Diarex
Trusted diarex 30caps
Neurocutaneous Syndromes Among the neurocutaneous syndromes that may give rise to Chronic Causes neonatal seizures is familial incontinentia pigmenti gastritis diet гогле order diarex overnight delivery, a mixed syndrome of different mosaicisms (139). Perinatal inflamma Some neonatal seizures result from long-standing disorders, tory vesicles are followed by verrucous patches that produce a such as cerebral dysgenesis, neurocutaneous syndromes, distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation and finally dermal genetic disorders, or very early onset epilepsy. The identification of cerebral incontinentia pigmenti maps to Xp11 and is considered its negative pattern. Better known as hypomelanosis of Ito, its cutaneous lesions appear as areas of hypopigmentation. Linear sebaceous nevi are a family of disorders with dis tinctive raised, waxy, sometimes verrucous nevi on the scalp or face, associated with hemihypertrophy, hemimegalen cephaly, and neonatal seizures (142). Epilepsy Syndromes of Early Infantile Onset In the 1970s, French neurologists coined the fifth-day fits (benign neonatal convulsions) to describe an electroclinical syndrome in which seizures unexpectedly arose between the fourth and sixth days of life (143). The seizures were usually partial clonic, often with apnea and status epilepticus. Computed tomography scan of the head showing which the bursts of cerebral electrical activity in the discontin right hemimegalencephaly with dysplastic and enlarged right cerebral uous parts of the record showed sharply contoured theta hemisphere. Brain magnetic resonance imaging provides better resolu tion and definition of the abnormality and reveals subtle involvement waves, especially in the central regions. Seizure originating from the right hemisphere (A), fol lowed by one arising from the left hemisphere (B) (odd channel numbers represent the left hemisphere and even channel numbers represent the right hemisphere). Note that the time axis of the electroencephalogram rhythm strip is slightly compressed. The time and amplitude calibration bar appears at the top of the figure: 1 second and 50 V. Migrating par tial seizures in early infancy: expand ing the phenotype of a rare neonatal seizure type. The abnormal myoclonic movements, detected by the bottom electromyographic channel (arrows), occur during the burst periods of the tracing. Clinical seizures include erratic fragments syndrome accompanied by multifocal spikes on the electroen of myoclonic activity, massive myoclonia, stimulus-sensitive cephalogram. Progressive cerebral atro Despite the decades-long recognition of neonatal seizures, phy is evident on neuroimaging scans (152). A recent case report treatment recommendations rest almost entirely on conven identified a disruption of the tyrosine protein kinase receptor tional wisdom and traditional practices. On the one hand, if the burden of loading doses of phenobarbital 15 to 20 mg/kg, with the in seizures will be minimal, the infant need not be exposed to tention of generating serum levels between 15 and 20 g/mL, acute and long-term drug therapy. Plasma ized, controlled study (158), thiopental was administered soon binding of phenobarbital in neonates varies from 0% to 45%. Seizures were diagnosed by clinical the mg/kg dose needed to provide a free plasma-bound signs and occurred in 76% of treated infants and in 73% of a level of 25 g/mL is calculated by the formula: plasma-bound control (placebo) group. For pheno after perinatal asphyxia resulted in a lower rate of recurrent barbital, the volume of distribution is assumed to be 1 L/kg. Another randomized study using achieve, but not exceed, free concentrations of 3 g/mL phenobarbital prophylactically in neonates with perinatal (162,165). The dosing formula: (3 g/kg) Vd (L/kg)/ asphyxia found a statistically significant decrease in the inci (% free binding) assumes a volume of distribution of 1 L/kg. There are also variable confirmation or identification of electrographic seizures. In rates of hepatic metabolism, decreases in elimination rates another study of 31 acutely ill neonates with electrographic during the first weeks of life, and variable bioavailability with seizures detected during continuous electroencephalograph different generic preparations. Six had an equivocal elec thus, dosage must be tailored to the individual patient after troclinical response. The remaining 10 had Phenytoin should be given by direct intravenous infusion at persistent electroclinical seizures. Serum binding of the drug reported a mixed response of electroclinical seizures to pheno is unpredictable in critically ill neonates, and excessively rapid barbital. In a comparison study (162), electrographic seizures administration or high concentrations can result in serious or ceased in 43% of the group treated with phenobarbital and in lethal cardiac arrhythmias. Furthermore, phenytoin is strongly 45% of the group given phenytoin; however, the lack of a alkalotic and may lead to local venous thrombosis or tissue placebo control precluded determination of absolute efficacy. The choice of a second-line drug for nonresponders two surveys of pediatric epileptologists in the United States was limited to lignocaine or benzodiazepines. According to a and Europe, phenobarbital was identified as the treatment of recent Cochrane review (163),. In a treatment review of five neonatal intensive clinical practice, other than in the treatment of prolonged or care units in the United States (170), phenobarbital was the frequent clinical seizures. Second-line therapy after treat domised controlled trials to support the use of any of the anti ment failure to the first was most frequently lorazepam convulsants currently used in the neonatal period. In summary, despite the frequent empiric selection of pheno Benzodiazepines, typically lorazepam (0. Side effects of acute administration include hypoten cern that phenobarbital itself may have deleterious effects on the sion and respiratory depression. Few drugs nate the clinical manifestation of the seizure while the electro for use in the newborn have been subjected to adequately pow graphic discharge continues (161,162). This disconnect is ered, randomized, placebo-controlled investigations to demon often termed uncoupling and poses serious concerns for the strate real safety and efficacy. Drugs with potential for the treat clinician and researchers in determining response rates to ment of neonatal seizures are no exception. However, in this critical time of early brain development, suppression of synaptic transmission may have incidental undesirable consequences, because neu ronal and synaptic pruning are activity dependent. Acute neonatal seizures are often followed by 1970s, it has been known that rat pups fed phenobarbital chronic postnatal epilepsy. A latent period, during which secondary have later reductions in brain weight and in total brain cell epileptogenesis develops, gives rise to spontaneous, unprovoked count (186). Likewise, benzodiazepines are Chronic Postnatal Epilepsy and the Need commonly administered for sedation or to reduce agitation, for Long-Term Treatment and no obvious adverse effects are associated with their use, although careful studies are lacking. Chronic postnatal epilepsy is relatively common in the wake of neonatal seizures. For many patients, perma nent, fixed brain injuries, such as resolving stroke, ischemia, References or traumatic lesions, serve as the nidus for future epilepsy. Neonatal convulsions: incidence and causes the brain how to have future seizures, resulting in a persistent in the Stockholm area. Outcomes in neonates with convul lowering of the seizure threshold (38) and the development of sions treated in an intensive care unit. Neonatal seizures after cesarean sec seizures represent the beginning of very early onset epilepsy, tion: higher risk with labor. The epidemiology of clinical neonatal 20% of survivors of neonatal seizures experienced one or seizures in Newfoundland: a population-based study. Partial and generalized seizures charac seizure durations in preterm and term neonates. Bumetanide enhances Phenobarbital hippocampal dentate granule cells during postnatal development.
Order diarex cheap
Close evaluation of the tail tip for erosive/necrotic lesions should also be performed gastritis celiac discount diarex 30 caps amex. Finally, the anal region should be closely evaluated for redness, swelling, or tissue prolapse. If this is the case, wear non-powdered latex gloves to prevent injury to the integument of the animal. Diagnostics 29 As noted above, there are several potential etiologies when an animal is experiencing buoyancy problems. If the pouch appears asymmetrically distended or symmetrically distended with attendant buoyancy problems, a percutaneous fine needle aspirate should be performed on the pouch contents. Any fluid aspirated should be dried and stained with Wright-Giemsa stain, Gram stain, and acid-fast stain. The pouch can also be flushed with sterile saline and the aspirate sent for culture. If a hyperinflated bladder is suspected, a bright light can be directed from behind the animal to visualize the location and borders of the distended organ. The needle should be directed between the scutes/plate margins for ease of penetration through the skin. The external area can be rinsed with sterile saline or a drop of a triple antibiotic ophthalmic solution applied prior to needle penetration. Diagnostic dips or baths or diagnostic washes of the branchial cavities can be performed to obtain an etiologic diagnosis since the gill tissue itself is so inaccessible. Because of the semi-closed nature of the branchial cavities, branchial washes with sterile, 0. Skin lesions should be swabbed with a few sterile, wet (using sterile saline), cotton-tipped applicators and evaluated by wet mount, gram stain, acid-fast stain, and/or Wright-Giemsa stain. Follow-up diagnostics to the initial skin swab include aerobic bacterial culture, mycobacterial culture, and cytological exam by a pathologist familiar with fish. Blood collection is technically very difficult due to the relative absence of accessible peripheral veins and the small size of most syngnathids. The ideal machine for taking radiographs of seahorses is a mammography unit in terms of optimal radiographic detail and contrast. Important structures to evaluate include swim bladder (size, shape, presence or absence of fluid), coelomic cavity (free air, fluid, masses), alimentary tract (aided by a small bolus of barium sulfate if needed), liver position and size, kidney position and size, gonadal position and size, and brood pouch contents. Larger seahorse species as well as the seadragons are particularly at risk for foreign body (usually substrate) ingestion which can easily be ruled in or out with plain film radiography. Ultrasonography of brood pouch contents should be made possible by using the smaller transducers (7. In low-alkalinity water it is recommended to buffer the solution at a ratio of 2 parts sodium bicarbonate:1 part tricaine (wt:wt). The seadragons have a prolonged recovery time at 100 ppm and 50-75 ppm is the recommended dose for these two species. Because of the long, rather narrow tube snout and the semi-closed nature of the branchial cavities, assisted ventilation is easily achieved with a 3. A syringe filled with fresh saltwater is then attached to the end of the red rubber catheter and pumped in a pulsatile manner every few seconds until the animal is spontaneously breathing at a normal rate. The success of assisted ventilation is easily assessed by watching the opercula move in and out. This technique has also been successfully used to resuscitate animals in respiratory arrest. Long-term anesthetic procedures should employ a flow-through system with oxygen supplementation in the sump or reservoir. Diseases Bacterial Disease Vibriosis has been the most frequently encountered clinical problem among all of the syngnathids maintained at the Shedd Aquarium. Vibriosis is typically a peracute to subacute process with high morbidity and mortality. There are three clinical presentations that are commonly encountered: erosive/ulcerative dermatitis often involving the tail tip, sudden death with no premonitory signs, and a syndrome characterized by bilateral edema of the periorbital tissue and edema of the soft tissue around the tube snout. Some cases present with edematous facial tissue as well as an erosive/ulcerative dermatitis. Post-mortem findings can include ulcerative dermatitis, bacterial cellulitis/myositis, and/or bacterial septicemia. Septic fish often had one or more of the following histological changes: reactive endocardium, pericarditis, necrotizing hepatitis, and renal necrosis. Vibrio alginolyticus is by far the most frequently isolated species from post-mortem kidney and liver cultures of syngnathids at Shedd Aquarium. Vibrio alginolyticus is a fairly ubiquitous microbe and is often isolated from random water samples as well as the live food items fed to the syngnathids, i. Therefore, it has been postulated that, due to the time it takes to make it through the trade route from native collector to our tanks when combined with the fact that newly collected animals are obligate live food eaters and are probably not being offered live food en route, new syngnathid acquisitions are often on a very poor plane of nutrition. This has been substantiated by post mortem exams wherein fat stores have often been completely depleted in many of the newly acquired specimens; in other words, the fish arrived in an emaciated condition. This malnutrition combined with the stress of capture, crowding, and possible substandard water quality conditions result in an immunocompromised fish host susceptible to both opportunistic and/or mildly virulent bacterial infections. Early and aggressive treatment with injectable antibiotics is indicated, but has been only moderately successful. At Shedd, we administer ceftazidime at 30 mg/kg intracoelomically every 48 hours for a minimum of five injections. Injecting into the tail and vertebral column (the back) musculature is also possible. A recent paper reports that Vibrio harveyi causes disease in seahorse, Hippocampus sp. The vast majority of documented mycobacteriosis cases in these fish at Shedd Aquarium have been caused by the two rapid-growing species, M. Mycobacteriosis is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in captive syngnathids. At Shedd Aquarium, Alligator Pipefish (Syngnathoides biaculeatus) and Longsnout Seahorses (Hippocampus reidi) were the two species of syngnathids that were most frequently reported as having mycobacterial infections according to culture results and histopathology reports. But as more facilities exhibit syngnathids, mycobacteriosis is being frequently encountered in many other species (I. Typically, it is encountered as isolated, sporadic cases but tank epizootics have been documented as well. In the peracute syndromes, affected individuals may be found dead without any premonitory signs. More often, however, it presents as a subacute to chronic, pyogranulomatous infection that may involve skin, subcutis and/or underlying skeletal muscle characterized by pyogranulomatous abscesses and/or draining fistulous tracts. Acid-fast stains applied to the exudates from these lesions will reveal acid-fast bacilli. The skin lesions tend to be the superficial signs of systemic infections involving any combination of organs and organ systems which often including the spleen, liver and kidney. There are cases that no obvious gross lesions are noted on any tissue, but on histological evaluation, abundant numbers of acid-fast bacteria are dispersed through organs such as the liver and kidney. To date, treatment of mycobacteriosis in syngnathids has not been attempted at the John G. In addition, there is every chance that antibiotic-resistant strains of these mycobacteria might be inadvertently created during long-term antibiotic treatments if the treatment dosages and durations happen to be insufficient or inconsistent. This fact, coupled with the subsequent exposure of unaffected fish and human caretakers, makes treatment of mycobacterioses in fish a rather risky proposition. In the event of a true mycobacterial epizootic, it is advised that all of the specimens in an affected tank should be humanely euthanized, the tank substrate and decor should be discarded, and the tank itself should be disinfected with a disinfectant with antimycobacterial properties. If a decision is made to treat a case of mycobacteriosis in a syngnathid due to its rarity or economic value, antibiotic choice(s) should be based upon 32 sensitivity of the isolate to one or compounds from the following suite of therapeutants: amikacin, cefoxitin, clarithromycin, doxycycline, minocycline, trimethoprim-sulfa, and imipenem. This list of antibiotic choices is based upon the current recommendations for management of atypical mycobacterial infections in man. Barrier protection with latex gloves is recommended when working with fish known to have mycobacterial infections. Parasites Metazoans the majority of the parasitic diseases that have been encountered at Shedd Aquarium involve metazoan endoparasites. Extraintestinal metazoa were the most frequently encountered group and usually involving encysted, quiescent digenetic trematodes or cestodes.
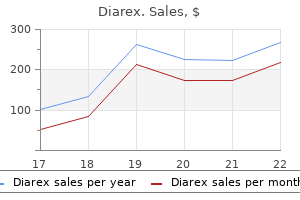
Generic diarex 30caps on-line
A survey conducted in the Knysna estuary between August and November 1990 encountered only 15 seahorses (Lockyear gastritis diet щенячий buy cheapest diarex and diarex, Hanekom, and Russell 1991). Indeed no recent records exist for the species from the Klein Brak estuary (Lockyear 1999). In contrast, Knysna seahorses may also inhabit the Breede River, Duiwenhoks, Kaffirkuils, and Groot Brak (Grange Pers. If the species and its habitat are to be managed effectively, a better understanding of H. It lives naturally in estuarine habitats that fluctuate in temperature and specific gravity. This ability to tolerate extremes makes it able to withstand changing parameters in the aquarium. The young are quite large when born and can take newly hatched Artemia immediately, making them easy to feed. Rotterdam Zoo reports higher survival rates when also offering the juveniles rotifers during the first two weeks after birth. However, it does fall victim to the usual range of seahorse diseases when placed under excessive stress or overcrowding. Habitat Parameters (display tank) Population: 60-70 adult individuals Volume: 1338 l Height: 80 cm Circulation: closed 49 Water: natural seawater Filtration: plenum with live sand bed, Eheim power filter with mechanical and carbon. Volume: 55 l Height: 30 cm Circulation: closed Water: natural seawater Filtration: Double Algarde air driven sponge filter Substrate: thin layer of coral sand Holdfasts: artificial sea grass, live rock. Light: fluorescent room light (no light directly above tanks) Photoperiod: 11 hours. Tanks contained 47 liters of natural seawater, a double sponge filter (Algarde 200 Biofoam), and an extra airline to increase airflow, primarily to aid food circulation. The display tank is a much more stable environment than the holding and rearing tanks. Therefore, the following reflects the two different systems the London Zoo employs. Holding tanks are siphoned of debris and uneaten food daily, and so 2-5% of the water is changed daily. In the display tanks, small hermit crabs, black sea cucumbers, brittle stars and even bristle worms help tremendously with uneaten food. When numbers reach a high density, the entire tank is stripped down and rinsed with fresh water; the sand is cleaned and soaked in fresh water overnight. The slugs are very effective at controlling the anemones, but they rapidly die off when the food supply is exhausted. Sponges from the filters in holding tanks are rinsed with tank water every week, or more often, depending on stocking levels. In the display tank, an Eheim power filter with carbon and filter wool provides chemical and mechanical filtration. In all tanks, a very strong airflow with multiple airlines is used helping to keep food in suspension longer and bringing it to the seahorses without the risk of powerheads. All frozen foods (Artemia, Mysis) are rinsed very thoroughly in freshwater through a fine net before feeding. This helps reduce the build-up of pollutants from the juice given off by thawed foods. Salifert kits were used to test the following water parameters on a bimonthly basis, with ideal maximum levels stated and those obtained given in brackets: dissolved oxygen 8 mg/l (4-7 mg/l), nitrate 25 m/l (2-90 mg/l), nitrite 0 mg/l (0-1. Since survival rate is high with good husbandry and diet, it is easy to become overpopulated with animals. In order to avoid overpopulation we have tried different ways of managing the population in our collection. The animals exhibited a number of stress signs: disease outbreaks increased and aggression was high between males. Animals in the display tank are allowed to reproduce as normal, and young are only removed when required. Some young survive in the display tank, feeding on naturally available foods and make it to adulthood. To keep the generations turning over, we can remove up to 20 individuals and raise them in the holding tanks. This is considered a priority species for the European Fish and Aquatic Invertebrate Taxon Advisory Group due to its Endangered status. However, this is now under review due to the small founder population outside of South Africa and problems acquiring permits to increase this population. There is also good legislation and management of the species within South Africa and it is most appropriate that any ex situ work required for this species is done within South African aquariums. First field studies of an Endangered South African seahorse, Hippocampus capensis. Sex-roles and the influence of size on mating competition in the Knysna Seahorse, Hippocampus capensis. A preliminary investigation of the reproductive behaviour of the Knysna Seahorse, Hippocampus capensis Boulenger, 1900. Mass mortality of marine and estuarine fish in the Swartvlei and Wilderness Lake systems, Southern Cape. Distribution, abundance, morphometrics and genetics of the Knysna Seahorse, Hippocampus capensis. Population genetics and phylogenetic placement of the endangered Knysna seahorse, Hippocampus capensis. An investigation into the effects of habitat complexity and food types on the behaviour of the Knysna Seahorse, Hippocampus capensis. Threatened fishes of the world: Hippocampus capensis Boulenger, 1900 (Syngnathidae). It is most commonly encountered from Cape Cod south to Florida and in the northern and eastern Gulf of Mexico. As with other seahorses, coloration is variable with gray, orange, brown, yellow, red, and black individuals being found. Reproduction has been reported from the early part of April (Roule 1928 in Breder and Rosen 1966) and possibly year-round in Florida (Reid 1954). It has been observed for the 54 male to have a birthing period of up to 3 days and then engage again in reproductive displays on the fourth morning. Reported brood sizes range from 10-800 and published sizes range from 119-550 (550, Vincent 1990; 119, Scarratt 1996; 250-300, Herald and Rackowicz 1951). This range is apparently dependent on the health and size of the contributing parents. Newborns (possibly juveniles) swim in clusters near surface and are possibly phototropic (Hardy 1978). Habitat Parameters the following information has been collated from responses to husbandry questionnaires by 12 public aquaria. Height: at least 45 cm and preferably 53 cm to allow egg transfer (if breeding is required) Holdfasts: artificial sea grass, Caulerpa spp. This is the list of commonly kept co-inhabitants obtained from the static husbandry sheet: African blue stripe pipefish, alligator pipefish, chain pipefish, Janns pipefish, northern pipefish, shrimpfish, greater pipefish, dusky pipefish, many banded pipefish, zebra pipefish, H. Holdfasts: Artificial sea grass, holding U shape structures made with plastic rope and weight in the extremes. Water treatment: Chlorine and Ozone 55 Lighting: Natural in the husbandry area and fluorescent in exhibition tank. Tank design for fry A 7 l (28x16x15 cm) nursery tank was used with a 34 l (50x33x20 cm) reserve water sump (t).
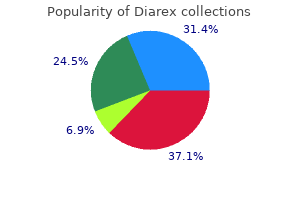
Discount 30caps diarex overnight delivery
Initiation of treatment with clozapine is a notable exception to this general approach as it requires a slow dose titration to minimize the risks of seizure gastritis and constipation buy diarex 30caps visa, orthostatic hypotension, and excessive sedation (Clozaril (clozapine) [product monograph] 2019). Subsequent dose increases, if needed, should be of 100 mg or less, once or twice weekly. In patients who have stopped or interrupted treatment with clozapine for 30 days or more, the initial dose titration for clozapine and the monitoring frequency for treatment initiation should be followed. However, it is important to consider whether factors are present that would influence treatment response if there is no significant improvement after several weeks of treatment. Such factors may include concomitant substance use, rapid medication metabolism, poor medication absorption, interactions with other medications, or other effects on drug metabolism. Determination of the blood concentration of the drug may also be helpful if the patient is being treated with a medication. For example, in a patient with negative symptoms, an untreated major depressive disorder may also be present. Although the incremental efficacy of higher doses has not been established (Samara et al. If a patient has had minimal or no response to two trials of antipsychotic medication of two to four weeks duration at an adequate dose (Howes et al. Particularly for patients with negative symptoms or depression, augmentation of antipsychotic therapy with an antidepressant medication may also be helpful (Helfer et al. Use of a benzodiazepine, such as lorazepam, is also suggested in patients who exhibit catatonia (Bush et al. For individuals with treatment-resistant schizophrenia who are unable to tolerate clozapine or not interested in pursuing a trial of clozapine, the limited available evidence suggests no benefit from high doses of antipsychotic medication and treatment related side effects are likely to be increased (Dold et al. However, a trial of a different antipsychotic medication may be helpful, particularly if there is no response or only a partial response to the most recently used medication. Monitoring During Treatment With an Antipsychotic Medication During treatment with an antipsychotic medication, it is important to monitor medication adherence, therapeutic benefits of treatment, and treatment-related side effects. There are many barriers to treatment adherence as well as facilitators and motivators of adherence, each of which will differ for an individual patient (Hatch et al. Use of a quantitative measure (see Statement 2) can assist in determining whether the antipsychotic medication is producing therapeutic benefits, including reductions in symptom severity and improvements in functioning. If an antipsychotic medication dose is being decreased, monitoring can help detect a return of symptoms prior to a more serious relapse. Some side effects are prominent with treatment initiation but dissipate, at least to some extent, with continued treatment. Still other side effects such as tardive dyskinesia, emerge only after longer periods of treatment or become more noticeable to patients as their acute symptoms are better controlled. Table 2 in Statement 1 gives suggestions for baseline assessments and monitoring frequencies for some side effects, clinical measurements, and laboratory studies. Specific attention may need to be given to clinical workflow to assure that indicated monitoring is conducted because rates of follow-up testing and screening for metabolic side effects of treatment appears to be low (Morrato et al. Other rating scales are aimed at identifying and assessing the severity of a specific type of side effect. Early in the course of treatment, common side effects include sedation, orthostatic changes in blood pressure, and anticholinergic side effects such as dry mouth, constipation, and difficulty with urination. It typically occurs within the first month of antipsychotic treatment, resumption of treatment, or with an increase in the dose of antipsychotic medication. Akathisia and medication-induced parkinsonism can also occur in the initial weeks of treatment or after increases in medication doses. Hyperprolactinemia, related to D2 receptor antagonism in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, can lead to breast enlargement, galactorrhea, sexual dysfunction, and, in women, menstrual disturbances. These include weight gain, hyperlipidemia, and glucose dysregulation including development of diabetes mellitus. Clozapine treatment is associated with a number of side effects that are less commonly seen with other antipsychotic medications. Severe neutropenia is most often seen early in treatment and is potentially life-threatening. Gastrointestinal effects of clozapine can also be significant and in some patients associated with fecal impaction or paralytic ileus. Allergic and Dermatological Side Effects Cutaneous allergic reactions occur infrequently with antipsychotic medications, but hypersensitivity can manifest as maculopapular erythematous rashes typically of the trunk, face, neck, and extremities. In terms of other dermatological side effects, thioridazine treatment is rarely noted to be associated with hyperpigmentation of the skin. A blue-gray discoloration of the skin has been reported in patients receiving long-term chlorpromazine treatment in body areas exposed to sunlight. Consequently, patients who are taking these medications should be instructed to avoid excessive sunlight and use sunscreen. Cardiovascular Effects Hyperlipidemia There is some evidence that certain antipsychotic medications, particularly clozapine and olanzapine, may increase the risk for hyperlipidemias (Buhagiar and Jabbar 2019; Bushe and Paton 2005; Meyer and Koro 2004; Mitchell et al. Some patients develop an elevation of triglyceride levels in association with antipsychotic treatment that rarely is sufficiently high as to be associated with development of pancreatitis (Alastal et al. It is unclear whether triglyceridemia with antipsychotic treatment is a direct result of the medication or an indirect result of increased triglycerides in the blood with concomitant diabetes (Yan et al. For cardiomyopathy the reported incidence is even less clear but appears to be considerably lower than rates of clozapine-associated myocarditis (Higgins et al. Other features can include fatigue, chest pain, palpitations, and peripheral edema. For example, primary tachycardia is common with clozapine treatment without signifying underlying cardiac disease. Fever can also occur with clozapine initiation, yet often resolve quickly and without evidence of myocarditis (Bruno et al. Recommendations for monitoring have varied but there is no evidence or consensus that preemptive screening is necessary or helpful. However, if myocarditis or cardiomyopathy is suspected, a recent systematic review suggests seeking cardiology consultation as well as monitoring C-reactive protein and troponin (I and T subtypes), and obtaining an electrocardiogram as indicated (Knoph et al. Though the Bazett formula remains most widely used for drug monitoring and research, alternative correction formulae, such as the Fridericia and Framingham formulae, have been shown to most accurately correct for rate and improve prediction of mortality. Clinicians should be familiar with an alternative correction formula to accurately predict risk (Aytemir et al. Although healthy patients may be able to tolerate some increase in resting pulse rate, this may not be the case for patients with preexisting heart disease. Management strategies for tachycardia with antipsychotic medications include reducing the dose of medication, discontinuing medications with anticholinergic or stimulant properties, and using the strategies described above to reduce any contributing orthostatic hypotension. If tachycardia is accompanied by pain, shortness of breath, fever, or signs of a myocardial infarction or heart rhythm problem, emergency assessment is essential. Endocrine Side Effects Glucose Dysregulation and Diabetes Mellitus Evidence from meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials, population-based studies, and case control studies suggests that some antipsychotic medications, clozapine and olanzapine in particular, are associated with an increased risk of hyperglycemia and diabetes (Hirsch et al. Complicating the evaluation of antipsychotic-related risk of diabetes is that some patients with first-episode psychosis seem to have abnormal glucose regulation that precedes antipsychotic treatment (Greenhalgh et al. In addition, obesity and treatment-related weight gain may contribute to diabetes risk. The clinician can also help in ensuring that patients are obtaining appropriate diabetes care, given frequent health disparities for individuals with serious mental illness (Mangurian et al. Other effects of hyperprolactinemia may include breast tenderness, breast enlargement, and lactation (Ajmal et al. The long-term clinical consequences of chronic elevation of prolactin are poorly understood. Chronic hypogonadal states may increase the risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis and fractures may be increased in individuals with schizophrenia, but a direct link to antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia has not been established (Bolton et al. In addition, some concern has been expressed about potential effects of hyperprolactinemia on the risk of breast or endometrial cancer; however, the available evidence suggests that such risks, if they exist, are likely to be small (De Hert et al. If a patient is experiencing clinical symptoms of prolactin elevation, the dose of antipsychotic may be reduced or the medication regimen may be switched to an antipsychotic with less effect on prolactin such as an antipsychotic with partial agonist activity at dopamine receptors (Ajmal et al. Although multiple factors are likely to contribute and rates vary widely depending on the study, it is clear that antipsychotic treatment contributes to sexual dysfunction (de Boer et al.
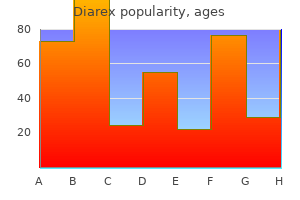
Purchase generic diarex from india
Oral dissolving tablet dissolves rapidly in saliva and may be swallowed with or without liquid gastritis diet зщктщ diarex 30 caps low price. Quetiapine Seroquel Tablet, Immediate Release: 25, 50, 100, Immediate 400-800 800 Once daily dosing for extended release and 200, 300, 400 Release: 50 divided dosing for immediate release. Inform patients with phenylketonuria that oral disintegrating tablets contain phenylalanine. Antipsychotic medications: pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of oral and short-acting intramuscular formulations15 Trade Oral Time to Protein Metabolic Metabolites Elimination Excretion Hepatic Renal name bioavaila peak binding enzymes/transporters half-life in impairment16 impairment bility level adults First-Generation Antipsychotics Chlorpromazi Thorazine 32% 2. Antipsychotic medications: relative side effects of oral formulations18 Trade name Akathisia Parkinsonism Dystonia Tardive Hyper Anticholinergic Sedation dyskinesia prolactinemia19 First-Generation Antipsychotics Chlorpromazine Thorazine ++ ++ ++ +++ + +++ +++ Fluphenazine Prolixin +++ +++ +++ +++ +++ + + 18 Source. Long-acting injectable antipsychotic medications: availability and injection related considerations20,21 Trade Available How supplied Injection site and Reactions at Comments name strengths22 technique23 injection site24 (mg, unless otherwise noted) First-Generation Antipsychotics 20 this table and the subsequent table on long-acting injectable antipsychotic medications include information compiled from multiple sources. Detailed information on issues such as dose regimen, dose adjustments, medication administration procedures, appropriate needle size based on injection site and patient weight, product reconstitution, handling precautions, and storage can also be found in product labeling. Avoid concomitant injection of Aristada Initio and Aristada into the same deltoid or gluteal muscle. Refer to labelling for detailed instructions on injection site, needle length, and instructions to ensure a uniform suspension. Abilify 2018; Aristada 2019; Aristada Initio 2019; Invega Sustenna 2018; Invega Trinza 2018; Jann et al. Drug-drug Interactions and Metabolism Careful attention must be paid to the potential for interactions of antipsychotic agents with other prescribed medications. In addition, drug interactions can influence the amount of free drug in the blood that is available to act at receptors. These shifts in blood levels can be quite significant and contribute to shifts in medication effectiveness or toxicity. Although the applicability of gene polymorphism testing to the clinical choice of an antipsychotic medication is still being explored (Bousman and Dunlop 2018; Koopmans et al. Pharmacokinetic Properties the absorption of some antipsychotic medications is affected by the presence of food in the stomach. Older individuals often exhibit additional physiological changes relative to younger persons including a reduced cardiac output (and concomitant reduction in renal and hepatic blood flow), reduced glomerular filtration rate, possible reduction in hepatic metabolism, and increased fat content. Later, maintenance treatment will aim to prevent recurrence of symptoms and maximize functioning and quality of life. Younger individuals who are experiencing a first episode of psychosis may be more likely to gain weight or develop adverse metabolic effects of antipsychotic medications (Correll et al. Determining the optimal dose of antipsychotic medication during acute treatment is complicated by the fact that there is usually a delay between initiation of treatment and full therapeutic response. Patients 90 may take between two and four weeks to show an initial response and longer periods of time to show full or optimal response. Once a therapeutic dose of the antipsychotic medication is reached, overly rapid or premature escalation of medication doses can affect tolerability. Available evidence suggests that patients who have not exhibited at least a 20% reduction in symptoms (or minimal improvement) by about two weeks on a therapeutic dose are unlikely to be much improved at four to six weeks as reflected by at least a 50% reduction in symptoms (Samara et al. Loss of libido and anorgasmia can occur in men and in women; erectile dysfunction and ejaculatory disturbances also occur in men (La Torre et al. Retrograde ejaculation has also been reported with specific antipsychotic medications. In addition, it is important to note that priapism can also occur in association 100 with antipsychotic treatment, particularly in individuals with other underlying risk factors such as sickle cell disease (Burnett and Bivalacqua 2011; Sood et al. When sexual side effects of antipsychotic therapy are of significant concern to the patient, a reduction in medication dose or change in medication may be considered in addition to an assessment of other potential contributing factors. Gastrointestinal Side Effects the most common gastrointestinal side effects of antipsychotic medications are related to anticholinergic side effects and include dry mouth and constipation as noted above. Patients and families should be educated about monitoring for constipation and, if present, constipation should be reported promptly to clinicians. With clozapine in particular, gastrointestinal hypomotility can be severe and can result in fecal impaction or paralytic ileus (Every-Palmer and Ellis 2017; Leung et al. To prevent development of constipation, particularly with clozapine, it is useful to minimize the doses and number of contributory medications such as other anticholinergic medications and opioids. National Library of Medicine 2017), including elevation of liver enzyme levels and cholestatic jaundice. Cholestatic jaundice is rare and has been primarily reported with chlorpromazine (U. It usually occurs within the first month after the initiation of treatment and generally requires discontinuation of treatment. However, given the relative infrequency of antipsychotic-induced jaundice, other etiologies for jaundice should be evaluated before the cause is judged to be antipsychotic medication. With clozapine, a complex polygenic trait appears likely, perhaps involving the human leukocyte antigen locus or a group of hepatic transporter genes (de With et al. However, data from the initial five years of monitoring through clozapine registries showed a rate of severe neutropenia of 0. For clozapine-treated patients as a group, the incidence of death due to severe neutropenia was 0. If severe neutropenia does develop, it is usually reversible if clozapine is discontinued immediately and secondary complications. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor has been used to accelerate granulopoietic function and shorten recovery time (Lally et al. For patients with a good clinical response to clozapine after multiple unsuccessful trials of other antipsychotic medications, the benefits and risks of rechallenge require thorough consideration and discussion with the patient and involved family members. Under such circumstances, case reports have suggested using granulocyte colony stimulating factor to reduce the risk of recurrence, although evidence is limited (Lally et al. A dystonic spasm of the axial muscles along the spinal cord can result in opisthotonos, in which the head, neck, and spinal column are hyperextended in an arched 102 position. Acute dystonia is sudden in onset and painful and can cause patients great distress. Additional factors that increase the risk of acute dystonia with antipsychotic medication include young age, male gender, ethnicity, recent cocaine use, high medication dose, and intramuscular route of medication administration (Gray and Pi 1998; Spina et al. For further discussion of acute dystonia, including its treatment, see Statement 11. For further discussion of medication-induced parkinsonism, including its treatment, see Statement 12. Generally, when treatment is resumed, doses are increased gradually, and a medication other than the precipitating agent is used, typically one with a lower potency at blocking dopamine D2 receptors. Although generalized tonic-clonic seizures are most frequent, other types of seizures may occur. The seizure risk with clozapine is increased by rapid increases in dose as well as at high blood levels or doses of the drug. In patients who do experience a seizure while taking clozapine or another antipsychotic medication, neurological consultation will be important for delineating the risks of a further seizure, determining whether anticonvulsant therapy. Although the majority of patients who develop tardive dyskinesia have mild symptoms, a small proportion will develop symptoms of moderate or severe degree. Tardive dyskinesia can have significant effects on quality of life and can be associated with social withdrawal (McEvoy et al. Although the impact appears to be influenced by the severity of tardive dyskinesia, individuals with mild symptoms can also experience negative effects on quality of life. For further discussion of tardive syndromes, including their treatment, see Statement 14. Pigmentary retinopathies and corneal opacities can occur with chronic administration of the 106 low-potency medications thioridazine and chlorpromazine, particularly at high doses. If patients do undergo cataract surgery, however, there have been case reports of intraoperative floppy-iris syndrome in individuals treated with antipsychotic medications, a complication that has been associated with use of medications that block alpha 1 adrenergic receptors (Chatziralli and Sergentanis 2011).
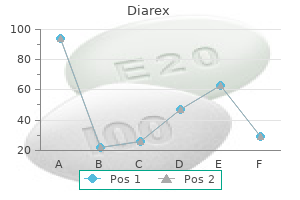
Glycine Max (Soybean Oil). Diarex.
- Use as a nutritional supplement in intravenous feedings.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Lowering cholesterol levels in people with high cholesterol.
- How does Soybean Oil work?
- What is Soybean Oil?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96231
Purchase cheapest diarex
A potential limitation of this surgery is the retention of one to two cm of anal transition zone wellbutrin xl gastritis purchase diarex with american express. In general bowel preparation has fallen out of favor in abdominal surgery due to concerns of electrolyte imbalances or dehydration. Bowel preparation has been challenged by newer studies that did not find any differences in wound healing or anastomotic leak (1-4) but even may lead to complications like hypermagnesemia (when Mg-Citrate used after colonectomy hypomagnesia possible), hypocalcemia (mostly with NaP causes hyperphosphatemia and concurrent hypocalcemia) among others. All types of mechanical preparation occasionally engender serious complications (7,8,9). Intra-operative anesthetic management Patients with a bowel obstruction or ileus are at risk for aspiration. In open procedures an epidural (also section 6) might be beneficial and your anesthesia maintenace will depend on the placement. Laparoscopic surgeries are thought to be less painful and hence oftentimes no epidural will be placed although epidurals also have the benefit of reducing postoperative ileus, even in laparoscopic surgery (11, 12). Ongoing muscle relaxation is often requested by the surgeons to facilitate visualization. Mostly restrictive fluid management in bowel surgeries is indicated as studies have shown benefits in terms of healing and bowel edema. The term fast track in colon surgery was first used by Professor Henrik Kehlet (10). Basically, fast track colon surgery can be seen as the global package of perioperative care encompassing preoperative, operative, and postoperative techniques, which in aggregate result in fewer complications, a reduction in cost, less postoperative pain, a reduction in the hospital length of stay, and quicker return to work and normal activities. Mechanical bowel preparation for elective colorectal surgery: a multicentre randomised trial. Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials of colorectal surgery with or without mechanical bowel preparation. What is the role of mechanical bowel preparation in patients undergoing colorectal surgery Postoperative hypocalcemic tetany caused by fleet phospho-soda preparation in a patient taking alendronate sodium: report of a case. Bowel preparation with polyethylene glycol electrolyte lavage solution is potentially hazardous in patients with carcinoma of the cardia: a case report. Randomized controlled trial to examine the influence of thoracic epidural analgesia on postoperative ileus after laparoscopic sigmoid resection. This document will not cover specific infection prevention policies and procedures; local and institutional guidelines should be followed. If chest imaging is abnormal and in patients for whom it is clinically indicated. Currently, there are several drugs being evaluated in clinical trials in several nations including lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin, hydroxychloroquine, darunavir/cobistat and interferons alpha and beta. At this point no recommendations can be made on specific therapies due to limited data and unknown risk vs benefit; additional recommendations will be forthcoming. If chest imaging normal and no symptoms (ie testing done for surveillance), no therapy is recommended. If chest imaging normal and mild upper respiratory symptoms (rhinorrhea, sore throat, etc), no therapy is recommended but can be considered if symptoms progress. Given uncertainty regarding the significance of detection in blood and current lack of testing capability, the following recommendations rely on donor infection and exposure history and testing in respiratory samples. At this time, it is not possible to make specific recommendations as to the exact timing between collection and cryopreservation and initiation of conditioning. Your case manager will be happy to work with you to make arrangements with the donor and donor center for cryopreservation. Donors within 28 days prior to donation should practice good hygiene and avoid crowded places and large group gatherings. Liang W, Guan W, Chen R, Wang W, Li J, Xu K, Li C, Ai Q, Lu W, Liang H, Li S, He J. Yang Y, Yang M, Shen C, Wang F, Yuan J, Li J, Zhang M, Wang Z, Xing L, Wei J, Peng L, Wong G, Zheng H, Liao M, Feng K, Li J, Yang Q, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Liu L, Liu Y. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections2020:2020. Predictive Value of Respiratory Viral Detection in the Upper Respiratory Tract for Infection of the Lower Respiratory Tract With Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Heart attacks, otherwise known as myocardial infarctions, are caused when the blood supply to a section of the heart is suddenly disrupted. Without the oxygen supplied by blood, the portion of the heart muscle fed by the blocked artery can become damaged. If blood flow is not restored, the cells within the heart muscle will start to die. Behaviors such as unhealthy diet, low levels of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the conditions that can cause heart attacks. Some factors, such as age and family history of heart disease, cannot be modified but are associated with a higher risk of heart attack. It is estimated that every year 610,000 Americans with have a new heart 4 attack and 325,000 Americans will have a recurrent heart attack. People who have had a heart attack 4 are 4 to 6 times more likely than the general population to die suddenly. The Economic Impact of Heart Attacks In 2004, acute heart attack was responsible for $31 billion in inpatient hospital charges and 695,000 4 4 hospital stays. Heart attacks cause significant economic impacts through loss of productivity and premature death. Heart attacks can be treated with medication, such as clot-busting drugs and/or aspirin, or angioplasty (also known as percutaneous coronary intervention). Angioplasty involves threading a small balloon into the blocked artery then inflating the balloon to open the artery. In some cases a doctor may perform bypass surgery where a vein or artery from another part of the body will be used to bypass the blocked artery in the heart to restore blood flow. The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation include reduced mortality, reduced symptoms, improved health-related quality of life, reduced hospitalization and use of medical 7 resources and increased positive lifestyle changes. However, only a third of heart attack survivors 4 participate in outpatient cardiac rehabilitation. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2011 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Chronic high blood pressure can cause hardening of the artery walls which can eventually cause decreased blood flow. High blood pressure is more common in people with lower educational attainment, lower household income, people older than 55 years, retirees and residents unable to work, and people of Native Hawaiian or Japanese ethnicity. High Blood Cholesterol: Blood cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is made in the body and is present in many foods. Too much cholesterol in the blood can cause a build-up on the artery walls (called plaque) that can narrow the artery allowing less blood to pass through. The prevalence of high blood cholesterol increases with age but is common across ethnicities, counties, and people of all educational and household income categories. High blood cholesterol is particularly common in retirees and those unable to work, Japanese, and older Hawaii residents. Diabetes: Diabetes is a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose or blood sugar that results from improper production or use of the hormone insulin. High blood sugar can lead to hardening of the blood vessels and is also linked to increases in blood pressure. Native Hawaiians and those with low educational attainment or low household income tend to have a higher prevalence of diabetes. Smoking: Smoking speeds up the progression of atherosclerosis, the process of plaque build-up and hardening of the arteries, and increases the likelihood of a blood 8 clot by causing platelets to clump together. Smoking is most common in the 25 to 34 year old age group, Native Hawaiians, adults with less than a high school education, those with lower household income, and in residents of Hawaii County compared to Honolulu County. Unemployed residents of Hawaii are more likely to smoke than students or homemakers and retirees (23. Overweight and obesity results from consuming more calories than are expended and strain the cardiovascular system by increasing the risk of high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and diabetes.
Syndromes
- Wet dressings (use only when instructed)
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Damage to nerves in the foot
- Do not clean your ears too often or too hard. Ear wax also helps protect your ears.
- Coma
- Amputation
- Exposure to radiation
Order on line diarex
Dental patients present with various levels of pain and a safe and effective approach can be challenging gastritis breathing generic 30caps diarex mastercard. Multimodal analgesia is the administration of two or more analgesic drugs with different mechanisms of action. Box 2 For example, it is not uncommon to observe increased body weight and activity, and better sleeping patterns/quality of life after treatment of oral disease. In general, pain associated with oral disease may create specific and/or nonspecific clinical signs which will improve after oral treatment. Signs of dental pain include ptyalism, halitosis, decreased appetite, rubbing or pawing the face, changes in demeanor and reluctance to play with toys. Perioperative pain control Opioids are the first line of treatment in acute pain management and they have been reviewed in detail elsewhere. This is of interest in dental patients, however there might be liability issues of prescribing these medications to be administered by owners. Most oral and maxillofacial disorders and therapies involve inflammation and tissue damage/trauma. This may be particularly important after significant oral surgery, such as full-mouth extractions due to feline chronic gingivostomatitis. Local anesthetic techniques of the oral cavity Local anesthetic drugs produce a reversible block of sodium and potassium channels and transmission of nociceptive input. These blocks require minimal training and can be used for a variety of dental procedures including extractions or surgery of the oral cavity such as maxillectomy, mandibulectomy, among others. Some considerations are presented below: Unfortunately, local anesthetic techniques are not widely employed in veterinary medicine due to the lack of familiarity with use. Drugs Table 4 shows common doses and concentrations of local anesthetics (Table 4). Levobupivacaine or bupivacaine may be preferred over lidocaine for local anesthetic techniques of the oral cavity due to its prolonged duration of action. Anesthesia of the lingual and mylohyoid nerves may occur during a mandibular nerve block and result in desensitization of the rostral two-thirds of the tongue. In dogs, bupivacaine alone or in combination with buprenorphine reduced isoflurane requirements by approximately 20%. Intraosseous or intraligamentary anesthesia might be an option when other techniques have failed, however these blocks do produce intrinsic pain at injection. Avoiding complications There are some important considerations before the administration of any local anesthetic block to avoid complications Calculation of toxic doses Local anesthetic toxicity may occur when dosage regimens and intervals of administration are not properly calculated. If bupivacaine is administered intravenously, dysrhythmias such as ventricular premature contractions may be observed. Complications after local anesthetic blocks of the oral cavity are rare but have been reported and include globe penetration most often requiring enucleation (Perry R et al 2015). Administration of a local anesthetic block should be performed in non-inflamed areas to improve efficacy. This foramen may be difficult to palpate in cats but the block can be still performed successfully. For desensitization of ipsilateral canine tooth, a maxillary nerve block is preferred and produces more consistent blockade. Caution must be taken with this block, as the infraorbital foramen is located just ventral to the orbit. The infraorbital canal is much shorter in cats and brachycephalic dogs than in normo and dolichocephalic dogs. To avoid eye penetration, the needle should be introduced ventrally and advanced only approximately 2 mm. The upper lip is elevated and the infraorbital foramen is located (approximately dorsal to the third premolar tooth). The level of sedation should be assessed before induction of anesthesia to determine best dosage regimens of each agent. Anesthetic blocks can be repeated according to the duration of procedure, interest of postoperative analgesia and using less than maximum recommended doses (see text). Alef M, von Praun F, Oechtering G (2008) Is routine pre-anaesthetic haematological and biochemical screening justified in dogs Stepaniuk K, Brock N (2008) Hypothermia and thermoregulation during anesthesia for the dental and oral surgery patient. Development and initial validation of a pain scale for the evaluation of odontostomatologic pain in dogs and cats: preliminary study. Proceeding of nd the Association of Veterinary Anaesthetists Meeting, 20-22 April 2016, Lyon, France. Reid et al (2017) Definitive Glasgow acute pain scale for cats: validation and intervention level. Section 4: Oral Examination and Recording A thorough oral diagnosis of every patient is based on the results of the case history, clinical examination and charting, dental radiography and laboratory tests if indicated. Examination of Conscious Patient Some procedures can be performed on a conscious patient during the first consultation. The results provide an overview of the level of disease and allows for the formation of the preliminary treatment plan. Oral/Dental Examination the examination starts with a thorough history including symptoms which may indicate dental disorders such as: halitosis, change in eating habits, ptyalism, head shaking etc. The examined criteria are: lymph nodes, dental deposits, periodontal status, nutrition and oral care (professional and homecare). Each criteria is scored with respect to the clinical findings and a total score is then determined. Abnormities are defined as either a skeletal malocclusion or malposition of single teeth (for more detail see chapter 1d: Malocclusion). Following induction of anaesthesia, the examination should be performed in a detailed and structured way with the charting performed simultaneously. After the visual inspection of the entire oral cavity, the tactile examination is performed in two steps utilizing the appropriate instruments. Following this, pocket depth and furcation exposure are evaluated with a periodontal probe. The photographs serve as proof for pre-operative dental condition as well as provide visual evidence to the owner. It is recommended to use a lip retractor or dental mirror to better visualize the entire dentition and surrounding structures. Intraoperative photograph: it is advised to take a photograph of any pathology revealed by the scaling. Dental examination with dental explorer: each tooth must be examined with a dental explorer, beginning with the first incisor of each quadrant and progressing distally caudally tooth by tooth to cover the entire arch. Additional therapy: Based on all available information (visual, tactile, and radiographic) determine and execute the final treatment plan. In this situation, a thorough examination with a dental explorer, a periodontal probe and a mirror will give fairly accurate information about status of the oral cavity. Recording A thorough examination can only be performed on an anaesthetized patient. They must also be kept as part of the medical record and may be used to illustrate, to the owner, when explaining the work performed. The first digit denotes the quadrant, which is numbered clockwise beginning at the upper right quadrant (1-4 for permanent dentition, 5-8 for primary dentition). The advantages of the Modified Triadan System are that it allows for easy identification of a tooth, is understood throughout the world (no language barrier), issuitable for all species, faster than writing out the tooth description, and ideal for digitalized recording and statistics. The basic clinical findings can be scored with a simple mouse click onto the dental charts. With a few clicks the clinic data and logo can be inserted, and an individual report created which will increase the customer loyalty. Journal of Nutrition 136: 2021S-2023S Gorrel C (2004) Odontoclastic resorptive lesions. The loss of periodontal attachment is less than 25% as measured either by probing of the clinical attachment level, or radiographic determination of the distance of the alveolar margin from the cementoenamel junction relative to the length of the root. Plaque removal and control consists of 4 aspects depending on the level of disease.
Cheap diarex 30caps on line
In regimens with minimal myelo among the elderly and in patients with substantial co suppression and minimal mucosal toxicity gastritis diet молодежка generic diarex 30caps amex, the risk morbidities. This is because en new options for donor sources and preparative regi graftment of allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cells mens. However, ful consideration of the individual case in light of ev with other regimens, depletion of recipient lympho idence-based data. The blue line represents the recovery of relatively radiotherapy/che motherapy-resistant cells such as plasma cells, tissue dendritic cells (eg, Langerhans cells) and, perhaps, tissue macrophages/microglia. B cells are also long-lived, radioresistant plasma cells survive many primarily regenerated from lymphoid progenitor cells, preparative regimens [53] and can produce substantial as evidenced by the appearance of primitive B cell sub circulating IgG without providing humoral responses sets as the harbinger of B cell immune reconstitution to specic pathogens. Here, mature T cells contained within recipient factors such as age, comorbidities, and infec the graft dramatically expand in vivo in response to T tious exposure prior to transplant contribute substan cell lymphopenia. This process is driven by a combina tially to the risk for posttransplant infectious tion of factors, among which are increased availability complications. Third, graft-asso antigens (either environmentally or via reactivation) ciated factors also play an important role. Memory T cells respond quickly to previously incidence of fungal infections, and improved overall encountered pathogens such as herpesviruses. Moreover, most of the published studies histocompatibility, disease status, graft type, graft con have focused on the association of immune assay Table 3. Additional studies are needed before any one of the immune tests presented here can be recommended for use in decision making on infection prophylaxis (see text). Future work is needed to augment the de studies are needed, rst to conclusively determine gree of immune reconstitution toward pathogens and what immune monitoring test has prognostic value malignancy and to identify accurate surrogate markers and ultimately to determine whether outcomes would of immunocompetence to guide the long-term improve if such a test were used to tailor infection pro management of this high-risk population. In general, In most patients, immunocompetence improves pro these strategies are dictated by national regulations, gressively with increasing time after transplant, an and, therefore, ratings are not included. Assessment of the donor should include to both the usual consequences of the disorder and elements related to safety for the donor (eg, uncon the ease of managing those consequences. Similarly, those with acute toxoplasmosis 2006, 3269 (39%) adult products and 829 (40%) should not donate until the acute illness has resolved. The to determine their general state of health and whether sole exception is testing for syphilis, where a syphilis they pose a risk for transmitting infectious diseases to specic test is used for determination of eligibility [80]. Evaluation of donors is achieved through Use of Potentially Unsafe Products screening and laboratory testing [76-78,80]. Screening and testing of autologous donors is recommended to Oversight by governments and unrelated donor ensure the safety of laboratory personnel and to pre registries generally precludes the use of a volunteer un vent cross contamination. Whether to select a related be specially labeled and handled as if potentially donor who is at risk for or who has an infectious disease infected [76-78,80]. Abbreviated screening is an inquiry about topoietic cell product from an infected or infectious do any changes in history, risk factors, or physical nd nor unless no other stem cell product can be obtained ings. This practice is critical because if new risk nd and the risk for death if transplantation is not per ings have developed, the potential donor might formed is deemed to be greater than the risk for mor require further evaluation or deferral. The physical examination of the donor is tar legal guardian acknowledging the possible transmis geted to detect stigmata associated with transfusion sion of an infectious agent during the transplantation. In the European Union, seropositivity as the only evidence of infectiousness) the testing specimen must be obtained at the time of do should be labeled as being a biohazard or as untested nation or within 7 days after donation unless the product for biohazards, as applicable. If storage is possible, the sample may be list all disease agents or diseases for which the donor obtained up to 30 days prior to donation; however, has shown reactive test results. Antibacterial prophylaxis is generally started at nation of collected stem cell units at the collection site, the time of stem cell infusion and continued until re during processing and transportation, and at the trans covery from neutropenia or initiation of empirical plant center [126-141]. Current, comprehensive dis antibacterial therapy for fever during neutropenia cussions of these issues are detailed in the Food and [148-152]. Local epidemiologi regulations [142], in the European Commission regu cal data should be carefully considered before applying lations [81], and in international standards established uoroquinolone prophylaxis, and once it is applied, the by the professional organizations [76,77,143]. Raad vate third-generation cephalosporins [158-160]; and In addition to general recommendations regarding quinolone-related development of a hypervirulent bacterial infections, this section provides specic rec strain of C. A review found a similar risk of infection re gardless of whether catheter dressings consisted of Preventing late disease (. Other al in catheter removal and, much less commonly, in death ternatives, including lock solutions containing [175,176]. In 1 retrospective study, the minocycline/ rifampin impregnated catheters did not affect the sus Recommendations Regarding ceptibility of staphylococci to tetracyclines or Streptococcus pneumoniae rifampin [181]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 15:1143-1238, 2009 Preventing disease this approach has not been systematically studied. Viridans Streptococci Recommendations Regarding Preventing exposure Bordetella pertussis Viridans streptococci are normal commensals, pri marily of the oral surfaces. In addition to standard pre source of viridans streptococcal bacteremia and sepsis. Ganciclovir or foscarnet can be considered as an Ganciclovir is often used as a rst-line drug for alternative drug for second-line preemptive therapy preemptive therapy. Cidofovir, a nucleoside analog, can be con as ganciclovir [230], it is currently more commonly sidered for second-line preemptive therapy, but careful used as a second-line drug, because of practical reasons monitoring of renal function is required, and it should (eg, requirement for prehydration and electrolyte be noted that crossresistance with ganciclovir can monitoring). Other autologous recipi ysis of a randomized, controlled study has shown com ents at high risk who experience moderately high levels parable results in patients treated with i. To date, no serious disease has been reported exercise caution and decrease the dose as needed. A vaccine-associated rash occurs in ap (whether after exposure to a person with wild-type var proximately 1% to 5% and 0. Because the risk Treatment may be completed with oral valacyclovir of vaccine virus transmission is low, particularly in if the patient can tolerate oral medication. Postexposure acyclovir or valacyclovir (Appen same for allogeneic or autologous recipients. Oseltamivir can be administered to persons z1 year Preventing disease of age and older. If 2 diagnostic samples taken z2 days apart made in these guidelines because of lack of treatment do not identify a respiratory pathogen despite persis data. Of note, the response to vaccination is likely to be poor in patients undergoing chemotherapy. Antiviral therapy should be initiated tive, treat as described in the bullets earlier for a donor prior to conditioning. Treatment should be contin reliable testing of the blood supply began in 1992 in ued for 24 to 48 weeks, depending on response. The donor should be assessed for chronic as exanthema subitum or sixth disease [386]. However, there are few reactivation is common during the early allogeneic reports on success of this method [381,382]. Acellular pertussis vaccine is pre ferred, but the whole-cell pertussis vaccine should be used if it is the only pertussis vaccine available. In females with pregnancy potential, vaccination with rubella vaccine either as a single or a combination vaccine is indicated. A post hoc anal to be colonized with uconazole-resistant Candida ysis of a randomized clinical trial has shown that species. Use of micafungin as a prophylac When considering continuation of antifungal ther tic agent is limited by the necessity of i. There have been case reports of sporadic resis should be mindful of drug interactions, especially with tance to echinocandin antifungal agents [426]. If antimold activity is warranted in antifun bolites with coadministration of different azole drugs gal prophylaxis, posaconazole and voriconazole are [432,433]. As ra strains among patients with aspergillosis and fusario diographic abnormalities may persist for a long period sis [435-437]. Therefore, hospital water should be of time among patients with hepatosplenic candidiasis, considered a potential source of nosocomial invasive complete resolution is not necessary before transplan mold infections.
Cheap diarex 30 caps online
Subdermal electrodes are used when other recording techniques are not feasible such as in the operating room and intensive care unit gastritis symptoms diarrhoea purchase diarex 30caps on line. Electrode placements systems use either a 10-20 system (black circles) or modified combinatorial system with 10-10 electrode placement (black circles + white circles). Respiratory monitors may also be important if respiratory problems are identified. A reference montage uses an active electrode site as the initial input, and then at least one neutral electrode to depict absolute voltage through amplitude measurement that is commensurate with the area of maximal electronegativity or postivity 1. Even multiple averaged sites of reference (or Laplacian montages for very focal recordings) may be useful for localized discharges. Bipolar montages may be arranged in many different spatial formats including longitudi nally, transverse fashion, or in a circumferential pattern. The longitudinal bipolar (also called double banana) is frequently represented through out this text. An anterior to posterior temporal and central connecting chain of electrodes arranged left alternating with right-sided placement is a typical array. Bipolar montages compare active electrodes sites adjacent to each other and signify absolute electrographic sites of maximal nega tivity (or positivity) by phase reversals 1. Recordings are usually performed with a visual display of 30 mm/sec (slower with sleep studies), amplifier sensitivities of 7 IV/mm, and fil ter settings of 1 to 70 Hz. Reducing the low filter settings promotes slower frequency representation, while reducing high filter settings decrease high frequency. Various generators of nonphysiological and physiological artifacts may deceive the interpreter to believe that the apparent sources are abnormal or epileptiform. In the example above, pulse artifact is seen that is usually seen in a sin gle channel as a periodic slow wave. Eye movement monitors demonstrating the in-phase cerebral ori gin of the diffusely slow background in this awake patient, and the out-of-phase movement of the eye blink artifacts during seconds 3 and 8. Normally, the eye functions as an electrical dipole with a relative positivity of the cornea compared to the retina. Electrodes recording above and below the eye will help to distinguish the brain as the gen erator (same polarity is every channel) from an artifact (opposite polarity in electrode sites above and below the eye). Artifact from three horizontal eye movements (looking left) followed by two vertical eye blinks. When the eyes move to the left yielding a pos itive phase reversal in F7 due to the cornea polarity, the homologous F8 electrode site demonstrates a negative phase reversal from the retina. Note the two lateral eye movements at the end of second 1 and during second 4 in Figure 1. The positive phase reversals noted at the F8 derivation is due to the proximity of the cornea. The homologous F7 electrode site is negative due to the conjugate effect from the retina. However, because vertical eye movements are often the source of confusion, bilateral infraorbital electrodes referred to the ipsilateral ear as a reference may better represent the eye as a dipole and demonstrate phase reversals that are out-of-phase with cerebral activity when due to eye movements (see above). Eye move ment monitors may be added during the recording if difficulty differ entiating cerebral function from extracerebral origin becomes desirable. The contractions are time locked to the photic stimulation and begin and cease commensurate with the flash, although there is often a brief delay between the flash and the myogenic potentials that appear. Spikes occur with rapid eye movements to the left, right, left, and right in the 4th to 6th second. Each rapid eye movement is associated with a positive potential represented by a phase reversal on eye deviation to the side of the lateral rectus contracting. Oz has continuous single electrode artifact, and a bifrontal burst of muscle artifact is seen in second 3 to 4. Myogenic potentials are composed of high-fre quency activity that is much briefer than the 20-msec potentials seen with epileptiform discharges. In addition, an aftergoing slow wave is absent, and having the individual relax their jaw muscles or capturing sleep will lead to waning or elimination of a myogenic artifact. Associated slow potentials during chewing reflect associated swallowing move ments created by the tongue. The tongue, like the eye, acts as a dipole with the tip of the tongue being positive relative to the root. The chewing that is an effect created by the temporalis muscles is accom panied thereafter by the glossokinetic movements of the tongue. Pseudogeneralized spike-and-wave during intermittent photic stimulation due to superimposition of a physiological artifact from eye flutter and frontally predominant muscle artifact. Identifying nor mal morphologies within the background and comparing the frequen cies of one or series of suspicious waveforms may help separate normal from abnormal. In the above example, combined artifacts (eye flutter and muscle artifact) create the appearance of a photoparoxys mal response during intermittent photic stimulation that could be a pitfall to novice interpreters. Identifying a single electrode artifact should prompt a technologist to check the impedance and resecure the electrode scalp-electrolyte interface, change the electrode with a per sistent artifact, and/or move the electrode to an alternate channel to determine if the channel itself is defective. This artifact should prompt a search for electrodes with an impedance of >5000 ohm when a single electrode is involved, as well as ensuring that ground loops and double grounds do not put the patient at a safety risk when generalized a 60-cycle artifact is found, as in the above example. However, notice the persistent right temporal myogenic artifact in the example above. In the above Sexample, the sphenoidal derivations were not functional and cre ated an electrode artifact that closely mimicked a temporal sharp wave. Note the lack of a believable cerebral field and the absence of any deflection in the true temporal and lateral temporal derivations despite the high amplitude reflected in the scale in the bottom right hand corner. In this way, the patient or unshielded electrodes act as an antenna and produce extracerebral sources of artifact similar to the way nearby power lines may create external 60-Hz interference by the inducting magnetic fields created from nearby current flow. It is the current flow that results in electrode depolarization, is amplified by the amplifiers, and creates the resultant noise. Electrical induced noise can be more evident for routine mechanical function at high gain (low sensitivity) settings. Some of these artifacts may be generated by high frequencies pro duced by nearby electrical machinery not directly connected to the patient. When this rhythm is atten uated with eye opening, it is referred to as the alpha rhythm. The alpha rhythm remains stable between 8 and 12 Hz even dur ing normal aging into the later years of life. The alpha rhythm is distrib uted maximally in the occipital regions, and shifts anteriorly during drowsiness. Voltage asymmetries of >50% should be regarded as being abnormal, especially when the left side is greater than the right. It is best observed during relaxed wakefulness, and has a side to side difference of <1 Hz. Normally, alpha frequencies may transiently increase immediately after eye closure (alpha squeak). Alpha variants include forms that are one-half (slow alpha) or two times (fast alpha) the frequency with similar distribution and reactivity. Paradoxical alpha occurs when alertness results in the presence of alpha, and drowsiness does not. While it resembles the alpha rhythm, it does not block with eye opening, but instead with contralateral movement of an extremity. It may be seen only on one side, and may be quite asym metrical and asynchronous, despite the notable absence of an under lying structural lesion. The mu rhythm may slow with advancing age, and is usually of lower amplitude than the existent alpha rhythm. When persistent, unreactive, and associated with focal slowing, mu like frequencies are abnormal. Breach rhythm in the right temporal region (maximal at T4) following craniotomy for temporal lobectomy.

