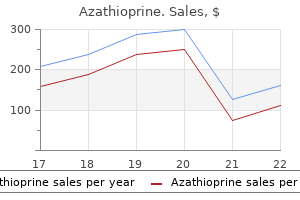
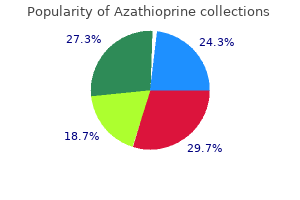
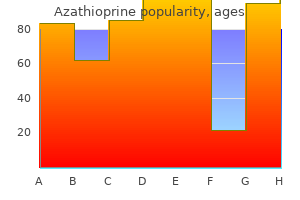
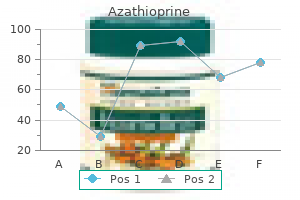
Azathioprine
Generic 50mg azathioprine with amex
This relation is not found in Kuijers review that deals with sub acute and chronic patients populations spasms pregnancy generic azathioprine 50 mg amex. These results are in line with the 353 moderate-quality evidence found in Fayad review for psychological status and depression. Pincus review also found a moderate-quality evidence for the role of somatization, scarce evidence for fear/anxiety, limited evidence for the role 352 of cognitive factors, limited evidence for the role of dysfunctional personality. In summary, this synthesis shows that it is more important to assess psychological factors like distress/depressive mood and to identify tasks with a high physical loading than to look at organizational aspects or social support at work. Physical exercises Exercise therapy encompasses a heterogeneous group of interventions ranging from general physical fitness or aerobic exercise to muscle-strengthening and various types of 138 flexibility and stretching exercises. A summary of evidence has been described in Part I of this study, under section Rehabilitation/Exercise therapy. Modified work and ergonomic workplace adaptations 348, 349, 366, 347 367 Four guidelines and one systematic review deal with modified work. They recognized that ergonomics has a role in formulating modified work to facilitate early 331 return to work. First of all, they recognized that modified work is often part of a multidimensional intervention. So the separate effects of modified work and the other components of the intervention cannot be disentangled. The three predominant categories are (1) light duty or work restriction or adapted job tasks; (2) reduction in the working hours/day and/or working days/week and (3) ergonomic changes to the workplace. Depending on the social system in different countries, modified work can also involve therapeutic return to work (as in Quebec) or work trial. The authors of the New Zealandguideline concluded that if the physical demands of the patients job are high, workplace modifications may be needed (strong evidence). So, occupational practitioners should advise the employer on how to seek specialist occupational health advice, provide a plan for progressive return to work, encourage ongoing contact with work, support a return to activity with pain relief, if needed give advice on monitoring and managing activities that cause pain, finally provide advice on changes to the rate, duration and nature of work. Multidisciplinary treatment programs and other interventions in occupational settings Multimodal treatment programs are based on the bio-psycho-social model of pain, which suggests that physical, psychological and social factors may play a role in decreasing pain 152 and disability and influence positively the return to work. To be considered as multidisciplinary, those programs should include the physical component and at least one of the two other basic components, psychological or social. The review of Tveito et al reached similar conclusions with moderate-quality evidence. Due to some shortcomings in the trials, they concluded that there was only moderate-quality evidence that multidisciplinary rehabilitation, which includes a workplace visit or more comprehensive occupational health care intervention, helps patients to return to work faster, results in fewer sick leaves and alleviates subjective disability. Concordant 371 conclusions were formulated in the Nielson et al systematic review. For those authors, multimodal biopsychosocial treatments that include cognitive-behavioral and/or behavioral components are effective for chronic low back pain and other musculoskeletal pain for up 367 to 12 months (moderate-quality evidence). Less intensive (< 30 hr) interventions did not result in improvements for the clinically relevant outcomes. The authors insisted also on the lack of sufficient data on the cost-effectiveness of the mentioned interventions. The authors conclude that there is a strong evidence for a short term effect of intensive exercise programs (at least if started about 4-6 weeks post-operative) on functional status and faster return to work; at medium term (12 months) however, an intensive program is not better than a moderate one regarding the global clinical improvement of the patients. Also there was no evidence that patients need to have their activities restricted after lumbar disc surgery. It is unclear nevertheless what the exact content of post-surgery rehabilitation should be and the optimal delay before starting it. They concluded that there is strong evidence that intensive multidisciplinary biopsychosocial interventions are effective in terms of return to work, and work-readiness. It is also influenced by psychological distress / depressive mood or social isolation of the worker (moderate-quality evidence) There is low-quality evidence for a possible influence of job satisfaction, stress at work and the various components of the Job Strain model (demands, control, and support). For workers with sub acute low back pain and sick leave for more than 48 weeks, multidisciplinary treatment programs in occupational settings may be an option (moderate-quality evidence). Epidemiological and clinical follow-up studies show that early return to work (or continuing to work) with some persisting symptoms does not increase the risk of re-injury but actually reduces recurrences and sickness absence over the following year. Undue caution will form an obstacle to return to work and lead to protracted sickness absence, which then aggravates and perpetuates chronic pain and disability. They do include to a variable extent; educational components, physical conditioning, some cognitive behavioral components and, for some of them, a structured intervention at the work place or some form of close interrelationship with some partners in the enterprise. This review also stresses that the outcome in terms of return to work is better in interventions combining exercises, functional conditioning and training in lifting techniques with an educational, back school type intervention. This review concluded to a high-quality evidence for the effectiveness on return to work rate at 6 months follow up but the results are conflicting at 12 months. High-quality evidence was also found for the reduction of the number of days of absence from work at 12 months and further between 2 years and 6. Insufficient evidence was observed regarding the impact of supernumerary replacement. Only some sickness funds (mutuelle/mutualiteit) would have specific databases with this link but these were not available for this study. The data related to chronic low back pain are thus included within a larger category dealing with all locomotor system diseases. A recent study shows that the locomotor system diseases are the first cause of invalidity among male workers (28%) and the second one, after mental disorders, in female workers (27%). Among employees, the first cause of invalidity is mental disorders among both men and women. In women the locomotor system diseases are the second cause (19%), while among men they are the third cause (16%) just after cardio vascular diseases. Other Belgian institutions were also considered as having possible data of interest: the institutions dealing with work accidents, those in charge of handicapped people and finally the occupational health services. A personal contact was furthermore taken with the two services known by the authors as having a medical (and not only administrative) database. Regarding the scientific use of data, 7 of the 10 responders agreed that their databases could be used for scientific purposes, 5 services are planning to have a computerized database for their medical data and 3 of them plan to do so within the next 12 months. This database allowed to evaluate the frequency of occupational accidents inducing a back injury and to assess their consequences in terms of sickness absence duration or permanent disability. It was thus possible to identify the low back problems among the medical examinations carried out when returning to work (after at least 28 days sick leave). In the Belgian health system, compensations benefits after work injury are more advantageous than sickness benefits. In the work accident context, the attribution of benefits depends on the decision of the work compensation (private) insurer, while sickness benefits are attributed on the basis of the decision taken by the treating physician: the attribution is automatic and can only be suspended by the medical adviser from the sickness fund. They are nevertheless briefly described hereafter, in order to show their level of validity, usefulness and completeness. It certifies and supports all Walloon institutions which deal with employment, training, and counseling for disabled people. Its mission is to offer the employers a good quality service in terms of training and promoting well being at work for their staff. It involves various departments including risk management, medical follow-up, publication and documentation, research and development. Any analysis would thus imply that a researcher would have to access each selected file (for instance all return to work examinations) on a terminal and encode the described complaint or problem. This means a likely underreporting of minor complaints (with no incidence on the present research) or of major complaints if fear of consequences for the employment and because of recall bias. In conclusion, the analysis of this database, despite the large population source available, was deemed not adequate for the present study. It has been institutionalized by the Royal Decree n? th 66, November 10 1967, as a result of the merging of various institutions having similar roles. An occupational accident is defined as an accident that occurs during and is related to the execution of the employment contract and results in a given body injury (Law on th occupational accidents April 10 1971, Belgian Official Journal). Its specific missions are: x Control of the occupational accident domain: -to control employers with regard to the respect of insurance and occupational accidents declaration -to control insurance companies on technical and medical aspects -to ratify agreements between insurance companies and claimants x Payment of the allocations for workers having an accident which leads to a permanent disability grade lower than or equal to 19%. This institution is an interface between the Social Security and the insurance companies, but it supplies also social assistance to the victims of occupational accidents and other beneficiaries. Their population covers the whole Belgian territory in terms of location of the enterprise (10 provinces); some accidents that occur outside Belgium are also recorded when the victim is employed by an enterprise located in Belgium. The analysis has been restricted to the accidents that occurred at the workplace because they are occupation specific. Those occurring on the way to (or from) work (5% of all occupational accidents on average) have been excluded.
Diseases
- Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
- Opticoacoustic nerve atrophy dementia
- Chromosome 7, monosomy 7q3
- Serum sickness
- Gitelman syndrome
- Bronchiolitis obliterans with obstructive pulmonary disease
- Leichtman Wood Rohn syndrome
- Gen?e-Wiedemann syndrome
Generic azathioprine 50 mg with amex
Safety and tolerability An overview of the results for safety and tolerability can be found in the results tables spasms parvon plus buy generic azathioprine 50 mg on-line. The very common adverse events, occurring in 1 in 10 people or more, are constipation, nausea, dry mouth, dizziness, headache, somnolence, vision blurred and dry skin. Antimuscarinic medicines should be used with caution in elderly patients due to the risk of cognitive impairment. Four people in the oxybutynin group (13%) also reported blurred vision compared with no people in the placebo group. Other adverse events were reported by 1 or fewer people in each group, and included diarrhoea, headache, dizziness and urinary diffculty. It should be noted that participants in this study were specifcally asked about the presence of dry mouth. Other adverse events were constipation and drowsiness, although there were no statistically signifcant differences between the groups. In the oxybutynin group, 7/66 people (11%) reported gastrointestinal complications, compared with 6/74 (8%) in the placebo group. Dry mouth and urinary complications were both reported by 3/66 people (4%) in the oxybutynin group compared with 0/74 (0%) in the placebo group. The dose of oxybutynin used for overactive bladder conditions is generally higher, ranging from 7. Since patients in the hyperhidrosis trials received a lower dose that was gradually titrated up, they may have tolerated oxybutynin better than people taking it for bladder conditions. The results of a quasi- randomised controlled trial involving 140 participants with drug-induced hyperhidrosis are also considered. In addition, all studies used immediate release oral oxybutynin; the relative effcacy and safety profle of modifed release and transdermal patch formulations of oxybutynin for the treatment of hyperhidrosis is not known. All studies were short in duration, ranging from 14 to 42 days, including the titration phase. Small studies may not have suffcient power to detect a treatment effect, and may not be large enough to identify less common adverse events. Although the baseline characteristics recorded were generally similar between the oxybutynin and placebo groups, none of the studies appear to have considered factors which may have affected the degree of hyperhidrosis, such as outdoor or sporting activities and local climate. None of these studies considered the effect of the local climate on hyperhidrosis. In addition to this, the anticholinergic effects of oxybutynin, most notably dry mouth, mean it is possible that participants may have known which treatment they were receiving. This may have further increased the chance of the participants guessing which treatment they were receiving. The scale used by Wolosker for assessing improvement in symptoms does not appear to have been validated. There are no validated objective methods to measure the intensity of hyperhidrosis (Schollhammer et al. It is unclear however, whether the scale used to measure improvements in quality of life in Wolosker et al. It is not clear from the studies whether topical treatments had been ineffective in all participants. It is unclear whether the results of these studies apply to a more general population with hyperhidrosis. An overview of the quality assessment of each included study can be found in evidence tables. Other systemic treatments mentioned in the clinical knowledge summary on hyperhidrosis are clonidine, diltiazem and benzodiazepines. Costs of other treatments See table 3 for the cost of other systemic treatments used for hyperhidrosis. Current or estimated usage No information on oxybutynin for hyperhidrosis was available at the time this evidence summary was prepared. Likely place in therapy Local decision makers need to take safety, effcacy, cost and patient factors into account when considering the likely place in therapy of oxybutynin for hyperhidrosis. The medicine appeared to be well tolerated, although dry mouth was frequently reported. The standard release formulation of oxybutynin, which was used in the studies, is inexpensive. Many people may prefer a topical treatment to risking the adverse effects of an oral treatment. The clinical knowledge summary on hyperhidrosis suggests systemic therapies, including oral antimuscarinics, as treatment options for people whose hyperhidrosis is not adequately managed through lifestyle modifcations and antiperspirants. Other treatments that may be considered include topical therapies (including topical glycopyrronium), iontophoresis, botulinum toxin injections, other systemic therapies (including clonidine, diltiazem, benzodiazepines) and surgery. Other common adverse events include dizziness, nausea, constipation and urinary retention. Many of the participants involved in the studies discussed in this evidence summary had localised hyperhidrosis, which may be more appropriately managed using local treatments including antiperspirants and iontophoresis. Information for the public about medicinesInformation for the public about medicines Evidence summaries provide an overview of the best evidence that is available about specifc medicines. They also give general information about the condition that the medicine might be prescribed for, how the medicine is used, how it works, and what the aim of treatment is. To get a licence, the manufacturer of the medicine has to provide evidence that shows that the medicine works well enough and is safe enough to be used for a specifc condition and for a specifc group of patients, and that they can manufacture the medicine to the required quality. Evidence summaries explain whether a medicine has a licence, and if it does what the licence covers. Off-label means that the person prescribing the medicine wants to use it in a different way than that stated in its licence. This could mean using the medicine for a different condition or a different group of patients, or it could mean a change in the dose or that the medicine is taken in a different way. These include giving information about the treatment and discussing the possible benefts and harms so that the person has enough information to decide whether or not to have the treatment. Questions that might be useful to ask about medicines Why am I being offered this medicine Clinical Autonomic Research 24(6), 297?303 Wolosker N, Schvartsman C, Krutman M et al. Yes bias/qualitybias/quality Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomised See table 8 Can the results be applied in your context (or to the local Yes population) In the placebo group, 1 participant was lost to follow-up and 1 withdrew from the study on day 2. Yes Aside from the experimental intervention, were the groups Yes treated equally Were all of the patients who entered the trial properly accounted Yes for at its conclusion Yes bias/qualitybias/quality c Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomised See key points StudyStudy the study had a short duration limitationslimitations Small study with limited statistical power to detect differences between the groups the quality of life questionnaire used was designed for palmar rather than plantar hyperhidrosis, with only 2/20 questions asking about foot sweating. Placebo controlled study, no active comparator External factors infuencing the degree of sweating were not assessed (for example, outdoor activities or vocational activities) It is not clear whether allocation was concealed a CommentsComments Patient questionnaire assesses the negative impact of hyperhidrosis on quality of life. Yes bias/qualitybias/quality a Was the assignment of patients to treatments randomised Were all of the patients who entered the trial properly Yes accounted for at its conclusion Actas prioritised Dermo-Sifliografcas 107(10), 845?50 (not the best available evidence) Campanati A, Gregoriou S, Kontochristopoulos G, and Offdani A (2015) Study not Oxybutynin for the Treatment of Primary Hyperhidrosis: Current State of the prioritised Art. Pediatric Dermatology 33(3), 327?31 (not the best available evidence) Harmsze A M, Houte Mv, Deneer V H et al. Acta (not the best Dermato-Venereologica 88(2), 108?12 available evidence) Karlsson-Groth A, Rystedt A, and Swartling C (2015) Treatment of Study not compensatory hyperhidrosis after sympathectomy with botulinum toxin and prioritised anticholinergics. International Journal of Dermatology 52(5), prioritised 620?3 (not the best available evidence) Wolosker N, Krutman M, Kauffman P et al. Revista Da prioritised Associacao Medica Brasileira 59(2), 143?7 (not the best available evidence) Wolosker N, Teivelis M P, Krutman M et al. The person is asked 10 questions covering a number of factors including symptoms, embarrassment, activities and relationships. My sweating is intolerable and always interferes with my daily activities A score of 3 or 4 indicates severe hyperhidrosis. Educates healthcare professionals in the aetiology, diagnosis and management of hyperhidrosis. About this eAbout this evidence summaryvidence summary Evidence summaries provide a summary of the best available published evidence for selected new medicines, unlicensed medicines or off-label use of licensed medicines. Anxiety about social liposuction, oral therapy, topical therapy, and 3Department of Outcomes situations and relationships, and problems with daily liv- sympathectomy. Subjective percep- in primary hyperhidrosis is poor, non-randomised, non- doi: 10. This review Previous articles in this aims to provide an update on identifying this condition, with a 15 year delay in presentation to primary care.
Buy azathioprine 50 mg amex
Major anomaly is one with a medical spasms in legs discount azathioprine 50mg, surgical or cosmetic importance and with impact on morbidity and mortality. Minor anomaly is one that does not have a serious surgical, medical or cosmetic significance and does not affect normal life expectancy or lifestyle. The development of the brain and spinal cord is an extremely complicated process which continues into second decade before final maturity is achieved. Furthermore, one third of all congenital abnormalities identified in the perinatal period arise from the central nervous system. These abnormalities are often evident at birth, but some cerebral malformations may not be immediately obvious. The neonates with dysmorphic feature or abnormal neurological behaviour may suggest cerebral malformations, and various imaging techniques are essential for further clarification. It is non-invasive highly sensitive, safe, easily repeatable, accurate and cost effective neuroimaging technique. It is a useful modality for detecting congenital and acquired anomalies of the brain and the most frequently occurring patterns of brain injury in both preterm and full-term neonates. During the late foetal and perinatal period and during early infancy, major maturational processes and growth of the brain take place Ultrasound Diagnosis of Congenital Brain Anomalies 77 (Barkovich et al, 2001; Carty et al 2001). Maturational processes include a major increase in volume, weight, and surface area of the brain; gyration; cell migration; germinal matrix involution; and myelination. Gyration is a phenomenon occurring late during fetal development and can be observed by the second month of intrauterine life. The primary sulci appear as shallow grooves on the surface of the brain that become progressively more deeply infolded and that develop side branches, designated secondary sulci. Gyration proceeds with the formation of other side branches of the secondary sulci, referred to as tertiary sulci. The timing of the appearance of these different types of sulci is so precise that neuropathologists consider gyration to be a reliable estimate of gestational age and consequently a good marker of fetal brain maturation (Figure 1. Comparative sagittal sections show a gyral pattern from 26-38+ weeks of gestation. It is possible to assess the gestation age of the infant from the ultrasound images (Figure. In extremely preterm infants (gestation age from 24?26 weeks), the brain surface is still very smooth and has a lissencephalic appearance. Familiarity with the normal ultrasonographic imaging appearances of the fetal/neonatal cerebral cortex at various stages of gestation is essential for the early detection of abnormal sulcal development. The germinal matrix is an abundant, highly cellular and vascular strip of subependymal tissue. During early gestation it lines the entire wall of the lateral ventricles and third ventricle. It produces neuroblasts and glioblasts and is the origin of migrating neurons (first trimester) and glial cells (second and third trimesters). After 34 weeks, remnants remain in the thalamo-caudate notch and temporal horns of the lateral ventricles. In the foetus and very preterm infant, the lateral ventricles are often wide and asymmetric (usually the left is larger than the right) with very wide occipital horns. The cerebral lateral ventricles have a complex threedimensional architecture that undergoes major developmental changes throughout gestation. Normal sizes of ventricles provide reassurance of the normal development of the neonatal brain. Lateral ventricles are slightly, but significantly, larger in male than in female fetuses. Therefore, it is not surprising that males are found to have borderline ventriculomegaly more frequently, and to have a significantly lesser degree of neurological compromise than females (Pilu et al, 1999). Some investigators failed to demonstrate a difference in the outcome between cases with stable or progressing ventriculomegaly and cases with spontaneous remission (Pilu et al, 1999). Mild ventriculomegaly may be the first sign of abnormal or delayed brain maturation. It is possible that isolated borderline ventriculomegaly may represent the earliest manifestation of brain damage from heterogeneous causes including primary cerebral maldevelopment (e. An additional scan series can be obtained in the axial plane through the temporoparietal bone. This is particularly true when trying to differentiate subdural from subarachnoid fluid in the subarachnoid spaces (Figure 4. Normal surface subdural and subarachnoid spaces in coronal view using a high frequency linear transducer (A) and color Doppler (B). Pulsed and continuous color Doppler neuroimaging are used to assess cerebral blood flow in many pathological states including hypoxic ischemic change and congenital abnormalities. Doppler flow measurements may help to distinguish between vascular structures and non-vascular lesions. Cerebral blood flow accounts for 22%?25% of the cardiac output in neonates and 15% of that in adults (Couture, 2001). Familiarity with the Doppler waveforms characteristic of cerebral arteries and veins in neonates is important for accurate diagnosis of brain abnormalities (Figure 5. Normal color Doppler wave forms from the anterior cerebral artery (A) and the superior sagittal sinus (B). The wave forms may be affected by age- and development-related hemodynamic differences (Chavhan et al, 2008, Romagnol et al, 2006). Values of cerebral blood flow velocities progressive increase with gestation age on consequence of progressive increase cardiac output, blood pressure and closing ductus arterosus (Vasiljevic et al, 2010). Values of Doppler indices (Pourcelot index or the resistance index and Gossling index or the pulsatility index) gradually increase with gestation age in consequence of progressive maturation and opening of vascular cerebral bed with a reduction of the cerebrovascular resistance (Vasiljevic et al, 2008; Deeg & Rupprecht, 1988). After the 3rd day of life, there is a gradual increase in peak systolic velocity and end-diastolic velocity. All cerebral arteries display a low-resistance flow pattern with continuous forward flow during systole and diastole (Figure 5. Because these arteries usually have a diameter of less than 5 mm, the spectral lines are broad and the spectral window is filled. Normal neonatal values and postnatal changes of cerebral blood flow velocities have been reported by several examiners (Deeg & Rupprecht 1989; Romagnol et al, 2006; Vasiljevic et al, 2010). These values we have obtained with color Doppler technique in seventy healthy neonates different gestation age during two years study period. Venous waveforms in the superior sagittal sinus may be continuous and monophasic or may fluctuate in synchronicity with arterial pulsations (Figure 5. Intracranial venous flow velocities gradually increase after birth (Dean & Taylor, 1995). The mean velocity in the superior sagittal sinus usually ranges between 8 and 12 cm/s in neonates. The transverse sinus usually can be assessed in neonates and shows an intracranial venous flow velocity of 2. However, great variations can be seen in flow velocity with factors such as head rotation, crying, and other activities. Cardiac output fluctuates in an unstable neonate, altering carotid artery and cerebral perfusion. Color Doppler imaging is also useful in defining the limit of the arterial system within the subarachnoid space. This helps differentiate fluid in the subdural space from adhesions within the arachnoid space, as the arterial system is confined to the subarachnoid space (Chavhan et al, 2008; Dean & Taylor, 1995) 2. There is a high incidence of spinal abnormalities in babies who have other congenital syndromes (e. In transverse planes or axial planes, the examination of the spine is a dynamic process performed by sweeping the transducer along the entire length of the spine and at the same time keeping in the axial plane of the level being examined. It is lined anteriorly by the ossification center in the body of the vertebrae and posteriorly by the two ossification centers of the laminae (Figure 6. Thoracic and lumbar vertebrae have a triangular shape, while the first cervical 82 Congenital Anomalies Case Studies and Mechanisms vertebrae are quadrangular in shape, and sacral vertebrae are flat.
Purchase azathioprine 50 mg with visa
This tailoring requires careful assessment of patients pain perceptions spasms falling asleep order azathioprine 50mg with mastercard, cognitive and emotional responses, coping skills, and social and environmental status. When access to providers and costs are limiting factors, evidence-based low-cost and scalable approaches delivered through telehealth and internet technologies may provide a low-burden, efective alternative to traditional treatment approaches. Health professionals should have sufcient understanding of the biopsychosocial model of pain and how to appropriately assess and refer patients for behavioral health treatment. Both a need for trained pain psychologists and appropriate incentives are required to fll the work gap. Although several organizations have identifed policy recommendations to close gaps in access to pain management services,287,288 coverage barriers persist. Although the literature exploring the efectiveness of interventions for patients with painful conditions and comorbid psychiatric concerns is limited, research suggests that regular monitoring and early referral and intervention can improve pain and psychiatric outcomes and prevent negative opioid-related outcomes. Conduct regular reevaluation and assessment, with a treatment plan and established goals, to achieve optimal patient outcomes. Individualized, Multimodal, Multidisciplinary Pain Management Medications Restorative Interventional Behavioral Complementary (Opioid and Therapies Procedures Health & Integrative Non-opioid) Approaches Health Figure 15: Complementary and Integrative Health Is One of Five Treatment Approaches to Pain Management 2. For improved functionality, activities of daily living, and quality of life, clinicians are encouraged to consider and prioritize, when clinically indicated, nonpharmacologic approaches to pain management. My right arm was ripped open down to my hand and I had some shrapnel in both of my legs and my left arm. Overall, I had 26 surgeries over 3 1/2 years in the hospital, where I started receiving alternative therapy. After I got out of being an inpatient, I told myself I was going to get of of all my meds and I did that. I watched too many fellow service members, comrades, turn into zombies just being pumped full of medications. If my foot stays down for a long period of time, it gets swollen, and I have limited feeling from my left knee down to my foot. I went through a form of visual and audio therapy and somehow that triggered those nerves to kick back in. I think a combination of acupuncture and digital medicine is, in a sense, the way of the future. Thats what Ive been doing and its worked for me and its worked for many other people. The current opioid crisis has spurred intense interest in identifying efective nonpharmacologic approaches to managing pain. The use of complementary and integrative health approaches for pain has grown within care settings across the United States over the past decades. As with other treatment modalities, complementary and integrative health approaches can be used as stand-alone interventions or as part of a multidisciplinary approach, as clinically indicated and based on patient status. Examples of complementary and integrative health approaches to pain include acupuncture, hands-on manipulative techniques (e. These therapies can be provided or overseen by licensed professionals and trained instructors. The use of complementary and integrative health approaches should be communicated to the pain management team. Overall, most complementary and integrative health approaches can provide improved relief, when clinically indicated, when used alone or in combination with conventional therapies such as medications, behavioral therapies, and interventional treatments, although more research to develop evidence-informed treatment guidelines is needed. The following paragraphs briefy describe complementary and integrative health approaches, which can be considered singularly or as part of a multimodal approach to the management of chronic and acute pain, depending on the patient and his or her medical conditions. This list is not inclusive or exhaustive but instead provides examples of common complementary and integrative health approaches. It involves manipulating a system of meridians where life energy fows by inserting needles into identifed acupuncture points. The therapeutic value of acupuncture in the treatment of various pain conditions, including osteoarthritis; migraine; and low-back, neck, and knee pain has growing evidence in the form of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Massage and manipulative therapies, including osteopathic and chiropractic treatments, are commonly used for pain management. Such interventions may be clinically efective for short-term relief323,324 and are best accomplished in consultation with the primary care and pain management teams. Studies on massage have considered various types, including Swedish, Thai, and myofascial release, but these studies do not provide adequate details of the type of massage provided. Systematic reviews note that the few studies looking at the efect of massage on pain use rigorous methods and large sample sizes. Mindfulness enables an attentional stance of removed observation and is characterized by concentrating on the present moment with openness, curiosity, and acceptance. Yoga has become popular in Western cultures as a form of mind and body exercise that incorporates meditation and chants. Yogas use of stretching, breathing, and meditation has also been therapeutic in the treatment of various chronic pain conditions, especially low-back pain. Modern tai chi has become popular for core physical strengthening through its use of slow movements and meditation. It has demonstrated long-term beneft in patients with chronic pain caused by osteoarthritis and other musculoskeletal pain conditions. Spiritual or religious beliefs can infuence a persons lifestyle, attitudes, and feelings about pain. People living with pain may use religious or spiritual forms of coping, such as prayer and meditation, to help manage their pain. Growing evidence indicates that spiritual practices and resources are benefcial for people with pain. The special populations section in this report was included to highlight several special populations considerations for pain management. The populations highlighted here are not exhaustive, and the special populations section on chronic relapsing conditions is intended to serve as a general category that applies to many painful conditions not specifcally mentioned. The origin of pain conditions in the pediatric age group is important because the developing pediatric nervous system can be especially vulnerable to pain sensitization and development of neuroplasticity. Psychological conditions resulting from chronic disease and pain syndromes can contribute to long-term pain. These psychological conditions can include difculty coping, anxiety, and depression. Incorporation of parents and family into pain care is especially important in the pediatric population because childhood pain can be afected by family and parental factors, including family functioning and parental anxiety, and depression. Overall, there is a substantial need for more trained pediatric pain specialists to address the often complex aspects of pediatric pain. There is a greater challenge in attracting top physicians to further specialize in pediatric pain fellowships, and this aspect of medical education would address an ongoing gap in this area. This limited access is further compromised by lack of reimbursement and coverage for services related to comprehensive pain management, including nonpharmacologic evidence-based pain therapies. However, a risk factor of a medication should not necessarily be an automatic reason not to give this medication to an elderly patient. Clinicians must assess the risk versus beneft of using medications while considering other modalities in this patient population. An estimated 40% of cancer survivors continue to experience persistent pain as a result of treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Persistent pain is also common and signifcant in patients with a limited prognosis, as often encountered in hospice and palliative care environments. Many oncologists and primary care physicians are not trained to recognize or treat persistent pain associated with cancer or other chronic medical problems with limited prognosis. Causes of pain such as recurrent disease, second malignancy, or late-onset treatment efects should be evaluated, treated, and monitored. Women use the health care system as patients, caregivers, and family representatives and can be particularly afected by costs, access issues, and gender insensitivity from health care providers and staf. Several diseases associated with pain ? in particular, chronic high-impact pain ? have a higher prevalence in women or are sex specifc, including endometriosis, musculoskeletal and orofacial pain, fbromyalgia, migraines, and abdominal and pelvic pain. Acute pain fares on top of the chronic pain condition can be a common occurrence that may afect daily routines and overall functionality, resulting in additional morbidity and the need for comprehensive pain care. I struggled with depression for a while and as recently as last February, I went through a period of depression. I would still go out and have fun with my friends, even though I was still going through all this pain. And that was so touching because at that time I didnt believe I was a strong person.
Rauwolfia Serpentina (Indian Snakeroot). Azathioprine.
- How does Indian Snakeroot work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Indian Snakeroot?
- Nervousness, trouble sleeping (insomnia), mental disorders such as schizophrenia, constipation, fever, liver problems, joint pain, spasms in the legs due to poor circulation, mild high blood pressure, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Indian Snakeroot.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96766
Order azathioprine 50mg line
Luckily spasms 1983 order genuine azathioprine, however, most smaller stones and even stones up to 8?10 mm diameter will pass spontaneously in less than two weeks, despite the often incapacitating pain they produce. However, if the stones are located such that they are unlikely to pass into the calyx, the risk for incapacitation during flight is low. If the urinary studies do not reveal any underlying risk factors for recurrent stone formation, then medical certification for aviation duties may be considered. However, environments that predispose to dehydration may encourage renal stone formation without other underlying factors. Haematuria may be the heralding sign for a medical condition, which may not necessarily be an aeromedical disqualifier, but may necessitate an aeromedical evaluation and disposition. Bleeding into the urinary tract from a source between the urethra and the renal pelvis should result in no protein, cells or casts. Haematuria at the beginning or end of the stream may indicate a urethral or prostatic source. Haematuria of any degree should never be ignored and, in adults, should be regarded as a symptom of urological malignancy until proven otherwise. Overall, it is uncommon for a patient with gross haematuria to have an unidentifiable source as opposed to the frequently negative urological examination in patients with microscopic haematuria. Renal parenchyma can be studied with ultra-sonography, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging. Stone eradication for patients with nephroureterolithiasis is necessary; definitive care for malignant or prostatic sources will have to be directed by urologists. Urinary neoplasms are often slow growing but they must be diagnosed and treated early to optimize survival and function. Glomerular disease must be evaluated and renal function assessed to determine proper treatment and to address worldwide aviation duty (e. Urinary incontinence can be subdivided into four categories: continuous, stress, urge, and overflow incontinence. Ectopic ureter and urinary fistulous disease are the predominant aetiologies, both of which warrant surgical remediation. Although stress incontinence is commonly associated with weakened pelvic support of the bladder neck and urethra in females, it may also be seen in males, most often after prostatic surgical procedures. Urge incontinence may be a heralding symptom of malignant or infectious disease since these may cause urothelial irritation. Neurogenic bladder, resultant from multiple aetiologies, can also induce urge incontinence. The diagnosis is often challenging, and the condition may be seen in patients with a chronic unrecognized problem. However, multiparous females and patients with previous pelvic surgeries or radiation or neurological symptomatology may be able to guide the examiner towards the source and type of their incontinence. Recording the situations, number of pads and estimated volumes (by weighing pads) may help bring about an understanding of the patients condition. In addition, objective recordings of intake and output of fluids along with timing may further elucidate the problem. Complete pelvic and 4 neurological examination will assist the clinical diagnosis of incontinence. Further examinations such as the Q-tip test, uroflowmetry, post-void residual assessment, cystoscopy, formal video urodynamics, and an assessment of periurethral and vault supporting structures should be performed. Continuous and stress incontinence typically warrant surgical treatment for definitive care, whereas urge incontinence tends to be best managed by medication. Treatment modalities including behavioural techniques such as biofeedback and pelvic floor exercises may alleviate the need for surgery. Of course, each category of incontinence requires a thorough urological evaluation to ensure adequate necessary care. Most incontinence is not of a degree in itself to warrant aeromedical disqualification and may be conservatively managed in many patients. If the condition requires surgical correction, the operative surgeon must document complete resolution and recovery prior to return to aviation duties. Anticholinergic medications are used for their direct relaxing effects on the smooth detrusor muscle of the bladder (m. These medications are usually well tolerated by most but they may worsen an existing myopia. They may also cause dry mouth, fatigue, constipation and even, on rare occasions, supraventricular tachycardia. Finally, anticholinergic medications will exacerbate closed-angle glaucoma and is an absolute contraindication in such patients. Since these side effects are of concern in the aviation environment, a ground trial is necessary. For similar reasons, any medications or herbal preparations used to treat this malady should be administered in carefully controlled settings and in consultation with the medical assessor of the Licensing Authority. Infections of the urinary system are globally categorized into two broad classifications: complicated and uncomplicated. Thorough urological investigation is mandatory in all but the simplest urinary infections in order to detect any anatomical or physiological pathology. Depending on the anatomical location, chronicity of infection, host factors, and source, an infection can result in incapacitation during flight. This concern is particularly applicable in the face of urinary obstruction, which should always be treated as an emergency which requires immediate intervention. Often a licence holder will have clinically recovered from an acute infection but will require further suppressive drug treatment for an extended period of time. In such cases the medical assessor/examiner will have to decide if the medications used for treatment are compatible with safe flying. Pyuria is defined as the presence of pus (white blood cells) in the urine and is indicative of the inflammatory changes consistent with infection. Bacteriuria without pyuria typically indicates simple bacterial colonization; however, the converse warrants evaluation for tuberculosis, stones or malignancy. For example, the term acute pyelonephritis relates to the inflammatory changes resulting from bacterial infection within the renal parenchyma. Clinical characteristics of this diagnosis include fevers, rigors, flank pain, bacteriuria and pyuria in the setting of infection proven by culture. Severe, complicated infections may produce sepsis, warranting emergent diagnosis and intensive monitoring. Complicated urinary infections may occur in immuno-compromised patients including those with diabetes, or in any patient with obstructed urinary system or aberrant urinary anatomy. At times, intra-renal and peri-renal abscesses may be an endpoint in the evolution of pyelonephritis, potentially warranting operative drainage. Irritative voiding symptoms such as dysuria, frequency, hesitancy and urgency (with or without a component of incontinence) are characteristic of acute cystitis. Prostatic infection may produce similar symptoms as well as obstructive symptoms including nycturia, incomplete voiding, and a weak stream. Urethritis warrants further investigation for sexually transmitted diseases or for anatomical abnormalities. Sexually transmitted diseases tend to occur more commonly in younger, more sexually active individuals. Coliform bacterial urethritis may be seen with complicated urinary fistulous disease or associated with anal intercourse. Rates are higher in men than in women, partially due to the fact that signs and symptoms in men are often more obvious. All patients should have a mid-stream clean-catch collection or catheter collected urinalysis with microscopic studies and urine culture prior to initiation of antimicrobial treatment. Urinary symptoms, pyuria, bacteriuria, and evidence of active inflammatory changes in the urine such as the presence of nitrite and leukocyte esterase may warrant empiric treatment prior to culture and sensitivity reporting. Urinary infection is less likely in the absence of pyuria and may require urine culture data for verification. Conversely, pyuria without bacteriuria may indicate 5 an atypical infectious aetiology such as genito-urinary tuberculosis, staghorn calculi, or other urinary stone disease. Finally, serum leukocytosis and positive blood cultures may indicate a complicated urinary infection in an acutely ill patient. Some helpful studies include intravenous urography, ultrasonography, computed tomography, and cystography. Ultrasonography may aid in the differentiation of epididymitis from testicular torsion. Fullness of the testicular tail with ipsilateral increased epididymo-testicular blood flow indicates the diagnosis of epididymitis.
Purchase discount azathioprine on-line
Recommendation: Nerve Ablation for Mortons Neuroma Nerve Ablation is recommended for Mortons Neuroma infantile spasms 2 year old cheap azathioprine 50 mg free shipping. Strength of Evidence ?Recommended, Insufficient Evidence (I) Level of Confidence - Low 2. Recommendation: Surgical Excision for Mortons Neuroma Surgical excision is recommended for Mortons Neuroma. Indications - select cases where pain and/or debility are significant and changing shoe wear, orthotics and glucocorticoid injection(s) fail to sufficiently control symptoms. Strength of Evidence ?Recommended, Insufficient Evidence (I) Level of Confidence - Moderate Rationale for Recommendations There are no quality sham-controlled trials for any ablative or surgical procedures. Ablative procedures or surgery are recommended in select cases where pain and/or debility are significant and changing shoe wear, orthotics and glucocorticoid injection(s) fail to sufficiently control symptoms. At 1 performing with Average age Transposition month is was 22 either a resection of procedure (T vs. Patients compared with was equally versus diagnosis of follow-up at 3 baseline in both significantly dorsal primary months, 12 groups at all reduced in techniques Mortons months and 33- follow-up periods. These our earlier results were published significant retrospective compared to study on baseline for both Mortons groups (p<0. Plantar dorsal group able to favour the approach Mean age approach group to fully bear dorsal for earlier among (n = 26). Bunions / Hallux Valgus Hallux valgus bunion is a lateral deviation of the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint with respect to the midline of the body, generally defined as over 14. Treatments include nonoperative (avoid tight-fitting or high-heeled shoes, wear wide- toes footwear, and shoe inserts) and operational (distal soft tissue procedures, first metatarsal osteotomies, proximal phalanx osteotomies, fusion, and resection arthroplasties) options. Physical Examination the feet should show valgus deviation of the great toe beyond the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Diagnostic Studies A careful history and physical examination is considered the most important diagnostic approach and in most cases, generally needs no further diagnostic testing for preliminary treatment. However, x-rays are commonly needed to evaluate alternate conditions such as osteoarthrosis, gout and degenerative joint disease. Also, x-rays are useful for measuring angles and surgical planning and are Recommended, Insufficient Evidence (I)]. Use of orthoses for hallux valgus should generally be limited to 1 of 2 conditions: 1) There should be demonstrable hyperpronation or radiographic evidence of hyperpronation with a talar flexion angle of 30 degrees or more on a standing study; or 2) there should be pain localized to the plantar aspect of the hallux metatarsal head with or without bunion pathology. Strength of Evidence ? Recommended, Evidence (C) Level of Confidence - Low Rationale for Recommendation There is one moderate quality trial that found custom orthotics were superior to no treatment over 6 months. Follow-up ability to work, superior to 49?10 years, at 6 months and significant in no control 47?9 1 year after surgery vs. Strength of Evidence ? Not Recommended, Evidence (C) Level of Confidence - Low Rationale for Recommendation One trial suggests a lack of post-operative efficacy and thus low intensity ultrasound is not recommended for treatment of patients having undergone osteotomy for hallux valgus. Placebo Group- Also, no an influence chevron sham significant on outcome 6 osteotomy. Strength of Evidence ? No Recommendation, Insufficient Evidence (I) Level of Confidence - Low Rationale for Recommendation There are no sham-controlled studies. A pragmatic comparative trial found no difference between manual manipulative treatment and a night splint at 1 week, although better outcomes were reported at 1 month and sustainability was not reported. Surgical Considerations Surgical procedures are generally attempted for moderate to severe hallux valgus. These procedures include distal soft tissue procedures, first metatarsal osteotomies, proximal phalanx osteotomies, fusion, and resection arthroplasties) options. Indications ? Select cases of mostly moderate hallux valgus where pain and/or debility are significant and changing shoe wear and orthotics fail to sufficiently control symptoms. However, some evidence suggests better outcomes with milder cases and those cases should have pain clearly localized to the bunion prominence while also demonstrating inadequate relief with shoe wear adjustments. Risk factors are not defined in quality epidemiological studies, but theorized to include biomechanical dysfunction, hereditary factors, high-heeled or poor fitting shoes, and trauma. Non-operative treatments include footwear modifications to improve toe box/room, padding, corticosteroid injections, and orthoses (Thomas 09) are Recommended Insufficient Evidence (I), Level of Confidence ? Low. There are various surgical procedures used (arthroplasty, flexor tendon transfer, flexor tenotomy, extensor tendon lengthening and metatarsophalangeal joint capsulotomy, fusion, and diaphysectomy) interventions. The incidence of ankle fractures has been estimated to be 107 to 184 per 100,000 person years,(625) (Lin 09) and accounts for approximately 9% of all fractures. Ankle Fractures Most ankle fractures are produced by abnormal motion of the talus, which either pushes off, or, by means of ligamentous attachments, pulls off an alveolus. Type B commonly results from external rotation, and is associated with or without tibiofibular ligament Type C are commonly from adduction (C-1), causing mediolateral oblique break above a ruptured tibiofibular ligament. Type C-2 results from abduction and external rotation, producing more extensive interosseous rupture and more extensive fracture high on the fibular. Both of these classification systems are noted to have significant shortfalls and therefore are used as guides rather than absolute rules in determining management course. Isolated medial malleolar fractures and pilon fracture do not fit into the Weber classification system. Further, the Weber Classification has not been found to be an accurate predictor of complex bimalleolar and trimalleolar fractures, and the Lauge-Hansen classification prediction model has been demonstrated to have significant discrepancies of predicted injury with actual injury. A disruption in one place along the ring is generally considered stable, whereas integrity compromise in two locations is unstable and may result in dislocation and poor outcome if not managed appropriately. In general, undisplaced or minimally displaced injuries are treated non-operatively, whereas displaced or unstable injuries are treated operatively. Tibial fractures involving the tibial plafond result from low or high-energy injuries, and can be described with either classification scheme or as a pilon fracture. Pilon fractures of the tibia result from a high-energy injury such as a fall from heights or motor vehicle accident. The resultant high-energy forces are transmitted axially, causing the talus to impact the tibial articular surface, resulting in fracture of the distal tibia. Fibula Fracture Fractures of the fibula are commonly caused by eversion injuries with ankle sprain, and may be in isolation or associated with tibia fractures. The Maisonneuve fracture, considered to be one of the most unstable ankle injuries,(653) (Charopoulos 10) occurs when an external rotational force is applied to the fixed foot. The course of damaged tissue runs from the tibia, fractured at the ankle, up through the interosseous membrane and ends with a fracture of the proximal third of the fibula, and may result in unstable syndesmosis and bony avulsion or disruption of the syndesmotic ligaments. It transfers vertical weight bearing forces to horizontal support structures of the foot through major articulations with the heel and ankle. Fracture of the talus may involve the head, neck, body, or lateral process (snowboarder fracture). These should be suspected when chronic pain, stiffness, weakness or instability continues for weeks to months following ankle trauma. Calcaneus fractures account for 1 to 2% of all fractures in adults, and often occur in industrial workers most typically jumping or falling from heights or involved in motor vehicle accidents. Approximately 8 to 10% of all displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures are bilateral. Fractures of the body are more severe as they are related to disruption of the talonavicular and cuneonavicular joints. Frequent cause of Lisfranc injury is when the patient has their foot on the brake and is involved in a car accident. Metatarsal Fractures Metatarsal fractures are usually the result of inversion injury, fall from height or dropping an object on the forefoot. Fifth metatarsal fractures are characterized by where they occur relative to the tuberosity. Avulsion fractures of the tuberosity are the most common fractures of the proximal 5th metatarsal. Phalangeal Fractures Injuries to the toes are usually secondary to stubbing injuries and direct blows from crush injuries. Initial Assessment It is important that clinicians understand the basic anatomy of the ankle and foot in order to assess injuries. The physician performing an initial evaluation of a patient with ankle injury should seek to identify conditions that require immediate treatment. Conditions that require immediate attention include open fracture, vascular compromise, compartment syndrome, and joint dislocation. Medical History the physician should attempt to obtain detailed information on mechanism of injury, symptoms, previous injury, and pertinent past medical history. Symptoms and the progress of symptoms over time should be documented, including pain at initial injury, ability to continue work activities, and pain quality over time.
Cheap azathioprine 50 mg with amex
The role of serendipity in the evolving indications for Integra dermal regeneration template muscle relaxant exercises buy azathioprine online. Sucessful use of a physiologically acceptable artificial skin in the treatment of extensive burn injury. Observations on the development and clinical use of artificial skin: An attempt to employ regeneration rather than scar formation in wound healing. Effect of Keratinocyte Seeding of Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Membranes on the Regeneration of Skin in a Porcine Model. The use of artificial dermis in the treatment of chronic and acute wounds: regeneration of dermis and wound healing. Stacking of a dermal regeneration template for reconstruction of a soft-tissue defect after tumor excision from the palm of the hand: a case report. Grafting of deeply burned problem zones in the lower extremity with a dermal substitute. A new technique to resurface wounds with composite biocompatible epidermal graft and artificial skin. Integra as a dermal replacement in a meshed composite skin graft in a rat model: a one-step operative procedure. Collier M; the use of advanced biological and tissue-engineered wound products; Nurs Stand. Artificial skin as a valuable adjunct to surgical treatment of a large squamous cell carcinoma in a patient with epidermolysis bullosa. Reconstructive surgery using an artificial dermis (Integra): results with 39 grafts. Dermal regeneration template for deep hand burns: clinical utility for both early grafting and reconstructive surgery. Experience with Bilaminate Bioartificial Skin Substitute and Ultrathin Skin Grafting in Non-Burn Soft-Tissue Wound Defects. Modulation of scar tissue formation using different dermal regeneration templates in the treatment of experimental full-thickness wounds. Evaluation of the advantages of Integra for covering Chinese flap donor sites: a series of 10 cases. Role of Embryonic Histogenesis in the Healing of Chronic Wounds Using Integra Dermal Regenerative Template. Scattering of Light from Histologic Sections: A New Method for the Analysis of Connective Tissue. Figus A, Leon-Villapalos J, Philp B, Dziewulski P; Severe multiple extensive postburn contractures: a simultaneous approach with total scar tissue excision and resurfacing with dermal regeneration template; J Burn Care Res; 2007 Nov- Dec;28(6):913-7. The Use of a Bilaminate Artificial Skin Substitute (Integra?) in Acute Resurfacing of Burns: An Early Experience. Use of dermal regeneration template in contracture release procedures: a Multicenter evaluation. Integra Bioengineered skin substitute for salvage of complex lower extremity wounds. Poster Presentation at the Symposium for Advanced Wound Care, San Diego, California April 24 -27, 2008. Gavenis K, Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Mueller-Rath R, Andereya S, Schneider U; In vitro comparison of six different matrix systems for the cultivation of human chondrocytes; In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. Aesthetic complex reconstruction of the lower leg: application of a dermal substitute (Integra) to an adipofascial flap. Successful Management and Surgical Closure of Chronic and Pathological Wounds using Integra. Strategies to improve the take of commercially available collagen/glycosaminoglycan wound repair material investigated in an animal model. The co-application of sprayed cultured autologous keratinocytes and autologous fibrin sealant in a porcine wound model. Use of an artificial dermis (Integra) for the reconstruction of extensive burn scars in children. Multicenter Postapproval Clinical Trial of Integra Dermal Regeneration Template for Burn Treatment. Safety and Efficacy of Integra Dermal Regeneration Template in Burn Wound Coverage. Herlin C, Louhaem D, Bigorre M, Dimeglio A, Captier G; Use of Integra in a Paediatric Upper Extremity Degloving Injury; J Hand Surg [Br]. Initial experience of Integra in the treatment of post-burn anterior cervical neck contracture. Presented in part at the 29 Annual Meeting of the British Burns Association, April 11, 1996. Development of new reconstructive techniques: use of Integra in combination with fibrin glue and negative-pressure therapy for reconstruction of acute and chronic wounds. Upward migration of cultured autologous keratinocytes in Integra artificial skin: a preliminary report. Cadaver Skin allagrafts and Transmission of Human Cytomegalovirus to Burn Patients. Management of facial burns with a collagen/glycosaminoglycan skin substitute- prospective experience with 12 consecutive patients with large, deep facial burns. Koenen W, Goerdt S, Faulhaber J; Removal of the outer table of the skull for reconstruction of full-thickness scalp defects with a dermal regeneration template; Dermatol Surg; 2008 Mar;34(3):357-63. Artifical Dermis as an Alternative for Coverage of Complex Scalp Defects following Excision of Malignant Tumors. Radical resection of giant congenital melanocytic nevus and reconstruction with meek-graft covered integra dermal template. Combination of a new composite biocompatible skin graft on the neodermis of artificial skin in an animal model. The Use of a Dermal Regeneration Template for the Repair of Degloving Injuries: A Case Report. Martinet L, Pannier M, Duteille F; Effectiveness of Integra in the management of complete forearm degloving injury: A case report; Chir Main; 2007 Apr; 26(2):124- 6. Messineo A, Innocenti M, Gelli R, Pancani S, Lo Piccolo R, Martin A; Multidisciplinary surgical approach to a surviving infant with sirenomelia; Pediatrics. Combined use of collagen-based dermal substitute and a fibrin-based cultured epithelium: a step toward a total skin replacement for acute wounds. Reconstructive Surgery with a Dermal Regeneration Template: Clinical and Histologic Study. Acceleration of Integra incorporation in complex tissue defects with subatmospheric pressure. Partial dermal regeneration is induced by biodegradable collagen-glycosaminoglycan grafts. Reepithelialization of a full-thickness burn from stem cells of hair follicles micrografted into a tissue- engineered dermal template (Integra). A case of successful delayed reconstruction using a collagen based dermal substitute of a chemical burn injury to the face caused by sulphuric acid. Vascularized Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Matrix provides a Dermal Substrate and Improves Take of cultured Epithelial Autografts. Use of island graft to isolate organ regeneration from scar synthesis and other processes leading to skin wound closure. The Use of Cultured Autologous Keratinocytes with Integra in the Resurfacing of Acute Burns. A collagen based dermal substitute and the modified Meek technique in extensive burns. Pham C, Greenwood J, Cleland H, Woodruff P, Maddern G; Bioengineered skin substitutes for the management of burns: a systematic review; Burns; 2007 Dec; 33(8):946-57. Results of early excision and full- thickness grafting of deep palm burns in children. Popescu S, Ghetu N, Grosu O, Nastasa M, Pieptu D; Integra-a therapeutic alternative in reconstructive surgery.
Azathioprine 50mg without a prescription
Subject had a history of hypersensitivity to bovine collagen and/or chondroitin 3 spasms left upper quadrant purchase 50mg azathioprine mastercard. Subject had participated in another clinical study involving a device or a systematically administered investigational study drug or treatment within 30 days of the randomization visit 6. Subject was currently receiving (within 30 days of the randomization visit) or was scheduled to receive a medication or treatment which, in the opinion of the Investigator, was known to interfere with, or affect the rate and quality of, wound healing (e. Subject had any of the following unstable conditions or circumstances that could interfere with treatment regimen compliance, such as the following: a) Ability to perform required dressing changes b) Ability to comply with treatment visit schedule c) Mental incapacity d) Current substance abuse 8. Subject had excessive lymphedema, which, in the opinion of the Investigator, could interfere with wound healing 9. Subject had unstable Charcot foot or Charcot with boney prominence that, in the opinion of the Investigator, could inhibit the wound healing 10. Subject had a history of bone cancer or metastatic disease of the affected limb, radiation therapy to the foot, or had had chemotherapy within the 12 months prior to randomization 14. Subject had been treated with wound dressings that included growth factors, engineered tissues, or skin substitutes (e. Subject had been treated with hyperbaric oxygen within 5 days of Screening or was scheduled to receive this therapy during the study 16. Subject had a non-study ulcer that required a treatment other than moist wound therapy. Subject was an employee or relative or any member of the Investigational site or the Sponsor. At the end of the Run-in period, and prior to Randomization, the subject was excluded if either of the following conditions were met: a) Subject did not continue to meet the entrance criteria (inclusion and exclusion) above, or b) the size of the study ulcer, following debridement, had decreased by more than 30% from the baseline assessment measured at Screening. Efficacy evaluations during this phase included weekly Investigator assessments of wound closure in addition to planimetric evaluations of ulcer size, as well as a Quality of Life questionnaire which subjects completed at the start and at the end of the Treatment Phase. Safety evaluations included assessment for adverse events and use of medications and new therapies. Subjects with 100% healed ulcers were considered treatment successes and entered the Follow-up Phase. Follow-up Phase: Four weeks after either the study ulcer was confirmed as completely healed or the final Treatment Visit was completed, subjects entered the 12-week Follow-up phase. Efficacy evaluations included clinical evaluation of the study ulcer site for breakdown and recurrence and administration of the Quality of Life Questionnaire. Safety evaluations during the Follow-up Phase for both treatment successes and treatment failures consisted of adverse event assessments at each visit and measurement of clinical laboratory parameters at the last Follow-up visit. Subjects who entered the Follow-up Phase as treatment successes were considered: o Follow-up successes if their ulcer did not recur o Follow-up failures if their ulcer recurred. All subjects entering and completing the Follow-up Phase (both healed and unhealed ulcers) were considered Follow-up Phase completers Diabetic Foot Ulcer Study Endpoints Primary Efficacy Endpoint the primary efficacy endpoint for the study was the percentage of subjects with complete closure of the study ulcer, as assessed by the Investigator, during the Treatment Phase. Secondary Efficacy Endpoints Secondary endpoints which were also evaluated included: 1. Percentage of subjects with complete wound closure of the study ulcer, as assessed by computerized planimetry, during the Treatment Phase. Incidence of ulcer recurrence at the site of the study ulcer during the Follow-up Phase. Patient Accountability During the Diabetic Foot Ulcer Clinical Trial, a total of 545 subjects were screened, and 307 subjects were randomized. In the Control Treatment group, 117 subjects completed the Treatment phase and 82 subjects completed the Follow-up phase. This population was used as the primary population for the analyses of primary and secondary efficacy endpoints. Per Protocol Population: all randomized subjects who were not associated with a major protocol violation. Analyses of efficacy endpoints using this population were considered as supportive. Study Population Demographics and Baseline Parameters the baseline demographics in the Integra and Control arms were comparable for all parameters evaluated, including, but not limited to , severity and type of diabetes, gender, race, age, and ulcer size area. The demographic groups represented in this study correlate to the population that is affected by diabetic foot ulcers. Adverse Events All adverse events that were reported in the study evaluating Integra for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers at a frequency of 5% in either cohort are presented in Table 1. This table includes adverse events that were both attributed to and not attributed to treatment. The adverse events are listed in descending order according to their frequency in the Integra cohort. A total of 798 adverse events occurred in 216 of the 307 randomized subjects as presented in Table 1. Of the 798 adverse events, 444 occurred in the Control arm, treated with the standard of care established within this trial. Diabetic Foot Ulcer Study Withdrawals due to Adverse Events and Investigator Decision During the Treatment Phase, of the 62 subjects that discontinued, 29 subjects (9. During the Follow-up Phase, of the 57 subjects that discontinued, nine (9) subjects (2. Effectiveness Results Diabetic Foot Ulcer Study Primary Endpoint Complete Wound Closure ? Investigator Assessment: A higher percentage of subjects treated with Integra had 100% complete wound closure of the study ulcer (51. The difference between the two treatment groups was statistically significant (p-value = 0. Complete Wound Closure ? Computerized Planimetry: Statistically significant results were obtained by planimetric measurement of complete wound closure. The agreement between the planimetric and Investigator assessments was found to be very strong with a Kappa coefficient of 0. The planimetry assessment of the time to healing correlated significantly with the Investigator assessment (p-value < 0. Rate of Wound Size Reduction: Subjects treated with Integra demonstrated a significantly higher rate of wound size reduction compared to subjects treated with control. Rate of wound healing (wound size reduction) determined by week, using planimetric measurements, was significantly higher (p-value = 0. However, this difference between the treatment groups ( = 8%) was not statistically significant (p- value = 0. Additionally, subjects treated with the Integra indicated significant reduction in Bodily Pain compared to subjects from the Control group (p-value = 0. A difference trending toward significance was noted for Role Physical category (p-value = 0. No significant differences were observed between the two treatment groups for other Quality of Life metrics including General Health, Social Functioning, Role Emotional, Mental Health or Vitality. Integra provides an alternative method for treatment of diabetic full-thickness foot ulcers which have not adequately responded to conventional ulcer therapy. References Copies of the following references, cited in the above section, are provided in full or abstract in Attachment 1. Where abstracts are provided, copies of the articles will be provided upon request. A comparison of the health-related quality of life in patients with diabetic foot ulcers, with a diabetes group and a nondiabetes group from the general population. Consensus recommendations on advancing the standard of care for treating neuropathic foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Clinical effectiveness of an acellular dermal regenerative tissue matrix compared to standard wound management in healing diabetic foot ulcers: a prospective, randomised, multicentre study. The efficacy and safety of Grafix for the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: results of a multi-centre, controlled, randomised, blinded, clinical trial. Scalp Reconstruction After Resection of Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma Utilizing a Dermal Regeneration Template: A Case Report. The use of a dermal regeneration template (Integra) for acute resurfacing and reconstruction of defects created by excision of giant hairy nevi. Integra Artificial Skin as a Useful Adjunct in the Treatment of Purpura Fulminans. Artificial Skin (Integra? Dermal Regeneration Template) for Closure of Lower Extremity Wounds. Use of Integra artificial skin is associated with decreased length of stay for severely injured adult burn survivors.
Order cheap azathioprine line
The mechanisms underlying polyamines uptake has been analyzed in several systems and discussed in previous reports (Belting muscle relaxant high discount azathioprine 50 mg on-line, 2003; Fransson et al. To date, Gpcs are also considered as potential carriers of cell-penetrating peptides. Cell- penetrating peptides are short cationic peptides extensively studied in medicine as drug delivery agents for the treatment of different diseases including cancer and virus infection (Rajendran et al. Therefore, Gpcs mediated uptake of cell-penetrating peptide is currently evaluated as a new strategy to enhance target-specific delivery of a large variety of entrapped therapeutic drugs. Research on Gpcs has further increased due to the discovery that they act at the interface between the extra cellular environment and the inner cellular domain to fine tune inputs triggered by key secreted regulatory proteins. Being mostly extracellular, Gpcs are involved in the regulation of various signalling pathways triggered by secreted peptides including that of Wnt, Fgf, Hh, bone morphogenic protein (Bmp), insulin-like growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor (Fico et al. The functional relevance of Gpcs as signalling modulators has come from the genetic analysis and embryological manipulation of Gpcs in different species and in cultured cells (Table 1). This table reports the major phenotypes observed by genetic and embryological studies on glypican genes and the main involved signals For example, in vitro studies have shown that Gpc4 positively modulated hepatocyte growth factor activity during renal epithelial branching morphogenesis (Karihaloo et al. Mice lacking Gpc3 are affected by overgrowth, renal cystic dysplasia and limb defects. Some of these phenotypes are consistent with defects in Wnt and Bmp signalling pathways, respectively (Grisaru et al. Additional studies have also shown that the developmental overgrowth observed in gpc3- null mice is, at least in part, a consequence of the hyperactivation of the Hh pathway indicating that Gpc3 inhibits Hh Gallet et al. Interestingly, Gpc5 stimulates the proliferation of rhabdomyosarcoma cells by eliciting a positive action on Hh signalling (Li et al. Signalling Mechanisms Underlying Congenital Malformation: the Gatekeepers, Glypicans 25 these findings reveal that members of the Gpc family can display opposite roles in the regulation of a given signalling protein. It has been proposed that Lon-2 negatively regulates Bmp signalling as lon-2 mutants recapitulate phenotypes caused by Bmp over-expression (Gumienny et al. Another example is the Zebrafish knypek, which encodes the gpc homolog to mammalian Gpc4/Gpc6 (Topczewski et al. In particular, reducing Gpc4 (Xgly4) disrupts cell movements during gastrularion (Ohkawara et al. We have also shown that loss-of Gpc4 function in Xenopus embryos impairs forebrain patterning and cell survival from early neural plate stages onwards, and that these early developmental defects result in brains affected by microcephaly at later stages (Fig. Inhibition of Fgf signalling results in dorsal forebrain phenotypes similar to those of Xgly4 depleted embryos, indicating that establishment and patterning of the dorsal forebrain territory may require modulation of Fgf signalling by Xgly4 (Galli et al. Side view of Xenopus embryos at tail bud stage showing expression of the dorsal forebrain marker emx-2 as detected by whole mount in situ hybridization (arrow in all panels). Xenopus embryos were injected at 2 cell stage with morpholino oligos to interfere with Gpc-4 activity. Injections were done by using control morpholino (controlMo), or morpholino targeting gpc-4 (gpc-4Mo). In Drosophila the Gpc Dally-like is required for Hh signalling in the embryonic ectoderm whereas both Gpcs Dally and Dally-like are required and redundant in Hh movement in developing wing imaginal discs (Han et al. Additional studies on the wing disc patterning have also demonstrated that in Dally and Dally-like mutants the distribution and signalling of Wnt and Bmp family members, Wingless (Wg) and Decapentaplegic (Dpp) respectively, are altered (Nybakken and Perrimon, 2002). Overall, these and other studies reveal that different cell types can take advantage of Gpc-mediated regulation to control signal supply during distinct developmental processes. In addition, they show that vertebrate and invertebrate Gpcs have diverse and specialized functions towards a given signalling protein including their capability of enhancing or suppressing its activity in a stage- and/or tissue-specific regulated manner. One question that has arisen is whether these properties are conferred by their unique structural motifs. Gpcs trafficking and shedding can both lead to a gain of signal, down-regulation properties and cell non-autonomous activities (Yan and Lin, 2009). These issues are the subjects of intense investigation, and a growing body of data is being published on Gpc mechanism of action. Also, the Gpc-dependant Fgf binding and activation of receptors is nearly abolished when cells are treated with chlorate to inhibit Gpc sulfatation (Steinfeld et al. Potential mechanisms of action may include immobilizing of the ligand, increasing its local concentration, presenting it to a signalling receptor, or otherwise modifying the molecular encounters between ligands and receptors. The expected overall effect is thus enhancing receptor activation at low ligand concentrations. This includes the binding and stimulation of Wg (the drosophila homolog of Wnt) signalling in the wing imaginal disc by Dally as well as the ability of human Gpc-5 to interact with Hh and enhance its growth promoting activity in rhabdomyosarcoma cells Yan and Lin, 2009; Li et al. Recent studies have revealed that the co-receptor function of Gpcs can also provide a new paradigm of cell-cell communication. In the stem cell niche associated with germ cells the Gpc Dally is critical for making and maintaining the female germ cells (Hayashi et al. However, in this stem cell niche, dally is expressed by the cap cells, which also produce the Dpp signalling molecule, but not in the receiving cells (germ cells), which instead express Dpp receptor (Hayashi et al. These findings have raised questions and interest about the underlying molecular mechanisms. Studies in cultured cells have provided evidence that Dally enhances Dpp signalling in trans through a contact- dependent mechanism allowing the complementation of co-receptor-receptor complexes in adjacent cells (Dejima et al. Therefore, unlike typical co-receptor functions, Dally can serves as a trans co-receptor for Dpp when it has to enhance its signalling on neighboring cells. So far the mechanism for contact-dependent signalling has been mainly attributed to membrane-bound ligands and receptors such as Delta-Notch and Ephrins and their receptor tyrosine kinases (Hainaud et al. The fact that Gpcs act as trans activator partners establishes new strategies for crosstalk between adjacent cells during tissue assembly and maintenance. As co-receptors and trans co-receptor, Gpcs modulate ligand-receptor encounters that can activate and inhibit cell proliferation, motility, and differentiation. Most insights have come from cell biological approaches undertaken to investigate how Gpcs affect Hh and Wg signalling and gradient formation. Concerning Wg, genetic analysis of Dally-like in the wing imaginal discs has highlighted a role for this Gpc in polarizing the Wg morphogenetic gradient. In the wing imaginal disc, Wg is secreted by a narrow strip of cells located at the dorsal?ventral boundary and spreads over a distance of up to 20 cell diameters. Wg first accumulates on the cell surface apical side in expressing cells to be then re-distributed to the basolateral membrane of receiving cells, where it is released in association with lipoprotein particles (Panakova et al. It has been proposed that polarizing Wg on the cell membrane allows the subsequent polarization of morphogen distribution within an epithelium, thus resulting in distinct tissue patterns (Marois et al. Therefore, one major question in the field is how Wg reaches the basolateral cell surface when it is secreted apically. Interestingly, Wg is no longer detected at the basolateral surface of cells away from the Wg source in mutant cells lacking Dally-like protein. Altogether, these findings support the view that Wg is secreted apically and it is then endocytosed with the help of Dally-like (Fig. Once internalized, Dally-like targets Wg by transcytosis to the basolateral compartment, where it is stabilized and can then spread farther away in a polarized manner (Fig. These findings also open the intriguing possibility that Dally-like-mediated basolateral polarization of Wg accounts for Wg activity in long-range signalling (Gallet et al. However, whether this mechanism underlies distinct Wg signalling activity remains a matter of debate (Williams et al. For example, Dally-like endocytosis from the cell surface catalyzes the internalization of Hh in flies. In this context, internalization of Hh occurs together with its receptor Patched (Fig. Removing Patched from the membrane alleviates the inhibition of the transmembrane protein Smoothened by Patched and enables Smoothened to activate Hh target genes (Fig. Indeed, through endocytosis Gpc-3 inhibits Shh activity rather than activating it as in flies (Fig. It has been proposed that Gpc-3 has high affinity for Shh and can, therefore, compete with Patched for Shh binding (Capurro et al. Upon binding, Gpc-3 targets Shh to endocytic vesicles for degradation, thus leaving the unliganded Ptc at the cell surface, and free to inhibit Smoothened (Fig. This possibility is also Signalling Mechanisms Underlying Congenital Malformation: the Gatekeepers, Glypicans 29 consistent with results showing that hyperactivation of Shh can in part explain the Simpson- Golabi-Behmel overgrowth syndrome caused by loss-of-function mutations in Gpc-3, and with other experiments revealing an increased expression of Shh target genes in Gpc-3 deficient mice and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (Capurro et al.

