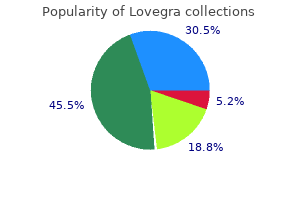
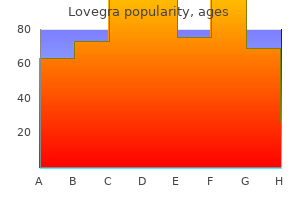
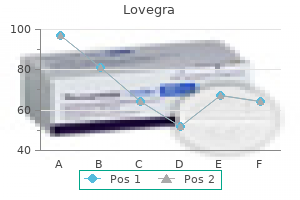
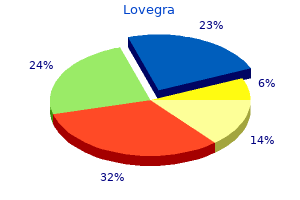
Lovegra
Lovegra 100 mg generic
Regarding bio-engineering aspects breast cancer kills discount lovegra 100mg on-line, the non-fatal accident is also easier to investigate in that injuries will be fewer and less severe than when an accident is fatal, and their precise cause and mode of production will be more obvious. The human factors investigation of a non-fatal accident essentially calls for a specialist in aviation medicine, and such specialists are available in many Contracting States. This is a problem in deductive reasoning from the outset, and the approach and expertise of a forensic pathologist are generally required. Few forensic pathologists have had much experience in investigating aircraft accidents, and these accidents pose problems that are quite distinct from those encountered in routine medico-legal pathology practice. Many articles have been published in appropriate journals, and there are also a few books available dealing specifically with this subject which will be of help to a pathologist inexperienced in this work. In either case its full value will not be achieved unless there has been pre-planning by aviation authorities and accident investigation units. It is to be expected that one or more of the aviation medicine specialists or pathologists designated to assist in aircraft accident investigation will be called upon to help in such pre-planning. This pre-planning should be based on the supposition of the largest likely disaster; a small accident merely means using fewer of the resources provided. In the main, however, medical evidence related to the reconstruction of the accident circumstances is associated with the autopsy of the victims of the accident. Here the medical investigations should be directed towards determining or excluding disease and its possible association with the accident and towards such aspects as alcohol, drugs and toxic substances as possible accident causes. However, in light aircraft with dual controls, one cannot be certain that a passenger was not actually flying the aircraft. Additionally, toxicological examination of passengers tissues may validate findings in the pilots body such as raised carbon monoxide levels. This is, however, not entirely true when the accident has occurred at a critical phase of flight, such as take-off or landing. He must also seek evidence to eliminate or confirm the involvement of a criminal act such as unlawful interference with the operation of the aircraft. A full examination of the flight crew may give valuable evidence about who was controlling the aircraft at the time of the crash. In this respect, identification has direct technical value to the investigation as distinct from judicial value. A main concern of this chapter is to illustrate why this opportunity must not be lost. A full examination, particularly when it can be based upon previous experience, may reveal evidence as to the sequence of events, the stage of flight and the degree of emergency anticipated. The pattern of injuries may indicate clearly the type of accident ? fire in flight, structural failure in flight, sudden or gradual deceleration at impact, etc. An examination of the passengers may be the prime method of demonstrating sabotage as an accident cause. Such evidence will be equally relevant in both fatal and non-fatal accidents but again there may be a difference of emphasis according to whether the accident involves a large or small aircraft. The Human Factors Group will be searching for evidence of injury resulting from seat structures ? with or without adequate harness restraint ? and the missile effect of the various contents of the cabin. Medical or pathological evidence will also be available as to the adequacy or inadequacy of walkways, exits and survival equipment. Identification is, therefore, pre-eminently a tool of investigation but it also has major medico-legal significance and judicial application. The head of the Human Factors Group must be prepared for any evidence determined by members of his group, particularly the pathologist, to be used for medico-legal purposes. The Human Factors Group will, therefore, have special needs for coordination with local or national authorities with particular regard to identification. These needs should be recognized during the pre-planning and should not be overlooked during the investigation. There is, however, no conflict of interests ? investigation and identification are interdependent as recognized in Annex 13. In the following sections of this chapter, they are discussed together under the same headings, in particular: a) tasks at the accident site; b) tasks at the mortuary; c) evidence to be derived from the pathological examination; d) consideration of the medical history of the crew and, where appropriate, interrogation of surviving crew and passengers. In the event that there are fatalities, he may also appoint a pathologist, ideally with experience in aviation pathology or at least in forensic pathology, to perform necessary full autopsy examinations on all those victims killed. If the pathologist has experience in aviation pathology, he may be appointed as head of the Human Factors Group but this will depend on the type of accident being investigated and on human factors considerations. The fatal accident is, generally, more difficult to investigate than the non-fatal accident, and it is for this reason that the role of the pathologist is stressed in this chapter. In the event that no pathologist experienced in aircraft accident investigation is available in the State investigating a major fatal accident, the Investigator-in-Charge should consider requesting other States to provide the necessary specialist(s). The pressures that exist following most fatal aircraft accidents are such that examination and disposal of the bodies must be handled as quickly as practicable and any delay avoided. Many factors may demand speed; the extreme example is that of a tropical climate with no refrigeration facilities. This does not have to be a lengthy or detailed briefing but sufficient only to allow the pathologist an opportunity to make a special point of searching, during the course of the normal complete examination, for supporting or contradictory evidence relative to any other evidence which may already be available to the Investigator-in-Charge. At frequent intervals during the investigation, the pathologist and the head of the Human Factors Group, or the Investigator-in- Charge as appropriate, should confer. The pathologist can thus get an up-to-date picture and learn of developments that may bear upon his work; he in turn can report any of his findings that could provide a lead for members of other groups. This is the principle of the Group System in which it is essential that the human factors team play a full part. He must, of course, be aware of all that has to be done there and the evidence he may expect to be collected or preserved by others. It is always a great advantage to the pathologist to be aware from the beginning of the general situation at the accident site. The general principles of the identification of the dead will be known to most physicians and certainly to all pathologists. It is necessary to record details about a body relating to its identification, the cause, and the circumstances of its death. Since ever-increasing numbers of persons may be killed in a given accident, it is expedient to reduce the number of forms for each body as far as possible, to reduce their complexity, and to provide forms that can be used and handled with ease. They should be at once simple yet comprehensive; they must be appropriate whether a body is substantially intact and fully clothed, or naked and partially disintegrated. Thus any form to be of value in an aircraft accident must be a compromise between a many-paged document, comprehensively listing every feature that might need to be recorded with ample space for their descriptions and, at the other end of the scale, an essentially plain piece of paper with minimum headings, placing upon the examiner the burden of remembering every detail to which attention should be given and recordings made. Only normal standard items are required, and pathologists who become involved in the work of aircraft accident investigation will ensure that arrangements are made for the particular instruments they favour to be made available. Both of these groups should cooperate as a team and their actions should be interrelated. It is preferable that the pathologist is in charge of this team since the examination of bodies is obviously his prime responsibility. The procedures to be undertaken will be enumerated as they would be undertaken in the event. The work is often eased if complete and readily identifiable bodies are examined first; these may be followed by whole bodies mutilated beyond recognition or by remains constituting more than half a body; the examination of detached members and body fragments is conveniently undertaken last. It cannot be overemphasized that seriously incorrect deductions may result from the examination of only a single class of injury. The remains selected for examination should be transferred to the mortuary table, removed from the container at the table and the container checked for any loose fragments or material that might have become detached during transit. Experience has shown that in such cases it is expedient to commence a new and distinct series of numbers to be used as cadaver numbers; in these circumstances the first thing to be done when the body is placed on the mortuary table is to give it a new cadaver number. The decision whether or not it is necessary to adopt this procedure must be made at the outset, and when it is adopted written and photographic records should be made as soon as a body is given its cadaver number so that the remains, the site number and the new cadaver number can be related. Only rarely will there be such features whose likely importance is obvious at this stage but it is a good rule to take too many photographs rather than too few and to be as comprehensive in written record as the size of the whole task load will allow. Jewellery and other personal possessions should be preserved for further examination and ultimate disposal to relatives; other items may need to be preserved as evidence. It is desirable to examine and keep fragments of any distinctive garment, laundry marks, manufacturers labels and so forth. The pathologist will examine the garments before, as, and after they are removed for evidence significant to the accident investigation; such evidence will generally be either unusual staining or damage that can be related to injury to the body and which may have arisen in some unusual way. All external features of possible help in identification of the body must be observed and recorded.

Buy online lovegra
All authors must certify in writing that the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Canadian Psychiatric Except for units of measure women's health center st luke's order 100mg lovegra, we discourage abbrevia- they qualify as an author of the paper. However, if a small number are necessary, use Order of authorship is decided by the co-authors. All authors must sign and return an risk reduction: Diet, physical activity, and chemopre- at first mention. Full guidelines paper will be accepted for publication, and may be used Material submitted for publication but not accepted Please see This involves increasing Workbook step by step to improve panel data professional-development/psp/ team-based health care through the creation and proactively manage patients panel-management#workbook care. This in turn helps divisions understand the needs of patient Management also benefts physicians and their whole. This data prompted him to open organize preventive screening and proactive his practice to new patients. Identifying services and team members physician reported that panel management appropriately to best serve patients. Keeping track of patient activities to bill clean up their data, and the Panel Development ?Afsaneh Moradi efectively for services provided (e. Proactive panel management improves practice ef- patients experience of care is more coherent, networks ciency in Cowichan Valley. Clinicians tions, and the chemotherapy drug melphalan, implications milieu through human can advise patients that among others. The fnding of an opioid in mussels re- and mussels is ecologically opioids from consumption 2-9 in urine or when people ceived extensive media coverage. For with infection (delirium and dementia); hu- strengthen their oncology skills so that they more information or to apply, visit Each participant can choose a Whistler, 26?29 Sep (thu?Sun) Rates: $75 for up to 1000 characters (maxi- maximum of three sessions based on seat avail- Join us for the 17th Annual St. If the course or event is over before Each session has two relevant cases to discuss and of course, recreation! Where can we tures evidence and research-based presentations in the second week of each month except go Michaels Hospital, Toronto); Managing care workers, diabetes educators, podiatrists, stress in a high-risk environment (Mr Will and other health care professionals who have Place your adat Phone: 604 675-3777; fax: 604 coordinate multidisciplinary diabetes care; Con- on our secure online payment site. Program details and approach to hospital acquired infection; ap- registration: ubccpd. Locum, contract, established phototherapy and Very busy, established family clinic in the evening and on long-term, permanent, we have it primary care dermatology practice located on Scott Road. Contact Andrew The practice consists mainly of medical records, lab, and for, we get you the roles! All equipment is included in the billing split the processes for licensure work including computer and furni- (80/20). Whether you are a ture included for price of strata physician looking for work across $400 000 per year. Each this is a full general practice, can this 12-exam-room, 3-physician requires physicians, we can help. For more informa- Hospital in a medical rental associate to join as a full-time Email: info@physiciansforyou. Patient tion with modern facilities and Physician required for the receive the table of demographics across all ages guaranteed income of $400 000. Considering a change of practice contact Laurie Fuller: 604 building is close to Royal Inland style or location Managed by Elicare available on Vancouver Island supply would allow a start-up The South Vancouver Medical Medical Group, relocation (Nanaimo and Victoria). Our home family or general practice, issues facing them at various Medical transcription specialists has been previously rented to physicians estate Concentrations of pharmaceutical compounds in contaminated water are typically orders of magnitude below levels considered acceptable. Your downtime is important and we want to help you make the most of it to do the things you love. Hemophilia cases were classifed as mild, decreasing by 35% for knee procedures and by 44% going orthopaedic surgery than patients without moderate, or severe. Postsurgical complica- to compare management and surgical outcomes Results: the study identifed 42 patients with tions were associated with 10 out of 46 procedures. Of these patients, 31 (74%) had severe Methods: Data were reviewed from the clinical hemophilia, 5 (12%) had moderate hemophilia, Conclusions: Over the study period orthopaedic charts and electronic medical records of patients and 6 (14%) had mild hemophilia. Pauls However, in the established prophylaxis era there had mild to moderate rather than severe hemo- Hospital from January 2004 to February 2017. Centralization of care has allowed for better subjects were adult orthopaedic surgery patients of patients with severe hemophilia. CliniCal Reductions in both coagulation factor utilization of hemophilia patients experiencing surgical procedure), joints involved (knees, ankles, el- and hospital length of stay have contributed to complications with orthopaedic foot and ankle bows, or others), coagulation factor utilized the cost-efectiveness of treatment. Hemophilia patients, less than 1% of normal of developing arthropathy related to recurrent Starting in 2004 adults especially those with activity. At the time this article was written hemophilia program) from January 2004 to inhibitor development, infections, thrombotic she was a physiotherapy specialist with February 2017. The primary outcomes considered were type University of British Columbia and the Provi- of hemophilia and severity, type of orthopae- dence Health Care Research Institute. We 8 tive orthopaedic procedures from January 2004 predominating in the established era (60% of300 did determine that in the established era almost 0 to February 2017. The number performed from 2004 to 2017, including four100 the preoperative to postoperative day 7 period. In addition, no surgical hemophilia now represent a larger proportion joints prone to trauma, and it is hypothesized revisions or repeat surgeries were required for of cases than they did before 2012. The second case of postsurgical early per case without untoward surgical complica- chronic infammation and joint arthropathy. This could be largely due to higher rates 6 days 4 1 day 4 Transition era of prophylaxis in recent years. Our review provides a long-term profle utilization over the study after arthroscopic proce- of these patients and shows the adequacy of support of patients. It is plausible that an extra day or two 13 years no cases of clinical thromboembolism Group N. He receives royalties for a book published by ment, particularly for patients with less severe Study limitations Lippincott, and institutional support from Wright disease who are not accustomed to administer- One limitation of this study was small sample Medical Group N. He is the use of prophylaxis in the later eras, as well the rarity of hemophilia itself. Another limita- a partner in the Cambie Surgery Centre, the Spe- as less invasive surgical procedures and more tion was inconsistent data collection for cer- cialist Referral Clinic, and the Footbridge Centre advanced rehabilitation programs, are likely tain outcomes. Factors asso- References management of musculoskeletal problems in the ciated with longer length of hospital stay after primary 1. Hypochrom ic m icrocytic anem ia F ound in: Irondeficiency Thalassaem ia And anyof the conditions leadingto m icrocytosis M icrocytosis found in: Hypochrom ia found in: Irondeficiencyanaem ia Irondeficiency Thalassaem ia Thalassaem ia Sideroblastic anaem ia And anyof the conditions leading L ead poisoning to m icrocytosis Anaem ia of chronic disease Case 3 59yF feeling w ashed out. Alw ays had low blood,tx w ith severalcourses of ironw ith no difference onhis health orblood counts. Such forward-looking statements are based on our current beliefs and expectations regarding future events, and are subject to significant known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Should one or more of these risks or uncertainties materialize, or should underlying assumptions prove incorrect, actual results may vary materially from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. There can be no guarantee that the investigational or approved products described in this presentation will be submitted or approved for sale or for any additional indications or labeling in any market, or at any particular time. Nor can there be any guarantee that such products will be commercially successful in the future. Neither can there be any guarantee that the acquisition described in this presentation will be completed, or that it will be completed as currently proposed, or at any particular time. There can be no guarantee that Novartis or any potential products that would be obtained with Endocyte will achieve any particular future financial results, or that Novartis will be able to realize any potential strategic benefits or opportunities as a result of the proposed acquisition. Novartis is providing the information in this presentation as of this date and does not undertake any obligation to update any forward- looking statementsas a result of new information, future events or otherwise. Until closing, Endocyte will continue to operate as a separate and independent company. Clinical trials of tropifexor in combination with Allergan and Pfizer compounds in accordance with collaboration agreements with those companies. Access Principles apply to how we research, develop and commercialize globally (though the focus of this slide is specifically R&D) 2. Psoriatic arthritis head-to-head study versus adalimumab Combination abbreviations: 5. Ankylosing spondylitis head-to-head study versus adalimumab tmx tamoxifen New indication 7. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 2 14 Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and 2. Presented at the 23rd International Annual Congress of the World Muscle Society, Mendoza, Argentina, October 2?6, 2018 4. Programs are not yet finalized markets as appropriate 47 | Novartis R&D and investor update | November 5, 2018 Value and pricing in life-long rare disease treatment 10-year drug cost vs.
Order lovegra 100 mg on line
One to two per cent die each year women's health center greensburg pa order generic lovegra online, half of these suddenly and usually due to ventricular arrhythmia. It may also present as a sustained ejection systolic murmur reflecting at least physiological obstruction in the left ventricular outflow tract together with a third or fourth heart sound. Outcome may be genetically determined but progress can be very slow and the condition benign. Half of the sudden deaths occurring in young male athletes > 35 years of age are due to the condition. Atrial fibrillation, especially if paroxysmal and uncontrolled, may prove incapacitating and also worsens the prognosis. A history of atrial fibrillation, whether paroxysmal or sustained, is disqualifying. In the former, both the left ventricle muscle mass and the end-diastolic diameter are related to lean body mass. The echocardiogram in the athlete will show a normal left atrial internal diameter (< 4. The causes include infiltrative conditions such as amyloidosis and sarcoidosis, storage diseases such as haemosiderosis and haemochromatosis, and endomyocardial disease, including fibrosis, the eosinophilic syndromes, carcinoid syndrome and radiation damage. Amyloidosis of the heart has a very poor prognosis by way of rapid deterioration of function complicated by rhythm disturbance. The prognosis has improved strikingly since the 1980s, and mortality is now about 20 per cent at five years. Thirty per cent will die suddenly, many from a life-threatening tachyarrhythmia, this outcome not being restricted to severe disease. In one study, nearly 50 per cent of 673 subjects with dilated cardiomyopathy were labelled idiopathic, while a further 12 per cent were considered to have myocarditis, and only three per cent were considered to be due to alcohol. An earlier study, however, suggested that alcohol was responsible in up to one-third of cases. The electrocardiographic changes are non-specific but incomplete left bundle branch aberration is common. Echocardiography will demonstrate global reduction in wall motion with dilation of the left, right or both ventricles. In the event of coronary artery disease being suspected, a pharmacological stress thallium 201 scan or coronary angiogram may be indicated. There is some evidence of a dose relationship in the incidence of subsequent myocardial abnormality; in one study of long-term survivors (median 8. Life-long cardiological follow-up with regular echocardiography and Holter monitoring is required. The presence of high-grade ventricular rhythm disturbances is both common and predictive of outcome. Mild global reduction in left ventricular systolic function (with the ejection fraction > 50 per cent) that has been stable for a period of at least one year and with no evidence of electrical instability may be considered for restricted certification, subject to close follow-up with echocardiography and Holter monitoring. It is commonly a self-limiting condition seen in young adults with the extent of systemic involvement being largely unknown. There is often no significant systemic illness and presentation may be fortuitous with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on routine chest X-ray. Or there may be erythema nodosum, malaise, arthralgia, iridocyclitis, respiratory symptoms or other constitutional upset. In those with systemic involvement, five per cent will also have cardiac involvement. Its aetiology is not understood, but a genetically determined sensitivity to pine pollen or an infective agent may be involved. Sudden death may be due to life threatening ventricular rhythm disturbance or granulomatous involvement of the conducting system. Dilation of the ventricles due to patchy involvement of the myocardium may lead to the development of a dilated or restrictive cardiomyopathy. Echocardiography may show patchy or generalized hypokinesia, especially if the basal myocardium is affected, with ventricular dilation and reduction of the ejection fraction. A scalene node biopsy will confirm systemic sarcoidosis if present but myocardial biopsy is often unhelpful due to the patchy nature of the disease. Full certification may be considered no sooner than two years after the initial observation, subject to regular follow-up. Any evidence of systemic involvement (except erythema nodosum) requires permanent restriction to multi-crew operation. Monomorphic ventricular rhythm disturbances with left bundle branch block and right-axis deviation, including sustained ventricular tachycardia, are commonly seen. A family history has an uncertain predictive value but early presentation (< age 20 years) is likely to be an adverse factor. However, our ability to disentangle those with innocent (and, perforce, asymptomatic) ventricular tachycardia from those with a potentially fatal outcome is not yet secure. For these reasons, associated right ventricular dilation disbars from all forms of certification to fly. A patient with such an anomaly on achieving adulthood naturally expects to lead as normal a life as possible which includes carrying on employment and pursuing hobbies and pastimes, some of which will have defined fitness requirements. These pursuits are not confined to aviation but include activities such as diving, vocational driving, and motor-racing. As we learn more about the long-term outcomes of these conditions, it is increasingly possible to make certificatory recommendations that are both safe and fair, although an individual may not remain fit for a conventional career span. At present only those who have a normal, or almost normal, event-free outlook with or without surgery can be considered. Cardiological review with appropriate, usually non-invasive, investigation and follow-up is mandatory in those accepted. Three-quarters are ostium secundum defects, one-fifth are ostium primum defects and one in 20 are sinus venosus defects. Early (age < 24 years) closure of the defect carries a very low operative mortality and normal life expectancy, but later closure is associated with a poorer outcome ? increasingly poor as the age of intervention rises ? due to atrial fibrillation, thrombo-embolism and the onset of right heart failure. The use of clam-shell and angel-wing devices is accepted and may encourage the closure of smaller defects although long-term outcome data are not yet available. Larger defects, or those complicated by atrial rhythm disturbance, may lead to unfitness or restricted certification only. Mitral regurgitation should be minimal and there should be no significant disturbance of rhythm or conduction. Sinus venosus defects bear the problem that significant rhythm disturbances are frequent both before and after correction. There is no increased risk of sudden or insidious incapacitation, although there is a small risk of endocarditis, and appropriate measures should be taken for its prophylaxis. Closure in childhood likewise carries a good outcome ? five per cent mortality at 25 years, but larger defects that have undergone closure do not appear to have a normal life expectancy with an 82 per cent 30-year survival compared with 97 per cent in age-matched controls. Age at surgery and the presence of pulmonary vascular change are predictors of survival. Stenosis of the infundibulum of the right ventricle and of the supravalvar region are much less common. The former may be present as a fibromuscular ring or as concentric hypertrophy in an otherwise normal heart with an intact interventricular septum. Supravalvar stenosis may be associated with multiple stenoses of the pulmonary trunk and its branches. Following surgery, 25-year survival is 95 per cent ? not quite normal ? but discretion may be exercised in best-risk subjects, judged by non-invasive and invasive means. Supra-valvar stenosis should normally disbar from all forms of certification to fly. Congenital abnormalities of the aortic valve or the aortic outflow tract requiring surgery in childhood carry a relatively poor prognosis, the 25-year mortality being 17 per cent. Nevertheless, in one small study there were no late deaths in the 16-year period following resection of isolated discrete subaortic stenosis. The 20-year survival of patients aged 14 years or younger at the time of operation was 91 per cent compared with an 84 per cent survival of those in whom surgery was delayed. Age at operation predicted subsequent hypertension, which was also associated with an increased risk of sudden death, myocardial infarction, stroke and aortic dissection. Echocardiographic follow-up should be determined by the presence or absence of a bicuspid aortic valve. Treated hypertension following late closure may be compatible with restricted certification. Such survivors do not have a normal life expectancy and late closure (>12 years) carries a less favourable outlook than early closure.
Best 100 mg lovegra
In addition menstruation fertility buy lovegra master card, the consultation must include a complete neurological assessment and review of all appropriate imaging and laboratory results and be consistent with the following Guidelines?Orthopaedic Spinal Consultation: Guideline Orthopaedic Spinal physical examination of the spine and related Consultation Goal To provide a thorough history and physical examination of the spine and related structures with interpretation of the appropriate radiographs. With this information the surgeon will formulate a treatment plan and follow up recommendation. Consultation Format the format of a consultation is generally divided into the headings of: history, physical examination, radiography, conclusion and plan. Within each heading the basic feature will be outlined as follows: April 1, 2020 A-71 Neurological Surgery (04-6) History Identification of the entrance complaint, characteristics of the pain (e. Physical Examination Evaluation of gait, frontal and sagittal alignment, range of motion of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine (flexion, extension, rotation and lateral bending), tenderness of the spine, examination of proximal joints to the line, neurologic examination including motor and sensory function, deep tendon reflexes, upper motor neuron signs, peripheral vascular exam, rectal exam if indicated. Face-to-face time is defined as only that time that the physician spends face-to-face with the patient. Non face-to-face time in which the physician spends time before or after the face-to-face time performing such tasks as reviewing records and tests, arranging for further services and communicating with other professionals or the patient in writing or by telephone is included in the consultation fee. Note: Tariff 9795 (cytological smears for cancer screening) may not be claimed in addition to tariff 8540. Note: Tariff 9795 (cytological smears for cancer screening) may not be claimed in addition to tariff 8495. April 1, 2020 A-83 General Practice (11) 6) Not payable where the sole purpose of the call is to: a) Book an appointment; b) Arrange for a transfer of care that occurs within 24 hours; c) Arrange for an expedited consultation or procedure within 24 hours; or d) Arrange a hospital bed for the patient. Specifically: 2) this tariff may be claimed by a general practitioner who performs a Complete History and Physical Examination of a patient to assess whether admission to hospital is appropriate or to admit the patient to hospital under the care of that physician, so long as that physician has not claimed tariff 8540, 8498, 8499, 8450, 8460, 8500, 8424, 8420, or 8421 in respect of that patient within the last 12 consecutive months prior to the assessment or admission. This tariff is to be claimed in lieu of tariff 8540, 8498, 8499, 8450, 8460, 8500, 8424, 8420, or 8421. General Practitioner to psychiatrist telephone consultation: 8006 Referring General Practitioner. April 1, 2020 A-85 General Practice (11) 3) Includes discussion of pertinent family/patient history, history of presenting complaint, and discussion of the patients condition and management after reviewing laboratory and other data where indicated. Any care plan resulting from the advice must be recorded in the patient chart of the General Practitioner. A-88 April 1, 2020 General Practice (11) 2) Tariff 8434 is payable only to the general practice physician who has provided the majority of the patients ongoing comprehensive care in relation to the active management of Coronary Artery Disease during the preceding twelve (12) months. Comprehensive Care 8454 Annual management of primary care for a patient between 50?74 years of age without a chronic disease. A-90 April 1, 2020 General Practice (11) ii) Ongoing coordination with other health care providers respecting management of patient condition(s) and patient care plan; and iii) Ongoing communication with patient, monitoring of patient condition(s) and patient care plan. April 1, 2020 A-91 General Practice (11) 14) In addition to medication management, the Physician or a member of their team, where required, must: a) Provide ongoing screening and monitoring of the Disorder using validated screening/diagnostic tools including identifying risk status; b) Make brief interventions, as required, helping patient identify goals and treatment readiness, and identify risky behaviours. A-92 April 1, 2020 Emergency Medicine (11-3) E M E R G E N C Y M E D I C I N E (11 - 3) these benefits cannot be correctly interpreted without reference to the Rules of Application. A Physiatry Family Conference may include, but is not limited to , discussions regarding the condition and care of the patient with serious and complex problems, including catastrophic or terminal illness, developmental and/or multiple handicap disorders, and chronic pain. Rules of Application 7 to 10 inclusive apply 8477 Physiatry Team Management Conference. April 1, 2020 A-97 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (12) 8647 Extended Regional History & Examination or Subsequent Visit, minimum of thirty (30) minutes of patient/physician contact time. In the event the patient is seen again within any twenty-one (21) day period, the physician shall claim tariff 8403?Regional History and Examination or Subsequent Visit. April 1, 2020 A-103 Malignant Disease Specialist (15) 8595 Consultation?Unassigned Patient. A claim for tariff 8403 within a twenty-one (21) day period does not preclude a physician from claiming tariff 8536 for further visits. Physician is eligible to claim as follows: Day 1?8536 Day 15?8403 Day 22?8536 8403 Regional History and Examination or Subsequent Visit. April 1, 2020 A-105 Radiation Oncology Specialist (15-8) 8510 Regional History and Examination, or Subsequent Visit. No services that relate to the course of treatment (including visits, patient care family conferences, case management conferences, telephone/facsimile/email communications) may be claimed in addition except as noted below. A-106 April 1, 2020 Radiation Oncology Specialist (15-8) 7233 Intermediate Radiation Treatment Management (Level 2). This exception does not apply to any physician who receives non fee-for-service remuneration pursuant to an agreement to which Manitoba Health is a party if the agreement specifically provides that the physician is entitled to submit fee-for-service claims. For the purpose of this exclusion, drop-in emergency clinics include drop- in/walk-in clinics which maintain regular hours of operation that fall within the periods of time specified in the After Hours Premiums tariffs. For greater certainty, these services include tariffs listed under the headings Induction of Labour, Management of Complications of First and Second Stages of Labour, and Management of Complications of Third and Fourth Stages of Labour, as well as tariffs 4824 and 4826. If any of these days fall on a Saturday or Sunday, the day will be observed as stated in the Physicians newsletter. A Special Call must be initiated by someone other than the physician (except when services are rendered outside the hospital) and requires the physician to travel from one (1) location to another (not within the same building complex) to attend the patient. A Special Call benefit will be paid even if the patient is deceased, on the arrival of the physician called, or, if the patient has left the premises prior to the physicians arrival provided the physician was not unreasonably tardy. Subject to the Exclusions listed below, all Special Call benefits may be claimed under the following tariffs: 8561 For special calls made to a patients home. In obstetrical care, on the day of the performance of an elective caesarean section. Detention time does not apply where the physician is detained when doing procedures such as fractures or operations, or for the purpose of waiting for reports of X-rays or the laboratory. It implies the presence of the physician at the bedside of the patient whose condition is critical and requires constant attention beyond the scope of the staff or family. At the termination of the critical period, as indicated by the physician being able to leave the patient in the care of the staff or family, detention time no longer applies for subsequent visits on that day or subsequent days. Unless a new crisis develops, an ordinary visit should be sufficient to adjust orders so that the patient can continue to be cared for by the staff. Should a new crisis develop or some unusual care require further detention time on the same day or subsequent days, a Special Report must be submitted to claim these tariffs. Transport means the physician is in transport with and providing all aspects of care to a critically ill patient, during the patients ambulance transfer to a hospital. No examinations or procedures may be claimed during the time of detention or transport. By Report 8565 Trip (without patient), preceding or following ambulance transfer of a critically ill patient, per fifteen (15) minute period (or major portion thereof). This service may include ordering blood tests, interpreting results, inquiring into possible complications and adjusting the dosage as necessary. This service may include administration of the medication, ordering blood tests, interpreting results, inquiring into possible complications and adjusting dosage(s) as necessary. Amant Centre, Manitoba Developmental Centre; v) a chronic care patient in an extended care facility, (in-patient or out-patient). B-6 April 1, 2020 General Schedule General Notes: 1) the claim must include the name and position of the person who initiated the communication, the name of the patient concerned, and the time of day the communication was completed. General Notes: 1) the claim must include the name and position of the person who initiated the communication, the name of the patient concerned, and the time of day the communication was completed. B-8 April 1, 2020 General Schedule 7) Services shall be documented in the patients record as required by the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Manitoba, and such documentation is required, upon request by Manitoba Health, to support the claim submitted. Note: 1) A maximum of five (5) communications per patient per thirty (30) day period may be claimed. This service may include ordering blood tests, interpreting results, inquiring into possible complications and adjusting the dosage as necessary. Note: 1) the conference must be a formal scheduled conference pertaining to one named patient. However, consecutive formal scheduled conferences, each pertaining to one named patient, are permitted. Note: 1) Tariff 8650 is payable for the first full fifteen (15) minute period and for each additional fifteen (15) minutes or major portion thereof. B-10 April 1, 2020 General Schedule 6) Only the psychiatrist who is most responsible for the care of the patient and whose active participation in the Shared Conference is documented may claim the tariff.
Purchase lovegra no prescription
This is assessed by the method of Southwick on the frog leg or lateral radiograph [1 menopause baby lovegra 100 mg online,7]. In the case of a fracture, the Delbet Classifcation based on fracture location is used [5]. However, in an acute or unstable slip, within 24 hours after the onset of symptoms, a tentative reduction attempt can be performed within situscrew fxation [1,2,8]. The addition of a second screw provides only minimal gain in stability with an increased complication risk and is therefore not recommended [1]. If problems arise from the screw fxation itself, it needs to be changed or reversed and not removed. In case of progression of the slip due to instability of the epiphysis a second screw can be added. The fxation must be secured until the growth plate closes to prevent further progression of the disease. In the two presented cases the screw was removed with the idea that after a few months the epiphysis had achieved enough stability. Removal of the screw therefore causes further progression of the slip and deformity. In both cases, it had considerable consequences for the patient as an additional and more invasive procedure was required. Removal of the osteosynthesis 131 Chapter 8 material after consolidation of these fractures has never been reported and in case of any doubt it is advisable to leave the screw in place [3,4]. The growth plate does not heal within several months and the original unstable situation persists until the growth plate is closed. Given the risk of progression of the slip, the fxation of the slipped epiphysis of the hip can only be removed after closure of the growth plate. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patients legal guardians for publication of this case report and accompanying images. Witbreuk M, Besselaar P, Eastwood D: Current practice in the management of acute/unstable slipped capital femoral epiphyses in the United Kingdom and the Netherlands: results of a survey of the membership of the British Society of Childrens Orthopaedic Surgery and the Werkgroep Kinder Orthopaedie. Finally, the negative consequences of prematurely removing the percutaneous placed screw, i. This chapter also reviews the present literature of the global incidence and gender diferences. The fundamental problem is the lack of knowledge about the role each of these changes plays. It is unclear whether such changes are causal or adaptive, because the biopsies were taken after the slip had occurred. This creates a prolonged phase of weakness and makes the physis vulnerable to the efects of increasing load, mainly in the pre-existence of obesity. Thyroid hormones directly and indirectly afect the physis and may facilitate or delay closure at the end of puberty. An association has been described with seasonal variation and thus, indirectly changes in vitamin D levels could play a role, which 9 could interfere with the bone mineralization. Consequently, recommendations would be to test for endocrine and metabolic changes in young children (< 10 and < 12 years of age for girls and boys respectively) and where young children fall within the tenth percentile for short stature. We compared these with 11 biopsies of normal physis taken during epiphysiodesis of the distal femur or proximal tibia with leg length diferences and in diferent amputations (Syme, below knee and 6thtoe). Finally, no diferences were observed in hormonal receptor expression of the eight hormonal receptors important in puberty. Contrarily, diferences in reposition of the femoral head, prophylactic percutaneous screw fxation and removal of screw showed no consensus between pediatric orthopaedic surgeons either within a country or among countries. The predominant treatment for the mild stable group is a percutaneous screw fxation to prevent further slippage. In conclusion, subcapital osteotomy can lead to perfect anatomical reduction, but there is a high risk of development of avascular necrosis. In the intertrochanteric osteotomy, the slip will be downgraded mostly to a mild slip, but with no avascular necrosis and is mostly positive in the long-term. The direct treatment of the disorder followed an appropriate procedure, by inserting one percutaneous screw in the correct position. The removal of the screw after 9 healing, however, preceded closure of the physis. An Imhauser intertrochanteric osteotomy was required for the deteriorated function in both patients. Most likely a combination of these two will cause a load on the weak physis, which it cannot resist. The increase of incidence in Asia may be indirectly attributable to a diet change. It appears sensible given obesity is a cause of numerous other problems, like heart disease, diabetes, asthma and social discrimination. The answers may be found in the extracellular matrix, in untested hormonal receptors, or in other pathways. The cause might never be found if we look at the physes after the slip has occurred. So should we take an extra step and explore the whole human genome in order to calculate the statistical chance of developing this disease Children can report pain in the upper leg or even anterior part of the knee, but actually it is referred pain from their hip. In pediatric orthopaedic surgery we encounter many rare diseases with low prevalence and incidence. Collecting data of patients and appropriate treatment should be centralised in one registry. Further questions that need to be asked entail the types of complications that develop in diferent patients and the reason for these Should we train more surgeons in advanced techniques of hip reconstruction, like the hip dislocation with subcapital osteotomy or should we use more 3D reconstruction techniques for preoperative planning In these difcult operations one might consider centralisation of the techniques or operations considering the high levels of complication rates, which are highlighted in the literature. Should we further consider the treatment possibilities of hips afected by osteonecrosis or early arthrosis and salvage operations even, for example, by early total hip reconstruction Is there a role for bisfosfonates or more modern medication that only inhibits osteoclasts Vervolgens is er een casereport geschreven over de negatieve gevolgen van het the vroeg verwijderen van de percutaan geplaatste schroef, dat wil zeggen voor het einde van de groei van het skelet. Er zijn verschillende behandelingsmethoden tussen, maar ook binnen landen, waarschijnlijk als gevolg van historische gewoontes en meestal zonder empirisch bewijs. In dit hoofdstuk wordt eveneens de huidige literatuur besproken inzake de wereldwijde incidentie en gender verschillen. Het fundamentele probleem is het gebrek aan kennis over de rol die elk van deze veranderingen teweegbrengt. Het is onduidelijk of dergelijke veranderingen causaal of adaptief zijn omdat de biopten werden genomen nadat de slipheeft plaatsgevonden. Belangrijke endocriene veranderingen op de groeischijf zijn in de gehele puberteit actief. Geslachtshormonen in de puberteit kunnen vertraagde seksuele rijping veroorzaken samen met een late sluiting van de groeischijf. Hierdoor ontstaat een periode van zwakte en dit maakt de groeischijf kwetsbaar voor de efecten van toenemende belasting, vooral bij de aanwezigheid van overgewicht. Schildklierhormonen zijn direct en indirect van invloed op de groeischijf en kunnen sluiting van de groeischijf aan het einde van de puberteit vergemakkelijken of vertragen. Een verband is beschreven met seizoensgebonden variatie en daardoor kunnen indirecte veranderingen van vitamine D een rol spelen, die kunnen interfereren met de botmineralisatie. Deze werden vergeleken met 11 biopten van normale groeischijven, die verkregen zijn tijdens epiphysiodesis van de distale femur of proximale tibia met beenlengte verschillen en in verschillende amputaties (Syme, onder de knie en 6e teen). Ook werden geen verschillen waargenomen in hormonale receptor expressie van de acht hormonale receptoren die belangrijk zijn in de puberteit. Echter er was geen consensus tussen de kinderothopeden binnen een land of tussen eerder genoemde landen in het repositioneren van de heupkop, de profylactische percutane schroef fxatie en het wel of niet verwijderen van de schroef. Het doel was om vroege impingement the voorkomen door de hoek van de kop ten opzichte van het acetabulum the veranderen. De belangrijkste behandeling voor de milde stabiele groep is een percutane schroefxatie om verder afglijden van de heupkop the voorkomen. Concluderend kan een subcapitale osteotomie leiden tot een perfecte anatomische positie van de kop, maar is er een grote kans op de ontwikkeling van avasculaire necrose. In de intertrochantaire osteotomie, zal de matige of ernstige slip meestal in ernst worden verminderd, maar zonder ontwikkeling van avasculaire necrose.
Buy lovegra 100 mg without prescription
All T excessive sweating restricted to the axillary area without patients were instructed to dry the axillary area and to apply accompanying other diseases womens health lowell ma cheap 100mg lovegra amex. Generally, it is worsened by the appropriate amount of 20% aluminum chloride solution emotional stress rather than heat or exercise. Presently, various treatments have been applied to were selected according to the following criteria : excessive treat the disease, such as antiperspirants, electrophoretic axillary perspiration at visitting our hospital, excessive sweating methods, administration of botulinum toxin to the vicinity of for more than one year. Thus, we performed this study to examine the instructed to apply the solution regularly according to the efficacy of 20% aluminum chloride solution as the first line severity of their symptoms. The satisfaction of patients was treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis without osmidrosis. In addition, the number of applications for desired Materials and Methods dryness, interval to maintain the relief of symptom and side effects were assessed. Application interval to maintain the treatment as the mechanical obstruction of the opening of 8,9) relief of symptom ranged from 5 to 45days(mean 12days). However, other possibilities have been reported Side effects were mild irritation and the occurrence of miliaria since perspiration did not occur even after the removal of the 12) in 7patients. Upon application of steroid cream, the side effects with the solution, vacuolization, atrophy and other structural subsided. Topic antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride are rimary hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating of unknown known to be first line of therapy for axillary hyperhidrosis, yet 16) P etiology. The prerequisites for sweat glands are abundant such as the hands, the feet, the obtaining satisfactory results are as follows. The area must be 16) thoracic sympathicotomy has been introduced recently for the dried prior to application. If the area was moist, hydrochloric 10) treatment of patients with axillary hyperhidrosis. The solution as severe compensatory hyperhidrosis occurs more frequently must be applied before go to bed as the activity of the eccrine in patients with axillary hyperhidrosis, they were not as sweat glands decrease during sleep at night. As perspiration satisfied as patients with the such palmar or craniofacial resumes on the next morning, the solution must be washed hyperhidrosis patients10,11). In fact, despite of such precautions, the Among various therapeutic modes for primary axillary irritation has been reported in 50% of patients14). In our study, hyperhidrosis excluding topical agents, electric treatment 7patients experienced mild irritation. In most cases, the irritation applying iontophoresis that pass ions or salts through the body can be managed with the application of topical steroid. To has been reported to be effective, particularly for the palmar neutralize irritating hydrochloric acid, triethanolamine has and tarsal hyperhidrosis. Particularly, in regard to its effectiveness administration of drugs, financial aspects, and its temporary for a short duration that has been indicated as it shortcoming effect must be considered2,16). We thus consider that 20 % cotomy has been performed only on patients unresponsive to aluminum chloride solution may be applied as the first line all other treatments. Although its effectiveness has been treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis not accompanying osmidrosis reported, it may cause the side complications effects such as with long lasting efficacy. Furthermore, it may be uncomfortable in ordinary life due to Conclusion severe anhidrosis1,11,16). For the treatment of hyperhidrosis, topical agents must be aluminum chloride has superior effect and it is simpler, applied prior to various other treatments described above. Furthermore, its has been reported to be superior to other topical agents in fast reaction may be anticipated. This suggests the potential of Alum inum hloride for H yperhidrosis the solution as the first line treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis 7. Holzle E, Braun-Falco O : Structural changes in axillary eccrine glands following long-term treatment with aluminum chloride hexahydrate not accompanying osmidrosis. Br J Dermatol 110 : 399-403, 1984 mechanism and prognosis of its clinical progresses, further 8. Role of the basic researches and clinical analysis of more cases and the resident microflora. Adar R, Kurchin A, Zweig A, Mozes M : Palmar hyperhidrosis and its Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 31 : 703-710, 1998 surgical treatment : a report of 100 cases. Postgrad Med J 55 : 868-869, 1979 hyperhidrosis treated with alcoholic solution of aluminum chloride 5. Local treatment with Arch Dermatol 123 : 893-896, 1987 aluminum-chloride hexahydrate 25% in absolute ethanol with and without 16. The pathophysiology of hyperhidrosis is management of hyperhidrosis and bromhidrosis, and outlines poorly understood, however, dysfunction of the sympathetic current treatment options. Generalised hyperhidrosis may be primary and idiopathic or secondary to hyperhidrosis is a deeply distressing condition for patients: it causes systemic disease. Treatment may require oral anticholinergic physical discomfort and social awkwardness, negatively impacts on agents. Focal hyperhidrosis is usually primary and responds daily activities, impairs performance and productivity of work, and to topical measures. Specialist referral for botulinum toxin A, results in higher rates of depression and reduced levels of confidence. Bromhidrosis usually responds to antiperspirants, patients with hyperhidrosis seek help from their general practitioner. As this conveys strong non-verbal signals,3 it can cause significant social Keywords hyperhidrosis; sweat; sweating; drug therapy embarrassment, especially if the patient has selective anosmia ? the inability to perceive odour. While bacterial metabolism of apocrine sweat usually causes the malodour, eccrine sweating can also become offensive after ingestion of certain foods, such as garlic and alcohol. Assessment and diagnosis of hyperhidrosis hyperhidrosis can be generalised or focal. Generalised hyperhidrosis affects the entire body and may be idiopathic or secondary to an underlying metabolic disorder or systemic disease. A number of conditions that have been associated with generalised hyperhidrosis are listed in Table 1. Patients most likely to require further investigation are those who are older, or those with severe hyperhidrosis of recent onset. Antiperspirants containing ? fasting blood glucose level aluminium chloride hexhydrate are sold in pharmacies; a prescription is. Propantheline bromide and oxybutynin are Aluminium chloride hexhydrate is used in a concentration of the most common anticholinergics used. Both are highly effective and 20% for axillary hyperhidrosis, while 25% for palmar and plantar relatively cheap. Glycopyrrolate is another a concentration of 10% can be used initially to avoid side effects, effective alternative, but expense is a limiting factor for many patients. Iontophoresis iontophoresis is a specialised treatment only available in some states. Figure 2 and Figure 3 provide a visual comparison for the effectiveness of this therapy. Iodine is applied to a dry medicare subsidises the use of botulinum toxin A for severe primary area of skin and starch is sprinkled on top. The iodine, axillary hyperhidrosis in patients aged 12 years or more who have failed starch and sweat react to form the dark sediment. The left palm has not yet been treated with iontophoresis or are intolerant to topical aluminium chloride hexahydrate after 1?2 Figure 3. Starch-iodine test after a patient has had iontophoresis to the left palm 7 days earlier. A comprehensive approach to the and increased progressively up to 10 mg/day until an improvement is recognition, diagnosis, and severity-based treatment of focal hyperhidrosis: seen. Body malodours and their topical treatment in whom the hyperhidrosis is having a significant impact on their agents. J inherit metab liposuction has also been shown to be a safe method of reducing Dis 2006;29:162?72. Axillary hyperhidrosis treated with alcoholic Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy is the last resort for the solution of aluminium chloride hexahydrate. Am J clin pneumothorax, and compensatory hyperhidrosis, the latter occurring in Dermatol 2003;4:681?97. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for Regular washing and axillary hair removal are helpful. Fragrant primary hyperhidrosis of the upper limbs: a critical analysis and long-term antiperspirants are first line treatment in the management of results of 480 operations.

Buy lovegra 100mg cheap
However menopause exhaustion buy generic lovegra line, this approach can be therapeutic bias, preferred loading strategy) used empirically with other acute or chronic and becomes part of the management conditions?with or without radiating pain program, which includes self-treatment. The (Long 1995)?even when the exact diagnosis results of this analysis can be useful in is in doubt. It is important to If the practitioner is unable to identify a emphasize that active involvement by the directional movement that brings about patient is considered essential for a centralization, decreased symptoms, or successful outcome. For patients who have only central or midline pain, the territory the major goal is to identify directional further shrinks toward midline and/or the movement(s) and loading strategies that intensity reduces to zero. This improvement improve the patients symptoms and is maintained and continues to centralize on mechanics. If this process begins on the very first visit, complete symptom Improvement may take the form of any of the recovery is expected and should occur following: rapidly. Peripheral symptoms are example, the location of the pain only reduced and centralize toward the spine. The treatment, although symptoms appear to be intensity of leg symptoms may decrease, slowly improving over time. Prognosis may chronic pain may become intermittent, or the still be good, but for slower recovery. Patients who does not significantly improve by the 7 have an obstruction resulting in decreased treatment, then further treatment with this movement in a particular direction (e. Patients experience either no improvement during the evaluation immediate improvement in a comparative or the symptoms get worse (e. The following steps should be taken when evaluating the patient: As the patient starts experiencing centralization, the practitioner records at Step 1: Anticipate loading strategies based on which repetition this happened. Step 2: Try to correct any fixed or antalgic breaking rhythm, the patient continues the posture. Repetitions are screen for any obvious catches or permitted within pain tolerance under deviations, and check for centralization supervision of the practitioner. Step 4: Observe repetitive end-range loading in If the patient experiences an increase in each of the tested positions. Although rare, the patients symptoms may peripheralize at first and then centralize. Note: Patients who experience an increase in pain from the stretching of fibrotic tissues need to be told that this pain is associated with the desired therapeutic outcome. If so, this shift needs to be corrected first and, once corrected, extension therapy should begin. Sagittal plane loading should begin first, starting with extension and, if needed, flexion. Correction consists of either the patient or the practitioner gently and steadily pushing the pelvis back toward neutral into the painful barrier, then gently backing off a few millimeters, and then returning to the new barrier. This process allows the patient to fixed lateral shift slowly stand up straighter. If the patient is having great have trouble lying in this position, place a difficulty, try introducing a few degrees of small pillow under the stomach. The change may only be for centralization or peripheral-ization of temporary, but will allow an opportunity to see symptoms. If this side glide is successful immediately presents itself, and 4) observe if but the antalgia returns, the procedure will be pain occurs during movement (consistent incorporated into the patients self-treatment with disc injury) or only at end range program. On rare occasion, the practitioner may wish Patients should report: to explore repetitive movements in rotation or. If necessary, they may support case, repetitive testing may not be themselves by placing hands on thighs. Record at which repetition the pain occurred, how the quality, location or persistence changed, and how many total repetitions were performed. If the patient is made worse, perform one more repetition with caution to confirm. On the other hand, if the symptoms improve, consider continuing up to 10 repetitions to see if the improvement is maintained. If at the end of 10 repetitions, the patient response is equivocal, additional repetitions can be done to try to clarify. For example, have small of the back and patients place the left hand on the left hip, extend backwards, right hand on lower right ribs, then push using them as a toward the spine with both hands; hold for a fulcrum. This same movement into movement is called left side glide because extension up to ten that is the direction the shoulders move. Methods to ensure appropriate end range: Besides encouraging the patient to go further?further?further, the practitioner may wish to place the hands on the patients sternum and sacrum to apply gentle overpressure into extension. It may be easier for the patient to perform this side glide correction by leaning against a wall. Methods to ensure appropriate end range: the practitioner may also wish to contact the patients hip and side to ensure adequate overpressure. The patient can be instructed to point the knees and toes so that they face Starting with feet flat and knees bent, have each other. Maintaining the bent-knee position, patients then lower the legs, resting the feet flat on the table/floor for a moment before repeating the movement. Repeat this cycle up to ten times, checking for symptom change after each repetition. Some patients may need more flexion, which can be accomplished by putting a pillow or towels press-up under the upper body and head. If patients can do this without peripheraliza- tion, they should next try a full press-up in which they extend back until their elbows lock into extension. The last press-up can be While lying prone, patients side glide their held for 30 seconds. If unsure, start by gliding the Methods to ensure appropriate end range: the practitioner may wish to manually hold (or hips away from side of leg pain. The practitioner may down, tracing out the three sides of an also test other levels by applying overpressure imaginary rectangle. If the patients symptoms have not satisfactorily improved, explore the same translational movement in the opposite direction up to ten times by reversing the patients hand positions for right-side glide at the desired level. In such a case, after completing the repetitions, place the patient in a posture in which s/he usually experiences pain to see if there is any immediate improvement. This testing position will usually be standing, but may have to be some other specific position right glide left glide (e. This Methods to ensure appropriate end range: position or activity may have been identified by the practitioner may apply overpressure. During transition movements, it is recommended to hold an anterior pelvic tilt, maintain abdominal bracing, and flex at the hip when bending forward. The practitioner may need to support the patient by applying pressure to the sternum and sacrum, locking the patient into lordosis. Likewise, poor treatment response maximally rotate the pelvis and legs toward may be associated with the patients failure to the floor and hold for up to 40 seconds. As long as this the practitioner should assess the exercise does not peripheralize the pain, repeat 2-3 each visit. As symptoms resolve, they can be the patients directional preference?the performed 1 to 2 times a day or more often if directions of movement that help centralize symptoms begin to return. Movements that help centralize pain are extension bias may be linked to insufficient incorporated into pain management protocols attention paid to the importance of and given as homework (e. A postural support may be which directions of movement make the pain necessary to help some patients remember to worse (what to avoid) and those that have maintain a seated lordosis. Sometimes after a disc derangement has been successfully treated, the patient is left. Base activity modification recommendations with adaptive shortening (a dysfunction on information regarding movement and direction that cause the least pain. The practitioner should be able to tell the exclusively extension exercises may have patient how rapidly the pain will respond to lost some ability to flex forward due to directional preference: quickly or over a shortening of tissue or contraction of a scar. It is important to finish help determine which other therapeutic the flexion exercises with some repeated interventions may be warranted, such as extension. Prone, patients lie on the table for 1-3 necessary to check the bias daily to ensure minutes in a relaxed position.

