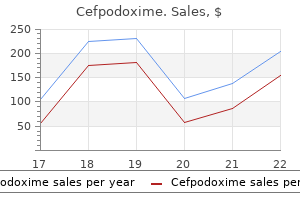
Cefpodoxime
Order cefpodoxime cheap online
When light rays pass from a medium of one density to a medium of a different density they are refracted or bent fast acting antibiotics for acne buy cefpodoxime 200mg low price. Before reaching the retina light rays pass successively through the cornea, aqueous humour, lens and vitreous which are all more dense than the air. The eye is considered to be emmetropic when incident parallel rays of light from infinity come to a focus on the retina (fovea centralis) with accommodation at rest. An emmetropic eye will have a clear image of a distant object without any internal adjustment of its optics. Retinal detachment (simple) is always due to break in the retina through which fluid seeps in, raising the retina from its bed. Complicated cataract (posterior cortical) is due to the disturbance to the nutrition of the lens. In pathological myopia, the patient should avoid an occupation where close work is necessary. In low degree of myopia, spectacles are rarely required for near work (after the Errors of Refraction 51 Temporal and supertractional nasal crescent presbyopic age). It should be undercorrected to avoid very bright and clear retinal images which are uncomfortable. Regular Astigmatism Normally cornea is flatter from side to side (horizontal meridian) perhaps because of the pressure of the eyelids. Regular astigmatism is present when the two principal meridians are at right angles. Thus, the more curved meridian will have more convergent power than the less curved. Retinal plane at A Compound hypermetropic astigmatism Both the foci are behind the retina. Partial or full thickness keratoplasty may be done depending on the depth of opacity as a last resort. When there are symptoms, suitable cylindrical lenses are prescribed for constant use. Aphakic eye Correction with convex lens Symptom There is gross dimness of vision because of acquired high hypermetropia. A linear semicircular corneo-scleral scar mark is seen in the upper half of cornea. There is greater refraction at the periphery of spherical lens than near the centre. Contact Lens Advantages There is minimum retinal image magnification, therefore it is useful in unilateral aphakia. Diplopia or seeing double objects may be present in severe cases and unilateral aphakia. It is treated by prescribing suitable correcting lenses for refractive difference of up to 2-3 D. The vision improves if the book is held further away from the ordinary reading distance, i. Presbyopia is treated by prescribing suitable convex spherical lenses for near work. This correction for near work is added to the correcting lenses for the distant vision. Mydriatics in Refraction the pupil is dilated by a suitable mydriatic depending on the age of patient. Streak retinoscopy Neutralisation When the shadow moves with the mirror, progressively stronger convex lenses are put in the trial frame until, i. Similarly, when the shadow moves against the mirror, progressively stronger concave lenses are put in the trial frame until the point of reversal is reached. The correction for near vision by convex spherical lenses is made over 40 years of age usually.
Cefpodoxime 200mg fast delivery
Moderate to severe anterior injection of antibiotics antibiotics for uti and bladder infections buy cefpodoxime overnight, systemic antibiotics and uveitis may occur in those patients who have corticosteroids, or vitrectomy. In such cases routine aggressive treatment some eyes may end up in treatment of the disease should be supplemented phthisis bulbi (Fig. It can be prevented by following onset endophthalmitis are late complications of the correct surgical technique and proper suturing cataract surgery (Table 27. The administration of acetazolamide or injection of air into the anterior chamber Table 27. Late endophthalmitis infected the infection travels inside the eye and Operations Upon the Eyeball and its Adnexa 467 Secondary glaucoma may supervene due to the formation of peripheral anterior synechiae as a result of shallowing of the anterior chamber. Sometimes, the lens matter and particulate material from iridocyclitis block the trabecular meshwork and cause elevation of the intraocular pressure. Bullous keratopathy is caused by a prolonged contact of the vitreous with the corneal endothelium, it may be associated with cystoid macular edema (Irvine-Gass syndrome). Intraoperative vitreous loss, lattice degeneration, traumatic cataract and high myopia are risk factors. Late onset postoperative endophthalmitis may occur due to infection by organisms of low virulence or fungal infection. Propionibacterium acnes infection manifests as a dense white plaque on the posterior the major disadvantages of aphakia. Cataract patients with intolerance for contact an established surgical procedure in the managelens ment of cataract. Patients with macular degeneration or retinitis implantation is the restoration of vision, both pigmentosa central and peripheral, approximating to the 4. Technique Relatively difficult to Easy to perform and less perform and time time consuming 1. Luxated Cannot be removed Can be removed by this the pupil and the iris and are either supported by lens by this procedure procedure the scleral spur in the angle of the anterior 3. Out of several types and possible styles, the Kelman style with four point fixation 4. Limbal Small for the delivery Large incision for the complications and their long-term results may not incision of the nucleus delivery of the lens in toto b. Retinal Incidence is Relatively higher incidence detachment insignificant sular support d. To insert implanted lens becomes unstable and gets subthe proximal feet, the haptic is pushed backwards luxated. The iris fold below the claw is or multipiece with J-shaped or C-shaped loops, then grasped with enclavation forceps and the are available (Fig. For small incision cataract surgery with or without phacoemulsification, foldable silicone, acrylic or hydrogel lenses are used (Fig. The superior haptic is grasped with McPherson forceps, flexed behind the optic and gently placed under the upper flap of the capsule. After a meticulous anterior vitrectomy the lens is implanted in the ciliary sulcus and sutured to the sclera by 9-0 or 10-0 Fig. Operations Upon the Eyeball and its Adnexa 471 ticated automated suction-cutting device is used for this purpose while maintaining the normal intraocular pressure. The technique avoids damage to the corneal endothelium and causes least damage at the site of entry into the eye. Pars plana surgery can be performed either for the anterior segment disorders or for the posterior segment diseases. Advanced vitrectomy removes vitreous opacities, relieves vitreoretinal traction and reattaches the retina by internal tamponade. It can posterior capsulotomy restores the vision in such be followed by endophotocoagulation. The pars plana surgery is a technique by which Therapeutic vitrectomy is done for debulking the the lens or the vitreous is removed through a small vitreous of debris, pus, blood and pathogenic incision in the region of pars plana. Topical anesthetic drops are not used as they cloud the cornea and interfere with the ophthalmoscopic examination. An accurate localization of retinal breaks is carried out by an indirect ophthalmoscopic examination. One must localize all the breaks and the sclera underlying them is marked by diathermy. Indenting the sclera and choroid towards the retinal break (scleral buckling) supports the break and Figs 27. Silicone tyres and sponges are used as an explant (episcleral placement) or an implant (intrascleral placement) for scleral buckling. After 3 weeks of the surgical results of rhegmatogenous detachoperation, a cosmetic shell can be fitted. Enucleation of the eyeball is indicated in the following conditions: Complications 1. Intraocular tumors (retinoblastoma, malignant Choroidal or vitreous hemorrhage, choroidal melanoma) detachment, elevation of intraocular pressure and 3. Perforating injury to the eye with loss of vision nonattachment of the retina are some of the 4. The Indications insertions of all the four rectus muscles are defined Evisceration is recommended in the following and a silk suture is passed near the insertion of conditions: each muscle. Then a muscle hook is passed under the tendon and one-by-one the rectus muscles are 1. Improper positioning of Evisceration can be done either under general or the blades of scissors may cause perforation of local anesthesia. The eyeball is drawn forward and the speculum and a stab incision is made at the attached tendons of the superior and inferior limbus (video). The inner surface of the sclera should be obtained for histopathological examiis cleaned with a swab and the cavity is sprayed nation to assess the extension of the growth. The edges within the scleral cup provided there is no active of the conjunctiva are sutured. The en masse removal of the contents of the orbit along with the eyeball is known as exenteration of Recession of Medial Rectus the orbit. It is done for the malignant tumors of the orbit and in the extraocular stage of intraocular General anesthesia is preferred in a child. The operation is performed under speculum is inserted, a fixation suture is passed general anesthesia. The exenterated orbit may be at the medial limbus and the eye is rotated laterally. The conjunctiva is incised vertically just covered by a prosthesis attached to the spectacle medial to the traction suture and the incision is frame. Postponement of recession, and the distance is measured from the operation may lead to the development of insertion of the tendon and marked on the sclera amblyopia and failure to restore binocular vision. Free cutting with a scissors, and the sutures are passed tenotomy or guarded tenotomy can also weaken through the superficial layers of the sclera at right the overacting muscle. In resection the length of angles to the long axis of the muscle at the points the tendon of the muscle is shortened to enhance already marked (Fig. Resection of Lateral Rectus Convergent strabismus is usually undercorrected, while divergent strabismus is fully correcResection of the lateral rectus muscle is performed ted or over-corrected. The medial rectus recession by rotating the eye medially by a suture placed at gives more correction than the resection, and the the lateral limbus. A conjunctival incision is made lateral rectus resection often results in more 2 mm lateral and concentric with the limbus and correction of strabismus than the recession. The desired length of Undercorrection, overcorrection, diplopia, enophthe muscle to be resected is measured with the thalmos, conjunctival cyst and granuloma are help of calipers and marked on the muscle itself. Two whip sutures are passed through the upper Encouraging results of strabismus surgery are and lower edges of the muscle nearly 1 mm obtained in accommodative esotropia and in behind the mark. Syringing Resection of medial rectus and recession of lateral rectus muscles (video) are performed to Persistent epiphora in a newborn occurs due to correct divergent strabismus.
Purchase generic cefpodoxime
The patient should avoid intense ultraviolet radiation as a prophylactic measure against recurrence bacteria biology generic cefpodoxime 200mg line. Epidemiology: the disorder usually affects immunocompromised persons between the ages of 40 and 60 who have underlying disorders. Etiology: the disorder is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which initially manifests itself as chickenpox. If activation or reinfection occurs, the latent neurotropic viruses present in the body can lead to the clinical syndrome of herpes zoster ophthalmicus (Fig. Prodromal symptoms of erythema, swelling, photosensitivity, and lacrimation may occur before the characteristic clear watery vesicles appear. The skin sensitivity at the tip of the nose should be evaluated on both sides in the initial stage of the disorder. Decreased sensitivity to touch suggests involvement of the nasociliary branch of the ophthalmic nerve, which can lead to severe intraocular inflammation. Complications: Involvement of the nasociliary branch of the ophthalmic nerve can lead to severe intraocular inflammation. Etiology: An abscess of the upper or lower eyelid can form as a sequela of minor trauma, insect sting, or spread of inflammation from the paranasal sinuses. Symptoms: the severe inflammation and swelling often make it impossible actively to open the eye (Fig. Orbital cellulitis or cavernous sinus thrombosis can occasionally occur as a sequela of eyelid abscess, especially when located at the medial angle of the eye. Application of a 2% mercury precipitate ointment over an extended period of time is also effective. Symptoms and diagnostic considerations: Hordeolum presents as painful nodules with a central core of pus. External hordeolum appears on the margin of the eyelid where the sweat glands are located (Fig. Internal hordeolum of a sebaceous gland is usually only revealed by everting the eyelid and usually accompanied by a more severe reaction such as conjunctivitis or chemosis of the bulbar conjunctiva. Differential diagnosis: Chalazion (tender to palpation) and inflammation of the lacrimal glands (rarer and more painful). Treatment: Antibiotic ointments and application of dry heat (red heat lamp) will rapidly heal the lesion. An underlying internal disorder should be excluded in cases in which the disorder frequently recurs. Epidemiology and etiology: Chalazia occur relatively frequently and are caused by a chronic granulomatous inflammation due to buildup of secretion from the meibomian gland. After introducing the chalazion clamp, the lesion is incised either medially, perpendicular to the margin of the eyelid, or laterally, perpendicular to the margin of the eyelid (this is important to avoid cicatricial ectropion). A higher incidence has also been observed in patients with diabetes, increased levels of plasma lipoprotein, or bile duct disorders. The disease usually affects children and teenagers and is transmitted by direct contact. The pinhead-sized lesions have typical central depressions and are scattered near the upper and lower eyelids (Fig. The cutaneous horn should be surgically removed as 25% of keratosis cases can develop into malignant squamous cell carcinomas years later. Differential diagnosis should exclude a basal cell carcinoma (see that section); the margin of a keratoacanthoma is characteristically avascular. They frequently (25% of all cases) develop into a malignant squamous cell carcinoma in later years if they are not surgically removed. Symptoms: Hemangiomas include capillary or superficial, cavernous, and deep forms. Diagnostic considerations: Hemangiomas can be compressed, and the skin will then appear white. Treatment: A watch-and-wait approach is justified in light of the high rate of spontaneous remission (approximately 70%). Where there is increased risk of amblyopia due to the size of the lesion, cryotherapy, intralesional steroid injections, or radiation therapy can accelerate regression of the hemangioma. Neurofibromatosis is regarded as a phacomatosis (a developmental disorder involving the simultaneous presence of changes in the skin, central nervous system, and ectodermal portions of the eye). Symptoms and diagnostic considerations: the numerous tumors are soft, broad-based, or pediculate, and occur either in the skin or in subcutaneous tissue, usually in the vicinity of the upper eyelid. They can reach monstrous proportions and present as elephantiasis of the eyelids (Fig. Morbidity in sunny countries is 110 cases per 100000 persons (in central Europe approximately 20 per 100000 persons). Basal cell carcinomas arise from the basal cell layers of the epidermis and the sebaceous gland hair follicles, where their growth locally destroys tissue. Symptoms: Typical characteristics include a firm, slightly raised margin (a halo resembling a string of beads) with a central crater and superficial vascularization with an increased tendency to bleed (Fig. Diagnostic considerations: the diagnosis can very often be made on the basis of clinical evidence. Treatment: the lesion is treated by surgical excision within a margin of healthy tissue. Prognosis: the changes of successful treatment by surgical excision are very good. The firm, painless swelling is usually located in the upper eyelid and is mobile with respect to the skin but not with respect to the underlying tissue. An apparent chalazion that cannot be removed by the usual surgical procedure always suggests a suspected adenocarcinoma. Orbital part of the Superior punctum lacrimale lacrimal gland Superior lacrimal canaliculus Fundus of the lacrimal sac Plica semilunaris Lacrimal sac Nasolacrimal duct Inferior concha Inferior punctum lacrimale Fig. A palpable lacrimal gland is usually a sign of a pathologic change such as dacryoadenitis. The tendon of the levator palpebrae muscle divides the lacrimal gland into a larger orbital part (two-thirds) and a smaller palpebral part (one-third). Several tiny accessory lacrimal glands (glands of Krause and Wolfring) located in the superior fornix secrete additional serous tear fluid. Its parasympathetic secretomotor nerve supply comes from the nervus intermedius. The sympathetic fibers arise from the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion and follow the course of the blood vessels to the gland. O A watery layer (ensures that the cornea remains clean and smooth for optimal transparency). With its hydrophobic properties, it prevents rapid evaporation like a layer of wax. Its task is to clean the surface of the cornea and ensure mobility of the palpebral conjunctiva over the cornea and a smooth corneal surface for high-quality optical images. It is hydrophilic with respect to the microvilli of the corneal epithelium, which also helps to stabilize the tear film. This layer prevents the watery layer from forming beads on the cornea and ensures that the watery layer moistens the entire surface of the cornea and conjunctiva. Lysozyme, beta-lysin, lactoferrin, and gamma globulin (IgA) are tear-specific proteins that give the tear fluid antimicrobial characteristics.
Cheap cefpodoxime online amex
Pressure with moist cotton swab can be applied on the central part of the cornea if the pupil remains blocked virus living or nonliving quality 200mg cefpodoxime. Initially pilocarpine is instilled every 30 minute and later hourly till maximum miosis is achieved. This is effective in pulling the iris away from the angle and opening the drainage channels. However, the tension is lowered by medical treatment before surgery to prevent occurrence of expulsive haemorrhage. Technique A drop of topical pilocarpine is instilled frequently 30 minutes before laser therapy. The laser with an anterior offset is then used to make an opening measuring 150-200 microns in size is made in the periphery of iris. By making a hole in the periphery of iris, pupillary block is relieved permanently. A partial thickness of a part of limbus (trabecular meshwork and canal of Schlemm) is excised under a scleral flap. The superficial flap of the sclera measuring 5 fi 5 mm is dissected anteriorly upto the limbus. The aqueous seeps out from the anterior chamber into the scleral window > It passes in between the two scleral flaps > It flows into the subconjunctival space. Postoperative management Topical broad spectrum antibiotic drops and ointment, cycloplegic and corticosteroids are given for a period of 2-3 weeks. Circumcorneal ciliary congestion is present around the limbus as reddish blue zone. Intraocular pressure is permanently raised when about two-third or more circumference of the angle is closed by peripheral anterior synechiae. Therefore after lowering the raised intraocular pressure with fi-blockers, acetazolamide and hyperosmotic agents; a filtration surgery (trabeculectomy) should be done. The iris is atrophic (white patches) and may have a broad zone of pigment around the pupil (ectropion of the uveal pigment) due to fibrosis of the iris tissue. Ocular structures like cornea, iris, anterior chamber can be easily identified unlike in phthisis bulbi. Essentially it is a histopathologial diagnosis, whereby the cytoarchitecture of the eye is maintained in the blind eye. In phthisis bulbi, in addition to atrophy there is disorganisation of the ocular cytostructure in the blind eye. Cyclodiathermy using surface electrodes may result in necrosis of scleral tissue and staphyloma formation ii. It causes tissue necrosis and often results in patients discomfort and ocular inflammation. Application of intense ultrasound to produce focal lesions of the sclera (over the pars plana). It is a more desirable procedure as it is effective, more predictable and pain free iv. Blockage at the angle of anterior chamber by the peripheral anterior synechiae and organised exudate. Neovascular glaucoma results commonly due to thrombosis of the central retinal vein and rubeosis iridis in diabetes mellitus. In glaucoma capsulare there are degenerative changes and exfoliation of the anterior lens capsule and anterior uvea. The conjunctival epithelium grows inside the anterior chamber and blocks the angle. The vitreous protruding through the pupil in the anterior chamber may cause pupillary block iii. Trabeculectomy is preferably done in lower temporal quadrant to facilitate the drainage of aqueous by gravity. Trans-scleral or transvitreal photocoagulation of the ciliary processes under direct vision causes partial destruction of the ciliary body. Therapeutic high intensity ultrasound is a more desirable approach in many cases because it is an effective, more reliable and pain-free procedure.
Order cefpodoxime
Corneal and uveal tract Absent Iritis antibiotic zyvox cost order cefpodoxime master card, cyclitis and anterior choroiditis may be involvement present. Systemic corticosteroids are given starting with high doses and gradually reducing to maintenance dose. Extreme corneal marginal ulceration or keratolysis may require corneal grafting usually as lamellar graft. Etiology Staphylomas are formed due to thinning of the sclera often associated with raised intraocular tension. Posterior staphyloma can be treated by reinforcement surgery by fascia lata or silicon band in cases of high myopia. Anatomically, they are continuous and so disease of one part may spread to the other. When pupil is constricted, more of the posterior surface of the iris is in contact with the lens capsule. It divides the space between the cornea and lens into the anterior and posterior chambers of eye. At the periphery, the iris is attached to the middle of anterior surface of the ciliary body. Parts Anterior surface of the iris can be divided into two zones by a zigzag line called the collarette. It is supplied by the cervical parasympathetic nerves via third cranial nerve and causes constriction of the pupil. It is relatively avascular therefore posterior segment of the eye is entered through the pars plana incision 3-5 mm behind the limbus. Suspensory ligament or zonule of Zinn is attached to them and the equator of the lens. The outer layers of retina are dependent for their nutrition the Uveal Tract 163 Structure of choroid upon the choroid. The potential space between this membrane and sclera is known as suprachoroidal space. The inner side of the choroid is covered by at thin elastic membrane lamina vitrea or membrane of Bruch. The Blood Supply the blood supply of the uveal tract is almost entirely derived from the posterior ciliary and anterior ciliary arteries. However, there is always associated inflammation of the adjacent structures such as retina, vitreous, scleral and cornea. Inflammation is insidious in onset, chronic in nature with minimum clinical features. It is characterized by the presence of fine keratic precipitates which are composed of lymphoid cells and polymorphs. Clinical features Features of low grade Features of acute inflammation inflammation i.
Purchase cefpodoxime 100 mg
May also occur secondary to trauma or especially with viral infections infection 3 antibiotics for uti no alcohol order cefpodoxime 200mg amex. Gently massage lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal temic antibiotics duct by frequently stroking skin from brow 4. If unresponsive to treatment, refer to ophthalarea along lateral aspect of nose (no clear mologist for surgical excision, curettage, or supporting data for effectiveness but often corticosteroid injections recommended) 2. Common acute or chronic bilateral infiammaage or earlier for evaluation and treatment if tion of the eyelid margins no improvement with antibiotics and massage 2. Irritation, burning sensation to eyes related to chronic infiammation, especially related 2. Refer for incision and drainage if unresponsive with staph type; may lead to eyelid margin to treatment distortion and possible ectropion 5. When seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is than adults and the primary etiology is extenpresent, frequent shampooing with selenium sion of a bacterial sinusitis (into the orbital sulfide recommended tissues) 5. Periorbital cellulitis is more common than sary; recurrences are common orbital cellulitis; often associated with skin disorders or infections of the eyelid such as insect Hordeolum (Stye) bites, impetigo, styes 3. Differentiate between orbital (within true unilateral or bilateral; can result in amblyopia, parorbit), periorbital, or preseptal (surrounding tial or complete blindness; some are not clinically orbital septum) cellulitis significant 2. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus surrounded by red refiex, or white plaque-like infiuenza vaccines have decreased annual case opacities rate of periorbital and orbital cellulitis (Prentiss, 4. Prompt referral to ophthalmologist for will show increased pressure diagnosis/treatment 2. Surgery is often first line, followed by mediof congenital cataracts; treat any underlying cal therapy; post-op steroids and cycloplegic disorder drops are essential to prevent adhesions 3. Even with treatment, still has high risk for disruption of aqueous fiuid circulation involving visual impairment; refer early for services for one or both eyes resulting in optic nerve damage visually impaired with loss of visual acuity and eventual blindness if untreated Strabismus 1. Historical risk factors include prematurity, fiow of tears (epiphora), blepharospasm family history, cerebral palsy, most chromo(eyelid spasm); triad occurs in about 30% somal and other major genetic anomalies, 2. Decreased vision (peripheral first) leading to prenatal drug exposure, fetal alcohol syntunnel vision drome, major head trauma, major congenital 3. Patients with congenital vision loss are more diameter 12 mm if one year of age needs likely to develop exotropia and those with immediate attention; eventually entire eye acquired vision loss are more likely to develop enlarges exotropia 2. Deep cupping of optic disc; enlargement of the of nose; no ocular deviation optic cup and increase of cup; disc ratio 0.
Diseases
- Phenol sulfotransferase deficiency
- Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
- Acromegaly
- Benign essential tremor syndrome
- Familial m Familial w
- Neuraminidase beta-galactosidase deficiency
- Acrodermatitis
- Arthritis
- Hypoparathyroidism nerve deafness nephrosis
- Gorham Stout disease
Purchase online cefpodoxime
Common sites of involvement in disseminated infection include the kidney bacteria legionella buy cefpodoxime 200 mg otc, liver, spleen, brain and gastrointestinal tract; pulmonary infections are rare. One common sign of deep-seated candidosis is the presence of white lesions within the eye (Candida endophthalmitis). Treatment the treatment of choice for most forms of systemic candidosis are: intravenous amphotericin B (conventional or liposomal) intravenous or oral fluconazole 9. Pneumocystis carinii Pneumocystis carinii is a fungus, but its morphology, behaviour and response to antimicrobial agents are more typical of a protozoan. In addition to pneumonia, other as yet unrecognized forms of Pneumocystis infection may exist. Malaria parasites Four species are encountered in human disease: Plasmodium falciparum, which is responsible for most fatalities; P. Life cycle: when an infected mosquito bites, sporozoites present in the salivary glands enter the bloodstream and are carried to the liver, where they invade liver parenchyma cells. They undergo a process of multiple nuclear division, followed by cytoplasmic division and, when this is complete, the liver cell ruptures, releasing several thousand individual parasities into the bloodstream. The red cell ruptures to release the individual merozoites, which then infect fresh red blood cells. Pathogenesis Malaria is characterized by severe chills, high fever and sweating, often accompanied by headache, muscle pains and vomiting. Falciparum malaria, unlike the other forms, may progress (especially in primary infections) to coma, convolutions and death. This condition, cerebral malaria, is associated with the adherence of parasitized red blood cells to the endothelium of brain capillaries. Toxoplasma gondii & Cryptosporidium parvum Toxoplasma gondii It is a unicellular spore forming coccidian protozoa important in nosocomial infections. Human infected by undercooked meat (ingestion of mature oocytes) or by handling cat feces. Tachyzoites localize in neural and muscle tissue and develop into tissue cyst bradyzoids. If a pregnant women becomes infected, tachyzoites can infect the fetus via bloodstream. IgA antibodies are typical for recent infections, IgG for fistatus afterfi an infection. The amoebae invade the colonic mucosa, producing characteristic ulcerative lesions and a profuse bloody diarrhoea (amoebic dysentery). Systemic infection may arise, leading to abscess formation in internal organs, notably the liver. Nevertheless, it is not possible readily to distinguish pathogenic from non-pathogenic strains in asymptomatic cyst excreters. Giardia lamblia this intestinal parasite lives attached to the mucosal surface of the upper small intestine. Vast numbers may be present, and their presence may lead to malabsorption of fat and chronic diarrhoea. The best pH for the pathogen is 6 so abnormal alkalinity favours acquisition of the disease. Treatment the organism is responsible for a mild vaginitis, with discharge, which ordinarily responds to treatment with metronidazole or tinidazole. Pathogenesis Following the bit of an infected tsetse fly, a localized trypanosomal chancre may appear transiently, but invasion of the bloodstream rapidly occurs. The trypanosomes enter the bloodstream, but do not multiply there; instead, they invade the cells of the reticulo-endothelial system and muscle, where they lose their flagellum and associated undulating membrane and adopt a more rounded shape. They multiply int he muscle and are liberated from ruptured cells which disseminate the infection and provide the parasitaemia needed to infect fresh bugs when they next feed. Pathogenesis Extensive cardiomyopathy, sometimes with gross distension of other organs (mega-oesophagus and mega colon). Leishmania Leishmania species are intracellular parasites of the reticulo-endothelial system. There are only two morphological forms: amastigostes (non-flagellate forms), which occur in the infected lesion, and promastigotes (flagellate forms that lack and undulating membrane), which occur in the insect vector. Pathogenesis Cutaneous leishmaniasis (oriental sore) causinga boil-like swelling on the face or other exposed oart of the body. The central part of the lesion may become secondarily infected with bacteria, but the leishmania organisms reside in the raised, indurated edge of the lesion. The most serious form of leishmaniasis is visceral leishmaniasis which is a life-threatening disease involving the whole of the reticulo-endothelial system. Ascaris lumbricoides & other intestinal nematodes Infection with intestinal roundworms is generally associates with conditions of poor hygiene. Low worm burdens are generally asymptomatic, but heavy infections may cause problems, especially in young children where they have been associated with impaired development. In warm, moist condition, infective larvae develop within fertile eggs, but do not hatch. If ingested, the eggs hatch in the duodenum and the larvae penetrate the gut mucosa to reach the bloodstream. They are carried to the pulmonary circulation, where they gain access to the lung and undergo two moults before migrating via the trachea to the intestinal tract. Havng completed their round-trip, theuy mature in the gut lumen and live for several years. Pneumonic symptoms may accompany the migratory phase and the adult worms may invade the biliary and pancreatic ducts. Moreover, heavy infection with those large worms can cause intestinal obstruction. Larvae hatch in the small intestine and penetrate the gut wall, but they are unable to complete their migratory phase. Instead, they find their way to remote parts of the bidy, a condition known as visceral larva migrans. Like those of ascaris, they develop infective larvae in warm, moist conditions, but the ova do not hatch outside the body. However, after ingestion and hatching, there is no migratory phase and adult worms develop directly in the large intestine. Infection is usually trivial, though massive infections can cause rectal prolapse in young children, and a form of dysentery is described. Hookworm the two species produce indistinguishable thin-walled eggs which hatch in soil. These are capable of penetrating unbroken skin, and in this way they gain access to the bloodstream to begin a migratory phase similar to that of ascaris. When they reach the gut they attach by their mouthparts to the mucosa of the small intestine. Hookworms ingest blood and, moreover, move from site to site in the gut mucosa, leaving behind small bleeding lesions. These two facts are responsible for the chief pathological manifestation of heavy infection with hookworms: iron deficiency anaemia. Strongyloides stercoralis Human infections arise after penetration of infective larvae through skin and there is a migratory phase involving the lungs. However, human infection appears to be restricted to female worms, which attach to the gut mucosa and produce eggs that contain fully developed larvae; these hatch within the intestinal lumen so that larvae, not eggs, are found in faecal samples.
Cefpodoxime 200mg low price
Schirmer Test Schirmer test measures the aqueous production and gives a gross idea of tear film function antibiotic viruses buy discount cefpodoxime. A positive test reveals a triangular staining of the nasal and the temporal bulbar conjunctiva in the exposed interpalpebral area. The time interval between the last blink the management of dry eye is not always and the appearance of first dry spot is measured satisfactory. Preservative-free tear substitutes remain the mainstay of the treatment of dry eye. It can provide valuable are useful in both mucin and aqueous deficiency information about the morphology and density of states. Moist chamber Work-up goggles and soft contact lenses may relieve Initially it is important to exclude hypersecretion discomfort in many cases. A chronic immunethe position of puncta and lower lid, size of mediated inflammatory process plays a role in the puncta, presence of a foreign body or debris in the pathogenesis of dry eye. Topical instillation the punctal orifice and a swelling or a discharging of corticosteroids and cyclosporine A drops sinus over the sac region should be identified. A slight pressure over the lacrimal sac may Systemic tetracycline is the treatment of choice in lead to reflux of pus or mucus through the punctum blepharitis associated with dry eye. It is equally important to rule out the presence If needed, surgery may be performed to correct the of a nasal pathology (like nasal polyp or atrophic lid deformities and inadequate blinking. Fluorescein Dye Disappearance Test: When a 2% Punctal obstruction is quite common due to foreign solution of fluorescein is instilled into the normal body, stenosis and ocular chemical burns. The test is of great significance in patients Canalicular obstruction may be congenital or with unilateral watering. Stricture of the canaliculus develops retention of dye at the interface of the lower eyelid following trauma and infection. Jones Primary Dye Test (The Jones Test I): It has the Nasolacrimal duct obstruction, especially the same principle as that of fluorescein disappeacongenital, is the most common cause of epiphora rance test. However, in this test an anesthetic in infants due to noncanalization of the duct. In a positive test the fluorescein is recovered from the nose, while in a negative test no dye is found on the cotton bud. A lacrimal canula attached to a syringe filled with normal saline is passed into the lacrimal Fig. If the saline passes into the nose, the passage is free of obstruction, if it passes into the nose with forced pressure on the syringe, a partial obstruction is present, and if no saline reaches the nose, an obstruction is present. In the latter situation, the saline will reflux either through the upper punctum (obstruction in the sac, at the junction of the sac and the nasolacrimal duct or in the nasolacrimal duct) or through the lower punctum (obstruction in the lower or common canaliculus). Dacryocystography: the lacrimal passage can be Radionucleotide Dacryocystography (Lacrimal studied radiologically by injecting a radio-opaque Scintillography): Radionucleotide dacryocystodye, isophendylate, into the canaliculus followed graphy is a noninvasive imaging technique to by taking posteroanterior and lateral exposures study the functional integrity of the lacrimal immediately. The technitium-90m in saline is instilled into the exposures are repeated after 30 minutes. The conjunctival sac and sequential images are retention of the dye in the lacrimal sac after 30 obtained with an Anger gamma camera. The minutes suggests a partial or complete obstrucimages can be reviewed on a video screen or tion of the nasolacrimal duct (Fig. It is a common disease occurring at any Blepharitis, chronic conjunctivitis, senile laxity age. It is usually divided into two forms: congenital of the lower lid and other causes of ectropion lead dacryocystitis and dacryocystitis in adult. Some relief may be obtained by cauterization just behind and below the site of the Etiology punctum with a diathermy. The punctum is pulled the congenital dacryocystitis or dacryocystitis of inwards following the contraction of the fibrous newborn (Fig. Alternatively, the punctum should be slit nous blockage of the lower end of the nasolacrimal open through its posterior border. Occlusion of the Punctum and Canaliculus Clinical Features the obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct is present Congenital anomalies of puncta and canaliculi in approximately 50% of the newborns at birth. The punctum and the canaliculus, particularly Patency may be restored spontaneously in some the lower one, may be blocked by cilium, concrecases after birth. Later, purulent discharge the patency is restored by the removal of the develops resulting in matting of the eyelashes. A cilium, dislodgement of concretion and sometimes gentle pressure over the lacrimal sac produces the by slitting the punctum and the canaliculus (threereflux of purulent discharge from the lower snip operation). Massaging of the lacrimal sac region and Acute dacryocystitis is an acute suppurative frequent instillation of antibiotic drops usually inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The massage increases the Etiology hydrostatic pressure and helps rupture the Acute dacryocystitis may occur due to various membranous obstruction. The index leads to secondary infection by Streptococcus finger is kept over the common canaliculus to pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus prevent the regurgitation through the puncta, aureus and Actinomyces. Acute dacryocystitis is then it is stroked downwards firmly 10-12 usually preceded by a chronic dacryocystitis or times at one sitting. The hydrostatic Clinical Features massage may cure the congenital obstruction in about 95% of cases. Probing of the lacrimal passage is warranted and marked swelling and redness of the sac region in failed cases. Postoperatively, steroid-antibiotic Later the sac becomes filled with pus and its drops should be instilled 4 times a day. Repeat distended anterior wall ruptures to give rise to a probing may be performed if epiphora persists pericystic swelling (Fig. Generally, the success rate develops which usually points below and to the of probing is quite high, but it decreases if the outer side of the sac owing to the gravitation of the pus. It often bursts spontaneously on the skin procedure is done after the age of 18 months. Repeated probing may lead to the formation Constitutional symptoms such as malaise and of stricture of the nasolacrimal duct. Dacryocystitis in Adults Treatment the dacryocystitis in adults may occur in an acute Local hot compresses several times in a day and or a chronic form. In case pus point is formed, an round, nontender, cystic swelling appears in the incision is made to evacuate it. On inflammation subsides, the case is treated on the application of pressure, a mucoid fluid regurgilines of chronic dacryocystitis. Occasionally, the fluid passes into the nose through a partially obstructed nasoChronic Dacryocystitis lacrimal duct. Low grade repeated infections for a prolonged Etiology period of time result in a small fibrotic sac which Chronic dacryocystitis (Fig. The presence of a lacrimal fistula obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct due to chronic discharging mucopus indicates a past acute inflammation. If an intraocular Generally, the sac harbors many pathogenic operation is performed in the presence of an occult organisms, viz. Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus lacrimal infection, there is a risk of development pneumoniae, Enterobacter, E. The sac may be secondarily affected In rhinosporidiosis the sac is filled with from tuberculous lesion of skin, conjunctiva, nose creamy pus and its walls lined by polypoid and bones. In tertiary syphilis lacrimal sac granulation tissue containing thousands of affections are common. It may be associated with rhinosoccur occasionally due to Rhinosporidium seeberi. Diseases of the Lacrimal Apparatus 417 Complications or without the nasolacrimal duct obstruction, a conjunctivodacryocystorhinostomy surgery is Chronic dacryocystitis is by far the most important helpful. Squamous Treatment cell papilloma and transitional cell carcinoma are the management of chronic dacryocystitis is common tumors of the sac. Orbit is formed thinnest wall of the orbit is lamina papyracea by seven bones: frontal, maxilla, zygomatic, which covers the ethmoid sinus. This bone can be sphenoid, palatine, ethmoid and lacrimal involved in blow-out fracture of the orbit.
Order cefpodoxime 200mg fast delivery
Diagram of a neurovascular unit antibiotic resistance peer reviewed journal discount cefpodoxime 100 mg online, a capillary enclosed in astrocyte end-feet during a nervous system infection by a flavivirus. This model of Flavivirus Neurotropism, Neuroinvasion, Neurovirulence and Neurosusceptibility: Clues to Understanding Flavivirusand Dengue-Induced Encephalitis 225 neuroinfection was the first to suggest that neurological alterations exhibited by infected animals, such as paralysis of posterior limbs, are principally associated with the death of infected neurons (Despres et al. Neurotropism the ability of some viruses to infect and replicate in neurons is called neurotropism and is determined by viral and cellular factors. Mostly virus determinants are associated with envelope glycoprotein gene mutations that favour interactions between the virus and molecules on the neuron surface. These interactions promote the fusion of the virus with the plasma membrane and can also trigger endocytosis or transcytosis of the virus. A wellknown example of viral neurotropism is that mediated by glycoprotein G of the rabies virus (a highly neurotropic virus), which interacts with the neurotrophin low-affinity receptor, the neural cell adhesion molecule or the nicotinic receptor present in muscular and neuron cells to infect cells. The interaction of rabies virus protein G with some of these molecules promotes virus entry and replication in the nervous system (Lafon, 2005). In flaviviruses, the envelope protein (E) is the principal component of the virion surface. It participates in the recognition and subsequent binding to the receptor and the fusion of the virus with the cell membranes (Lindenbach et al. As was previously stated, the E flavivirus protein partially determines cellular tropism. However, the molecular determinants that promote the entry into susceptible cells are not well known, and the mechanisms that define their neurotropism are even less clear (Lobigs et al. Thus, this amino acid motif is proposed as the main site of interaction between flaviviruses and their viral receptors (Becker, 1990; Lee & Lobigs, 2000; Lobigs et al. However, mutations in non-structural viral proteins could also determine the success of the infection, particularly the replication of the virus in neurons (Duarte dos Santos et al. Neurovirulence Neurovirulence is the capacity of viruses to cause disease and alterations in the nervous system and can be affected by both viral and host-related factors. When the Asian strain started circulation in the American continent, it was caused serious dengue outbreaks with haemorrhagic symptoms in patients with primary infections who were from Central and South American countries (Clayde et al. The Asian genotype is frequently associated with severe dengue and haemorrhagic symptoms in Asian patients, and experimentally, this genotype is more virulent and replicates with higher efficiency in macrophages, while the American genotype is associated with signs of dengue fever and its replication is slower in cultured macrophages (Barreto dos Santos et al. This difference could explain the efficiency of virus replication and virus production in infected cells with this genotype, which in turn could be related to the inefficiency of the immune system to control and eliminate this virus (Cologma & Rico-Hesse, 2003; Leitmeyer et al. Infiltration of monocyte cells into the cerebral parenchyma was also detected, as was the appearance of neurological symptoms such as meningo-encephalitis and paralysis associated with neuronal degeneration. The immune response that occurs in nervous tissue during flavivirus infection varies in intensity and can support the control and clearence of the virus and establish a neuroprotective state that stimulates the repair of tissue damaged by the infection (Griffin, 2003). To promote virus clearance, monocytes and lymphocytes enter the cerebral parenchyma, attack infected cells, and release soluble mediators, which stimulate and maintain the local immune response activating astrocytes, microglia and the cerebrovascular endothelium. Additionally, the infected or damaged neurons themselves can express and release some of these mediators (Chakraborty et al. The activation of glial cells is partially due to their infection by flaviviruses. Lastly, infiltrating macrophages modulate the type of immune response that occurs in the tissue during infection and can clear free viral particles and infected and damaged cells present in the tissue, although these cells can also seemingly promote the entering of some flaviviruses, acting as Trojan horses by releasing viral particles within the nervous tissue (Chaturvedi, 2006; Chaturvedi et al. Finally, neurotropic flaviviruses as well as non-neurotropic flaviviruses preferably infect neurons in vitro and in vivo (Chambers & Diamond, 2003; Johnson & Roehring, 1999; Samuel & Diamond, 2006; Shrestha et al. Nevertheless, it has been reported that other Flavivirus Neurotropism, Neuroinvasion, Neurovirulence and Neurosusceptibility: Clues to Understanding Flavivirusand Dengue-Induced Encephalitis 229 nervous tissue cells such as oligodendrocytes, astrocytes and microglial cells (Chen et al. The cellular, metabolic and molecular factors that increase the susceptibility of neurons to flaviviruses are unknown. Thus, cell death in nervous tissue, such as neurons, has been associated with the development of neurological alterations resulting from infection. Neurosusceptibility Neurosusceptibility refers to the vulnerability of a host to neurological alterations during an infection with neurotropic viruses. This vulnerability can be affected by the age, species, immune status and genetic background of the individual. This resistance to infection is maintained, even if previouslyinfected neonatal neurons are implanted in animals greater than 14 days old. These results demonstrate that the neuronal and physiological maturity of nervous tissues is determining factors in favouring infection and neuronal alteration (Ogata et al. This vulnerability is due principally to the type of response that neonates generate against viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic infections (Marodi, 2006). Some clinical reports demonstrate that neonatal immunity is predominantly of the Th2 type, which specifically stimulates immune tolerance and inhibits the Th1 type response, which in turn activates immune cells to control and eliminate pathogens. This hypo-reactivity of antigen-presenting cells causes them to inefficiently recognise and present viral or bacterial antigens. The enzootic life cycle of flaviviruses includes vectors and reservoirs such as birds, monkeys or other wildlife, as well as humans. The known reservoirs for flaviviruses are birds and small mammals, which suggests that there are some species-specific characteristics that restrict the transmission of these viruses. Additionally, in these models, certain symptoms associated with infection are exhibited that are uncommon in infected humans, such as neurological alterations (Tan et al. Nevertheless, while these models have increased our understanding of some of the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the development of the haemorrhagic signs observed during infection, their interpretation should be tentative given that these animals present an incomplete immune response to the virus due to their modified genomes. Therefore, it will be necessary to perform new studies with new experimental strategies to expand our knowledge and understand the interactions between flaviviruses and nervous tissue. The study of this phenomenon will provide information that permits an understanding of viral pathogenesis that is of great importance for public health in tropical countries. Jacqueline Chaparro-Olaya who spared her time to go through the manuscript at various stages and offered valuable suggestions. Dengue virus infection of human endothelial cells leads to chemokine productions, complement activation, and apoptosis. Mouse neuroinvase phenotype of West Nile virus strain varies depending upon virus genotype. West Nile virus neuroinvasion and encephalitis induced by macrophage depletion in mice. Genetic determinant responsible for acquisition of dengue type 2-virus mouse neurovirulence. Interaction of West Nile Virus with Primary Murine Macrophages: Role of Cell Activation and Receptors for Antibody and Complement. Looking at the blood-brain barrier: Molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Interaction of West Nile Virus with alpha v beta 3 integrin mediates virus entry into cells. Recent advances in deciphering viral and host determinants of dengue virus replications and pathogenesis. American genotype structure decrease dengue virus output from human monocytes and dendritic cells. Heat shock protein 70 in Neuro2a cell is a putative receptor for Japanese Encephalitis virus. Human isolates of dengue type I virus induce apoptosis in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Apoptosis in the mouse central nervous system in response to infection with mouse neurovirulent dengue virus.
Buy cheap cefpodoxime online
The common intraoperative complications of Advantages of Phacoemulsification cataract surgery are summarized in Table 27 kinds of antibiotics for acne order cefpodoxime now. Phacoemulsification is currently the most popular Retrobulbar hemorrhage may develop following the surgical procedure for the removal of cataract. It retrobulbar or peribulbar injection for regional has several advantages (Table 27. It usually takes two weeks for the hemorrhage to Limitations of Phacoemulsification resolve. The oozing points on the sclera Operations Upon the Eyeball and its Adnexa 465 Table 27. Delayed formation of the anterior chamber traumatized eye or due to previous poorly 7. Prolapse of the Striate keratitis develops due to damage to the vitreous after the nuclear delivery can happen corneal endothelium during excessive manipubecause of posterior capsular rent that occurs most lation within the anterior chamber or by prolonged commonly during cortical irrigation-aspiration. It usually disappears In these cases one should proceed slowly, clear within a few days, but causes significant loss of the vitreous from the anterior chamber and avoid corneal endothelial cells. It can be a total lens dislocation due to endothelial damage results in corneal edema. Even the nuclear is grossly reduced owing to the use of sutures and fragments may get posteriorly dislocated in the construction of self-sealing incision. Hypertension, arteriosclerosis, diabetes and raised Postoperative hyphema usually appears on the fifth intraocular pressure are known risk factors. Severe day due to leakage from the newly formed vessels ocular pain, soakage of the eye pad and prolapse in the section. Mydriatic-miotic instillations, of the vitreous and the uveal tissue in the wound topical corticosteroids and oral serratiopeptidase are the presenting features. Massive age of the blood and reformation of the anterior hyphema needs paracentesis. The pressure tion often develops on the 2nd or 3rd day after must be lowered by oral acetazolamide. It is marked by severe pain, edema of lids, Mild anterior uveitis occurs in almost all cases of chemosis of the conjunctiva, corneal haze, extracapsular lens extraction, therefore, postopehypopyon, acute uveitis and dull fundus glow. The obstruction may be confirmed as well Balloon Dacryoplasty as overcome in some cases by syringing and Balloon catheter dilatation is an effective proceprobing. A lacrimal canula attached to a syringe is inserted through the punctum Lacrimal Intubation and the canaliculus, and the passage is syringed with slight pressure. Probing Dacryocystectomy When the syringing fails to overcome the obstruction, probing is planned. The removal of the sac is known as dacryocystecthe canula used for syringing is removed and tomy. Then the probe is swung the dacryocystectomy is indicated in following into vertical position and passed downwards, conditions: backwards and laterally through the naso1. Procedure the operation is done under general anesthesia in children and under local infiltration anesthesia in adults. Xylocaine 2% with adrenaline is injected at the junction of inferior orbital margin and anterior lacrimal crest. The solution is also infiltrated in the region of medial palpebral ligament, the nasolacrimal duct and posterior lacrimal crest. The anterior lacrimal crest is defined with the help of a blunt dissection and the Fig. Vikas Mahatme and Chitra Pande, Nagpur) the anterior lacrimal crest is divided to expose the Operations Upon the Eyeball and its Adnexa 477 lacrimal sac. Thereafter, the attachments of the overlying periosteum is lifted and a small opening sac with the lacrimal fossa are freed. The sac is (12 fi 10 mm) is made with a bone punch to expose drawn forward and twisted and is severed from the nasal mucosa (Fig. The upper end of the duct is made in the medial wall of the lacrimal sac to is curetted and the incision is closed by sutures. Then an HExcessive bleeding may be encountered shaped incision is made in the nasal mucosa with during the operation owing to damage to the the horizontal incision in the middle to raise 2 angular vein. The posterior flap of the sac is sutured to the posterior flap of the nasal mucosa (Fig. Contraindications Complications In the presence of a gross nasal pathology, Complications of dacryocystorhinostomy are not atrophic rhinitis, nasal polyp and lupus, the frequent. Marked fibrotic sac, the angular vein or vascular nasal mucous memosteomyelitis of the lacrimal fossa and tuberbrane. The formation of clot may obstruct the culous dacryocystitis are other conditions where communication. Cryopexy involves application of freezing cold Cryopexy may be performed under topical or by a cryoprobe attached to a cryomachine infiltrative or general anesthesia. One mm diameter Rapid freezing produces both extracellular and tip is used for vitreous surgery, 1. It is also used for prophylactic purpose for the treatment of areas of retinal degenerations and breaks. Neovascular and absolute glaucomas: Cryo application to the ciliary body reduces the intraocular pressure by destruction of the Fig. Tumors: Cryotherapy may be used for the treatment of small solitary hemangioma, basal cell carcinoma and retinoblastoma. Retinopathy of prematurity: Cryotherapy is often used in the management of retinopathy of prematurity. Miscellaneous: Cryopexy may be used for the management of giant papillae of vernal keratoconjunctivitis, molluscum contagiosum, pars planitis and advanced cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Repeated freezingproperties of a laser beam are monochromatism, thawing can produce tissue adhesion, vascular coherency, collimation and concentration in a occlusion and tissue necrosis. Common indications of cryo therapy are given the laser can be delivered to the eye by a slitbelow. Miscellaneous: Laser can also be used for Photocoagulation is a thermal effect of laser and dilatation of pupil (photomydriasis), coreoutilized for coagulation of new blood vessels plasty for updrawn pupil and suturolysis after (Fig. The excimer laser (Argon fluoride that accumulates in the target tissue and a specific 193 nm) can break bonds of cells and reduce them laser light corresponding to the absorption peak to molecules that diffuse away in a short time. Benzoporphyrin derivative, verteporfin, and a diode laser (690 nm) are used in photoIndications dynamic therapy to treat the subretinal neovascular membrane in diseases like age-related 1. The photosensitizer molecule is excited the excimer laser ablates the optical part of following the light absorption from the laser. On healing the energy from the excited molecule is transferred to cornea gets flattened. The postoperative release free-radicals and production of singlet recovery is slow and the residual corneal haze oxygen. Cataract Surgery: Techniques, over correction of myopia are some of the Complications and Management. Paresis of accommodiseases of the central nervous system is not dation and convergence may also be seen. Middle ear infection is the chief cause of cerebral abscess affecting the temporal lobe. The Acute suppurative meningitis frequently causes cerebellar abscess occurs even more frequently papillitis due to descending infection. The cerebellar abscess develop papilledema on the side paralysis of abducent nerve is common, third and of the abscess, and in bilateral papilledema the fourth cranial nerves may also be involved. This Moderate degree of bilateral papillitis or, occasiosign has a localizing value and differentiates the nally, papilledema is found in tuberculous meninabscess from a tumor. The terminal cases of tuberculous meningitis persists longer after the operation for an abscess may show small multiple choroidal tubercles. Unilateral third nerve paralysis Encephalitis is quite frequent but is often incomplete. Partial Diplopia and general lethargy are common third nerve paralysis with contralateral hemisymptoms of encephalitis. Ptosis is often present plegia indicates abscess of the temporal lobe due to the involvement of third cranial nerve.

