Vasotec
Purchase vasotec canada
West Nile blood pressure norms chart quality 5mg vasotec, Banzi, Kunjin, Spondweni and Zika viruses are aviviruses; the group C bunyaviruses are Apeu, Caraparu, Itaqui, Madrid, Marituba, Murutucu, Nepuyo, Oriboca, Ossa and Restan. The rst epidemic of Rift Valley fever outside Africa occurred in 2000 in the Arabian peninsula (probable vector Ae. Group C virus fevers occur in tropical South America, Panama and Trinidad; Oropouche fever in Brazil, Panama, Peru and Trinidad; Kunjin virus in Australia. Birds are a source of mosquito infection for West Nile virus; rodents serve as reservoirs for group C viruses. Other arthropods may be vectors, such as Culicoides paraensis for the Oropouche virus. Viraemia, essential for vector infection, often occurs during early clinical illness in humans. Since infection leads to immunity, susceptibles in endemic areas are mainly young children. Keep patient in screened room or in quarters treated with an insecticide for at least 5 days after onset or until afebrile. Screen blood for West Nile nucleic acid in North America during summer and fall, before transfusion. Epidemic measures: 1) Use approved mosquito repellents for people exposed to bites of vectors. Diagnostic methods for conrming other tick-borne viral fevers vary only slightly, except that serum is used for virus isolation instead of erythrocytes. Virus has been isolated from Dermacentor andersoni ticks in Alberta and British Columbia (Canada). The wildlife cycle is maintained by ticks, which remain infective throughout life. Preventive measures: Personal protective measures to avoid tick bites; control of ticks and rodent hosts (see Lyme disease, 9A). A presumptive diagnosis is based on the clinical picture and the occurrence of multiple similar cases. The disease is seasonal in temperate zones north of the equator, occurring between April and October, and is prone to affect military personnel and travellers from nonendemic areas. Rodents (gerbils) have been implicated as a reservoir for Eastern Hemisphere sandy viruses. The vector of the classic virus is a small, hairy, blood-sucking midge (Phlebotomus papatasi, the common sandy), which bites at night and has a limited ight range. Sandies of the genus Sergentomyia have also been found to be infected and may be vectors. Phlebotomines become infective about 7 days after biting an infected person and remain so for their normal life span of about 1 month. Relative resistance of native populations in sandy areas is probably attributable to infection early in life. Preventive measures: Personal protective measures to prevent sandy feeding; control of sandies is the principal objective (see Leishmaniasis, cutaneous and mucosal, 9A2). Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: In selected endemic areas; in most countries, not a reportable disease, Class 3 (see Report ing). Epidemic measures: 1) Educate the public about conditions leading to infection and the importance of preventing sandy bites by use of repel lents, particularly after sundown. There may be bleeding from gums, nose, lungs, uterus and intestine, but only in serious or fatal cases does this occur in large amounts, often associated with severe liver damage. In the Russian Federation, an estimated 5 infections occur for each hemorrhagic case. Specic IgM may be present during the acute phase; conva lescent sera often have low neutralization antibody titres. Seasonal occurrence in the Russian Federation is from June to September, the period of vector activity. Immature ticks are believed to acquire infection from the animal hosts and by transovarian transmission. Nosocomial infection of medical workers, occurring after exposure to blood and secretions from patients, has been important in recent outbreaks; tertiary cases have occurred in family members of medical workers. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: In selected epidemic areas; in most countries, not a reportable disease, Class 3 (see Reporting). A papulovesicular eruption on the soft palate, cervical lymphadenopathy and conjunctival suffusion are usually present. The febrile period ranges from 5 days to 2 weeks, at times with a secondary rise in the third week. Diagnosis is made through isolation of virus from blood in suckling mice or cell cultures (virus may be present up to 10 days following onset) or through serological tests. The Novosibirsk district reported 2 to 41 cases per year between 1989 and 1998, mostly in muskrat trappers. Live worms, passed in stools or occasionally from the mouth, anus, or nose, are often the rst recognized sign of infection. Some patients have pulmonary manifestations (pneumonitis, Loffier syndrome) caused by larval migration (mainly during reinfections) and characterized by wheezing, cough, fever, eosinophilia and pulmonary inltration. Heavy parasite burdens may aggravate nutritional deciency and, if chronic, may affect work and school performance. Serious complications, sometimes fatal, include bowel obstruction by a bolus of worms, particularly in children; or obstruction of bile duct, pancreatic duct or appendix by one or more adult worms. Diagnosis is made by identifying eggs in feces, or adult worms passed from the anus, mouth or nose.
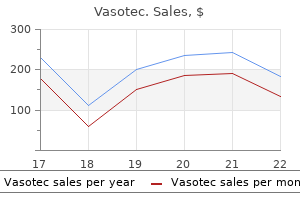
Buy generic vasotec 10mg on line
The patient often appears awake with eyes Hepatic encephalopathy open but will make no voluntary or responsive move Hepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric synd ment blood pressure 40 over 30 vasotec 10 mg low price. It is characteristic but not invariable for the limbs to retain Table 1 Clinical grading of hepatic encephalopathy the posture in which they have been placed by the Grade Clinical state Survival examiner, no matter how unusual. The appearance is superficially similar to akinetic mutism, but clinical I Mild mental confusion, euphoria, depression 100% evidence of brain damage is lacking. A similar state occurs as a result of total paralysis of the musculature in severe cases of Guillain Barre syndrome and pharmacologic neuromuscular Chronic hepatic insufficiency with portal-systemic blockade. It is characterised by drowsiness, conf usion, disordered sleep, slurred speech, inappropriate A variety of disorders may cause an alteration in behaviour followed by agitation, confusion, delirium consciousness by interrupting the delivery of energy and coma. Nevertheless, sis, severe cardiac failure, polycythaemia, drug toxicit fatty acids and mercaptans exacerbate the encephalo 40 ies. A observations in relation to the serum ammonia level and 41, 42 worsening of the encephalopathy may be precipitated by state of consciousness. Ammonia liberates glucagon which 43 tremor, asterixis, dysarthria and ataxia known as chronic stimulates gluconeogenesis, which stimulates skeletal progressive hepatocerebral degeneration. The high levels the toxins and mechanisms which may be responsible of tyrosine and phenylalanine decrease the synthesis of for the development of hepatic encephalopathy the neurotransmitters, dopamine and noradrenaline, and 34 include: the increased levels of tryptophan increases the cerebral 39 levels of the inhibitory neurotransmitter, serotonin. Ammonia False neurotransmitters such as octopamine and Approximately 40% of the daily ammonia phenylethanolamine (derived from bacterial action on production is generated from bowel organisms acting on tyramine in the gut) are increased, increasing cerebral gastrointestinal protein and urea, and 50 60% is levels of these agents. The daily urinary excretion of imbalance or abnormal neurotransmitters, decreased nitrogenous compounds is approximately 460 mmol levels of octopamine and increased levels of (400 mmol as urea, 40 mmol as ammonium, 12 mmol as noradrenaline and dopamine have been observed in 45 creatinine, 2 mmol as amino acids, and 5 mmol as uric patients dying from hepatic encephalopathy. Mercaptans In the central nervous system, ammonia combines Methionine is metabolised to a group of compounds with alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate, which in known as mercaptans, which experimentally are able to 26 turn combines with ammonia (a reaction that requires cause coma. An endogenous benzodiazepine resistance to lactulose may occur), where it is metab. It also acidifies Glutaminergic dysregulation the bowel contents, thereby trapping ammonia (by Glutamate mediated neurotransmission is altered in converting ammonia to its ionised form, which is less acute liver failure with experimental evidence of a easily absorbed from the intestine) and suppresses 56 decreased neural reuptake of glutamate, increased extra proteolytic bacterial flora. The ammonia level may cellular glutamate and an imbalance of glutamine recep also be reduced, by bacteria incorporating it into 57 tor neurotransmission, resulting in an increase in N bacterial proteins. In one report, not afford any significant protection against the lactulose enemas (300 mL of 50% lactulose added to development of cerebral oedema or intracranial hyper 700 mL of tap water, as a retention enema for 1 hr) tension resulting from acute hepatic failure. To explain improved the clinical grade of hepatic encephalopathy 58 these findings, it has been suggested that the changes in within 12 hr. While it has not been ibiting glutamine synthetase (and therefore glutamate widely used, some believe that it is the treatment of 53 60 production). Manganese Neomycin Similarities between manganese toxicity and chronic Oral neomycin 1 g 6-hourly (or any nonabsorbable hepatic encephalopathy along with the observation that aminoglycoside. While some studies Resuscitation and management of precipitating factors have shown an additive effect of nonabsorbable By treating the precipitating factors. Nonetheless, it is recommmended that a combin intravenous supplements of vitamin K, vitamin C, ation of a nonabsorbable disaccharide with a non thiamine, folate and other B group vitamins. Lactulose is a synthetic nonabsorbable disaccharide Oral metronidazole (200 mg 6-hourly) is as effective as that passes unchanged to the lower bowel (unless there neomycin and may be used in patients who have renal 126 Critical Care and Resuscitation 2002; 4: 119-132 M. Vancomycin (1000 mg 12-hourly) all episodes of increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure may also be effective, even in patients who have greater than 25 mmHg, for 15 min or longer, or greater 62 1, 71 lactulose resistant portal systemic encephalopa-thy. The 72 Eradication of Helicobacter pylori may also be of oedema is predominantly cytotoxic and may be 1, 73 benefit in patients with chronic hepatic failure and responsive to mannitol. However, no large studies have been performed show ing any benefit of one treatment compared with another. Dietary protein Resolution of intracranial hypertension often precedes In patients who have no excessive protein losses and all other signs of improvement in patients who recover who are not bleeding, the enteral or parenteral daily 76 spontaneously. This will prevent paracetamol proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole 40 mg daily) or H2 induced hepatotoxicity in most cases, if given within 8 antagonists (ranitidine 150 mg daily) will reduce the hr of ingestion. It is less effective after this time and 67 incidence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Charcoal haemoperfusion is common in cirrhotic patients due to increased loss of and polyacrylonitrile membrane haemodialysis to zinc in the urine) should be corrected (using 600 mg dialyse out the middle molecules, have not significantly 63 zinc sulphate oral zinc sulphate daily for 1 3 months). Nonetheless, while most of the current cerebral oedema, treatment is often directed at reducing hepatic support devices are probably safe, no system so intracerebral pressure. This includes; far has been shown to be superior or to unequivocally 82 confer significant clinical benefit. Modified intra uced cerebral blood flow, impaired cerebral oxygen venous amino acid preparations to normalise serum utilisation, cerebral oedema, abnormal neurotransmitter amino acid levels have also been used but are of no composition (due to alterations in serum amino acid 39, 92 proven value. While oral L-dopa has been reported levels similar in some respects to that observed with 109-112 to temporarily improve the conscious level in patients hepatic encephalopathy) and disruption of the 93 with hepatic encephalopathy, L-dopa, and carbidopa blood brain barrier (caused by the circulating inflamm were shown to be no better than a placebo in a atory mediators, tumor necrosis factor-, interleukin-1, controlled trial of patients who had hepatic 19, 20, 113 interleukin 2 and interleukin-6). In patients with chronic renal failure, a uraemic encephalopathy (with drowsiness, irritability, confusion, Other encephalopathies in the critically ill patient seizures) can occur when the plasma urea nitrogen levels Apart from the numerous electrolyte, endocrine, reach 50 mmol/L or greater. The encephalopathy may vascular, toxic and other causes listed in Table 2, also be due to hyper or hypocalcaemia, desequilibrium hypertensive, postanoxic and D-lactic acidosis are often syndrome (rapid reduction in extracellular urea levels forgotten as causes of encephalopathy. Septic encephalopathy Pre-eclampsia is a syndrome consisting of hypertension, Septic encephalopathy is a diffuse yet reversible proteinuria, subcutaneous oedema hyperreflexia and cerebral dysfunction that occurs in up to 70% of patients hyperuricaemia. Continuous infusion of is not a form of malignant hypertension but a form of haloperidol controls agitation in critically ill patients. This usually only agitated, critically ill patients Crit Care Med occurs in patients in whom the initial hypoxic insult has 1994; 22:378-379. It can follow severe asphyxia associated Myocarditis and cardiomyopathy associated with with carbon monoxide poisoning, cardiac arrest or clozapine. The use of intravenous interval following the hypoxic event, with gradual alcohol for prevention of withdrawal in alcoholic burned neurological deterioration. Massive doses of midazolam infusion cognitive, psychiatric, cerebellar, pyramidal and 1, 115 for delirium tremens. Neurologic complications in critically ill short bowel syndrome, D-lactic acid may be produced patients. The encephalopathy associated fatigue, weakness, behavioural changes, headache, with septic illness. The visual changes, nystagmus) when the plasma D-lactate 116 neurological complications of sepsis. Bacterial keratitis in the critically ill and nine patients receiving postoperative care. Position of the American Academy of Neurology on and bioavailability of midazolam in man. Br J Clin certain aspects of the care and management of the Pharmacol 1983; 16:43S-49S. Midazolam Executive Board, American Academy of Neurology, infusion for basal sedation in intensive care: absence of April 21, 1988, Cincinnati, Ohio. Late improvement in Accumulation of midazolam after repeated dosage in consciousness after post-traumatic vegetative state. N patients receiving mechanical ventilation in an intensive Engl J Med 1996; 334:24-25. Ann Intern Med mercaptans and ammonia or fatty acids in the production 1973; 78:81-84. Biochemical monitoring of encephalopathy in patients: a double-blind, randomized trial. Successful use of blood-brain aminoacid transport: a unified theory of vancomycin hydrochloride in the treatment of lactulose portal-systemic encephalopathy. Changes in brain catecholamine levels in coma by benzodiazepine antagonist (Ro 15-1788). The Improvement of hepatic encephalopathy treated with neurobiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Could an endogenous benzodiazepine ligand antagonists and antacids in the prevention of acute contribute to hepatic encephalopathy. Kanematsu T, Koyanagi N, Matsumata T, Kitano S, hepatic encephalopathy: a causal relationship. Major complications of acute either severe or fulminant hepatitis due to drugs or of and chronic liver disease.
Cheap 5 mg vasotec fast delivery
During the peer to-peer conversation prehypertension questions order vasotec 10mg otc, factors such as patient acuity and setting of service may also be taken into account. Where not specified, indications and prerequisite information apply to persons of all ages. Technology Considerations In general, conventional radiographs should be obtained prior to advanced imaging. Implanted surgical hardware, including joint prostheses, may produce sufficient local artifact to preclude adequate imaging through the region containing hardware. Infusion of gadolinium may also confer an unacceptable risk in persons with advanced renal disease. Diagnostic accuracy is quantified using sensitivity and specificity, predictive values, and likelihood ratios. Hazard ratio is analogous to odds ratio and is reported most commonly in time-to-event analysis or survival analysis. A hazard ratio of greater than 1 or less than 1 means that there are differences in the hazard rates between the 2 groups. Positive likelihood ratios, especially those greater than 10, help rule in a disease. An odds ratio of 1 means that the exposure does not affect the odds of the outcome. An odds ratio greater than 1 means that the exposure is associated with higher odds of the outcome. An odds ratio less than 1 means that the exposure is associated with lower odds of the outcome. Positive predictive value is defined as the number of true positives divided by the number of test positives. Negative predictive value is defined as the number of true negatives divided by the number of test negative patients. May be divided into very low (less than 5%), low (less than 20%), moderate (20%-75%), and high (greater than 75%) although these numbers may vary by condition. Relative risk is analogous to odds ratio; however, relative risk is calculated by using percentages instead of odds. A relative risk of 1 means that there is no difference in risk between the 2 groups. A relative risk of greater than 1 means that the outcome is more likely to happen in the exposed group compared to the control group. A relative risk less than 1 means that the outcome is less likely to happen in the exposed group compared to the control group. Defined as the true positive rate (number of true positives divided by the number of patients with disease). Defined as the true negative rate (number of true negatives divided by the number of patients without the disease). Direct contact by other methods, such as by telephone or electronic messaging, may substitute for in person evaluation when circumstances preclude an office visit. Clinical Indications the following section includes indications for which advanced imaging of the extremities is considered medically necessary, along with prerequisite information and supporting evidence where available. Indications, diagnoses, or imaging modalities not specifically addressed are considered not medically necessary. It is recognized that imaging often detects abnormalities unrelated to the condition being evaluated. Such findings must be considered within the context of the clinical situation when determining whether additional imaging is required. General prerequisites for extremity imaging include conservative management and clinical reevaluation, as defined above. Documentation of compliance with a plan of therapy that includes elements of conservative management may be required. Congenital and Developmental Conditions Blount disease (Pediatric only) Advanced imaging is considered medically necessary for preoperative evaluation when there is clinical concern for physeal bony bars and radiographs are nondiagnostic. Radiographs are also useful to exclude other causes of foot pain which can mimic the presentation of tarsal coalition, especially acutely. The information provided by radiographs generally complements that provided by other modalities, so radiographs should be performed even when other imaging is planned. Radiographs are the appropriate initial imaging study in osteomyelitis because they can demonstrate findings suggestive of the diagnosis, but can also exclude or provide information to suggest other diagnoses. The sensitivity of radiography is reportedly 43%-75% and the specificity is 75%-83%. Abnormal radiographs are helpful, but the diagnosis cannot be excluded on the basis of negative radiographs. Initial evaluation for septic joint should include radiography (to outline anatomic detail, evaluate for radiodense foreign bodies or soft-tissue gas, and exclude alternate diagnoses such as fracture, degenerative changes, or tumor). Advanced imaging is considered medically necessary for evaluation of acute shoulder pain in adults and acute or chronic shoulder pain in pediatric patients following initial radiographs when imaging is required to establish the diagnosis and the patient is a candidate for corticosteroid or anesthetic injection. Advanced imaging of the extremity is considered medically necessary for management of established juvenile idiopathic arthritis when radiographs are insufficient to determine appropriate course of therapy, particularly intra-articular therapy. Base investigations usually include erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein and full blood count, with consideration given to rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody, and human leukocyte antigen B27. While many types of stress fractures are diagnosed clinically and managed conservatively, 17 high-risk fracture sites are susceptible to nonunion. The pretest probability of scaphoid fracture when radiographs do not demonstrate a fracture but the history and physical examination are consistent with the diagnosis is 25%. Subcapital hip fractures are often complicated by avascular necrosis unless surgically treated; as such, accurate detection is important. Clinically, these fractures most commonly present with hip pain after trauma, and the patient may be unable to bear weight. Advanced imaging is considered medically necessary when radiographs are nondiagnostic or not sufficient to establish a diagnosis and/or direct management. When advanced imaging is warranted, having radiographs available at the time of advanced imaging allows the radiologist to more appropriately protocol the study, as well as to determine which study will best assess the clinical and radiographic concerns. Brachial plexus mass Advanced imaging is considered medically necessary when the results of imaging are essential to establish a diagnosis and/or direct management. Radiographic findings are nonspecific, and radiographs may be normal in up to approximately 20% of cases. Radiographic changes including osteopenia, joint space narrowing, and degenerative changes may less commonly be present. Plain radiography provides limited information about the popliteal cyst, but may provide additional information on joint and bone abnormalities such as loose bodies in the cyst or the general findings of osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis. However, there are some radiographic findings that are characteristic of certain masses. Early surgery should be considered only when there is evidence of symptomatic suprascapular nerve compression. Imaging is not indicated in patients with full or limited movement and nontraumatic shoulder pain of less than 4 weeks duration. Imaging and surgical intervention should only be considered after conservative treatment has failed. All three modalities are more accurate in identifying full thickness tears than partial thickness tears. For ultrasound, based on 25 studies and 2774 shoulders, the sensitivity was 91% and specificity was 86%.
Buy generic vasotec 5mg line
Hand washing and young children Good hand washing habits should be taught to young pupils as early as possible heart attack waitin39 to happen order genuine vasotec line. Gloves Disposable gloves should be worn when dealing with blood, body fuids, broken or grazed skin, and contact with mucous membranes. Suitable bins should be provided for female staff and pupils to dispose of sanitary protection. Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette Respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette are effective ways to reduce the spread of germs when coughing and sneezing. Preventing blood and body fuid exposures It is important to avoid unnecessary direct contact with blood or bodily fuids. However, should blood come in contact with intact and undamaged skin there is no risk of transmission of blood borne viruses. If blood splashes into the eye or mouth, it is important to rinse with lots of water. It is not unusual for children to cough or vomit swallowed blood after they have had a severe nose bleed. Intact skin provides a good barrier to infection, and staff should always wear waterproof dressings on any fresh cuts or abrasions on their hands. Dealing with bites Human mouths carry a wide variety of germs, some of which can be transmitted to others by bites. Human bites resulting in puncture or breaking of the skin can cause certain bacterial or viral infections so it is important they are managed promptly. Animal bites Unlike human bites, most animal bites do not become infected but they should still be taken seriously. If a bite breaks the skin, wash with soap and water then seek medical advice about the possible need for treatment to prevent infection. If someone becomes generally unwell or the bite looks infected they should seek medical advice. How to manage a spill of blood or body fuids Sometimes accidents occur on school premises, which result in the environment becoming contaminated with body fuids including blood, vomit, urine or faeces. This can present a potential risk of infection spreading to others so it is important that all spills are cleaned up as soon as possible. Note: If a spill occurs on carpet or upholstery, clean the area initially with a general purpose detergent, warm water and disposable paper towels/cloth and arrange for the carpet to be steam cleaned with an industrial carpet cleaner as soon as possible. If bleach splashes into your eyes, rinse immediately with lots of cold water (for at least 15 minutes) and consult a doctor. School staff should be aware that if they implement standard precautions at all times there should be no need to routinely disclose to them confdential information or sensitive diagnoses. Everyone (pupils and staff) has a right to be treated equally, just as everyone has a right to be protected from exposure to germs. There are now many safe and effective vaccines against many serious and deadly illnesses. Some vaccines are given routinely to all the population, others only to individuals thought to be at high risk of certain infections. Immunisation involves giving a person a killed germ, a live but weakened germ or just a critical part of the germ. This induces activation of the immune system and results in immunity to that specifc germ. The principle of immunisation is simple: it gives the body a memory of infection without the risk of natural infection. The incidence of many of the common infectious diseases of childhood would be further reduced if all children entering school were appropriately immunised. However, there are a very small number of children in whom specifc immunisations are truly contraindicated. Immunisation of all suitable children would ultimately reduce the number of infected children in the community and thus reduce the likelihood of a susceptible child being exposed to infection. Immunisation Schedule In 2008 there was a major change to the childhood immunisation schedule for children born on or after 1st July 2008. The main changes were the introduction of two additional vaccines, pneumococcal vaccine and hepatitis B vaccine. Children born before that date would not have routinely received either pneumococcal or hepatitis B vaccines. Parents should be encouraged to ensure that their children receive all immunisations at the appropriate age, as shown in Table 4. It is also very important that pupils going on work experience or school trips abroad should be appropriately vaccinated, especially if they will be working or interacting with young children or other vulnerable groups. Exclusion All school staff should be aware of the need for self exclusion if they develop symptoms of gastrointestinal illness, fever or skin rashes, any one of which may pose a risk of infection to pupils and staff. Exclusion periods are provided in Chapter 9 Management of Specifc Infectious Diseases under the relevant infectious diseases. Infectious Diseases Relevant to Staff the following are diseases relevant to staff. As already stated above, immunisation should be in accordance with national immunisation guidelines. Those whose bloods test shows that they are not immune should be offered vaccination. There is no indication for school staff elsewhere to receive hepatitis B vaccine routinely since good implementation of standard precautions should provide adequate protection against blood and body fuid exposure (see Chapter 3). Furthermore, now that hepatitis B vaccine has been included in the routine childhood immunisation schedule, vaccinated children should not pose a risk in the future. There is no need for staff with chronic hepatitis B infection to be excluded from working in a school setting. As a result, staff who are pregnant or in another recognised risk group for infuenza should ensure that they are fully immunised against infuenza (risk groups for seasonal infuenza can be found on the website of the National Immunisation Offce at. Infection with measles during pregnancy can result in early delivery or even loss of the baby. Rubella may have devastating consequences on the developing baby if a non-immune mother is exposed in early pregnancy.
Purchase vasotec 5 mg with visa
Clin dromes associated with chronic liver disease and an extensive portal Neurophysiol 2006; 117:2243-2251 blood pressure device order 10mg vasotec amex. The acquired (non Wilsonian) type of Incidence, natural history, and risk factors of hepatic encephalopathy after chronic hepatocerebral degeneration. Introduction to the revised Ameri shunt in cirrhotic patients: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol can Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Position Paper on acute 2011; 26:943-951. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Position Paper on management of portal hypertension. Cordoba J, Ventura-Cots M, Simon-Talero M, Amoros A, Pavesi M, tality and economic burden associated with hepatic encephalopathy in Vilstrup H, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: diagno starch enemas in acute portal systemic encephalopathy. A longitudinal systems biology analysis of lactulose withdrawal (tap water) to treat acute portal-systemic encephalopathy: a double in hepatic encephalopathy. Critical icker frequency for quantication of low-grade hepatic ence Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. Value of the critical icker frequency in patients with Lactulose, rifaximin or branched chain amino acids for hepatic ence minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Safety of ornithine phenylacetate in cirrhotic decom covert hepatic encephalopathy. Kircheis G, Nilius R, Held C, Berndt H, Buchner M, Gortelmeyer R, 2013; 58:1122-1132. Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Marchetti P, Angeli P, Iemmolo R, Caregaro patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy: results of a L, et al. Clinical features and survivial of cirrhotic patients with sub placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Montagnese S, Biancardi A, Schiff S, Carraro P, Carla V, Mannaioni of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open-label, randomized G, et al. Different biochemical correlates for different neuropsychiatric controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Treatment of hepatic encephal talisation for intracerebral haemorrhage: a Danish population-based opathy with metronidazole. Double-blind randomized clinical trial comparing neomycin and rhosis and episodic hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized double placebo in the treatment of exogenous hepatic encephalopathy. Non-absorbable disaccharides for encephalopathy in acute variceal bleed: a randomized controlled trial hepatic encephalopathy: systematic review of randomised trials. Portosystemic pressure gradient during transjugular intrahepatic analyses of randomized controlled trials. Evaluation threshold to avoid medically uncontrolled low pressure gradient for liver transplantation in adults: 2013 Practice Guideline by the related complications Laleman W, Simon-Talero M, Maleux G, Perez M, Ameloot K, can Society of Transplantation. Long-term management of the successful adult liver encephalopathy: a multi-center survey on safety and efficacy. Hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation in a Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 27:1329-1335. Garcia-Martinez R, Rovira A, Alonso J, Jacas C, Simon-Talero M, ized trial of patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Amodio P, Biancardi A, Montagnese S, Angeli P, Iannizzi P, Cillo U, Franco J, et al. Ali trial comparing lactulose, probiotics, and L-ornithine L-aspartate in ment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 25(Suppl 1):3-9. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; trolled trial of probiotics in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Analysis of hospitalizations comparing rifaximin versus lactu gut ora modulation using prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics on lose in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in with cirrhosis and refractory ascites: relevance of serum sodium con patients with cirrhosis. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: Severe muscle depletion in patients on the liver transplant wait list: its results of a patient population survey. Kalaitzakis E, Olsson R, Henfridsson P, Hugosson I, Bengtsson M, status in liver cirrhosis with malnutrition. Weissenborn K, Krause J, Bokemeyer M, Hecker H, Schuler A, Osterrieth Complex Figure. Pattern of motor and dence from psychometric studies and magnetic resonance spectros cognitive decits in detoxied alcoholic men. Laskus T, Radkowski M, Bednarska A, Wilkinson J, Adair D, with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Virol 2004; 78: ease specic health related quality of life measure for primary biliary 5170-5183. Molecular and bioinformatic evidence of hepatitis C virus evolu ciations and impact of symptoms in primary biliary cirrhosis using a tion in brain. Larry Strausbaugh for his many contributions and valued guidance in the preparation of this guideline. Application of Transmission-Based Precautions in Ambulatory and Home Care Settings. Recommendations for Application of Standard Precautions for the Care of All Patients in All Healthcare Settings. For susceptible exposed persons for whom vaccine is contraindicated, provide varicella zoster immune globulin as soon as possible after exposure and within 10 days. Interim Measles Infection Control [July 2019] See Interim Infection Prevention and Control Recommendations for Measles in Healthcare Settings dev. The transition of healthcare delivery from primarily acute care hospitals to other healthcare settings. The successful experience with Standard Precautions, first recommended in the 1996 guideline, has led to a reaffirmation of this approach as the foundation for preventing transmission of infectious agents in all healthcare settings. The continued occurrence of outbreaks of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses in ambulatory settings indicated a need to re-iterate safe injection practice recommendations as part of Standard Precautions. The addition of a mask for certain spinal injections grew from recent evidence of an associated risk for developing meningitis caused by respiratory flora. This document is intended for use by infection control staff, healthcare epidemiologists, healthcare administrators, nurses, other healthcare providers, and persons responsible for developing, implementing, and evaluating infection control programs for healthcare settings across the continuum of care. As with the 1996 guideline, the modes and factors that influence transmission risks are described in detail. New to the section on transmission are discussions of bioaerosols and of how droplet and airborne transmission may contribute to infection transmission. This section of the guideline also presents information on infection risks associated with specific healthcare settings and patient populations. New in this guideline is a figure that shows a recommended sequence for donning and removing personal protective equipment used for isolation precautions to optimize safety and prevent self-contamination during removal. Appendix A: Type and Duration of Precautions Recommended for Selected Infections and Conditions Appendix A consists of an updated alphabetical list of most infectious agents and clinical conditions for which isolation precautions are recommended. The type and duration of recommended precautions are presented with additional comments concerning the use of adjunctive measures or other relevant considerations to prevent transmission of the specific agent. Management of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms in Healthcare Settings (2006). Evolution of the 2007 Document the Guideline for Isolation Precautions: Preventing Transmission of Infectious Agents in Healthcare Settings 2007 builds upon a series of isolation and infection prevention documents promulgated since 1970. These previous documents are summarized and referenced in Table 1 and in Part I of the 1996 Guideline for Isolation Precautions in Hospitals 1.
Buy vasotec 10mg without a prescription
Postvaccination levels can be determined after for Primary Immunodeciencies 3 to 4 weeks blood pressure value chart buy 10mg vasotec with amex. Similar protection against invasive pneumococcal infections, but not considerations apply to measurement of antibodies against pneu pneumonia and mucosal infections, such as otitis media and mococcal capsular polysaccharides. There is no natural exposure to immunodecient phenotype is desirable for the following this prokaryote virus in human subjects; it will elicit a response reasons: (1) unequivocal diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment; even in infants. The test is applied rarely for clinical diagnostic (2) accurate genetic counseling and planning for future purposes and exists mainly as a research tool. For information, contact Dr Hans Ochs, phenotype associations; and (4) identication of candidates for 33, 34 Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington, Seattle, gene-specic therapies. Es In vitro lymphocyte responses to mitogens are nonspecic and tablishing a molecular diagnosis also permits in utero diag indicate the ability of T cells to be activated by powerful stimuli. These results can be informative in fully should be considered, even in female patients, when other possi immunized infants beyond 6 to 12 months of age. Carrier status should be determined Autoimmune cytopenias are common in many forms of for all potentially affected relatives of patients with severe immunodeciency, and blood cell counts should be followed. Patients with paraproteins Early diagnosis and therapy are the keys to survival and a better and other medical conditions affecting the cardiovascular system 50, 51 quality of life for immunodecient patients. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy ment therapy but should be studied if suspected. Additional is indicated for all disorders with signicantly impaired antibody recommendations can be found in specic product prescribing production. Therapeutic IgG is also used for combined Permanent central venous catheters can be associated with 53 defects with signicantly impaired antibody production. In association with low IgG levels, bial therapy should be considered for immunodecient patients. IgG might not be adequate to eradicate infections in immunocompro therapy will be indicated for many of these patients (except those mised hosts. Anecdotal data suggest that in some of these phylaxis should be considered for patients with immunode cases the reaction might be due to the occurrence of high levels of ciency. The frequency of monitoring de antibody deciency, even with immunoglobulin replacement. Evidence of benet for pre equacy of IgG replacement is determined by the trough (preinfu vention of recurrent otitis media exists in studies of immunocom 58 sion) or steady-state IgG level in association with the clinical petent children. The dose might need to be adjusted for excessive infec prevention of bacterial infections after chemotherapy-induced 59 tions (poor clinical response), growth or weight change, or other neutropenia. A higher rate of isolation of antibiotic-resistant or processes, such as enteric loss or increased metabolism. The ganisms has been found in some but not all studies of otitis media 58 steady-state IgG level is also useful for monitoring adherence prophylaxis. Inonestudyof18childrenwithotorrheaofmorethan for the prevention of respiratory tract infections. In one study of functional endoscopic sinus surgery in 23 pe Summary statement 17. Lung imaging and function should be diatric patients, 5 required intravenous antibiotics in addition to sur 63 monitored regularly in patients with a history of or who are at risk gery for resolution of chronic rhinosinusitis. It is unknown whether functional assessment is sufficient unrelated donor and cord blood donor transplants is 65, 66 by itself to monitor disease status and progression. Regimens for prophylaxis of bacterial respiratory measles-mumps-rubella, oral typhoid, varicella, and yellow fever. Patients receiving or 5 mg/kg every other day or 250 mg every IgG replacement therapy will have circulating antibodies against other day polio, measles-mumps-rubella, and varicella. Inactivated or subunit vaccines can be 28 days off administered to immunocompromised patients. Because there might be some protective tolerated, other drugs can be considered, including cefuroxime, cefprozil, immunity after inoculation, even in immunocompromised hosts, cefpodoxime, ciprooxacin or other quinolone, or others, depending on the individual circumstances of the patient. Immunization beyond routine depends on implementation of universal neonatal screening for T guidelines can be considered therapeutic in some circumstances, cell cytopenia. Patients and families should establish long but there are insufficient data yet to say how often such a case term relationships with health care professionals, including phy 74 might occur. Irradiation screening test results and in determining which advanced tests to renders lymphocytes incapable of undergoing cell division if 10, 41, 55 pursue. Physical examination should include careful in they are activated and reduces the occurrence of transfusion spection for signs of infection. The presence of lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly might be signs of lymphoproliferative disease or malignancy. Depending on the gene defect, other types of study in an infant should prompt immunologic evaluation. Symptoms include irritability, erythroderma, situations predisposing to lymph loss (chylothorax and lym pachydermia, diarrhea, lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenome phangiectasia), or stress associated with severe illness or infec galy, and failure to thrive. A signicant number of patients evaluation and therapy must be initiated as quickly as possible. Den numbers of persons or those likely to harbor infectious agents itive therapy before signicant infectious complications arise is (eg, young children in day care) and protective isolation when also associated with improved outcomes. Alternative prophylactic regimens include pentamidine isethio these modied cells are then infused back to the patient. Therapy might need to be prolonged because Some immunologic and clinical features of these disorders are 113, 115, 142-183 clearance is usually delayed in comparison with immunocompe listed in Table E9. IgA levels are tution of in vivo and in vitro T-cell functional reconstitution were 190 often also low. T cells proliferate normally in vitro in immunoglobulin levels, specic antibody production, or both response to mitogenic stimuli in patients with these disorders. It is extremely important to rule out mild or early conveniently activated by nonspecic stimuli, such as a combi forms of known humoral or combined deciencies to maximize the nation of phorbol ester and calcium ionophore. Similar methods likelihood of their detection and provide the best opportunities for can also be applied to platelets. Skin care clinical score of 2, 3, or 4 depending on the severity of these man for eczema might also be needed. X-linked neu considered for patients less than 5 years of age with suitable tropenia is dened as congenital neutropenia in the absence of stem cell donors. The scoring system is not generally applied in clinical term improvement or resolution of thrombocytopenia and im 201, 202 practice. IgG and/or IgM levels, normal or increased IgA levels, and low, Summary statement 50. These abnormalities might not orders should be considered in all children with frequent infec appear until late in the course of the disease. More than 50% of tions and characteristic neurological, skeletal, and/or cutaneous patients display some degree of impairment in vaccine antibody manifestations, including ataxia, microcephaly, and telangiecta responses or isohemagglutinin production. T cells have Cerebellar ataxia, oculocutaneous telangiectasias, growth mild to moderately reduced proliferation to mitogens in vitro in retardation, increased risk of malignancy, and variable immune one third to one half of patients. Diminished cutaneous antigen re deciency are the most prominent and consistent clinical features sponses are observed in more than 80% of patients. Thus they are not helpful for making an early cytometric analyses can be performed on lymphocytes from diagnosis. Abnormal ndings are considered although viral and fungal infections can also occur. Molecular analysis is required in this circum increased immunoglobulin levels, IgG subclass deciencies stance. Low IgA levels, abnormalities of IgG subclasses (eg, IgG2 incidence of intellectual disability. Hypo mismatch repair syndrome were found to have decient class 223 gammaglobulinemia G and Awith normal IgM levels are reported switch recombination defects. Only the rst patient presented in about one third of patients, supporting a defect in class-switch with increased IgM and low IgG levels; the other patients had recombination. Immunologic opmental delay, short stature, dysmorphic facies, and hypogam abnormalities include low IgG and IgA levels and leukopenia. Infectious complications, to anomalies of chromosomes 1, 9, and 16, which are found in 219, 220 including opportunistic microorganisms suggesting T-cell lymphocytes of all patients and are pathognomonic. These dysfunction, were reported in approximately 70% of patients; consist of multiradial chromosomes, breaks, deletions, and these presented from 3 months to 4 years of age and consisted pri isochromosome formation.
Order 5mg vasotec
Many body sites have normal blood pressure chart age 60 generic vasotec 10mg with amex, com between the physicians, nurses, and laboratory staf should be mensal microbiota that can easily contaminate the inappro encouraged and open with no punitive motive or consequences. The diagnosis of infectious disease is best achieved by apply Therefore, specimens from sites such as lower respiratory ing in-depth knowledge of both medical and laboratory science tract (sputum), nasal sinuses, superficial wounds, fistulae, along with principles of epidemiology and pharmacokinetics and others require care in collection. Actual tissue, aspirates, and fluids are always specimens the result of strong partnerships between the clinician and the of choice, especially from surgery. This document illustrates and promotes of choice for many specimens because swabs pick up extra this partnership and emphasizes the importance of appropriate neous microbes, hold extremely small volumes of the speci specimen management to clinical relevance of the results. Swabs are expected from the nasopharynx and Medical Microbiology, the American Board of Pathology, or the to diagnose most viral respiratory infections. Flocked swabs American Board of Medical Laboratory Immunology or their have become a valuable tool for specimen collection and have equivalent certifed by other organizations. Clinicians should been shown to be more effective than Dacron, rayon, and cot recommend and medical institutions should provide this kind ton swabs in many situations. The flocked nature of the swab of leadership for the microbiology laboratory or provide formal allows for more efficient release of contents for evaluation. To request the laboratory to provide testing apart sibility of the medical personnel, not usually the laboratory, from the procedure manual places everyone at legal risk. It is the key to accurate laboratory diag biota changes and etiologic agents are impacted, leading to nosis and confirmation, it directly affects patient care and patient potentially misleading culture results. Susceptibility testing should be done only on clinically signif infection control, patient length of stay, hospital and laboratory icant isolates, not on all microorganisms recovered in culture. Clinicians and other medical personnel should consult accurate, significant, and clinically relevant. The laboratory should set technical policy; this is not the storage of patient specimens they collect are managed properly. Specimens must be labeled accurately and completely so Throughout the text, there will be caveats that are relevant to spe that interpretation of results will be reliable. However, there are some strategic tenets of specimen results without more specific site and clinical information management and testing in microbiology that stand as community (eg, dog bite wound right forefinger). Future modifications of the document are to at all times for all medical personnel to review or consult and it be expected, as diagnostic microbiology is a dynamic and rap would be particularly helpful to encourage the nursing staff to idly changing discipline. Pediatric parameters have been updated review the specimen collection and management portion of the in concordance with Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines and manual. Comments and recommenda tion personnel, who may know very little about microbiology or tions have been integrated into the appropriate sections. Another unique feature is that in most chapters, there fungi often require special broth media or lysis-centrifugation vials are targeted recommendations and precautions regarding select for detection, most Candida spp grow very well in standard blood ing and collecting specimens for analysis for a disease process. Within each chapter, didemia do not yield positive results in almost half of patients. The most common etiologic agents of period, such as 2 hours, it is expected that the sample should culture-negative endocarditis, Bartonella spp and Coxiella bur be refrigerated afer that time unless specifed otherwise in that netii, ofen can be detected by conventional serologic testing. It is a collaborative effort between clinicians and laboratory require >2 culture bottles depending on the system. For neonates experts focusing on optimum use of the laboratory for positive and adolescents, an age and weight appropriate volume of blood patient outcomes. Infants and children: 2 As much blood as can be Organisms will usually survive in inoculated culture vials blood culture sets (see conveniently obtained even if not incubated immediately. Malassezia spp re above) from children; volume quire lipid supplementation; lysis-centrifugation is recom depends on weight of mended for their recovery. There may be circumstances in which it is prudent to omit the anaerobic vial and split blood spec imens between 2 aerobic vials. Such requests should be made in consultation with the microbiology laboratory director. The timing of blood culture orders should be dictated by Skin contaminants in blood culture bottles are common, very patient acuity. In urgent situations, 2 or more blood culture sets costly to the healthcare system, and frequently confusing to cli can be obtained sequentially over a short time interval (min nicians. To minimize the risk of contamination of the blood cul utes), afer which empiric therapy can be initiated. Recommended Volumes of Blood for Culture in Pediatric Patients (Blood Culture Set May Use Only 1 Bottle) Recommended Volume of Weight of Blood for Culture, mL Patient, Total Patient Total Volume % of Total kg Blood Volume, mL Culture Set No. Two recent studies have documented equiv the anaerobic bottle (faster time to detection). Infections Associated With Vascular Catheters povidone-iodine followed by alcohol is recommended. Tese procedures may include abbreviated iden of a positive culture from an indwelling catheter segment or tip tifcation of the organism, absence of susceptibility testing, and in the absence of positive blood cultures is unknown. The next a comment that instructs the clinician to contact the laboratory essential diagnostic component is demonstrating that the infec if the culture result is thought to be clinically signifcant and tion is caused by the catheter. This usually requires exclusion of requires additional workup and susceptibility results. Some investigators have Physicians should expect to be called and notifed by the concluded that catheter tip cultures have such poor predictive laboratory every time a blood culture becomes positive since value that they should not be performed [13]. Routine culture of intrave Key points for the laboratory diagnosis of bacteremia/ nous catheter tips at the time of catheter removal has no clinical fungemia: value and should not be done [13]. When a microbiologic diagnosis of less common etio tories): one from catheter or port and one from peripheral logic agents is required, especially when specialized techniques venipuncture obtained at the same time using lysis-centrifu or methods are necessary, consultation with the laboratory gation (Isolator) or pour plate method. In this section, infections are categorized to obtain the correct length (5 cm) of the distal catheter tip. Other routes of infection include direct extension tip or an endoluminal brush (not performed routinely in most from a contiguous structure, movement along nerves, or intro laboratories). Infected (Mycotic) Aneurysms and Vascular Grafts fora and should not be sent to the microbiology laboratory Infected (mycotic) aneurysms and infections of vascular grafts for direct smears, culture, or molecular studies. Pericarditis and Myocarditis culture and are required for optimal recovery of mycobacteria Numerous viruses, bacteria, rickettsiae, fungi, and parasites and fungi. When the specimen volume is less than required have been implicated as etiologic agents of pericarditis and for multiple test requests, prioritization of testing must be myocarditis. Whenever possible, specimens for whelming majority of patients with myocarditis, an etiologic culture should be obtained prior to initiation of antimicrobial diagnosis is never made and patients are treated empirically. If anaerobes are suspected, then the culture should consist of an aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culture. If anaerobes are suspected, then the culture should consist of both a routine aerobic and anaerobic culture. Serum should be separated from red cells as soon as from cultures is routinely performed unless contamination possible. Continued Transport Issues and Etiologic Agents Diagnostic Procedures Optimum Specimens Optimal Transport Time Other: B.
Buy generic vasotec 10mg online
Preventive measures: Protect against puncture wounds by wearing shoes and protective clothing arrhythmia monitoring device buy vasotec mastercard. Resection of small lesions may be helpful; amputation may be required for an extremity with advanced lesions. In suspected Acanthamoeba infections, diagnosis is made by microscopic examination of scrapings, swabs or aspirates of the eye and skin lesions; or by culture on nonnutrient agar seeded with Escherichia coli, Klebsiella aerogenes or other suitable Enterobacter species. Amoebae have been misidentied as macrophages and have been mistaken for Entamoeba histolytica when microscopic diagnoses are made under low magnication. Naegleria trophozoites colonize the nasal tissues, then invade brain and meninges by extension along the olfactory nerves. Eye infections have occurred primarily in soft contact lens wearers; homemade saline used as a cleaning or wetting solution and exposure to spas or hot tubs have been implicated as sources of corneal infection. Apparently healthy individuals develop Naegleria infection; immunodecient individuals have increased suscep tibility to infection with Acanthamoeba and probably Balamuthia. Naegleria and Balamuthia have not been found in asymptomatic individ uals; Acanthamoeba has been found in the respiratory tract of healthy people. Preventive measures: 1) Educate the public to the dangers of swimming in lakes and ponds where infection is known or presumed to have been acquired, and of allowing such water to be forced into the nose through diving or underwater swimming. In practice, this is difficult since the amoebae may occur in a wide variety of aquatic bodies, including swimming pools. No infection is known to have been acquired in a standard chlorinated swimming pool. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: Not reportable in most countries, Class 3 (see Reporting). Despite the sensitivity of the organisms to antibiotics in laboratory studies, recoveries have been rare. For eye infections, no standard treatment has been reported; topical propamidine isethionate has been reported to be effective; clotrimazole, miconazole and pimaricin have been used in small numbers of patients with some response. Epidemic measures: Multiple cases may occur following ex posure to an apparent source of infection. Any grouping of cases warrants prompt epidemiological investigation and the prohibi tion of swimming in implicated waters. Primary hazards are droplet or aerosol exposure of mucous membranes (eye, nose, or mouth) to trophozoites and tissue homogenates. Members of the Nocardia asteroides complex are most likely to cause respiratory and disseminated infections, with high associated mortality, and a particular propensity to cause brain abscess. Biopsy or autopsy usually clearly establishes involve ment, although histopathology may be non-specic. Occasional outbreaks may occur from environmental sources, and transmission through health care workers is probably rare. Imipenem and amikacin is an effective combination for intracerebral dis ease, but N. Minocycline may be tried in patients allergic to sulfon amides who do not have a brain abscess. Surgical drainage of abscesses may be needed in addition to antibiotherapy; intracerebral lesions in immunocompromised patients should be considered early for biopsy because of the wide differential diagnosis and variable antibiotic susceptibility C. Adult worms are found in these nodules, which occur supercially, and also in deep-seated bundles lying against the periosteum of bones or near joints. The female worm discharges microlariae that migrate through the skin, often causing an intense pruritic rash when they die, with chronic dermatitis-altered pigmentation, oedema and atrophy of the skin. Microlariae frequently reach the eye, where their invasion and subse quent death causes visual disturbance and blindness. Microlariae may be found in organs and tissues other than skin and eye, but the clinical signicance of this is not yet clear; in heavy infections they may also be found in blood, tears, sputum and urine. Laboratory diagnosis is made through microscopic examination of fresh supercial skin biopsy incubated in water or saline with observation of microlariae; through evidence of microlariae in urine; or through the nding of adult worms in excised nodules. Differentiation of the micro lariae from those of other larial diseases is required where the latter are also endemic. Other diagnostic clues include evidence of ocular manifes tations and slit-lamp observations of microlariae in the cornea, anterior chamber or vitreous body. In low density infections, where microlariae are not found in the skin and are not present in the eyes, the Mazzotti reaction (characteristic pruritus after oral administration of 25 mg of diethylcarbamazine citrate or topical application of the drug) may be used. This test may be dangerous in heavily infected individuals and has been abandoned in many countries. In sub-Saharan Africa, the disease occurs in an area extending from Senegal to Ethiopia down to Angola in the west and Malawi in the east; also in Yemen. In some endemic areas in western Africa, until recent years, a high percentage of the population was infected, and visual impairment and blindness were serious problems. People abandoned the river valleys and migrated to safer higher ground, where the soil was far less fertile. The disease can be transmitted experimen tally to chimpanzees and has been found rarely in nature in gorillas. Onchocerca species found in animals cannot infect humans but may occur together with O. Microlariae, ingested by a blacky feeding on an infected person, penetrate thoracic muscles of the y, develop into infective larvae, migrate to the cephalic capsule, are liberated on the skin and enter the bite wound during a subsequent blood-meal. In Africa, vectors could be infective 7 days after a blood-meal; in Guatemala the extrinsic incuba tion period is measurably longer (up to 14 days) because of lower temperatures. Reinfection of infected people may occur; severity of disease depends on cumulative effects of the repeated infections. Preventive measures: 1) Avoid bites of Simulium ies by wearing protective clothing and headgear as much as possible or by use of an insect repellent such as diethyltoluamide. H-14, a biological insecticide formulated as an aqueous suspension, can be used at a dose 2. H-14, which has a much shorter carry and therefore needs numerous application points along the river. Aerial spraying may be used to ensure coverage of breeding places in large-scale control operations such as in Africa. Because of mountainous terrain, such procedures generally are not feasible in the Americas.

