Entocort
Purchase entocort 100mcg
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3656? Subacute granulomatous (de Quervain) thyroiditis: 3661 allergy medicine knocks me out buy entocort with visa. Nishihara E, Ohye H, Amino N, Takata K, Arishima T, Sunitinib-induced autoimmune thyroiditis in a patient Kudo T, Ito M, Kubota S, Fukata S, Miyauchi A 2008 with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report. Kubota S, Nishihara E, Kudo T, Ito M, Amino N, induced thyrotoxicosis due to destructive thyroiditis: a Miyauchi A 2013 Initial treatment with 15 mg of pred- case report. Miyauchi A, Takamura Y, Ito Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, Losa M, Motti E, Beck-Peccoz P, Spada A, Mantovani G Matsuzuka F, Amino N, Toyoda N, Nomura E, Nishi- 2014 Thyrotropin-secreting pituitary adenomas: outcome kawa M 2008 3,5,3? J Clin Endocrinol due to increased conversion of administered levothyr- Metab 99:2069?2076. Arch Intern Med Bennet A, Caron P 2015 Primary medical treatment of 140:1230?1231. Sarinnapakorn V, Sridama V, Sunthornthepvarakul T generation somatostatin analogs: a case study of seven 2007 Proptosis in normal Thai samples and thyroid pa- patients. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am of patients with Graves? disease in Chinese of Taiwan. Da Young Lee, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Eun Jun, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim. Knowing the Baseline Neutrophil Level Can Help a Physician Decide Whether to Prescribe Antithyroid Drugs. Relational Stability in the Expression of Normality, Variation, and Control of Thyroid Function. Tetsurou Satoh, Osamu Isozaki, Atsushi Suzuki, Shu Wakino, Tadao Iburi, Kumiko Tsuboi, Naotetsu Kanamoto, Hajime Otani, Yasushi Furukawa, Satoshi Teramukai, Takashi Akamizu. Recommendations are also provided on 131 Therapy Committee is to provide advice to nuclear history and examinations before I therapy, patient 131 medicine clinicians on how to treat benign thyroid counselling and precautions associated with Itherapy. The recom- Furthermore, potential side effects and alternative treat- mendations were formulated based on recent literature ment modalities are reviewed. Special attention is paid to and expert opinion regarding rationale, indications and these aspects in the treatment of children undergoing this 131 contraindications for the use of I procedures, as well as procedure. The recommendations should be taken in the context of good practice of nuclear medicine and do not substitute for national and international legal or regulatory provisions. These generic recommendations cannot be rigidly applied to all patients in all practice settings. The guidelines should not be deemed inclusive of all proper procedures or exclusive of other procedures reasonably directed to obtaining the same results. The data of guidelines should always be considered in determining their current applicability. The Dosimetry Committee was involved in the writing of these guidelines, and they have been reviewed by the Oncology Com- mittee, the Paediatrics Committee and the Physics Committee. The guidelines have been brought to the attention of the National Societies of Nuclear Medicine. Handkiewicz Junak 50937 Cologne, Germany Department of Nuclear Medicine and Endocrine Oncology, M Sklodowska Curie Memorial Cancer Center M. Luster and Institute of Oncology, Department of Nuclear Medicine, University of Ulm, 44100 Gliwice, Poland 89081 Ulm, Germany Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging (2010) 37:2218?2228 2219 Keywords Radioiodine therapy. Children indication for radioiodine treatment, while silent thy- roiditis and subacute thyroiditis are never treated with 131 radioiodine. Purpose treatment of so-called subclinical hyperthyroidism caused by any one of first three entities [1]. This group medicine practitioners to: includes patients who are euthyroid but who may benefit from a reduction in thyroid volume. Evaluate patients who might be candidates for I treatment of benign thyroid disease C. Background information and definitions or recurrent Graves? disease, in those with a suspicion of malignancy, and when there is a severe compression of A. Definitions neighbouring structures or a necessity for immediate effec- tiveness. This difference is obvious, as in nonimmune hyperthy- 131 administration of I as sodium iodide. Benign condition in this context means Graves? disease thyroid hormone production which is activated by somatic (diffuse toxic goitre), toxic or nontoxic goitre and mutations. Malignant conditions are not included in these guide- instances, agranulocytosis and hepatitis; success of this lines (see respective document available at Background solitary hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules, or it can be administered if hyperthyroidism is not controlled or recurs 131 Oral administration of I has been used to treat benign after initial antithyroid drug treatment, such as in Graves? conditions of the thyroid gland since the 1940s. Patients with hyperthyroidism, which is a consequence therapy is often considered the first-line therapy, and the of excessive thyroid hormone action. The causes of physician should not wait until the patient becomes hyperthyroidism include the following: (1) autoimmune symptomatic. Radioiodine treatment is indicated in Indications patients with medical contraindications to thyroid surgery, & Graves? disease patients with slight or moderate compressive symptoms, & Toxic multinodular goitre patients with a large goitre, and patients who whish to & Solitary hyperfunctioning nodule avoid surgery. The interdisciplinary approach to patients & Nontoxic multinodular goitre followed by well-balanced decision making and informed & Goitre recurrence consent allow individualized selection between the alterna- & Ablation of residual thyroid tissue in case of malignant tive treatment options. Special consideration should be ophthalmopathy after surgery, but during an inactive 131 given to the patient?s profession as I is without risk of state of the orbitopathy. Procedure transported in the plasma to the thyroid, where it is concentrated, oxidized, and then incorporated into thyro- A. After storage in thyroid follicles, Tg is subjected to proteolysis and the released the facility requirements will depend on national legisla- hormones are secreted into the circulation. If inpatient normal thyroid function up to 20?30% of orally adminis- therapy is required by national legislation, this should take tered iodine is taken up by the thyroid. In hyperthyroid place in an approved environment with appropriately patients this fraction is increased in extreme cases even up shielded rooms. The average the administration of I should be undertaken by range of the beta particles in soft tissue is approximately appropriately trained medical staff with supporting nursing 0. Indirect effects produce knowledge of the pathophysiology and natural history of free radicals that in turn react with critical macromolecules. Aims of treatment Clinicians involved in unsealed source therapy must also be knowledgeable about and compliant with all applicable In patients with hyperthyroidism, the aim of treatment with national and local legislation and regulations. Patient history with special emphasis on previous treat- may lower the uptake of radioiodine as well the ments (e. Thyroid Tc scintigraphy and radioiodine 24-h uptake: carbimazole, which do not possess sulphydryl groups T24 should be >20%, if lower other treatment modalities and probably do not have radioprotective effects) should be considered. The potentially negative impact of thyrostatic absolutely required when fixed activities are used. Assessment of thyroid target volume (ultrasonography) [11?13] if tolerated by the patient. Propylthiouracil [7] and intrathoracic extension in those with a large which has a more distinct radioprotective action that goitre (magnetic resonance imaging/computed tomog- may further reduce the effectiveness of radioiodine raphy) [8]. It has to be realized, however, that should be stopped at least 2 to 3 weeks (if possible assessment of the target volume by computed tomog- 8 weeks) before radioiodine treatment [14]. Beta raphy using contrast agents will impair the radioiodine adrenergic antagonists (usually propranolol at a dose 131 uptake for weeks to months, making therapy with I adjusted to clinical symptoms) may be helpful for the impossible during that time. In patients with Graves? ophthalmopathy, if not already imaging 24 h after injection is a strategy to confirm on steroid therapy, prednisolone should be adminis- autonomously functioning nodules and to exclude tered. In this respect, however, it has to be 99m Tc-pertechnetate ?trapping only? nodules. In patients with thyrotoxicosis induced by amiodarone for pregnancy within 72 h before the administration of or in those receiving compounds that contain iodine 131 I. Contraception has been stopped sufficiently long for the excess iodine 131 for 4 months after I therapy is also necessary. This can take up to 2 years result is evaluated 6 months after therapy, this interval is (average 6 months) in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxi- recommended in clinical practice to avoid interference cosis [17]. In this respect, the assay of urinary iodine with retreatment in the event of recurrent disease.
Buy entocort with mastercard
Several mutation analysis panels are not only helpful as diagnostic tests seasonal allergy treatment guidelines 200 mcg entocort mastercard, but may also serve as prognostic markers. As these molecular tests are improved further making them more accurate and less expensive, they will continue to become a more integral part of the thyroid nodule evaluation. Funding: this research was funded in part by the Elizabeth and Michael Ruane Center for Endocrine Tumors Fund. Management of Thyroid Nodules with Atypical Cytology on Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy. Use of molecular markers in samples obtained from preoperative aspiration of thyroid. Galectin-3 expression analysis in the surgical selection of follicular thyroid nodules with indeterminate? Molecular Testing for Mutations in Improving the Fine-Needle Aspiration Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules. Molecular Testing for Somatic Mutations Improves the Accuracy of Thyroid Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy. Targeted next-generation sequencing panel (Thyro Seq) for detection of mutations in thyroid cancer. Highly accurate diagnosis of cancer in thyroid nodules with follicolar neoplasm/suspicious for a follicular neoplasm cytology by Thyroseq v2 next generation sequencing assay. Impact of the Multi-Gene ThyroSeq Next-Generation Sequencing Assay on Cancer Diagnosis in Thyroid Nodules with Atypia of Undetermined Signi? Braf mutationin papillary thyroid cancer: Pathogenic role, molecular bases, and clinical implications. The impact of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features on the performance of the A? Molecular diagnostics and the training of future tissue- and cell-based pathologists. Nomenclature Revision for Encapsulated Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Paradigm Shift to Reduce Overtreatment of Indolent Tumors. Cytological features of ?invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features? and their correlation with tumor histology. Impact of reclassifying noninvasive follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma on the risk of malignancy in the Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology. The Impact of Noninvasive Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma on Rates of Malignancy for Fine-Needle Aspiration Diagnostic Categories. Cytological Diagnoses Associated with Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasms with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features According to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Molecular cytopathology for thyroid nodules: A review of methodology and test performance. A meta-analytic review of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: Has the rate of malignancy in indeterminate lesions been underestimated? Young investigator challenge: the morphologic analysis of noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features on liquid-based cytology: Some insights into their identi? Young Investigator Challenge: Molecular testing in noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features. Pre-operative features of non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasms with papillary-like nuclear features: An analysis of their cytological, Gene Expression Classi? Molecular genotyping of the non-invasive encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Most nodules are benign; therefore, many nodules are biopsied to identify the small number that are malignant or require surgery for a de? Since 2009, many professional societies and in- vestigators have proposed ultrasound-based risk strati? Key Words: Thyroid nodule, thyroid cancer, management guidelines, ultrasound J Am Coll Radiol 2017;-:-. Dr Berland received personal fees from Nuance Communications during hHammers Healthcare Imaging, New Haven, Connecticut. Dr Beland has received personal fees from Hitachi iDepartment of Internal Medicine, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Aloka America outside the submitted work. Our recommendations are intended to Korea, mortality has remained extremely low [6]. In the serve as guidance for practitioners who incorporate ultra- United States, overdiagnosis of thyroid cancer, de? In 2015, committees convened by the bidities, life expectancy, and other relevant considerations. The plethora, complexity, and lack of congruence composition (one point) will also gain at least one more of these systems has limited their adoption by the ultrasound point for the echogenicity of its solid component. Do not add further points Hyperechoic/isoechoic/hypoechoic: ments parallel to sound beam for Irregular:Jagged, spiculated, or sharp Macrocalcifications:Cause acoustic for other categories. Peripheral:Complete or incomplete Very hypoechoic:More hypoechoic Extrathyroidal extension:Obvious points for predominant solid than strap muscles. Punctate echogenic foci:May have Assign 1 point if echogenicity cannot Assign 0 points if margin cannot be small comet-tail artifacts. This suggested to us that diagnosing every thyroid malignancy should not be our goal. Like other Structure professional societies [17,19], we recommend biopsy of To make the system easy to understand and apply, the high-suspicion nodules only if they are 1 cm or larger. However, our thresholds for mildly suspi- be characterized as spongiform solely on the basis of the cious and moderately suspicious nodules (2. The Machens et al [26] contended that the cumulative risk for appearance of the solid component is more important than distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid the overall size of the nodule or the proportion of solid versus cancer rose at a threshold of 2 cm. They therefore cystic components in determining whether biopsy is war- advocated biopsy of nodules larger than 2 cm. Solid material that is eccentric and has an acute angle However, our review of their graphs suggested a with the nodule?s wall is suspicious, as is solid material with gradual, slight increase that began at a larger size. More moderately or highly suspicious characteristics, such as important, Machens et al based their analysis on tumor decreased echogenicity, lobulation, and punctate echogenic size in resected specimens, not on ultrasound foci [35-38]. Subsequent research has demonstrated a not been shown to reliably discriminate between benign and signi? Readers are encouraged to refer to the lexicon white paper for detailed descriptions of all the categories and features [8]. If the margin cannot be determined for ponents of thyroid nodules, they may correspond to the any reason, zero points should be assigned. Notably, small echogenic foci malignancy and is an unfavorable prognostic sign [43]. They are not presence of border abutment, contour bulging, or loss suspicious in this circumstance and should not add to of the echogenic thyroid border [44,45]. These include a uniformly hyperechoic (?white knight?) appearance, as well as a variegated pattern of Echogenic Foci hyperechoic areas separated by hypoechoic bands remi- ?Large comet-tail artifacts? are echogenic foci with V-shaped niscent of giraffe hide, both in the setting of Hashimoto?s echoes >1mmdeeptothem. Because of their scarcity, the committee colloid and are strongly indicative of benignity when found chose not to formally incorporate these patterns in the within the cystic components of thyroid nodules. Given published data that show a in recommending against routine biopsy of nodules weakly positive relationship with malignancy [52], smaller than 1 cm, even if they are highly suspicious. However, because some decision making between the referring physician and the publications suggest that they are more strongly patient. The report should indicate whether the nodule associated with malignancy than macrocalci? Some authors have Additionally, nodules in critical submarginal locations called attention to interrupted peripheral calci? Therefore, the report with protruding soft tissue as suspicious for malignancy, should also indicate whether the nodule abuts the trachea but with low speci? Although some interob- may not be apparent if the current sonogram is server discrepancy is inevitable because of variable compared only with the immediately preceding one, it conspicuity, consistent technique improves measurement is important to also review measurements from earlier accuracy and reproducibility. Nodules should be measured in three axes: (1) maximum dimension on an axial image, (2) maximum dimension perpendicular to the previous measurement on Timing of Follow-Up Sonograms the same image, and (3) maximum longitudinal dimen- There is little consensus in the literature regarding optimal sion on a sagittal image (Online Fig. The wide shape, but this discrepancy should rarely present a committee believes that scanning intervals of less than 1 problem in practice.
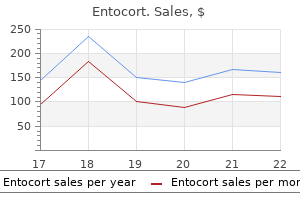
Cheap 100 mcg entocort with mastercard
Lowering of proteinuria in response to antihypertensive therapy world health organization multinational study of vascular disease predicts improved renal function in late but not in early diabetic in diabetes allergy medicine before bed purchase entocort online from canada. Effect of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin predict glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine. J Am Soc system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: Nephrol 2000;11:155A. Mauer M, Zinman B, Gardiner R, Suissa S, Sinaiko A, Strand T, in diabetic ketoacidosis. Effect of candesartan on microalbuminuria and albumin diagnosis in a longitudinal study. Should ratio measurements on random urine samples for prediction all patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria of significant proteinuria: A systematic review. Clin Chem receive angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: a meta-analysis 2005;51(9):1577-86. In: the Cochrane Library, Issue voided urine samples to estimate quantitative proteinuria. Kidney Blood Combination therapy with an angiotensin receptor blocker and an Press Res 2007;30(4):203-11. Nakao N, Yoshimura A, Morita H, Takada M, Kayano T, Ideura type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria. An evaluation of risk factors for adverse drug events associated nephropathy: post hoc analysis from the Reduction of Endpoints with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and hyperlipidemia in chronic progressive renal disease. Am J Cardiol risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 or more 2008;101(7):975-9. Meta-analysis: the effect of of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. The natural dietary protein restriction on prognosis in patients with diabetic course of microalbuminuria in insulin-dependent diabetes: a 10- nephropathy. Severe dietary protein restriction in overt diabetic excretion as a predictor of diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy: benefits or risks? Meloni C, Tatangelo P, Cipriani S, Rossi V, Suraci C, Tozzo C, et 1996;19(11):1243-8. Effect of pregnancy on progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized trial. Low protein diets for A prospective study of serum lipids and risk of diabetic macular chronic kidney disease in non diabetic adults (Cochrane Review). Intensified blood glucose and age-related cataract: the Blue Mountains Eye multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus Study. Effect of a age-related cataract and progression of lens opacities: the Beaver multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. Al-Khoury S, Afzali B, Shah N, Covic A, Thomas S, Goldsmith blood-glucose control on late complications of type I diabetes. Anaemia in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease - Lancet 1993;341(8856):1306-9. Lancet in moderate kidney insufficiency: the Kidney Early Evaluation 1998;352(9131):854-65. Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial, Cochrane Library, Issue 3, 2005. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arch Ophthalmol management and outcomes in diabetic kidney disease in routine 1998;116(3):297-303. Effectiveness of screening and monitoring tests for diabetic progress of established diabetic nephropathy to end-stage renal retinopathy-a systematic review. Practical community screening for diabetic retinopathy Incidence of blindness due to diabetic eye disease in Fife 1990-9. The case for biennial retinopathy screening in children and and Complications Trial. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in children Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Sampling for quality assurance of grading decisions in sight-threatening retinopathy in Type 1 diabetes in a systematic diabetic retinopathy screening: designing the system to detect screening programme. The role of haemorrhage and exudate detection sight-threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in automated grading of diabetic retinopathy. Early vitrectomy for severe vitreous hemorrhage in diabetic Opthalmologists; 2005. Photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema: Early Treatment Publications/2007/12/11103453/0 Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report no. Writing Committee for the Diabetic Retinopathy ultra-widefield scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (Optomap). Arch and specificity of photography and direct ophthalmoscopy in Ophthalmol 2007;125(4):469-80. Invest Ophthalmol nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy and visual outcome after Vis Sci 2007;48(11):4963-73. Romero-Aroca P, Fernandez-Ballart J, Almena-Garcia M, using non-mydriatic fundus photography in a mobile unit. J Cataract Refract Surg uptake in a well-established diabetic retinopathy screening 2006;32(9):1438-44. Instant electronic imaging systems are superior to Polaroid at Lancet 2007;370(9600):1687-97. Int of retinopathy in type 2 diabetes: identification of prognostic Ophthalmol 2008;28(1):7-17. Diabetic Retinopathy triamcinolone or laser alone for treating diabetic macular edema: Screening: Clinical Standards. Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network: provision: the effectiveness of a low vision clinic. Optom Vis Sci Three-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing focal/ 1994;71(3):199-206. The provision of low vision two-year results of a double-masked, placebo-controlled, care. Simvastatin retards progression and economic aspects of foot problems in diabetes. Effectiveness of the diabetic foot risk atorvastatin as an adjunct in the management of diabetic macular classification system of the International Working Group on the edema. Diabetes vascular endothelial growth factor aptamer, for diabetic macular Care 1999;22(7):1029-35. Ahmadieh H, Ramezani A, Shoeibi N, Bijanzadeh B, Tabatabaei between callus formation, high pressures and neuropathy in A, Azarmina M, et al. Graefes Arch Clin Exp patients at high risk for lower-extremity amputation in a primary Ophthalmol 2008;246(4):483-9. Bevacizumab-augmented retinal laser photocoagulation in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intravitreal bevacizumab (avastin) program to reduce amputations and hospitalizations. Diabetes injection alone or combined with triamcinolone versus macular Res Clin Pract 2005;70(1):31-7. Effect of lisinopril on progression of retinopathy pressures and arterial calcification in diabetic occlusive vascular in normotensive people with type 1 diabetes. Effect of ruboxistaurin on the visual acuity decline associated preventing diabetic foot ulceration (Cochrane Review). Antibiotic therapy padded hosiery to reduce abnormal foot pressures in diabetic for diabetic foot infections: comparison of two parenteral-to-oral neuropathy. Good practice guidance for the use of antibiotics in patients Res Clin Pract 1995;28(1):29-34. Improved survival of the diabetic foot: the role of a negative pressure wound therapy using vacuum-assisted closure specialized foot clinic.

Discount 200mcg entocort amex
Inability to perceive the monoflament force is as- sociated with large-fbre neuropathy allergy medicine for sore throat buy discount entocort 200mcg line. Although guidelines suggest varying numbers of testing points, 10 monoflament test sites per foot is suggested to capture the largest proportion of patients with loss of protective sensation. Although other forms, including hand-made monoflaments, are available, they may vary widely in accuracy due to differences in flament diameter and length. Because nylon has memory properties, monoflaments should be rested for two hours following 100 applications (20 points/patient = fve visits). The effective length of use of nylon monoflaments before replacement is required remains to be studied. Vibration testing: Neuropathy is also demonstrated by an inability to sense vibration from a standard tuning fork. A biothesiometer or neurothesiometer can also be used for assessing the perception of vibration. Emotional Health Mental health and diabetes have received growing interest from researchers and clinicians. For persons with diabetes, depression, major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, generalized anxiety disorder and eating disorders are more prevalent than in 20 | Best Practice Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers | Foundations of Best Practice for Skin and Wound Management How to Use a Monoflament the Semmes-Weinstein monoflament uses a 5. Touch the monoflament to the patient?s arm or hand (avoid the hand if the person with diabetes has glove and stocking neuropathy) so they understand what to expect when monoflament testing is performed on the foot. Before you touch the monoflament to their foot, have the patient close their eyes and instruct them to say ?yes? when they feel the sensation of the monoflament on their foot. Hold the monoflament perpendicular to the foot and touch the skin only once, until the monoflament bends into a C-shape. Figure 3: Monoflament Testing Sites Bottom Top right foot left foot right foot left foot the general population. Patients with serious Patients with diabetes need to be assessed for lifestyle choices mental illnesses, particularly those that may impact the health of their feet: with depressive symptoms or syn-? Pur- chasing offoading (pressure redistributing) devices, boots and footwear, for example, is unachievable for many patients. Therefore, an environmental assessment is impor- tant to determine if the patient has socio-economic supports in place to engage in a sustainable plan of care and self-management. Other socio-economic determinants may include education level, adequate housing, access to nutritious food,40 social net- work, access to services or equipment as well as family knowledge, comfort or capacity in providing support or care. With an aging population and increased chronic disease burden, including diabetes, health-care costs are increasing. Health- care delivery for persons with diabetes is highly variable between regions, leading to signifcant heterogeneity in outcomes. Due to the high variability of health-care de- livery for persons with diabetes between regions, an assessment of regional services is required to determine the availability of services. To address the needs of the grow- ing 11 million Canadians living with type 1 and type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes, an organized, interprofessional and collaborative approach to care is critical to improve diabetes-associated outcomes. Discussion: the clinician should describe the characteristics of any ulcers using a validated wound assessment tool. Wound assessment can help the clinician determine the ability of the wound to heal, plan treatment, facilitate communication, monitor treatment and predict and verify outcomes. There are several different classifcation systems available that may be used in the assessment of diabetic foot ulcers. The University of Texas system (see Table 7) is the most predictive and positively correlates to the risk of amputation and other adverse outcomes. To create an optimal plan of care, the wound needs to be assessed and categorized as neuropathic, ischemic or neuroischemic. Table 8: Categories of Diabetic Foot Ulcers44 Feature Neuropathic Ischemic Neuroischemic Sensation sensory loss pain degree of sensory loss Callus/necrosis callus present and often thick necrosis common minimal callus; prone to necrosis Wound bed pink and granulating, pale and sloughy with poor poor granulation surrounded by callus granulation Foot temperature warm with bounding pulses cool with absent pulses cool with absent pulses and pulses Other dry skin and fssuring delayed healing high risk of infection Typical location weight-bearing areas of the tips of toes, nail edges and margins of the foot and toes foot, such as metatarsal heads, between the toes and lateral the heel and over the dorsum borders of the foot of clawed toes Prevalence45 35% 15% 50% Used with kind permission from Wounds International. Once the assessment is completed, risk of diabetic foot complications can be deter- mined by referring to Step 2 of the Inlow 60-second Diabetic Foot Screen. Any form of trauma to the insensate foot (sharp blow, thermal injury, pressure or friction) can result in disruption of the skin barrier and penetration of bacteria. The underlying immune disturbance and perfusion issues that are common in persons with diabetes allow for the infammatory reaction to progress to infection. The severity of pathway-dia- the infection should be defned based on the extent, depth and presence of systemic fndings. Table 9 shows the University of Texas ulcer classifcation system,51 which grades infection based on the extent of the wound, presence of infection and degree of vas- cular compromise. Table 9: University of Texas Diabetic Wound Classifcation System Stage Grade 0 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 A pre- or post-ulcerative superfcial wound not wound penetrating to wound penetrating to lesion completely involving tendon, capsule tendon or capsule bone or joint epithelialized or bone B infection infection infection infection C ischemia ischemia ischemia ischemia D infection and ischemia infection and ischemia infection and ischemia infection and ischemia Hand-held infrared skin temperature devices can be used to detect early signs of infammation and tissue injury and have been validated in clinical wound assess- ment. Diabetic foot osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis in the diabetic foot is a highly challenging diagnosis that can occur in up to 60% of hospitalized patients with diabetic foot infections and in up to 20% in outpatients with less severe infections. A defnitive diagnosis of diabetic foot osteomyelitis requires both histologic evidence of bone infection and isolation of a bacterial pathogen from a bone sample. A sterile helping clinicians predict and pre- blunt metal probe is inserted through a wound, and if bone is vent the occurrence of diabetic foot struck (hard, gritty end-feel), the likelihood of osteomyelitis is 48 ulcers. The most effective method greatly increased in populations with high prevalence of osteo- for amputation prevention may myelitis, such as persons with diabetes. They are also useful for assessing for foot deformities, fractures, the presence of gas in the soft tissue and radiopaque foreign bodies. Bony changes seen on plain X-rays can be slow- er to develop, but X-rays are low-cost and readily available. X-rays have poor positive predictive value even when they are positive, unless subsequent radiographic evidence is positive. There is insuffcient evidence, however, for routine use of these biochemical tests for diagnosis of diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Health-care providers must respect the individual?s right to choose the inter- ventions they prefer. Discussion: From a long-term health perspective, a primary goal for those with dia- betes should involve the prevention of diabetic foot ulcers. Therefore, factors that can cause skin breakdown or infuence healing need to be identifed. Discussion: Prevention of an initial wound or additional wounds on the contralateral limb or other parts of the foot is a goal that should be given paramount consideration. In the presence of wounds, the health-care professional must identify whether the wound is healing, non-healing or non-healable. A A1c Aim for a glucose control Discussion: Health-care professionals must always remember target of 7% or less. Clinicians must also blood pressure control target of consider other goals of care, such as wound stabilization, pain less than 130/80 mmHg. A special note on pain: Reducing painful diabetic neuropathy D Drugs Protect against heart can be a key goal for patients living with diabetic foot compli- attack and stroke with appropri- cations. F Footcare Perform a daily ex- Many clinicians struggle with the decisions surrounding limb amination. It is important to note that some patients may S Smoking and stress Stop elect to undergo amputation, as the wound may be interfering smoking and manage stress with their occupation, attitude, social support system, access to effectively. Foundations of Best Practice for Skin and Wound Management | Best Practice Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers | 29 Step 3: Assemble the Team Step 3: Assemble the Team Discussion: Assessment, prevention and management of diabetic foot problems require the collaboration of an integrated team in the hospital and community set- tings. The team must work closely and collaboratively to address the complex lifestyle, self-care and emotional and social impacts of living with diabetes and being at risk for foot complications. Clinicians require clear protocols and clinical pathways that refect the continued and integrated care needs of patients across all settings and that can be communicated among all team members. Discussion: the professional members of the team need to be trained and empow- ered to work with patients with diabetes since the knowledge and skills necessary to assess and treat a person with a diabetic foot ulcer are not usually taught in an en- try-level health-care-professional curriculum. Caring for individuals with diabetes at risk of developing foot complications or those who already have foot ulceration requires that clinicians have the skills to address glycemic control, infection, offoading of high-pressure areas, lower-extremity vascular status and local wound care while supporting a self-management approach to care. If not, strategies must be established to ensure Patients First that fuid, effective collaboration and 72 the frst team members should be the patient and their communication ensue. The next team member is usually the disabilities, including visual impairment primary care provider, depending on the needs of the and mental health issues, or those who patient and allocation of resources within the community. Specialized assessment equipment endocrinology, dermatology, vascular surgery, microbiolo- and training are required to assess gy, orthopedics (casting, bone debridement) and infectious the vasculature of a person with dia- 11,69 disease, as well as social workers, cultural/ethnic health betes. Appropriate referral for any liaisons, registered dietitians, spiritual care providers and patient diagnosed with or suspected of mental health workers (psychologists). In Multidisciplinary team refers to a addition, professionals need to recognize the impact of living with neuropathy, team of health-care workers from which can reduce motivation to heal or prevent injury.

Buy discount entocort 200mcg on line
This situation both suggests an inherent metabolic or anatomical abnormality and would leave the individual with a single kidney containing a stone placing them at significant risk of a future stone event in a solitary kidney allergy treatment for horses discount entocort 200mcg visa. Donors who have a past history of stones and those who have donated a stone- bearing kidney should be counselled about symptoms of renal/ureteric colic and anuria and information should be provided regarding the availability of local urological expertise. Donors should also be advised to maintain a high fluid intake for life (at least 2. Progression of nephrolithiasis: long-term outcomes with observation of asymptomatic calculi. The natural history of nonobstructing asymptomatic renal stones managed with active surveillance. Prevalence and early outcome of donor graft lithiasis in living renal transplants at the Mayo Clinic. The evaluation of living renal transplant donors: clinical practice guidelines: Ad Hoc Clinical Practice Guidelines Subcommittee of the Patient Care and Education Committee of the American Society of Transplant Physicians. Living renal donor allograft lithiasis: a review of stone related morbidity in donors and recipients. Clinical characteristics of potential kidney donors with asymptomatic kidney stones. A report of the Amsterdam Forum on the care of the live kidney donor: data and medical guidelines: Council of the Transplantation Society. Ex vivo ureteroscopic treatment of calculi in donor kidneys at renal transplantation. Incidental renal stones in potential live kidney donors: prevalence, assessment and donation, including role of ex vivo ureteroscopy. All donors should have a full blood count and clotting screen as part of their assessment. In addition, the risks of general anaesthetic are much greater in this population. In addition, visible and non-visible haematuria are well described, often as a result of papillary necrosis. Careful screening for the presence of existing renal involvement is required, with particular attention to a history of macroscopic haematuria. There have been a few reports of minor tubular dysfunction in some patients with thalassaemia trait but there is no other reported association with renal disease (6). Other haemoglobin variants Other haemoglobinopathies may be encountered when screening donors of non- northern European heritage and in general should not pose a problem with kidney donation except where they form part of a compound heterozygote with Hb S (e. Such patients behave like patients with sickle cell disease and therefore should not be accepted as living kidney donors. Red cell membrane disorders these include hereditary spherocytosis and hereditary eliptocytosis, inherited haemolytic anaemias of variable severity. Renal function is not significantly impaired in these conditions and organ donation is acceptable in mild forms where treatment has not been required. However, such a decision has to be taken with great care and following discussion with the donor and their haematologist. Although the risk of disease transmission is considered negligible, the potential recipient should also be counselled re a potential increased risk associated with donation. As such there is a theoretical possibility of carry-over in a donor kidney to the recipient. However, those receiving bridging anticoagulation are more likely to have bleeding complications. These data should inform discussion with potential donors in this category and may represent a relative contraindication to donation but, in general, the risks should be discussed with a haematologist. Association of sickle cell trait with chronic kidney disease and albuminuria in African Americans. A long-term study of prognosis in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Incidence and clinical complications of myelodysplastic syndromes among United States Medicare beneficiaries. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Bleeding, recurrent venous thromboembolism, and mortality risks during warfarin interruption for invasive procedures. This may aid diagnosis for the recipient, clarify any mode of inheritance and identify at risk relatives. The diagnosis of many familial renal diseases still relies on a high index of suspicion coupled with biochemical, radiological and histological investigations. It may also be revealed only through a detailed pedigree, which must be obtained for all individuals with renal disease who are being considered for transplantation. In such cases, confirmation of all diagnoses within the family is essential to identify whether there is a clinically significant genetic predisposition to renal disease that may be relevant to potential donation (3). However, in most cases the family history is due to polygenic influences such as diabetes, certain types of glomerulonephritis and hypertension for which no additional genetic testing or screening is required above that recommended for routine donor evaluation (3). Where the diagnosis is a known genetic disease or the family history is suggestive of a monogenic (Mendelian) disease, the pedigree will aid in the identification of the mode of inheritance (typically autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X-linked) and the identification of at risk relatives. This information is important to clarify the lifetime risk to a genetically related potential donor of developing significant renal disease. The genetic basis of many familial renal diseases has been elucidated, providing the opportunity to use molecular investigations for diagnostic testing in the recipient and predictive testing in the potential living related donor (4). Genetic testing may also aid the prediction of the likelihood of disease recurrence in the transplanted kidney. As genetic testing may be offered to individuals and families, involvement of clinical genetics services or specialist renal genetics services should be considered at an early stage to support the donor assessment team. This will be of value in identifying risks to family members and for the type and use of genetic testing for diagnostic and exclusion purposes. It should also be noted that molecular testing can take in excess of 3 months and, with the increasing use of gene panels containing many genes, the likelihood of identifying a genetic variant that requires further interpretation is increased. Projects such as the 100,000 Genomes project may facilitate the latter and further necessitates interaction with genetic services at an early stage of donor/recipient evaluation At risk relatives must be carefully evaluated for specific disease manifestations and consideration given to genetic testing to definitively clarify risk and therefore suitability as a potential donor. Parents will be obligate gene carriers and second degree relatives will be at 50% risk of also being gene carriers. It remains unclear what the risk of progression to proteinuria and renal impairment is for carriers, but this has been described (6,7). Molecular testing can be used to confirm the diagnosis in the affected individual and carrier status in parents and other relatives. It is currently unclear whether mutation carriers who do not have non-visible haematuria on repeat testing can be donors. Despite this uncertainty, carriers with no renal abnormality by age 45 might be considered as donors in a similar manner to X-linked Alport syndrome. The majority, >95%, will develop non-visible haematuria by adulthood but have a life-time risk of progressive renal disease of 5-20%. Gene testing for both conditions is available and is important for diagnostic confirmation and the carrier testing of other female family members. Therefore careful evaluation of renal function, possibly including renal biopsy, may be indicated in X-linked diseases to provide accurate risks for potential female donors who have been shown to be carriers. In all familial renal diseases, a genetically related potential donor can be offered predictive genetic testing if the familial mutation has been identified. This should only be offered by experienced individuals, usually via a regional clinical genetics service, because of the potential impact of identifying clinical or genetic status to an otherwise clinically asymptomatic individual. Any person found to carry the familial mutation would normally be excluded as a potential donor if this predicted development of disease, and should also be referred for appropriate follow-up. Genetic testing is currently available for diseases where a mutation has a high probability of predicting development of disease. These tend to be associated with a much smaller predictive value of developing disease and are relevant to populations and not families.
Echte Kamille (German Chamomile). Entocort.
- Dosing considerations for German Chamomile.
- Intestinal gas, travel sickness, nasal swelling (inflammation), hayfever, diarrhea, restlessness, sleeplessness, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), fibromyalgia, stomach and intestinal disorders, menstrual cramps, and other conditions.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Is German Chamomile effective?
- How does German Chamomile work?
- Colic in breastfed infants when used in combination with other herbs.
- What is German Chamomile?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of German chamomile and five other herbs is used.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96914
Purchase generic entocort from india
Subclinical and overt thyroid dysfunction and risk of all- cause mortality and cardiovascular events: a large population study allergy treatment urdu purchase entocort with visa. Prediction of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in elderly people from one low serum thyrotropin result: a 10-year cohort study. The guideline Thyroid seeks to address appropriate monitoring of Treatment As with the management of hypothyroidism the monitoring of subclinical thyroid dysfunction. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment Campaign subclinical thyroid dysfunction should be conducted routinely. Patient Group signs and symptoms and circumstances should be used in conjunction with a broad range of thyroid hormone tests to decide if thyroid hormone replacement should be considered. As the scope recognises, most thyroid dysfunction is caused by autoimmune disease. Untreated subclinical hypothyroid thyroid dysfunction, caused by autoimmunity will lead to further thyroid damage, increased symptoms and increased patient dissatisfaction along with decreased life quality and chances. This fact calls for consideration of screening as a routine and regular aspect of health care. The guideline Thyroid seeks to address appropriate monitoring of Treatment It is imperative that subclinical thyroid dysfunction is reviewed. Campaign Consideration should be given to the distinction and labelling of Group ?subclinical? as equating to ?no need for treatment?, when this is not always the case. Which in itself is an issue, as many primary care providers are not adequately trained in the varying aspects of thyroid disease. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment symptoms and increased patient dissatisfaction along with decreased life quality and chances. Initially monitoring of any subclinical thyroid dysfunction should include careful monitoring of full thyroid function blood tests. It is particularly important to establish the need for monitoring thyroid eye disease and for informing patients about nutritional choices that may help control the levels of antibodies. As noted in line 126 subclinical hyperthyroidism, promotes the risk of cardio-vascular disease. Madariaga et al [2014] conducted a ?Meta-Analysis? of the prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in Europe. Their findings suggest that the figure is likely to be 11% but they acknowledge that half of these are unaware they have thyroid disease. This is particularly worrying as individuals are not aware of health problems that are leaving them with increased risk of further more serious complications. This fact calls for consideration for screening to be a routine and regular aspect of health care. The Incidence and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Europe: A Meta-Analysis Ane Garmendia Madariaga Silvia Santos Palacios Francisco Guillen- Grima Juan C. We believe that information Primary care professionals will be a key supports a shared decision culture. Information should extend to the audience for the guideline when it is test results, different treatment options, explanations of published. Information needs to be better defined, more comprehensive, and more inclusive of all current knowledge. It is particularly important that all options and subsequent consequences of treatment are made clear and understood, by patients. Consideration for ongoing research should be included and made available to patients before treatment decisions are made. General practitioners need to be aware of the importance and urgency in early diagnosis. However, it is also associated with Hashimoto?s Thyroiditis, thyroid carcinoma and both primary hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Sabini E, Leo M, Mazzi B, Rocchi R, Latrofa F, Nardi M, Vitti P, Marcocci C, Marino M. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment. This was not Thyroid raised as a high priority issue during scope Treatment Whilst it is understood that Acute Thyroid Dysfunction is likely to be development and stakeholder meetings. The two ends of the thyroid disease spectrum may result in acute thyroid dysfunction. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment can lead, to what is called a myxoedema crisis, a medical emergency, which can lead to coma and death. Myxoedema is termed from the presence of mucin in the tissue, which may cause swelling and thickening skin. Thyroid storm, also known as thyrotoxic crisis, is a rare complication of thyrotoxicosis and can happen after, trauma, childbirth, surgery, infection and stroke. Common but extreme severity of symptoms such as: Racing heart >140bpm; high fever; persistent sweating: shaking; agitation; restlessness; confusion; diarrhoea and possible unconsciousness, are likely to be evident I. Diagnosis and management of thyrotoxicosis Bijay Vaidya, Simon H S Pearce [2014]. Hypothyroidism affects 4-10% of women, which includes a of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. In pregnancy, most appropriate way of signposting to this the prevalence of overt and subclinical hypothyroidism is estimated guidance will be considered during at 0. Overt Hypothyroidism in pregnancy has been shown to be associated with adverse pregnancy complications and detrimental effects upon foetal neurocognitive development. Risks include premature birth, low birth weight and miscarriage, gestational hypertension and placental abruption. Findings also supported a delay in motor skill development, language development and attention at 7-9 years of age. We recommend that the scope includes guidance on the treatment of Overt Hypothyroidism and that it should always be treated in pregnancy with thyroid hormone. If treatment had been started earlier, the benefit would have been shown to be far greater. These papers tell us that if you are going to treat, to do it early on in pregnancy. Hypothyroidism can occur due to initial presentation of Hashimotos, inadequate treatment of a woman already known to have hypothyroidism, or over-treatment of a hyperthyroid woman with antithyroid medicine. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment myopathy, congestive heart failure, pre-eclampsia, placental abnormalities, low birth weight infants and postpartum haemorrhage. Babies born with hypothyroidism can have severe cognitive development and abnormalities if not treated properly. Thyroid hormone requirements increase in pregnancy so an adjustment in the need of Levothyroxine dose should be monitored. In comparison, a strategy assessing thyroid function every 6 weeks detected only 73% of abnormal values. However, a study demonstrated that more than 50% of women with Hashimotos thyroiditis required an increase in the pregestational thyroid hormone dose in the postpartum period. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment study of more than 4,000 Dutch mothers and their children, and it supports a growing view that autism spectrum disorders can be caused by a lack of maternal thyroid hormone, which past studies have shown is crucial to the migration of fetal brain cells during embryo development. The most common cause of thyroid hormone deficiency is a lack of dietary iodine - because both the thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, contain that element. Nevertheless, the behavioural outcomes of children exposed prenatally to mild thyroid hormone insufficiency are understudied. This finding suggests that intrauterine exposure to insufficient thyroid hormone levels influences neurodevelopment in offspring. Maternal Mild Thyroid Hormone Insufficiency in Early Pregnancy and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in Children. Please insert each new comment in a new row Please respond to each comment multiple autonomous nodules. Fetal hyperthyroidism with fetal tachycardia, goitre and hydrops is a potential cause of pregnancy loss. Although this condition is typically self-limiting it may cause significant neonatal morbidity and is occasionally fatal. In the absence of thyroid testing, recognition of neonatal hyperthyroidism may prove challenging, especially in the infants of mothers with undiagnosed hyperthyroidism. Thyroid Research Group, Institute of Molecular & Experimental Medicine, Cardiff University School of Medicine, Should all women be screened for thyroid dysfunction in pregnancy?
Syndromes
- Chest pain
- WBC (white blood count)
- Severe pain in the throat
- You develop symptoms of alcoholic liver disease.
- Foot problems, such as hammer toe and high arches
- Tumor or cancer in the spine
- Weakened tooth enamel
- Vomiting, refusal to suck, passage of loose green stools
- Inflammatory bowel disease
Buy 200mcg entocort overnight delivery
A deep puncture is no more painful than a superficial one and makes repeated punctures unnecessary allergy shots vs medicine order entocort american express. The site should not be squeeze or pressed to get blood since this dilutes it with fluid from the tissues. Rather, a freely flowing blood should be taken or a moderate pressure some distance above the puncture site is allowable. Stop the blood flow by applying slight pressure with 46 Hematology a gauze pad or cotton at the site. Only small amounts of blood can be obtained and repeated examinations require a new specimen. Venous Blood Collection A venous blood sample is used for most tests that require anticoagulation or larger quantities of blood, 47 Hematology plasma or serum. The veins that are generally used for venipuncture are those in the forearm, wrist or ankle. The veins in the antecubital fossa of the arm are the preferred sites for venipuncture. They are larger than those in the wrist or ankle regions and hence are easily located and palpated in most people. Puncture of the external jugular vein in the neck region and the femoral vein in the inguinal area is the procedure of choice for obtaining blood. Attach the needle so that the bevel faces in the same direction as the graduation mark on the syringe. The gauge and the length of the needle used depend on the size and depth of the vein to be punctured. The needle should not be too fine or too long; those of 19 or 21G are suitable for most adults, and 23G for children, the latter especially with a short shaft (about 15mm). The point of the needle will thus be embedded in the stopper without puncturing it and loosing the vacuum in the tube. Identify the patient and allow him/her to sit 50 Hematology comfortably preferably in an armchair stretching his/ her arm. Prepare the arm by swabbing the antecubital fossa with a gauze pad or cotton moistened with 70% alcohol. Apply a tourniquet at a point about 6-8cm above the bend of the elbow making a loop in such a way that a gentle tug on the protruding ends will release it. Alternatively, the veins can be visualized by gently tapping the antecubital fossa or applying a warm towel compress. Grasp the back of the patient?s arm at the elbow and anchor the selected vein by drawing the skin slightly taut over the vein. If the needle is properly in the vein, blood will begin to enter the syringe spontaneously. With the syringe and needle system, first cover the needle with its cap, remove it from the nozzle of the 52 Hematology syringe and gently expel the blood into a tube (with or without anticoagulant). With the vacutainer system, remove the tube from the vacutainer holder and if the tube is with added anticoagulant, gently invert several times. By providing sufficient amount of blood it allows various tests to be repeated in case of accident or breakage or for the all-important checking of a doubtful result. It also frequently allows the performance of additional tests that may be suggested by the results of those already ordered or that may occur to the clinician as afterthoughts. It is a bit a lengthy procedure that requires more preparation than the capillary method. Difference between peripheral and venous Blood Venous blood and peripheral blood are not quite the same, even if the latter is free flowing, and it is likely that free flowing blood obtained by skin puncture is more arteriolar in origin. The total leucocyte and neutrophil counts are higher by about 8% and the 54 Hematology monocyte count by 12%. Conversely, the platelet count appears to be higher by about 9% in venous than peripheral blood. The multiple sample needle used in the vacutainer method has a special adaptation that prevents blood from leaking out during exchange of tubes. These blood gas measurements are critical in assessment of oxygenation problems encountered in patients with pneumonia, pneumonitis, and pulmonary embolism. Arterial punctures are technically more difficult to perform than venous punctures. Increased pressure in the arteries makes it more difficulty to stop bleeding with the undesired development of a hematoma. Arterial selection includes radial, brachial, and femoral arteries in order of choice. Make sure the syringe, needle and test tubes are dry and free from detergent as traces of water or detergent cause hemolysis. Do not eject the blood from the syringe through the needle as this may cause mechanical destruction of the cells. Blood should not be stored in a freezer because the red cells will hemolyse on thawing. What are the anatomical sites of collection in these sources in the different age groups? What are the advantages as well as the draw backs of taking/using blood samples from each of these sources? How do you minimize or avoid the occurrence of hemolysis in blood samples for hematological investigations? What is the difference between samples collected from these two sources in terms of hematological parameters? In other words, certain steps are involved in blood coagulation, but if one of the factors is removed or inactivated, the coagulation reaction will not take place. The substances responsible for this removal or inactivation are called anticoagulants. While clotted blood is desirable for certain laboratory investigations, most hematology procedures require an anticoagulated whole blood. Calcium is either precipitated as insoluble oxalate (crystals of which may be seen in oxalated blood) or bound in a non-ionized form. Sodium citrate or heparin can be used to render blood incoagulable before transfusion. It is especially 60 Hematology the anticoagulant of choice for platelet counts and platelet function tests since it prevents platelet aggregation. It exerts its effect by tightly binding (chelating) ionic calcium thus effectively blocking coagulation. This concentration does not appear to adversely affect any of the erythrocyte or leucocyte parameters. Nine volumes of blood are added to 1 volume of the sodium citrate solution and immediately well mixed with it. Balanced or double oxalate Salts of oxalic acid by virtue of their ability to bind and precipitate calcium as calcium oxalate serve as suitable anticoagulants for many hematologic investigations. Three parts of ammonium oxalate is balanced with two parts of potassium oxalate (neither salt is suitable by itself, i. Heparin Heparin is an excellent natural anticoagulant extracted from mammalian liver or pancreas. It is more expensive than the artificial ones and has a temporary effect of 62 Hematology only 24 hours. Heparin prevents clotting by inactivating thrombin, thus preventing conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. It is unsatisfactory for leucocyte and platelet and leucocyte counts as it causes cell clumping and also for blood film preparation since it causes a troublesome diffuse blue background in Wright-stained smears. Write the proportion of the volume of blood to the volume of each if these anticoagulants. However, these same automated results may also point 65 Hematology to the need to examine the blood film microscopically to confirm the presence of disease suggested by the results or for early detection of disease. Of course, in a laboratory without access to such automated information, the microscopic examination of the peripheral blood film is invaluable.

Purchase cheapest entocort and entocort
Civics allergy forecast new hampshire generic entocort 100mcg with visa, Standard 28: Understands how participation in civic and political life can help citizens attain individual and public goals. Civics, Standard 29: Understands the importance of political leadership, public service, and a knowledgeable citizenry in American constitutional democracy. Language Arts, Standard 1: Uses the general skills and strategies of the writing process. Language Arts, Standard 3: Uses the grammatical and mechanical conventions in written compositions. Language Arts, Standard 5: Uses the general skills and strategies of the reading process. Language Arts, Standard 8: Uses listening and speaking strategies for different purposes. Language Arts, Standard 9: Uses viewing skills and strategies to understand and interpret visual media. Thinking and Reasoning, Standard 1: Understands and applies the basic principles of presenting an argument. Working With Others, Standard 4: Displays effective interpersonal communication skills. Be prepared to share your findings with the class and take notes during other group presentations. What happens if an autopsy is delayed rather than being performed within 24 hours of death? Do you think it is important to have a forensic pathologist involved in every death investigation? How might national standards increase the quality of death investigations in America? How does the Criminal Justice and Forensic Science Reform Act propose to combat the problems with death investigation? How much would it cost per person per year to run a good medical examiner?s office? What benefits can society expect to get if additional money is spent on death investigation? What keeps states from replacing coroners with more qualified death investigators? Enter the chain of events-diseases, injuries, or complications-that directly caused the death. If the facility uses a separate pronouncer or other person to indicate that death has taken place with another person more familiar with the case completing the remainder of the medical portion of the death certificate, the pronouncer completes Items 24-28. If a certifier completes Items 24-25 as well as items 29-49, Items 26-28 may be left blank. If the date cannot be approximated, enter the date the body is found and identify as date found. Enter the exact hour and minutes according to a 24-hour clock; estimates may be provided with ?Approx. Part I (Chain of events leading directly to death) ?Only one cause should be entered on each line. If a mechanism of death seems most appropriate to you for line (a), then you must always list its cause(s) on the line(s) below it (for example, cardiac arrest due to coronary artery atherosclerosis or cardiac arrest due to blunt impact to chest). Tobacco use may contribute to deaths due to a wide variety of diseases; for example, tobacco use contributes to many deaths due to emphysema or lung cancer and some heart disease and cancers of the head and neck. Check ?no? if, in your clinical judgment, tobacco use did not contribute to this particular death. The item must be completed for decedents ages 14 years or over and may be completed for those less than 14 years of age if warranted. An injury may occur at work regardless of whether the injury occurred in the course of the decedent?s ?usual? occupation. Examples of injury at work and injury not at work follow: Injury at work Injury not at work Injury while working or in vocational training on job premises Injury while engaged in personal recreational activity on job premises Injury while on break or at lunch or in parking lot on job premises Injury while a visitor (not on official work business) to job premises Injury while working for pay or compensation, including at home Homemaker working at homemaking activities Injury while working as a volunteer law enforcement official etc. Student in school Injury while traveling on business, including to/from business contacts Working for self for no profit (mowing yard, repairing own roof, hobby) Commuting to or from work ?42 - Enter the complete address where the injury occurred including zip code. Indicate if more than one vehicle involved; specify type of vehicle decedent was in. Driver/operator and passenger should be designated for modes other than motor vehicles such as bicycles. Other applies to watercraft, aircraft, animal, or people attached to outside of vehicles (e. Rationale: Motor vehicle accidents are a major cause of unintentional deaths; details will help determine effectiveness of current safety features and laws. Part I is for reporting a chain of events leading directly to death, with the immediate cause of death (the final disease, injury, or complication directly causing death) on line a and the underlying cause of death (the disease or injury that initiated the chain of events that led directly and inevitably to death) on the lowest used line. A condition can be listed as ?probable? even if it has not been definitively diagnosed. Enter the chain of events-diseases, injuries, or complications-that directly caused the death. Rupture of myocardium Minutes resulting in death) Due to (or as a consequence of): Sequentially list conditions, b. Acute myocardial infarction 6 days if any, leading to the cause Due to (or as a consequence of): listed on line a. Enter the chain of events-diseases, injuries, or complications-that directly caused the death. Aspiration pneumonia 2 Days resulting in death) Due to (or as a consequence of): Sequentially list conditions, b. Complications of coma 7 weeks if any, leading to the cause Due to (or as a consequence of): listed on line a. Terms such as senescence, infirmity, old age, and advanced age have little value for public health or medical research. If after careful consideration the physician cannot determine a sequence that ends in death, then the medical examiner or coroner should be consulted about conducting an investigation or providing assistance in completing the cause of death. The infant decedent should have a clear and distinct etiological sequence for cause of death, if possible. Maternal conditions may have initiated or affected the sequence that resulted in infant death, and such maternal causes should be reported in addition to the infant causes on the infant?s death certificate (e. If the infant is under 1 year of age, no cause of death is determined after scene investigation, clinical history is reviewed, and a complete autopsy is performed, then the death can be reported as Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. When processes such as the following are reported, additional information about the etiology should be reported: Abscess Carcinomatosis Disseminated intra vascular Hyponatremia Pulmonary arrest Abdominal hemorrhage Cardiac arrest coagulopathy Hypotension Pulmonary edema Adhesions Cardiac dysrhythmia Dysrhythmia Immunosuppression Pulmonary embolism Adult respiratory distress syndrome Cardiomyopathy End-stage liver disease Increased intra cranial pressure Pulmonary insufficiency Acute myocardial infarction Cardiopulmonary arrest End-stage renal disease Intra cranial hemorrhage Renal failure Altered mental status Cellulitis Epidural hematoma Malnutrition Respiratory arrest Anemia Cerebral edema Exsanguination Metabolic encephalopathy Seizures Anoxia Cerebrovascular accident Failure to thrive Multi-organ failure Sepsis Anoxic encephalopathy Cerebellar tonsillar herniation Fracture Multi-system organ failure Septic shock Arrhythmia Chronic bedridden state Gangrene Myocardial infarction Shock Ascites Cirrhosis Gastrointestinal hemorrhage Necrotizing soft-tissue infection Starvation Aspiration Coagulopathy Heart failure Old age Subdural hematoma Atrial fibrillation Compression fracture Hemothorax Open (or closed) head injury Subarachnoid hemorrhage Bacteremia Congestive heart failure Hepatic failure Paralysis Sudden death Bedridden Convulsions Hepatitis Pancytopenia Thrombocytopenia Biliary obstruction Decubiti Hepatorenal syndrome Perforated gallbladder Uncal herniation Bowel obstruction Dehydration Hyperglycemia Peritonitis Urinary tract infection Brain injury Dementia (when not Hyperkalemia Pleural effusions Ventricular fibrillation Brain stem herniation otherwise specified) Hypovolemic shock Pneumonia Ventricular tachycardia Carcinogenesis Diarrhea Volume depletion If the certifier is unable to determine the etiology of a process such as those shown above, the process must be qualified as being of an unknown, undetermined, probable, presumed, or unspecified etiology so it is clear that a distinct etiology was not inadvertently or carelessly omitted. The following conditions and types of death might seem to be specific or natural but when the medical history is examined further may be found to be complications of an injury or poisoning (possibly occurring long ago). The place of residence is not necessarily the same as ?home state? or ?legal residence?. Never enter a temporary residence such as one used during a visit, business trip, or vacation. Place of residence during a tour of military duty or during attendance at college is considered permanent and should be entered as the place of residence. If the decedent had been living in a facility where an individual usually resides for a long period of time, such as a group home, mental institution, nursing home, penitentiary, or hospital for the chronically ill, report the location of that facility in item 7. If the decedent was an infant who never resided at home, the place of residence is that of the parent(s) or legal guardian. Never use an acute care hospital?s location as the place of residence for any infant. This item is used in establishing proper insurance settlements and other survivor benefits. If the place of death is unknown but the body is found in your State, the certificate of death should be completed and filed in accordance with the laws of your State. Information in this section will not appear on the certified copy of the death certificate.
Order entocort 200 mcg overnight delivery
In general allergy shots while breastfeeding generic entocort 200 mcg with amex, in cases of Hashimoto?s thyroiditis, the expressions of death receptor 24. It is membrane bound and found this expression pattern supports enhanced apoptosis as the in the cytoplasm and in high concentration on the apical mechanism underlying the loss of thyrocytes in Hashimoto?s microvillar surface of thyrocytes. Both cell-mediated and humoral responses contribute to tissue injury in autoimmune thyroid disease. Complement attack initiated via the classic or Pathologic Mechanisms of Disease, p. All of these enhance the tomy in grave?s disease: a retrospective analysis,? Indian Journal of Surgery, vol. Nagataki, ?Cellular immunity in autoimmune thyroid disease,? Bailliere?s Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Pre-existing autoimmune thyroiditis: from epidemiology to mechanisms,? Hashimoto?s thyroiditis is the major risk factor for develop- Endocrine Reviews,vol. Huber, ?The etiology of autoimmune thyroid have also shown that there is an increased frequency of disease: a story of genes and environment,? Journal of Autoim- autoimmune thyroiditis in women with breast cancer [93]. Iwatani, ?Increases of atrophic or goitrous autoimmune thyroiditis,? Journal of Clinical the T1/T2 cell ratio in severe Hashimoto?s disease and in the Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Davies, ?T-cell receptors ?Evidence for a major role of heredity in Graves? disease: a and autoimmune thyroid disease?signposts for T-cell-antigen population-based study of two Danish twin cohorts,? Journal of driven diseases,? International Reviews of Immunology,vol. Tomer, ?Amino acid substitutions in the by bystander damage and not molecular mimicry,? Nature thyroglobulin gene are associated with susceptibility to human Medicine,vol. Davies, ?By-stander National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, activation in autoimmune thyroiditis: studies on experimental vol. Tomer,?Sib- associated molecule-4 polymorphism and relapse of Graves? ling recurrence risk in autoimmune thyroid disease,? Tyroid, hyperthyroidism afer antithyroid withdrawal,? Journal of Clin- vol. Concepcion, and the onset of Graves? disease and toxic nodular goitre,? Clinical T. Davies, ?Tyroid epigenetics: geneity and gene interactions,? Journal of Clinical Endocrinology X chromosome inactivation in patients with autoimmune and Metabolism,vol. Scott, disease: a follow-up study of 69 patients,? Journal of Clinical ?Pregnancy: a clue to normal regulation of B lymphopoiesis,? Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Da Silva, ?Sex hormones, glucocorticoids and autoimmu- study of chronic autoimmune hypothyroidism in Danish twins,? nity: facts and hypotheses,? Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Davies, ?Infection, thyroid disease and habits and Graves? ophthalmopathy,? Journal of Endocrinological autoimmunity,? Endocrine Reviews,vol. Burman, ?Persistent thyroid autoimmunity afer subacute Graves? disease,? The Journal of the American Medical Associa- thyroiditis,? Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Immunology,vol. Raghupathy, ?T1-type immunity is incompatible with suc- other lifestyle factors and the risk of Graves? hyperthyroidism,? cessful pregnancy,? Immunology Today,vol. Davies, ?The thyroid immunology of the postpartum Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Burek, ?Iodine: an environmen- defciency and goitre incidence in parts of Yewa area of Ogun tal trigger of thyroiditis,? Autoimmunity Reviews,vol. Mets, ?The prevalence of autoantibodies in an elderly Endocrinology and Metabolism, vol. Zanetti,?Deter- alyzed chronic kidney disease,? Al Ameen Journal of Medical minationofIgGsubclassesandavidityofantithyroidperoxidase Science,vol. Kaptein, ?Tyroid function in renal failure,? Contributions parison with patients with overt hypothyroidism,? Hormone to Nephrology, vol. Rao, ?Searching for pathogenic epitopes inthyroglobulin:parameters andcaveats,?Immunology Today, vol. Smallridge, ?Postpartum thyroid dysfunction: a frequently undiagnosed endocrine disorder,? Endocrinologist,vol. Ericson, ?Cytokines and thyroid epithelial integrity: Interleukin-1 induces dissociation of the junctional complex and paracellular leakage in flter-cultured human thyrocytes,? JournalofClinical Endocrinology and Metabolism,vol. Hypothyroidism: screening and subclinical disease,? The British Medical Journal,vol. Drexhage,?Antigen- presenting dendritic cells as regulators of the growth of thyro- cytes: a role of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6,? Endocrinology, vol. The female preponderance can now be explained at least in part by fetal microchimerism and X-chromosome inactivation. Current smokers as well known are at increased risk for Graves? disease, but surprisingly at diminished risk for Hashimoto?s thyroiditis. He was Chair of the Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism in the Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam from 1995 to 2008. He is past president of the European Thyroid Association and served on the Executive Committee of the European Society of Endocrinology. There is transfer of fetal cells into the maternal Female sex circulation, already in the? Fetal microchimerism has indeed Venn diagram illustrating the multifactorial etiology of been found in blood and thyroid tissue from women with autoimmune thyroid disease. Similarly, for environmental exposures: one the frequency and/or concentration of thyroid antibodies environmental factor may constitute a risk for both will be. In this review, we adjustment for maternal age and other important con- focus on what has been learnt in the last 10 years on the founders (6, 7, 8). In a population- based Danish cohort, women with children, compared with childless women, were at a relative risk of 1. Taken together, the data puzzled physicians for a long time, and only recently there suggest that parity is somehow involved in the deve- have been some clues. Fetal microchimerism might contribute, but its During pregnancy the serum concentrations of thyroid effect is rather limited. The potential role of microchimer- antibodies decrease, related to generation of maternal ism in developing thyroid autoimmunity is further regulatory T-cells (Treg) early in pregnancy that maintain a supported by twin studies: both female and male twins state of tolerance to fetal alloantigens in order to prevent of opposite-sex pairs, as opposed to monozygotic pairs, rejection of the fetus (1). After delivery, there is a rebound have an increased frequency of thyroid antibodies (12). The gene encodes for a member of the immuno- although more recently associations with Hashimoto?s globulin receptor superfamily, expressed on B-cells. First, it has provided a deeper insight into the derived from large cross-sectional population-based sur- molecular mechanisms involved in the immunopatho- veys and from prospective observational studies. Fourthly, application of knowledge about susceptibility genes is slowly entering clinical practice. One may expect that susceptibility genes are going to play a substantial role in personalized medicine. Decreased risk Environmental factors: new players of Hashimoto?s disease Smoking Smoking is a well-established risk factor for Graves? Figure 2 disease. In the prospective DanThyr study, patients with newly found with the type of alcohol (wine vs beer), smoking diagnosed autoimmune hypothyroidism had more often habits, gender, or iodine intake. Finally, indicate a cause-and-effect relationship in view of the using Danish nationwide registers, mothers who smoke strength and the consistency of the associations and the during pregnancy have a subsequent decreased risk of presence of a dose?response effect. One alcohol suppresses autoimmunity remains incompletely may hypothesize involvement of nicotine, which reduces understood. Alcohol has also a direct toxic effect on the the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomye- thyroid gland, which, however, is dif? Anatabine a tobacco alkaloid with a structure similar to nicotine reduces the Selenium incidence and severity of experimental autoimmune thyroiditis (45). Glutathione peroxidases and thioredoxin reductases are selenoproteins involved in regulation of the redox state and protection from oxidative damage. It has thus been hypothesized that even consumption was lower in subjects developing auto- mild nutritional selenium de? Selenium supplementation has proven to were not different between cases and controls, neither prevent deterioration of mild Graves? ophthalmopathy at baseline nor at the time of seroconversion (67). The selenium dose used controls were not always matched to cases for the many so far is 200 mg daily. In the Dutch trial, it increased plasma other conditions affecting vitamin D levels.

