 2 weeks; may progress to suppuration. Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome (granulomatous conjunctivitis with pretragal adenopathy) can occur after direct or indirect conjunctival inoculation; neurological com plications such as encephalopathy and optic neuritis can also occur. Prolonged high fever may be accompanied by osteolytic lesions and/or hepatic and splenic granulomata. Cat-scratch disease can be clinically confused with other diseases that cause regional lymphadenopathies. Diagnosis is based on a consistent clinical picture combined with serological evidence of antibody to Bartonella. Histopathological examination of affected lymph nodes may show consistent characteristics but is not diagnostic. Pus obtained from lymph nodes is usually bacteriologically sterile by conventional techniques. Apia felis, a previously described candidate organism, plays a minor role if any. Dog scratch or bite, monkey bite or contact with rabbits, chickens or horses has been reported prior to the syndrome, but cat involvement was not excluded in all cases. Needle aspiration of suppurative lymph adenitis may be required for relief of pain, but incisional biopsy of lymph nodes should be avoided. Meyer Director of Publications Terence Mulligan Production Manager Printed and bound in the United States of America Cover Design: Michele Pryor Typesetting: Cadmus Set in: Garamond Printing and Binding: United Book Press, Inc. Minimally symptomatic lesions may occur on the vaginal wall or cervix; asymptomatic infections may occur in women. Diagnosis is by isolation of the organism from lesion exudate on a selective medium incorporating vancomycin into chocolate, rabbit or horse blood agar enriched with fetal calf serum. Most prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, where incidence may be higher than that of syphilis and approach that of gonorrhoea in men. The disease is much less common in temperate zones and may occur in small outbreaks. Beyond the neonatal period, sexual abuse must be considered when chancroid is found in children. Fluctuant inguinal nodes must be aspirated through intact skin to prevent spontaneous rup ture. Epidemic measures: Persistent occurrence or increased inci dence is an indication for stricter application of measures outlined in 9A and 9B above. When compliance with treatment is a problem, consideration should be given to a single dose of ceftriaxone or azithromycin. Empirical therapy to high-risk groups with or without lesions, including sex workers, to clinic patients reporting contact with sex workers, and to clinic patients with genital ulcers and negative darkelds may be required to control an outbreak. Interventions providing peri odic presumptive treatment covering sex workers and their clients have an impact on chancroid and provide valuable information for strategies to eliminate the disease in areas of high prevalence.
Poison Lettuce (Wild Lettuce). Ketoconazole Cream.
- Dosing considerations for Wild Lettuce.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Wild Lettuce work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Whooping cough, asthma, urinary tract problems, cough, hardening of the arteries, insomnia, restlessness, painful periods, muscle and joint pain, and use as a topical antiseptic.
- What is Wild Lettuce?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96360
15gm ketoconazole cream with mastercard
Impact of Male and Female Weight bacteria 5utr 15gm ketoconazole cream with amex, ovarian electrocautery versus gonadotropin Smoking, and Intercourse Frequency on therapy in infertile women with clomiphene Live Birth in Women With Polycystic Ovary citrate-resistant polycystic ovary syndrome; Syndrome. Laparoscopic ovarian diathermy after the impact of a gonadotropin-releasing clomiphene failure in polycystic ovary hormone antagonist on gonadotropin syndrome: is it worthwhile Randomized Trial of a Lifestyle Program Randomized controlled trial comparing in Obese Infertile Women. Controlled with polycystic ovary syndrome: a Ovarian Stimulation Using randomized controlled trial. Fresh versus clomiphene-resistant women with polycystic Frozen Embryos for Infertility in the ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Effectiveness of lifestyle intervention in polycystic ovary syndrome predominantly in subgroups of obese infertile women: a the hyperandrogenic phenotype. Comparison Gonadotrophins versus clomifene citrate between two clomiphene citrate protocols with or without intrauterine insemination in for induction of ovulation in clomiphene women with normogonadotropic resistant polycystic ovary syndrome. Mohammadi Yeganeh L, Moini A, Shiva M, rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, D-chiro-inositol) et al. Methylprednisolone for prevention of for women with polycystic ovary syndrome, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in oligo amenorrhoea and subfertility. Clomiphene citrate plus cabergoline versus Laparoscopic drilling by diathermy or laser clomiphene citrate for induction of ovulation for ovulation induction in anovulatory in infertile euprolactinemic patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. In vitro fertilization, endometriosis, Assisted hatching and intracytoplasmic nulliparity and ovarian cancer risk. Practice patterns and outcomes with the use of single embryo transfer in the United 118. Rashidi M, Aaleyasin A, Aghahosseini M, et hyperstimulation cycles: a randomized trial. A randomized clinical trial to evaluate randomized clinical trial in unexplained optimal treatment for unexplained infertility: infertility. Long-term outcome in couples fertilization-embryo transfer cycles of with unexplained subfertility and an recipients who used shared oocytes versus intermediate prognosis initially randomized those who used altruistic donors. Effects of piroxicam administration on intrauterine insemination cycles: a pregnancy outcome in intrauterine prospective randomized study. Effectiveness of insemination cycles in couples with corifollitropin alfa used for ovarian unexplained infertility. Comparison of Assisted Reproductive Technology and modified agonist, mild-stimulation and Newborn Size in Singletons Resulting from antagonist protocols for in vitro fertilization Fresh and Cryopreserved Embryos Transfer. Use of Letrozole versus Stimulation Improves the Outcomes of In clomiphene-estradiol for treating infertile Vitro Fertilization: A Prospective, women with unexplained infertility not Randomized and Controlled Study. Clinical Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected outcome of intracytoplasmic injection of sperm injection versus conventional spermatozoa morphologically selected under intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a high magnification: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Melanoma risk after Salivary testosterone concentrations in ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization. Hershko-Klement A, Sukenik-Halevy R, associated with intracytoplasmic sperm Biron Shental T, et al. Use ejaculated extreme severe oligo-astheno of Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection and teratozoospermia sperm: a comparative Birth Outcomes in Women Conceiving study. Risk of borderline and invasive ovarian Triggering with human chorionic tumours after ovarian stimulation for in vitro gonadotropin or a gonadotropin-releasing fertilization in a large Dutch cohort. Outcomes less than age 38 years reduces multiple birth of in vitro fertilization with preimplantation rates, but not live birth rates, in United genetic diagnosis: an analysis of the United States fertility clinics. State Insurance Mandates and Multiple Birth Abnormal implantation after fresh and Rates After In Vitro Fertilization. Impact of preimplantation genetic screening on donor oocyte-recipient cycles in the 207. Frozen-thawed embryo transfer in a natural Identification of Future Research Needs in or mildly hormonally stimulated cycle in the Comparative Management of Uterine women with regular ovulatory cycles: a Fibroid Disease. Incorporating stakeholder perspectives in Birthweight in infants conceived through in developing a translation table framework for vitro fertilization following blastocyst or comparative effectiveness research. Practice Committee of the American Society Trends and outcomes for donor oocyte for Reproductive Medicine. A growing number of women also experience infertility secondary to cancer 12-14 treatment. Treatment Strategies Treatment options are usually dependent on the underlying etiology of infertility. However, there is a growing consensus that live birth is the most 22, 23 important patient-centered outcome. Trade-offs in outcomes (particularly multiple gestations), time to pregnancy, and out-of-pocket costs might be different among the various treatment strategies even if cumulative live birth rates are identical. The literature suggests that observed associations between infertility treatment and female reproductive cancers, particularly ovarian cancer, are likely the result of the underlying infertility rather than treatment itself. There is, however, some uncertainty surrounding some 24-26 cancer outcomes in subgroups of patients. Some adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm birth, are associated with infertility treatment; however, many of the conditions associated with infertility are also associated with 19, 21, 27, 28 these adverse outcomes, complicating assessment of comparative effectiveness. Finally, infertility clearly has an emotional impact, and the comparative effects of infertility treatments on quality of life are an important consideration for both women and men. The utilization and outcomes of infertility treatment differ among different racial and ethnic groups, even after adjusting for insurance 33-36 coverage. In addition, there are complex ethical and legal considerations, 39 including the balance between fair compensation and inducement, and sharing information 40 about donors with recipients. Complexity of Decision Making for Treatments of Infertility Infertility treatment is a topic where decision making is particularly complex for patients, clinicians, and policymakers. Decision making involves both partners (although the intensity and risks of treatment are quite different), consideration of outcomes for both parents and infants over short and long-term time frames, trade-offs between short-term success and long-term adverse outcomes, and in some cases preferences for process as well as outcome. In addition, time is an important consideration, particularly for women aged 35 and older. There is clear variation in patient preferences for different treatments and outcomes, and there has been relatively little empirical work focused on the decision-making aspects of infertility treatment. There are large differences in the costs of different infertility treatments and variation in the degree of coverage for infertility diagnosis and treatment, and many patients face significant out 41 of-pocket costs. There is substantial evidence that the availability of coverage affects access to 42-45 treatment and treatment choices. Time lost from work may also be a consideration (particularly in the context of the need to make out-of-pocket payments). There are a number of areas where controversy or uncertainty about the evidence adds to the difficulty of decision making. Limitations of the Evidence Base Methodological limitations of the literature contribute to the uncertainty. In addition, mechanisms for capturing outcomes from patients who receive care at multiple clinics have been put into place. For all questions, we consider only treatment options begun after completion of a diagnostic evaluation. What are the comparative safety and effectiveness of available treatment strategies for couples with male factor infertility and no evidence of an underlying diagnosis associated with infertility in the female partner The figure illustrates how a wide range of treatments for infertility may result in intermediate outcomes such as time to pregnancy and/or final outcomes such as live birth (single or multiple) or costs in couples with different underlying causes of infertility. Short and long-term adverse effects may occur at any point during treatment and may affect donors, patients, and/or children. Optimal treatment strategies may vary by important patient characteristics and/or by setting/provider. Organization of this Report the remainder of the report details our methodology and presents the results of our literature synthesis, with summary tables and strength of evidence grading for major comparisons and outcomes. In the discussion section, we offer our conclusions, summarized findings, and other information that may be relevant to translating this work for clinical practice and future research.
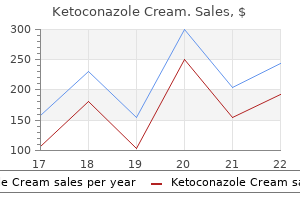
Best order ketoconazole cream
Gestational hypertension in pregnancies supported by infertility treatments: role of infertility bacteria taxonomy purchase on line ketoconazole cream, treatments, and multiple gestations. Progesterone luteal support after ovulation induction and intrauterine insemination: a systematic review and meta-analysis. A comparison of live birth rates and perinatal outcomes between cryopreserved oocytes and cryopreserved embryos. Endometrial infusion of human chorionic gonadotropin at the time of blastocyst embryo transfer does not impact clinical outcomes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. In vitro fertilization outcomes in women with surgery induced diminished ovarian reserve after endometrioma operation: Comparison with diminished ovarian reserve without ovarian surgery. Is frozen embryo transfer cycle associated with a significantly lower incidence of ectopic pregnancy Neonatal outcomes after early rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection: an analysis of a 5-year period. Cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorders, and developmental delay in children born after assisted conception: a systematic review and meta analysis. Obstetric and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies conceived with embryos cultured in a time-lapse monitoring system. Propofol or thiopental sodium in patients undergoing reproductive assisted technologies: Differences in hemodynamic recovery and outcome of oocyte retrieval: A randomized clinical trial. Effect of ethnicity on live birth rates after in vitro fertilisation or intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment. Vascular endothelial growth factor antagonist reduces the early onset and the severity of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Use of fertility drugs and risk of uterine cancer: results from a large Danish population-based cohort study. Use of fertility drugs and risk of ovarian cancer: Danish Population Based Cohort Study. Risk of breast cancer after exposure to fertility drugs: results from a large Danish cohort study. Birth defects in assisted reproductive technology and spontaneously conceived children: A meta-analysis. The Groningen assisted reproductive technologies cohort study: developmental status and behavior at 2 years. Trends and correlates of good perinatal outcomes in assisted reproductive technology. The freezing method of cleavage stage embryos has no impact on the weight of the newborns. Male gender explains increased birthweight in children born after transfer of blastocysts. Uterine flushing with supernatant embryo culture medium in vitrified warmed blastocyst transfer cycles: a randomized controlled trial. Perinatal morbidity after in vitro fertilization is lower with frozen embryo transfer. Premature birth, low birth weight and birth defects after assisted reproductive therapies. Results of the Fast Track and Standard Treatment Trial and the Forty and Over Treatment Trial, two prospective randomized controlled trials. Costs of infertility treatment: results from an 18-month prospective cohort study. Pregnancy complications and neonatal outcomes in multiple pregnancies: A comparison between assisted reproductive techniques and spontaneous conception. Treatment period and medical care costs to achieve the first live birth by assisted reproductive technology are lower in the single embryo transfer period than in the double embryo transfer period: a retrospective analysis of women younger than 40 years of age. Assisted reproduction using donated embryos: outcomes from surveillance systems in six countries. Congenital malformations in singleton infants conceived by assisted reproductive technologies and singleton infants by natural conception in Tehran, Iran. Evaluation of the growth process of infants conceived by assisted reproductive techniques at royan institute from birth to 9 months. The risk of female malignancies after fertility treatments: a cohort study with 25-year follow-up. Parental Infertility, Fertility Treatment, and Childhood Epilepsy: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Matched-samples comparison of intramuscular versus vaginal progesterone for luteal phase support after in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Resource allocation of in vitro fertilization: a nationwide register-based cohort study. Cognitive development of singletons born after intracytoplasmic sperm injection compared with in vitro fertilization and natural conception. Economic consequences of overweight and obesity in infertility: a framework for evaluating the costs and outcomes of fertility care. Complications and outcome of assisted reproduction technologies in overweight and obese women. Long-term pediatric skin eruption-related hospitalizations in offspring conceived via fertility treatment. Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an effective oral alternative for preventing premature luteinizing hormone surges in women undergoing controlled ovarian hyperstimulation for in vitro fertilization. Evaluation of the effect of indomethacin and piroxicam administration before embryo transfer on pregnancy rate. Oocyte retrieval at 140-mmHg negative aspiration pressure: A promising alternative to flushing and aspiration in assisted reproduction in women with low ovarian reserve. Luteal phase support with decapeptyl improves pregnancy outcomes in intracytoplasmic sperm injection with higher basal follicle-stimulating hormone or lower mature oocytes. Absolute position versus relative position in embryo transfer: A randomized controlled trial. Is the use of donor sperm associated with a higher incidence of preeclampsia in women who achieve pregnancy after intrauterine insemination The effect of legislation on outcomes of assisted reproduction technology: lessons from the 2004 Italian law. Follicle-stimulating hormone administered at the time of human chorionic gonadotropin trigger improves oocyte developmental competence in in vitro fertilization cycles: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Asian ethnicity and poor outcomes after in vitro fertilization blastocyst transfer. Frozen blastocyst embryo transfer using a supplemented natural cycle protocol has a similar live birth rate compared to a programmed cycle protocol. Effect of male body mass index on clinical outcomes following assisted reproductive technology: a meta-analysis. Efficacy of letrozole and clomiphene in patients with multiple-cause infertility undergoing intrauterine insemination. The socio-economic conditioning of difficulties in adaptation to pregnancy following assisted reproductive techniques. No advantage of fresh blastocyst versus cleavage stage embryo transfer in women under the age of 39: a randomized controlled study. Incidence and potential causes affecting monozygotic twin formation following in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer. Clinical outcomes following cryopreservation of blastocysts by vitrification or slow freezing: a population-based cohort study. Assisted Reproductive Technology and Birth Defects: Effects of Subfertility and Multiple Births. Effect of delayed initiation of gonadotropin in luteal long protocol on in vitro fertilization. Maternal medication and herbal use and risk for hypospadias: data from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study, 1997-2007.
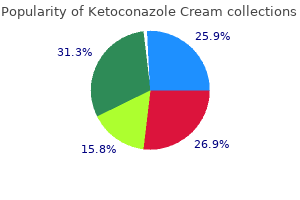
Buy ketoconazole cream 15 gm without prescription
The following sections highlight the primary uses and methods for selecting this equipment antibiotics chicken cheap 15 gm ketoconazole cream visa. The selection of glove type for non-surgical use is based on a number of factors, including the task that is to be performed, anticipated contact with chemicals and chemotherapeutic agents, latex sensitivity, sizing, and facility policies for creating a latex-free environment17, 732-734. For contact with blood and body fluids during non-surgical patient care, a single pair of gloves generally provides adequate barrier protection734. While there is little difference in the barrier properties of unused intact gloves736, studies have shown repeatedly that vinyl gloves have higher failure rates than latex or nitrile gloves when tested under simulated and actual clinical conditions731, 735-738. For this reason either latex or nitrile gloves are preferable for clinical procedures that require manual dexterity and/or will involve more than brief patient contact. It may be necessary to change gloves during the care of a single patient to prevent cross-contamination of body sites559, 740. When applying Standard Precautions, an isolation gown is worn only if contact with blood or body fluid is anticipated. The routine donning of isolation gowns upon entry into an intensive care unit or other high-risk area does not prevent or influence potential colonization or infection of patients in those areas365, 747-750. Full coverage of the arms and body front, from neck to the mid-thigh or below will ensure that clothing and exposed upper body areas are protected. Several gown sizes should be available in a healthcare facility to ensure appropriate coverage for staff members. Isolation gowns should be removed in a manner that prevents contamination of clothing or skin (Figure). Masks should not be confused with particulate respirators that are used to prevent inhalation of small particles that may contain infectious agents transmitted via the airborne route as described below. Last update: July 2019 Page 53 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and eyes are susceptible portals of entry for infectious agents, as can be other skin surfaces if skin integrity is compromised. The protective effect of masks for exposed healthcare personnel has been demonstrated93, 113, 755, 756. Procedures that generate splashes or sprays of blood, body fluids, secretions, or excretions. Healthcare facilities may find that different types of masks are needed to meet individual healthcare personnel needs. Newer styles of goggles may provide better indirect airflow properties to reduce fogging, as well as better peripheral vision and more size options for fitting goggles to different workers. Whether this was due to preventing hand-eye contact or respiratory droplet eye contact has not been determined. Disposable or non-disposable face shields may be used as an alternative to goggles759. Face shields extending from chin to crown provide better face and eye protection from splashes and sprays; face shields that wrap around the sides may reduce splashes around the edge of the shield. Removal of a face shield, goggles and mask can be performed safely after gloves have been removed, and hand hygiene performed. Respiratory protection currently requires the use of a respirator with N95 or higher filtration to prevent inhalation of infectious particles. Information on various types of respirators may be found at [This link is no longer active: The optimal frequency of fit testng has not been determined; re-testing may be indicated if there is a change in Last update: July 2019 Page 55 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) facial features of the wearer, onset of a medical condition that would affect respiratory function in the wearer, or a change in the model or size of the initially assigned respirator12. That recommendation has been maintained in two successive revisions of the Guidelines for Prevention of Transmission of Tuberculosis in Hospitals and other Healthcare Settings12, 126. Since the majority of healthcare personnel have natural or acquired immunity to these viruses, only immune personnel generally care for patients with these infections774-777. This is an acceptable practice providing the respirator is not damaged or soiled, the fit is not compromised by change in shape, and the respirator has not been contaminated with blood or body fluids. The prevention of sharps injuries has always been an essential element of Universal and now Standard Precautions1, 780. These include measures to handle needles and other sharp devices in a manner that will prevent injury to the user and to others who may encounter the device during or after a procedure. This has included focusing attention on removing sharps hazards through the development and use of engineering controls. These include keeping gloved and ungloved hands that are contaminated from touching the mouth, nose, eyes, or face; and positioning patients to direct sprays and splatter away from the face of the caregiver. The performance of procedures that can generate small particle aerosols (aerosol-generating procedures), such as bronchoscopy, endotracheal intubation, and open suctioning of the respiratory tract, have been associated with transmission of infectious agents to healthcare Last update: July 2019 Page 57 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) personnel, including M. Use of a particulate respirator is recommended during aerosol-generating procedures when the aerosol is likely to contain M. Of these, single patient rooms are prefered when there is a concern about transmission of an infectious agent. In the absence of obvious infectious diseases that require specified airborne infection isolation rooms. When there are only a limited number of single-patient rooms, it is prudent to prioritize them for those patients who have conditions that facilitate transmission of infectious material to other patients. In the absence of continued transmission, it is not necessary to provide a private bathroom for patients colonized or infected with enteric pathogens as long as personal hygiene practices and Standard Precautions, especially hand hygiene and appropriate environmental cleaning, are maintained. Some studies have shown that being in the same room with a colonized or infected patient is not necessarily a risk factor for transmission791, 803-805. However, for children, the risk of healthcare-associated diarrhea is increased with the increased number of patients per room806. Thus, patient factors are important determinants of infection transmission risks, and the need for a single-patient room and/or private bathroom for any patient is best determined on a case-by-case basis. Cohorting is the practice of grouping together patients who are colonized or infected with the same organism to confine their care to one area and prevent contact with other patients. Assigning or cohorting healthcare personnel to care only for patients infected or colonized with a single target pathogen limits further transmission of the target pathogen to uninfected patients740, 819 but is difficult to achieve in the face of current staffing shortages in hospitals583 and residential healthcare sites820-822. Furthermore, the inability of infants and children to contain body fluids, and the Last update: July 2019 Page 59 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) close physical contact that occurs during their care, increases infection transmission risks for patients and personnel in this setting24, 795. Signs can be posted at the entrance to facilities or at the reception or registration desk requesting that the patient or individuals accompanying the patient promptly inform the receptionist if there are symptoms of a respiratory infection. Placement of potentially infectious patients without delay in an examination room limits the number of exposed individuals. Patients with underlying conditions that increase their susceptibility to infection. In home care, the patient placement concerns focus on protecting others in the home from exposure to an infectious household member. Persons who are not part of the household may need to be prohibited from visiting during the period of infectivity. For example, if a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis is contagious and being cared for at home, very young children (<4 years of age)833 and immunocompromised persons who have not yet been infected should be removed or excluded from the household. Transport of Patients Several principles are used to guide transport of patients requiring Transmission-Based Precautions. In general, these procedures do not need to be changed for patients on Transmission-Based Precautions. Also, increased frequency of cleaning may be needed in a Protective Last update: July 2019 Page 61 of 206 Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings (2007) Environment to minimize dust accumulation 11. Special recommendations for cleaning and disinfecting environmental surfaces in dialysis centers have been published 18. In all healthcare settings, administrative, staffing and scheduling activities should prioritize the proper cleaning and disinfection of surfaces that could be implicated in transmission.
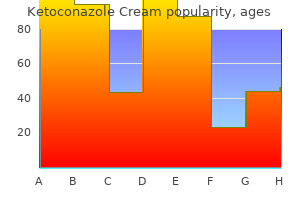
Quality 15 gm ketoconazole cream
Sub therapeutic levels of the antimicrobial agents may be a result of noncompliance antibiotics to treat kidney infection cheap ketoconazole cream 15 gm without a prescription, malabsorption, suboptimal drug metabolism, and resistant uropathogens unre sponsive to attempted therapy [3]. In these cases, infection typically resolves after altering the therapy according to antimicrobial sensitivities determined by a proper urine culture. Bacterial persistence and reinfection occur after sterilization of the urine has been documented. In the case of bacterial persistence, the nidus of infection in the urinary tract is not eradicated. The uropathogen frequently resides in a location that is shielded from antimicrobial therapy. These protected sites are often anatomic abnormalities, including infected urinary calculi [4], necrotic papillus [5], or foreign objects, such as an indwelling ureteral stent [6, 7] or urethral catheters [8], which once infected may not be sterilized. Identification of the anatomic abnormality is essential because surgical intervention (extirpation) may be nec essary to eradicate the source of infection (Box 1). Rarely, a fistula between the urinary tract and gastrointestinal tract serves as the source of reinfection [11]. Serotyping (or careful examination of antimicrobial pediatric urinary tract infections 381 Box 1. Similar to bacterial persistence in abnormal conditions with rein fection such as fistulae, surgery may be necessary to correct the source of infec tion (Box 1). Inpatient hospital costs for children with pyelonephritis total more than $180 million per year in the United States [14]. In immunocompromised children and children with indwelling catheters, Candida may be isolated from the urine [22]. Nosocomial infections are typically more difficult to treat and are caused by various organisms, including E. Pathogenesis Bacterial clonal studies strongly support entry into the urinary tract by the fecal-perineal-urethral route with subsequent retrograde ascent into the bladder [10]. In girls, the moist periurethral and vaginal areas promote the growth of uropathogens. The shorter urethral length increases the chance for ascending infection into the urinary tract. Once the uropathogen reaches the bladder, it may ascend to the ureters and then to the kidneys by some as-yet undefined mechanism. Additional pathways of infection include nosoco mial infection through instrumentation, hematogenous seeding in the setting of systemic infection or a compromised immune system, and direct extension caused by the presence of fistulae from the bowel or vagina. The urinary tract (ie, kidney, ureter, bladder, and urethra) is a closed, normally sterile space lined with mucosa composed of epithelium known as transitional cells. This washout effect of the urinary flow usually clears the pediatric urinary tract infections 383 Box 2. The urine itself also has specific antimicrobial characteristics, including low urine pH, polymorphonuclear cells, and Tamm Horsfall glycoprotein, which inhibits bacterial adherence to the bladder mucosal wall [25]. If uropathogens are cleared 384 chang & shortliffe inadequately by the washout effect of voiding, then microbial colonization potentially develops. Colonization may be followed by microbial multiplication and an associated inflammatory response. To promote survival, various uropathogens possess siderophore sys tems capable of acquiring iron, an essential bacterial micronutrient, from heme [34]. Uropathogenic strains of E coli have a defensive mechanism that consists of a glycosylated polysaccharide capsule that interferes with phagocytosis and complement-mediated destruction [35]. This susceptibility has been attributed to an incompletely developed im mune system [36]. Breastfeeding has been proposed as a means of supplementing the immature neonatal immune system via the passage of maternal IgA to the child [37], providing the presence of lactoferrin [38], and providing the effect of anti-adhesive oligosaccharides [39]. Bacteriuria is 10 to 12-fold more common during the first 6 months of life for uncircumcised boys [9, 16]. Although the available data associate a medical benefit and economic benefit [9] to neonatal circumcision, previously conducted clinical studies have been criticized for potential selection and sampling bias [44]. The flora of the colon and urogenital region is a result of native host immunity, existing microbial ecology, and the presence of microbe-altering drugs and foods. A recent investigation by Schlager and colleagues [12] sup ported the theory that a subset of the colonic microflora expressing particular virulence factors is most likely to infect the urinary tract. Infections associated with urinary tract malformation generally appear in children younger than 5 years of age. Surgical intervention may be required to correct the anatomic abnormality (see Box 1). These urinary tract malformations increase the likelihood that infections of the lower urinary tract (ie, bladder and urethra) will ascend to the upper tracts with possible pyelonephritis and potential renal deterioration [48]. Importantly, children with known urinary malformation may be on chronic antimicrobial prophylaxis. Inability to empty the bladder, as in the case of neuro genic bladders, frequently results in urinary retention, urinary stasis, and subopti mal clearance of bacteria from the urinary tract. Clean intermittent catheterization is helpful for emptying the neurogenic bladder, but catheterization itself may introduce bacteria to this normally sterile space. Uropathogenic strains of E coli also are more likely to be shared during sexual intercourse than commensal E coli [57]. The physical examination is pediatric urinary tract infections 387 also frequently of limited value because costovertebral angle and suprapubic tenderness are not reliable signs in the pediatric population. In older children younger than 2 years, the most common symptoms include fever, vomiting, anorexia, and failure to thrive [60]. Abdominal pain and fever were the most common presenting symptoms in children between 2 and 5 years of age [62]. After 5 years, the classic lower urinary tract symptoms, including dysuria, urgency, urinary frequency, and costovertebral angle tenderness, are more common [62]. Regardless of age, all children should have their sacral region examined for dimples, pits, or a sacral fat pad, because the presence of these signs is associated with neurogenic bladder. In all boys, a scrotal examination should be performed to evaluate for epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis. Urine, which should be obtained before the initiation of antimicrobial therapy, can be collected by various methods. The simplest and least traumatic method is via a bagged specimen, which involves attaching a plastic bag to the perineum. Clinicians, however, are discouraged from obtaining a urine specimen in this fashion because there is an unacceptably high false-positive rate of 85% or higher [60]. The catheterized specimen is considered reliable provided that the initial portion of urine that may be contaminated by periurethral organisms is discarded. The disadvantage of urethral catheterization is that it is invasive and periurethral organisms may be introduced into an otherwise sterile urinary tract. Suprapubic aspiration is considered the gold standard for accurately identifying bacteria within the bladder. The culture information should be interpreted in the context of the clinical scenario when determining the appropriate therapy. Because urine culture typically requires at least 24 hours of incubation, urinalysis and urine microscopy are often used to guide initial empiric therapy. Under high-power magnification, the presence of bacteria represents approx A 4 imately 3 10 bacteria/mL [48]. Urine microscopy, however, cannot distinguish a uropathogen from contaminating bacteria. Hoberman and Wald [66] reported 3 that the positive predictive value of pyuria (10 white blood cells/mm) and bacteriuria is as high as 84. Certain bacteria, particularly gram-negative bacteria, reduce nitrates to nitrites. This test may produce false-negative results if it does not contain the first voided specimen, the bacteria are gram-positive organisms, or there has not been enough time for bacterial metabolism to produce nitrites.
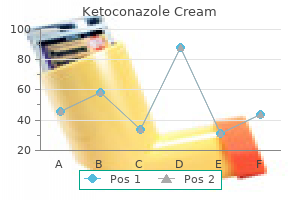
Ketoconazole cream 15 gm amex
Everett Chalmers Hospital pharmacy department in Fredericton for use on request by any facility in the province infection 1 order genuine ketoconazole cream online. If pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine has been previously received then wait 1 year 10 before giving pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate vaccine. A single life time booster of pneumococcal 23-valent polysaccharide vaccine is recommended 5 years 6 after the initial dose. This is despite limited efficacy data and a low overall risk of 6 Haemophilus influenzae sepsis in patients greater than 5 years of age. Booster doses are recommended every 3 5 years in individuals vaccinated at 6 years 6 of age or younger and every 5 years for individuals vaccinated at greater than 6 years of age. In addition, all routine immunizations and yearly influenza vaccination should be given as there are no contraindications to the use of any vaccine in patients with functional or anatomical 6 hyposplenia. When an elective splenectomy is planned, the necessary vaccines are 6 recommended to be given two weeks before removal of the spleen. The following orders will be carried out by a nurse only on the authority of a physician/nurse practitioner. A check box preceding an order indicates the order is optional and must be checked off to be implemented. Adapted with permission from Antimicrobial Handbook-2010 Capital Health, Nova Scotia Approved Sept 2013 47 Splenectomy Information for Patients Role of the spleen: the spleen has many functions, including removal of damaged blood cells. However, you may be at risk of developing infections caused by certain types of bacteria which are normally removed by the spleen. Where malaria is endemic, preventative measures including antimalarial medications, insect repellent and barrier precautions should be used. You may be at risk of developing a serious infection If you notice any signs of infection, including fever, sore throat, chills, unexplained cough, vomiting or diarrhea. Adapted with permission from Antimicrobial Handbook-2010 Capital Health, Nova Scotia Approved Sept 2013 48 Wallet card for Asplenic Patients Please complete card and give to patient on hospital discharge. Breaking the Cycle: Treatment Strategies for 163 Cases of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Disease. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: Update of the Treatment Guidance Document for Clostridium difficile Infection. Best practice in general surgery guideline #4: Management of Intra-abdominal infections. Macrolides, Quinolones and amoxicillin/clavulanate for chronic bronchitis: a meta-analysis. Comparison of First-Line with Second-Line Antibiotics for Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis A Metaanalysis of Randomized Controle Trials. Different durations of corticosteroid therapy for exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. British Thoracic Society Guidelines for the Management of Community Acquired Pneumonia in Adults: Update 2009. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of America for the treatment of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureas infections in adults and children. Short-Course Nitrofurantoin for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis in Women. Short-term Effectiveness of Ceftriaxone single dose in the initial treatment of acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis in women. If severe disease or risk factors for resistance (>65 yo, antibiotics within 30 days, recent hosp, 10% penicillin non-susceptible S. Consider pertussis especially with cough paroxysms, post-tussive emesis, or during known Promote appropriate antibiotic use by labeling acute outbreaks. See references for additional treatment options and other important information especially if early pyelonephritis is suspected. Appropriate antibiotic use for acute respiratory tract infection in adults: Advice for high-value care from the american college of physicians and the centers for disease control and prevention. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Principles of appropriate antibiotic use for acute pharyngitis in adults: Background. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in adults. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of acute bacterial sinusitis in children aged 1 to 18 years. Diagnosis, microbial epidemiology, and antibiotic treatment of acute otitis media in children: A systematic review. Principles of judicious antibiotic prescribing for upper respiratory tract infections in pediatrics. American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on Diagnosis and Management of Bronchiolitis. Imaging tests are no longer recommended for Cannot tolerate oral medication: uncomplicated cases. See references for more details, additional treatment options, including re-treatment after initial treatment failure, supportive care, and other important information. Streptococcal pharyngitis is primarily a disease of children 5-15 yo and is rare in preschool children. See references for more details, additional treatment options, and other important In children and adolescents, negative rapid tests information. These substances are among the top 20 substances leading to death in children <5 yo. Unless hospitalized, neither albuterol nor nebulized racemic epinephrine should be administered to infants and children with bronchiolitis. There is no role for corticosteroids, ribavirin, or chest physiotherapy in the management of bronchiolitis. See references for more details, additional treatment options, and other important information. We will not discriminate either directly or indirectly and will not tolerate harassment or victimisation in relation to gender, marital status (including civil partnerships), gender reassignment, disability, race, age, sexual orientation, religion or belief, trade union membership, status as a fixedterm or part-time worker, socio-economic status and pregnancy or maternity. Consider high-dose nasal corticosteroid (if over Second choice or first 12 years). Lower respiratory tract infections Note: Low doses of penicillins are more likely to select for resistance. Do not use fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin) first line because they may have long-term side effects and there is poor pneumococcal activity. Reserve all fluoroquinolones (including levofloxacin) for proven resistant organisms. Consider a delayed Acute cough and higher risk of complications (at Consider a delayed prescribing strategy face-to-face examination): immediate or backup antibiotic. With Nitrofurantoin advise patient on the risk of pulmonary and hepatic fibrosis, and the 500mg single dose symptoms to report if they develop during when exposed to a treatment. Antibiotic treatment is not routinely needed for Non-pregnant women asymptomatic bacteriuria in people with a urinary and men first choice if catheter. England Gastrointestinal tract infections Topical azoles are more effective than topical 2. Review within 48 hours or sooner if Ciprofloxacin 7days (Locally agreed) symptoms deteriorate. Second line, pregnant, breastfeeding, allergy, or intolerance: azithromycin is most effective. As lower cure rate in pregnancy, test for cure at least 3 weeks after end of treatment. Gonorrhoea Use Ciprofloxacin only If susceptibility is known Access Public Health prior to treatment and the isolate is sensitive to supporting evidence and England ciprofloxacin at all sites of infection.
Syndromes
- Male: 4.7 to 6.1 million cells/mcL
- Prolonged poor appetite
- Delusional behavior
- Pneumonia
- A health care provider should do a complete breast exam every year.
- 1 - 3 years: 340 mcg/day
- Once it is made, store formula in the refrigerator in individual bottles or a pitcher that has a closed lid. During the first month, your baby may need at least eight bottles of formula per day.
Purchase ketoconazole cream overnight delivery
The hypothesis of action of colchicine is that it can block infammasome mediated infammatory and biochemical joint degradation bacteria 2012 discount 15 gm ketoconazole cream free shipping. While two small trials (one comparing colchicine to placebo; one comparing the combination of colchicine and an anti-infammatory medication to the anti-infammatory medication alone) indicate colchicine may provide symptomatic relief (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document), its effcacy and safety remains unproven. In the trials, participants who received colchicine reported more gastrointestinal adverse effects, and the beneft to risk profle needs to be investigated in larger studies. The most commonly reported adverse events encountered with colchicine were gastrointestinal adverse events (eg loose bowel movements, pain in the abdomen), which were usually mild. Methotrexate is a chemotherapy agent and immune system suppressant, which is commonly used to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases (eg rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis). Rationale There is very low-quality evidence from one small trial of 56 participants who used 7. In terms of cost and access, methotrexate is a relatively cheap and widely available. Harms the side effects of methotrexate can include gastrointestinal side effects, haematological abnormalities and elevated liver transaminases. Side effects resulting in discontinuation of the drug vary in frequency from 15% to 17%, but have been shown to reduce to 4% in the second year of treatment. Corticosteroids are medications that mimic the effects of the hormone cortisol, which is produced naturally by the adrenal glands. Cortisol helps to lower the levels of prostaglandins and downplays the interaction between certain white blood cells involved in the immune response. Corticosteroid injections are frequently used for the short-term symptom relief of a fare of joint symptoms or when a rapid reduction in symptoms is required. Rationale the studies upon which the recommendation is based were at serious risk of bias and generally small in size. The overall quality of the evidence was judged to be low to very low (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document). For hip pain, the clinical benefts were demonstrated for up to 12 weeks; however, there is lack of long-term data. In addition, considering the complexity of the hip joint, image guidance would be required, which would further add to the costs. Harms Serious and total adverse events were not signifcantly increased, compared with placebo. However, there are concerns of more rapid cartilage loss with repeated injections with no beneft in long-term symptom outcomes at two years, so these injections should be used judiciously. Hyaluronate is a naturally occurring component of cartilage and synovial fuid, and responsible for the rheologic properties of synovial fuid, enabling it to act as a lubricant or shock absorber. The therapeutic goal of intraarticular hyaluronate administration is to provide and maintain intraarticular lubrication. It has also been reported that hyaluronate exerts anti-infammatory, analgesic and possibly chondroprotective effects on the articular cartilage and joint synovium. For knee pain, function and adverse events, the overall quality of the evidence was judged to be moderate. Despite some inconsistency on the conclusions among the analyses, a positive effect, albeit small and not clinically relevant, was demonstrated for pain and function. No effect on pain nor function was demonstrated, and the risk of total and serious adverse events and local reactions was greater in the viscosupplementation group. In addition, for a hip injection, image guidance would be required, further adding to complexity and cost. However, the increased risk of total and serious adverse events concerned the working group, and when cost and the complexity of the intervention were taken into account, a conditional against recommendation was agreed upon. These reactions usually occur after sensitisation with the second or third injection of a series, or with a repeat treatment course. Platelets contain signifcant amounts of cytokines and growth factors, which are capable of stimulating cellular growth, vascularisation, proliferation, tissue regeneration and collagen synthesis. Rationale the studies upon which the recommendation is based were at serious risk of bias and inconsistency, and were generally small in size (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document). With the concern of potential reporting bias and low-quality data, the benefcial effects are likely to be overinfated. Harms Most common treatment-related adverse events were local swelling and transient regional pain. Stem cells are cells that have the ability to divide and develop into many different types of cell in the body, and can be categorised as pluripotent and multipotent. Rationale the two studies upon which the recommendation is based were at very serious risk of bias and were small in size. The between-group differences reported for pain and function appeared to be remarkably good (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document). Consistent with a recent position statement from the Australian College of Sports and Exercise Physicians, stem cell administration should be part of a rigorously designed study and the priority for individual health and welfare. There are two groups reporting minor adverse events, including mild pain and effusion after the injections, which persisted for no more than seven days. Hypertonic dextrose injection, also termed as prolotherapy, is an injection-based treatment used for a variety of painful chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions. The core practice principle of prolotherapy is injection of relatively small volumes (0. The hypothesised mechanisms for pain relief include stimulation of local healing, reduction of joint instability through the strengthening of stretched or torn ligaments and stimulation of cellular proliferation. No clinically signifcant effects were found for pain at 24 and 52 weeks follow-up. In terms of function, no clinically signifcant effects were found for pain at 24 weeks, but a marginally signifcant effect was recorded at 52 weeks (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document). As prolotherapy is relatively cheap and accessible, it is likely to be injudiciously used. Harms the study reported self-limited bruises after dextrose (n = 3) and saline (n = 5) injections. This was an expected side effect and deemed to be of minimal clinical relevance because of its transient nature. No serious adverse events were reported; however, this may be because the study sample size is not large enough to detect uncommon adverse events. In general, these are readily available and relatively inexpensive ($30 per month per supplement). These supplements are usually taken in the form of an oral capsule on a daily basis. As can be seen in the evidence summary, there is frequently marked heterogeneity in the evidence (Appendix 5 of the Guideline for the management of knee and hip osteoarthritis: Technical document). Individuals should be assisted in making informed decisions by considering the potential and known risks and benefts of the therapies they seek to use to relieve pain. Careful consideration should be given to the available information, and claims of curative potential and marked treatment effects that can be achieved with the use of these agents. It is important to be cautious when advocating for these supplements; however, when someone feels marked therapeutic beneft, do not underestimate the potential for placebo effects, particularly if these are safe and inexpensive. For people who are very enthusiastic about taking complementary and alternative therapies (eg supplements), it is generally advised they do so cognisant of potential side effects and interactions with regular medication use, and to use these for a period of time (eg four to six weeks) and cease if there is no beneft gained. Studies examining the use of supplements are often of low quality constrained by small sample sizes, industry publication bias and potential for positive publication bias. The working group discussed that in the context of low-quality to very low-quality studies, despite some suggestion of benefcial effects, it is prudent to use caution. Boswellia serata, also known as Indian frankincense, is a tree that is native to India and Arabian Peninsula. The resin of Indian frankincense contains substances that may decrease infammation. The working group discussed that, in the context of low-quality to very low-quality studies, despite potential benefcial effects, it is prudent to use caution and advocate that further research is needed before a frm recommendation on Boswellia serrata can be made. There is insuffcient research to recommend a particular dose, and there is concern about variation in the concentration and bio-availability of curcuma in a range of products marketed for arthritis.
Buy cheap ketoconazole cream
Practice Guidelines from the Infectious al program to reduce catheter-associated 18 iv antibiotics for sinus infection order ketoconazole cream 15gm online. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014 pitals: 2014 update. A tar rounds on reducing the unnecessary use urinary catheter use: a qualitative assess geted infection prevention intervention in of urinary catheterization in hospitalized ment of a statewide initiative. A reminder Centers for Disease Control and Preven Enhancing resident safety by preventing reduces urinary catheterization in hospi tion, 2014. Jt Comm J Qual Patient progress-report/hai-progress-report-2014 initiative to reduce catheter-associated Saf 2005; 31:455-62. Many commercial diets are acceptable, but some urinary conditions respond better to specialized diets. Once the urethra becomes completely blocked, the kidneys overweight cats that get little exercise, use an indoor litter box, have are no longer able to remove toxins from the blood or maintain a little or no outdoor access, or eat a dry diet. For example, uroliths and most common diagnosis in cats less than 10 years of age with lower diabetes can increase the risk of urinary tract infection. Diseases such as kidney disease and diabetes are a diagnosis made after all diseases that might cause similar signs are and concentration and presence of crystals, bleeding, inflammation more common in cats older than 10 years of age, and alter the acidity ruled out. These are collections of Urethral Obstruction that result in variable degrees of minerals that form in the urinary tract of cats. These cats strain to will start by addressing any uroliths are calcium oxalate and struvite (magnesium ammonium urinate and produce little or no urine. While a special, stone-dissolving diet can be prescribed to constipated and straining to pass stool, but straining in the litterbox is include feeding only canned food dissolve struvite stones, calcium oxalate stones need to be removed more often a sign of urethral obstruction. Antbiotc streamlining or de-escalaton refers to the process of convertng patents from a broad spec trum antbiotc, which covers several diferent types of disease-causing bacteria to a narrow spectrum 1 antbiotc that targets a specifc infectng organism. Usually, it involves changing or reducing the number of antbiotcs, but occasionally it may require discontnuing therapy completely if no infecton is established. Vital signs may be abnormal and diagnostc exams suggest an infec Table 32-1 provides examples of interventons ton is present. The later can be the human body responds to infecton by triggering a infuenced by previous or current antbiotcs that cascade of reactons to fght the invading organisms. If the correct therapy is being provided, the signs and clinical status, thereby producing signs and patent should begin to stabilize. The normal fora of humans is complex and consists tract of more than 200 species of bacteria and yeasts. Questons should be asked to determine Information whether or not treatment is necessary (see Table 32-4). General Guidelines for Microbiological Signs and Symptoms of Common Testing Infections Knowing how the microbiology laboratory does its In additon to the signs listed in Table 32-2, there are testng can help when interpretng C&S results. A culture with no growth is considered to be a symptoms in any patient who has a presumed or negatve culture. Elements of a Culture and Sensitivity Individual hospital testng practces may vary, but generally susceptbility testng is performed on all Report routne bacterial cultures that are deemed to be posi Pharmacists who are involved in the antbiotc stream tve. However, in most hospitals susceptbility testng lining process must understand how to interpret a C&S is not routnely performed on the following: report. Some Random urine cultures with less than 10, 000 examples are included in Table 32-6. The susceptibility defini tion varies based on the organism and the antibiotic being tested. Today, several assays that employ with these organisms is imperatve in antbiotc stream various technical approaches. The literature indicates that factors that can either change the way a patient implementaton of rapid molecular identfcaton tests responds to a medicaton or that can infuence the within healthcare insttutons should be coupled with medicaton selecton. These factors are listed manner to ensure a signifcant reducton in the tme in Table 32-8. Combining two or more antbiotcs may be neces Features to consider when selecting a rapid sary when treatng certain types of infectons. Others are combined One-tme fee versus lease because a broader spectrum of coverage is needed Licensing and sofware updates in polymicrobial infectons. For example, gentamicin Cost per test is typically added to a beta-lactam antbiotc for the treatment of gram-positve endocardits. Common Bacteria and Antbiotc Treatment Optons Selected Antibiotics with Types of Infections Caused by a, b Bacteria Activity Against this Bacteria this Bacteria Gram positive Enterococcus spp. However, piperacillin/tazobactam together clinician prior to making an interventon.
Buy cheap ketoconazole cream 15gm on line
Control of patient antibiotic resistant uti in pregnancy buy 15 gm ketoconazole cream overnight delivery, contacts and immediate environment; Epidemic measures and Disaster implica tions: See Staphylococcal food intoxication (section I, 9C and 9D). If septicemia, effective antimicrobials (aminoglycosides, third-generation cephalosporins, uoroquinolones, tetracycline). The disease appears 12 hours to 3 days after eating raw or undercooked seafood, especially oysters. One-third of patients are in shock when they present for care or develop hypotension within 12 hours after hospital admission. Three quarters of patients have distinctive bullous skin lesions; thrombocytope nia is common and there is often evidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Over 50% of patients with primary septicemia die; the case-fatality rate exceeds 90% among those who become hypotensive. During warm summer months it can be isolated routinely from most cultured oysters. In immunocompetent normal hosts, infections typically occur after exposure of wounds to estuarine water. Septicaemic disease in hosts with underlying liver disease, severe malnutrition or immunocompetence has, rarely, been associated with V. Vibrio species other than O1 and O139 have never been associated with large outbreaks. The clinical picture of infections with these strains is different from cholera and does not deserve reporting as such. Progression to contig uous tissues is slow, over a period of years, with eventual large verrucous or even cauliower-like masses and lymphatic stasis. Microscopic examination of scrapings or biopsies from lesions shows characteristic large, brown, thick-walled rounded cells that divide by ssion in two planes. Conrmation of the diagnosis should be made by biopsy and attempted cultures of the fungus. Primarily a disease of rural barefoot agricultural workers in tropical regions, probably because of frequent penetrating wounds of feet and limbs not protected by shoes or clothing. Preventive measures: Protect against small puncture wounds by wearing shoes or protective clothing. Clinical complaints may be slight or absent in light infections; symptoms result from local irritation of bile ducts by the ukes. Loss of appetite, diarrhea and a sensation of abdominal pressure are common early symptoms. Rarely, bile duct obstruction producing jaundice may be followed by cirrhosis, enlargement and tenderness of the liver, with progressive ascites and oedema. It is a chronic disease, sometimes of 30 years duration or longer, but rarely a direct or contributing cause of death and often completely asymptomatic. Diagnosis is made by nding the characteristic eggs in feces or duodenal drainage uid, to be differentiated from those of other ukes. In other parts of the world, imported cases may be recognized in immigrants from Asia. During digestion, larvae are freed from cysts and migrate via the common bile duct to biliary radicles. Eggs in feces contain fully developed miracidia; when ingested by a susceptible operculate snail. Parafossarulus), they hatch in its intestine, pene trate the tissues and asexually generate larvae (cercariae) that emerge into the water. On contact with a second intermediate host (about 110 species of freshwater sh belonging mostly to the family Cyprinidae), cercariae penetrate the host sh and encyst, usually in muscle, occasionally on the underside of scales. The complete life cycle, from person to snail to sh to person, requires at least 3 months. Shipments of dried or pickled sh are the likely source in nonendemic areas, as are fresh or chilled freshwater sh brought from endemic areas. International measures: Control of sh or sh products imported from endemic areas. Opisthorchis felineus occurs in Europe and Asia, and has infected 2 million people in the former Soviet Union; O. These worms are the leading cause of cholangiocar cinoma throughout the world; in northern Thailand, rates for the latter are as high as 85/10 000 population. The biology of these atworms, the characteristics of the disease and methods of control are essentially the same as those for clonorchiasis. The primary infection may be entirely asymptomatic or resemble an acute inuenzal illness with fever, chills, cough and (rarely) pleuritic pain. About 1 in 5 clinically recognized cases (an estimated 5% of all primary infections) develops erythema nodosum, most common in Caucasian females and rarest in American males of African origin. Primary infection may heal completely without detectable sequelae; may leave brosis, a pulmonary nodule that may or may not have calcied areas; may leave a persistent thin-walled cavity; or most rarely, may progress to the disseminated form of the disease. An estimated 1 out of every 1000 cases of symptomatic coccidioidomy cosis becomes disseminated. Coccidioidal meningitis resembles tuberculous meningitis but runs a more chronic course. Serial skin and serological tests may be necessary to conrm a recent infection or indicate dissemination; skin tests are often negative in disseminated disease, and serological tests may be negative in the immunocompro mised. It grows in soil and culture media as a saprophytic mould that reproduces by arthroconidia; in tissues and under special conditions, the parasitic form grows as spherical cells (spherules) that reproduce by endospore forma tion. Elsewhere, dusty fomites from endemic areas can transmit infection; disease has occurred in people who have merely travelled through endemic areas. More than half the patients with symptomatic infection are between 15 and 25; men are affected more frequently than women, probably because of occupational exposure. Infection is most frequent in summers following a rainy winter or spring, especially after wind and dust storms. It is an important disease among migrant workers, archaeologists and military personnel from nonendemic areas who move into endemic areas. Since 1991, a marked increase of coccidioidomycosis has been reported in California.
Discount generic ketoconazole cream uk
Infants can remain colonized for sev eral months after birth and after treatment for systemic infection infection on finger buy ketoconazole cream 15gm low price. Intrapartum chemoprophy laxis should be given to all pregnant women identifed as carriers of group B strepto cocci. Colonization during a previous pregnancy is not an indication for intrapartum chemoprophylaxis. Such treatment is not effective in eliminating carriage of group B streptococci or preventing neonatal disease. Women expected to undergo cesarean deliveries should undergo routine culture screen ing, because onset of labor or rupture of membranes can occur before the planned cesarean delivery, and in this circumstance, intrapartum antimicrobial prophylaxis is recommended. If clindamycin susceptibility testing has not been performed, intravenous vancomycin (1 g every 12 hours) should be administered. Antimicrobial therapy is appropriate only for infants with clinically suspected systemic infection. All other maternal antimicrobial agents or durations before delivery are considered inadequate for purposes of neonatal management. Cohorting of ill and colonized infants and use of contact precau tions during an outbreak are recommended. Nutritionally variant streptococci, once thought to be viridans streptococci, now are classifed in the genera Abiotrophia and Granulicatella. Outbreaks and nosocomial spread in associa tion with Enterococcus gallinarum also have occurred occasionally. Groups C and G streptococci have been known to cause foodborne outbreaks of pharyngitis. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of isolates from usually sterile sites should be per formed to guide treatment of infections caused by viridans streptococci or enterococci. Abiotrophia and Granulicatella organisms can exhibit relative or high-level resistance to penicillin. Invasive enterococcal infections, such as endocarditis or meningitis, should be treated with ampicillin if the isolate is susceptible or vancomycin in combination with an ami noglycoside. The role of combination therapy for treating central line-associated bloodstream infections is uncertain. Although most vanco mycin-resistant isolates of E faecalis and E faecium are daptomycin susceptible, daptomycin is approved for use only in adults for treatment of infections attributable to vancomycin resistant E faecalis. Common practice is to maintain precautions until the patient no longer harbors the organism or is discharged from the health care facility. For these patients, early instruction in proper diet; oral health, including use of dental sealants and adequate fuoride intake; and prevention or cessation of smoking will aid in prevention of dental carries and poten tially lower their risk of recurrent endocarditis. Larvae migrate to the lungs and can cause a tran sient pneumonitis or Loeffer-like syndrome. Symptoms of intestinal infection include nonspecifc abdominal pain, malabsorption, vomiting, and diarrhea. This condition, which frequently is fatal, is characterized by fever, abdominal pain, diffuse pulmonary infltrates, and septicemia or meningitis caused by enteric gram-negative bacilli. Transmission involves penetration of skin by infective (flariform) larvae from contact with infected soil. Infections rarely can be acquired from intimate skin contact or from inadvertent coprophagy, such as from ingestion of contaminated food or within institutional settings. Adult females release eggs in the small intestine, where they hatch as frst-stage (rhabditiform) larvae that are excreted in feces. A small percentage of larvae molt to the infective (flariform) stage during intestinal transit, at which point they can penetrate the bowel mucosa or perianal skin, thus maintaining the life cycle within a single person (autoinfection). Because of this capacity for autoinfection, people can remain infected for decades after leaving a geographic area with endemic infection. The use of agar plate culture methods may have greater sensitivity than fecal microscopy, and examination of duodenal contents obtained using the string test (Entero Test), or a direct aspirate through a fexible endoscope also may demonstrate larvae. Gram-negative bacillary meningitis is a common associated fnding in disseminated disease and carries a high mortality rate. Prolonged or repeated treatment may be necessary in people with hyperinfection and disseminated strongyloidiasis, and relapse can occur. Examination of stool for larvae and serum for antibod ies to S stercoralis is recommended in patients with unexplained eosinophilia, especially for those who are immunosuppressed or for whom administration of glucocorticoids is planned. However, organ isms rarely are found in lesions more than 24 hours after treatment has begun. The primary stage appears as one or more painless indurated ulcers (chancres) of the skin or mucous membranes at the site of inoculation. Lesions most commonly appear on the genitalia but may appear elsewhere, depending on the sexual contact responsible for transmission (ie, oral). The polymorphic maculopapular rash is generalized and typically includes the palms and soles. This stage also resolves spontaneously without treatment in approximately 3 to 12 weeks, leaving the infected person completely asymp tomatic. A variable latent period follows but sometimes is interrupted during the frst few years by recurrences of symptoms of secondary syphilis. Latent syphilis is defned as the period after infection when patients are seroreactive but demonstrate no clinical manifestations of disease. The incidence of acquired and congenital syphilis increased dramatically in the United States during the late 1980s and early 1990s but decreased subsequently, and in 2000, the incidence was the lowest since reporting began in 1941. Since 2001, however, the rate of primary and secondary syphilis has increased, primarily among men who have sex with men. Rates of infection remain disproportionately high in large urban areas and in the southern United States. Primary and secondary rates of syphilis are highest in black, non-Hispanic people and in males compared with females. Congenital syphilis is contracted from an infected mother via transplacental trans mission of T pallidum at any time during pregnancy or possibly at birth from contact with maternal lesions. The rate of transmission is 60% to 100% during primary and secondary syphilis and slowly decreases with later stages of maternal infection (approximately 40% with early latent infection and 8% with late latent infection). The World Health Organization estimates that 1 million pregnancies are affected by syphilis worldwide. Polymerase chain reaction tests and immunoglob ulin (Ig) M immunoblotting have been developed but are not yet available commercially. Presumptive diagnosis is possible using nontreponemal and treponemal serologic tests. These tests mea sure antibody directed against lipoidal antigen from T pallidum, antibody interaction with host tissues, or both. Occasionally, a nontreponemal test performed on serum sam ples containing high concentrations of antibody against T pallidum will be weakly reactive or falsely negative, a reaction termed the prozone phenomenon. A reactive nontreponemal test result from a patient with typical lesions indicates a presumptive diagnosis of syphilis and the need for treatment. However, any reactive nontreponemal test result must be confrmed by one of the specifc treponemal tests to exclude a false-positive test result. False-positive results can be caused by certain viral infections (eg, Epstein Barr virus infection, hepatitis, varicella, and measles), lymphoma, tuberculosis, malaria, endocarditis, connective tissue disease, pregnancy, abuse of injec tion drugs, laboratory or technical error, or Wharton jelly contamination when umbili cal cord blood specimens are used. Treatment should not be delayed while awaiting the results of the treponemal test results if the patient is symptomatic or at high risk of infec tion. A sustained fourfold decrease in titer, equivalent to a change of 2 dilutions (eg, from 1:32 to 1:8), of the nontreponemal test result after treatment usually demonstrates adequate therapy, whereas a sustained fourfold increase in titer from 1:8 to 1:32 after treatment suggests reinfection or relapse. The nontreponemal test titer usually decreases fourfold within 6 to 12 months after therapy for primary or secondary syphilis and usu ally becomes nonreactive within 1 year after successful therapy if the infection (primary or secondary syphilis) was treated early.

