Baclofen
Buy baclofen cheap online
Table 2 highlights the spectrum of independent spasms homeopathy right side discount baclofen master card, are unrelated to the pharmacologic actions of drug allergic reactions and syndromes that will be discussed the drug, and occur only in susceptible individuals. Unpre dictable reactions are subdivided into drug intolerance, drug in greater detail in this parameter. Both the p-i concept (pharmacologic interaction with immune type A and type B reactions may be influenced by genetic receptors) is a recently proposed addition to drug hypersen predisposition of the patient. In this scheme, a drug binds nonco In this parameter, drug allergy is defined as an immuno valently to a T-cell receptor, which may lead to an immune logically mediated response to a pharmaceutical and/or for response via interaction with an major histocompatibility mulation (excipient) agent in a sensitized person. In this scenario, no sensitization is required because fication of drug allergies is impeded by our limited there is direct stimulation of memory and effector T cells, analogous to the concept of superantigens. Although the Gell-Coombs classification served a useful purpose in its the structural characteristics of certain drugs, such as time, it does not account for many common clinical problems. Our knowledge of IgE-medi Other drug-specific risk factors include the dose, route of ated drug allergy is derived chiefly from the vast amount of administration, duration of treatment, repetitive exposure to research involving penicillin allergy. Host risk factors include edge of drug allergy mechanisms is limited but emerging. The history Possible clinical tests might include but are not limited to a should focus on such items as previous and current drug use, chest x-ray examination, a complete blood cell count with the toxicity and allergenicity of previously and currently used differential, sedimentation rate, nuclear and cytoplasmic au drugs, and the temporal sequence of events between initiation toantibody tests, and other specific immunologic tests. Physical examination retrospective diagnosis of anaphylaxis may be determined by should include all systems that could possibly account for the detecting an increase in serum total tryptase levels above clinical presentation. Cutaneous manifestations are the most baseline or in serum mature tryptase (also known as common presentation for drug allergic reactions. The most useful test for detecting IgE-mediated drug allergic reactions may present with noncutaneous phys drug reactions caused by many large-molecular-weight bio ical findings, these findings are generally nonspecific and are logicals and penicillin is the immediate hypersensitivity skin not nearly as helpful in diagnosis and management decisions. Relatively few studies with small numbers of patients Therefore, the emphasis in this parameter on the physical have evaluated the specificity and sensitivity of third-gener examination focuses on cutaneous findings. Therefore, although a positive in vitro test result for terns have been reported in drug allergy, including exan penicillin specific IgE is highly predictive of penicillin al thems, urticaria, angioedema, acne, bullous eruptions, fixed lergy, a negative in vitro test result does not adequately drug eruptions, erythema multiforme, lupus erythematosus, exclude penicillin allergy. Patients who, based on their history Patch testing is the most reliable technique for diagnosis of and/or diagnostic test results, are unlikely to be allergic to a contact dermatitis caused by topically applied drugs. Patients who have a diagnosis of contact dermatitis usually can be verified by relatively higher likelihood of being allergic to a drug should patch testing. In recent years there have been reports con undergo an induction of drug tolerance procedure. Table 2 lists the various other immunologic drug allergic are no absolute histologic criteria for the diagnosis of drug syndromes discussed in the parameter. However, certain drugs are more frequently associ What has often been referred to as drug desensitization is ated with specific types of reactions. Significant updates on more appropriately described in this parameter as a temporary the following drugs and biologic agents have been made in induction of drug tolerance. Drug tolerance is defined as a this updated parameter and are discussed elsewhere in more state in which a patient with a drug allergy will tolerate a drug detail. Drug tolerance does not indicate either a permanent state of tolerance or that the mechanism Antimicrobials involved was immunologic tolerance. All procedures to induce drug tolerance ciated with higher costs, increased antibiotic resistance, and involve administration of incremental doses of the drug. Ideally, both major and minor determinant as long as the patient continues to take the specific drug. Penicillin challenges of Where there is a definite medical indication for the agent in individuals skin test negative to penicilloylpolylysine and question, either induction of drug tolerance or graded chal penicillin G20,21 have similar reaction rates compared with lenge procedures may be considered, depending on the his individuals skin test negative to the full set of major and tory of the previous reaction and the likelihood that the minor penicillin determinants. If there is a low Varying degrees of allergic cross-reactivity between peni likelihood of drug allergy, a graded challenge or test dose to cillin and cephalosporins have been documented. Overall, the specific drug in question may provide a useful confirma most patients with a history of penicillin allergy tolerate tion that administration of the drug will not result in an cephalosporins,22 but there are rare reports of anaphylactic immediate reaction. There is no allergic cross-reactivity between pen reactions may be the result of excipients rather than the active icillin and monobactams. There is no evidence to suggest is to switch to docetaxel because most are able to tolerate it. Red man syndrome reactions can be pre undiluted drug has been found to identify patients at risk of vented by slowing the rate of infusion and premedicating with reactions, and skin testing should be repeated before each histamine receptor antihistamines. Re ance protocols have been reported, but they are not uniformly ports of IgE-mediated anaphylactic reactions to quinolones successful. Many allergic reac drug is inadvertently continued, interstitial fibrosis may ensue. In a random garis are rare immune-mediated reactions that have been ized trial of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole induction of drug described to occur during treatment with metformin and/or tolerance vs rechallenge (single dose), the success rates were sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents. Abacavir, a nucleoside-analogue reverse transcrip induced by this class of drugs. Very rarely, immediate-type tase inhibitor, causes severe hypersensitivity in 4% to 5% of allergic reactions to corticosteroids have been described. Mild thrombocytopenia is due to platelet immunomodulator agents have been introduced for several aggregation and occurs in 1% to 3% of patients treated with autoimmune diseases. Severe thrombocytopenia is caused several of these have already occurred, it is too early to assess by immune complexes, a component of which is heparin dependent IgG specific for platelet factor 4. Allergic reactions to im usually occurs after approximately 5 days of treatment with munosuppressant and anti-inflammatory drugs may be en unfractionated heparin and is associated with development of countered in the treatment of chronic cutaneous diseases. A recent outbreak of anaphylactic Dermatologic immunosuppressant drugs, such as macrolides reactions to heparin in the United States and Germany was (eg, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, pimecrolimus, and sirolimus), attributed to a contaminant in heparin lots, an oversulfated dapsone, and mycophenolate mofetil, have been reported to form of chondroitin sulfate. This oversulfated chondroitin cause drug allergic reactions in addition to their known pre sulfate contaminant has been shown in vitro and in vivo to dictable adverse reactions. Because ana pain and angioedema are somewhat analogous to C1 inhibitor phylactic reactions cannot be distinguished from anaphylac deficiency in which symptoms are due to local production of toid, nonimmune occurrences, it has been recommended that bradykinin. Documen blood products include urticaria, anaphylaxis (particularly in tation of IgE-mediated reactions is extremely rare. A pharmacologic induction of blocker exposure and/or the presence of cardiovascular drug tolerance procedure (also known as aspirin desensitiza conditions is associated with greater risk for more serious tion), during which tolerance to aspirin can be induced and anaphylactoid reaction. Cough occurs in not fit precisely into a specific category of adverse drug up to 20% of patients, is typically dry and nonproductive, and reactions. The angioedema frequently involves the donic acid molecules are preferentially metabolized in the 153,154 face or upper airway and can be life-threatening or fatal. Because the clinical treatment, slowing infusion rates, or induction of drug toler experience with these drugs varies (ie, phase 4 experiences), 184 ance. In patients with immediate-type reactions, successful the spectrum of reported allergic reactions may not yet be fully known for all of them. A separate type of classification induction of tolerance to rituximab, infliximab, and trastu for adverse reactions to biological agents has been proposed zumab has been reported using a 6-hour protocol in combi based on the mechanism of reactions (Table 3). Hypersensitivity reactions may be either antibody or ical trials and during the postmarketing surveillance period. Immune or cytokine dysregulation may result mechanism of these reactions is unclear. Many cases experi in secondary immunodeficiency, autoimmunity, or allergic or enced either delayed-onset (2 hours) or protracted progression of atopic disorders. Cross-reactive reactions may occur when signs and symptoms after dose administration. The Omalizumab the biologic agent is intended for a pathologic cell type but Joint Task Force report recommended that patients receiving cross-reacts with normal cells.
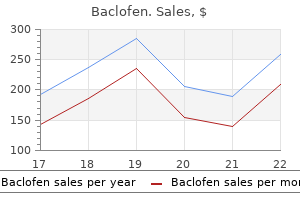
Baclofen 10mg on-line
This is particularly important with children as a higher chair would give them mechanical advantage back spasms yoga generic baclofen 10 mg without a prescription. Independent rising without pushing on chair or knees, arms folded across chest or extended. Pull up with aid of table-patient takes support from table with hips flexed while extending knees. Independent-no aids other than having ankles held down by therapist which is within the range of normal; must achieve sitting balance. Turn to side, and then push up-patient will roll to side, and then push up with both arms to achieve sitting balance. To hands and knees and then sit up-roll to prone, to hands and knees, and then to side sit or other sitting balance. Chair to standing-patient pulls himself to feet with aid of chair, then pushes on chair to achieve upright position d. Chair to sitting, then to standing patient pulls himself to sitting position in chair, then pushes himself to upright position, using chair. Hand grip Measured with hand grip dynamometer taking highest of two readings for left and right hands. The essential tenodesis effect of contracure in the face of severe loss of muscular support should be monitored by the therapist. Stretching of tight muscles and prevention of contractures Overenthusiastic stretching of contractures should be avoided because it produces pain ad stimulates the stretch reflex. To maintain normal strength, the maximal daily tension exerted must be greater than 20% of maximal muscular strength. But heavy exercise may potentially accelerate weakness leading to metabolic bankruptcy. Although weakening is symmetric in many of the muscular dystrophies, joint contractures are not so. Standing and walking are the best functional physical therapy for accomplishing this. Osteogenesis imperfecta is a systemic heritable disorder of connective tissue whose cardinal manifestation is bone fragility. The current standard of care includes a multidisciplinary approach with surgical intervention when imately 90% of individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta, mutations in either of the genes encoding the pro 1 or pro 2 chains of type I collagen necessary, proactive physiotherapy, and consideration for the use of bisphosphonates all in attempts to improve quality of life. E-mail: mation into account, clinical phenotypes resulting from certain baseld@ohsu. Mild to moderate, calci cation of the Histology: abnormal lamellation interosseous membrane, radial head on polarized light microscopy. It should be noted that the severity bone fractures often after little or no trauma. Short stature and bone deformity are common to be incorporated into the triple helix and is thus degraded features of the disorder. The rst fractures may occur at bones, either from mechanical forces exerted by muscle/tendon birth or with diapering. Coxa vara, which has an when the infant begins to walk and, more importantly, to fall. The majority of affected individuals do not quency often increases again in the 5th decade of life and walk without assistance and many use a wheelchair because of accounts for more than 25% of lifetime fractures. Joint hypermobility may be present and may increase the risk Intellect is normal unless intracerebral hemorrhage has oc of premature joint degeneration with resultant osteoarthritis and curred. Scleral hue is variable, often blue or gray, and fetuses die in utero or are spontaneously aborted, more typi sclera can be blue in infancy but lighten with age. Death usually results from pulmonary insuf ciency Basilar impression is characterized by invagination of the mar related to the small thorax, rib fractures, or ail chest because of gins of the foramen magnum upward into the skull, resulting in unstable ribs. Those who survive the rst few days of life may protrusion of the odontoid process into the foramen magnum. Weight and length are small for can cause headache with coughing, trigeminal neuralgia, loss of gestational age. The sclerae are typically dark blue and connec function of the extremities, or parasthesias. The skull is large for the body individuals with basilar impression may perceive that water size and soft to palpation because of poor mineralization, his temperature differs below and above the umbilicus. Fractures in the newborn period, simply with basis of the bone histology and certain clinical characteristics handling of the infant, are common. Affected Facial features individuals frequently have hyperplastic callus formation. Although molecular pathogenesis has not been with body size and frontal bossing is frequently noted. The initial conductive hearing loss results from fractures of tiate these subtypes. Infants tend to have congenital fractures the bones of the middle ear with contracture and scarring of the and signi cant undermineralization of their bones. The xation of the stapes is not result from abnormal hydroxylation of type I collagen in carti unlike otosclerosis and surgical techniques such as stapedotomy lage. Spontaneous scleral rupture and uveal prolapse has been documented and an awareness of the potential to eye injury may be emphasized. The There have been several patients described with joint hyper variability of this nding is marked and at risk of subjective mobility and skin laxity, a clinical phenotype more in keeping assessment. It has been suggested to standardize scleral color with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome but who have an increased dis using the Munsell system,28 but the value of this approach position to fractures. Serum biochemistry Bowel obstruction can occur as a result of protrusio acetabuli Serum concentrations of Vitamin D, calcium, phosphorous, but seems to be uncommon. Both chest wall pathology and severe ky phoscoliosis associated with vertebral compression can contrib As with any disorder, a detailed history is a crucial element ute to restrictive lung disease. This in combination with a physical hypertension and subsequent cor pulmonale, requiring oxygen examination focused toward anomalies encountered in connec support. Mitral valve prolapse and aortic dilatation with or tive tissue disorders and a radiologic review of the skeleton aids without regurgitation have also been reported. In the more severe presentations, vertical Fractures of varying ages and stages of healing, often of growth falls off the growth curves by the end of the rst year of the long bones but may also involve ribs and skull. The life and actual growth velocity is slower than the general pop metaphyseal chip fractures characteristic of child physical ulation. Development in other areas Wormian bones are suggestive of, but not pathognomic, is usually normal. They are present in up to 60% of affected children notable between the ages of 2 and 3. Bone density standards for children are not yet available increase, as it does with unaffected women, and reduce mobility in universally but with increased use of this modality in small moderately affected women. The prevalence of physical abuse is much bits, orbital craniosynostosis, frontal bossing, and hydrocephalus.
Syndromes
- Do cramps accompany the bleeding?
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Congenital myopathies (usually due to a genetic disorder)
- Chills
- Sarcoidosis
- Certain medicines
- Small soft skin lumps on, behind, or in front of the ear
- Blue or blue-gray spots on the back, buttocks, base of spine, shoulders, or other body areas
- Changes in your mitral valve are causing major heart symptoms, such as angina (chest pain), shortness of breath, fainting spells (syncope), or heart failure.
- Cafe-au-lait spots (light brown birthmarks)
Purchase baclofen with paypal
Different ethical principles are given greater or lesser consideration in the process of resolving any particular dilemma and a 65 John L spasms in neck generic baclofen 25 mg fast delivery. See also Devereaux, Definitive Care for the Critically Ill During a Disaster, supra note 8, at 61-2S. The 2006 Adult Clinical Workgroup articulated the following ethical framework in 67 support of this specific effort to allocate ventilators in a pandemic: Ethical Framework for Allocating Ventilators Duty to Care Duty to Steward Resources Duty to Plan Distributive Justice Transparency A. Duty to Care First and most importantly, an ethical allocation scheme must respect the fundamental obligation of health care providers to care for patients. Indeed, in an influenza pandemic, health care providers try to care for and save the lives of as many patients as possible. However, the existing medical standard of care necessitates that doctors, nurses, and other health care professionals offer care at the bedside to individual patients, not to populations. Even during a pandemic, medical staff may be unwilling to overlook their responsibilities to their patients. An ethically sound allocation system must sustain rather than erode this relationship between patient and provider. Physicians must not abandon, and patients should not fear abandonment, in a just system of allocation. In the delivery of day-to-day health care in the United States, the preferences of capable patients are generally the deciding factor in whether recommended treatments will or will not be initiated. However, patient preference is not and cannot be the primary factor in devising an allocation system for ventilators in an influenza pandemic; more patients will want ventilators than can be accommodated. A public health emergency such as an influenza pandemic, by virtue of severe resource scarcity, imposes harsh limits on decision-making autonomy for patients and health care providers. Nonetheless, a just scheme must endeavor to support autonomy, when possible, in ways that also honor the duties of care 66 See generally Benjamin Berkman, Incorporating Explicit Ethical Reasoning Into Pandemic Influenza Policies, 26 J. For example, where an eligible patient for ventilator therapy has appropriately articulated the wish to forgo such treatment, that expression of autonomy should be honored. Furthermore, an allocation system should stress the provision of care that may be possible when ventilator therapy is not. An ethically sound allocation system includes alternative forms of medical intervention and/or palliative care for patients not eligible for ventilator therapy. Duty to Steward Resources the second element in the ethical framework for allocating ventilators is the obligation for government and health care providers to responsibly manage resources during a period of true scarcity. The effort to balance this obligation to the community of patients against the primary duty to care for each patient generates the ethical tension in devising an allocation system. Even under ordinary, non-emergency circumstances, health care providers may question whether the estimated benefit of an intervention merits the use of scarce resources. For example, health care providers currently struggle to decide whether a blood transfusion (or antibiotics, or surgical intervention) is appropriate or justified for a particular patient, given that the quantity of a particular resource is limited. Yet an emergency on the scale of a severe influenza pandemic forces health care providers to confront limits far more starkly than they now do. Patients, some of whom might survive under ordinary circumstances, cannot be given the standard level of resources at the expense of numerous other patients who will likely die without any resources at all. Providers need to balance the obligation to save the greatest possible number of lives against that of the obligation to care for each single patient. As the number of affected patients increase, accommodating these two goals require more and more difficult decisions. An allocation system incorporates ethical decision-making processes so that the duty to steward resources and the limitations it may place on individual care is recognized as fair and acceptable under emergency circumstances. Duty to Plan A motivating force in designing an allocation system is the knowledge that planning is an obligation. An absence of a plan leaves allocation decisions to exhausted, over-taxed, front-line health care providers, who already bear a disproportionate burden in an emergency. A failure to produce an acceptable plan for a foreseeable crisis amounts to a failure of responsibility toward both patients and providers. In addition, health care providers are aware that some who served in the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina faced accusations of criminal conduct. Appropriate guidance may help prevent both the actuality and the fear of similar consequences for those who provide care in a future emergency. Although plans are obligatory, the Guidelines represent a starting point for the public and decision-makers to discuss how scarce resources, particularly ventilators, should be allocated. The Task Force acknowledged that current access to health care is unequal; no allocation system for a crisis can resolve inequities in pre-existing health status resulting from unequal access. In addition, because the clinical parameters of an influenza pandemic are as yet uncertain, increasing the difficulty of predicting survival or duration of critical symptoms, the specifics of the clinical ventilator allocation protocol may evolve as data about the pandemic viral strain 36 Chapter 1: Adult Guidelines become available during a pandemic. Nevertheless, the government has a duty to plan for foreseeable emergencies, and this work product embodies the current, best efforts at an effective, fair plan aimed at saving the most lives in an influenza pandemic where there are a limited number of available ventilators. Distributive Justice A just system of allocation must be applied consistently and broadly to be fair to all. In addition, the same allocation system should be implemented across the State, and the decision to implement clinical ventilator allocation protocols must be authorized by the State. The timing and content of a just allocation system cannot fall to individual hospitals, but must be coordinated with the State. A just and equitable health care system cannot allow for more expansive access at a prestigious private facility and more restrictive access at a community or public hospital. Cooperative agreements to pool scarce resources among local hospitals may help alleviate initial shortages. The allocation of ventilators from State and federal stockpiles must take into account the ratio of local populations to available resources, and supplement those resources accordingly. Ethically sound responses to a public health emergency must not exacerbate disparities in access to care. Rather, planners must designate appropriate resources for the most vulnerable, whom are most likely to suffer the greatest impact in a public health emergency. Transparency Any just plan allocating ventilators requires robust efforts to promote transparency, by seeking broad input in the design of the plan and educating the public. The Department of Health and the Task Force will continue to publicize the Guidelines, and share them with health care leaders and the community. The assessment of public comment and feedback has been integrated into the Guidelines and contributes to the development of a just allocation process. The ongoing process of obtaining and incorporating feedback helps promote public trust in the Guidelines. Triage Decision-Makers: Officer or Committee A physician attending to a patient should have neither the main nor the sole responsibility for determining whether his/her patient is eligible for ventilator therapy. Neither a triage officer nor any members of the triage committee should have any direct contact with patients. Use of a separate person/team to triage is essential for an effective clinical ventilator allocation protocol for several reasons. First, this framework permits attending physicians to 37 Chapter 1: Adult Guidelines fulfill their obligation to care for their individual patients without facing a conflict of interest; they can advocate for their patients and not also be responsible for deciding to withhold or withdraw ventilator treatment. Second, separating the attending physicians from the triage decision-makers also ensure that the person(s) in this role is a senior/supervisory clinician. This person(s) will have access to real-time information, which helps with balancing the need for ventilator treatment versus resource availability. Further, this person(s) will make allocation decisions consistently across a group of patients. Finally applying role sequestration enhances the capacity for maintaining professionalism by helping to decrease burnout and stress for health care providers providing direct critical care during the epidemic and for the decision-makers, and for all clinicians to sustain their integrity as healers.
Cheap baclofen 10mg free shipping
Baseline genotype as a predictor of virological failure to emtricitabine or stavudine in combination with didanosine and efavirenz muscle relaxant tv 4096 baclofen 10 mg for sale. Should We Be Testing for Baseline Integrase Resistance in Patients Newly Diagnosed With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Prevalence of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor Resistance in British Columbia, Canada Between 2009 and 2016: A Longitudinal Analysis. Effect of splenectomy on T lymphocyte subsets in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Combined treatment of symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection with native interferon-alpha and zidovudine. Hypersensitivity reactions during therapy with the nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor abacavir. Switching the third drug of antiretroviral therapy to maraviroc in aviraemic subjects: a pilot, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Prevalence and predictive value of intermittent viremia with combination hiv therapy. The advantages of therapeutic drug monitoring in patients receiving antiretroviral treatment and experiencing medication-related problems. Patients with previous treatment failures Fewer options exist for regimen simplification in virologically suppressed individuals in whom several previous regimens have failed over time. Eight (8%) of the 95 patients who remained on dolutegravir monotherapy had virologic failure. In three (38%) of these eight patients, mutations associated with resistance were detected in the integrase gene [23]. In the monotherapy arm, treatment failure was more frequent in patients co-infected with hepatitis C virus [64% vs. Preliminary data from Botswana suggest there may be an increased risk of neural tube defects in infants born to individuals who were receiving dolutegravir at the time of conception [27]. Targeted laboratory testing should be repeated if the patient has pre-existing laboratory abnormalities or if there are potential concerns with the new regimen. In the absence of any new complaints, laboratory abnormalities, or evidence of viral rebound at 3 months, clinical and laboratory monitoring of the patient may resume on a regularly scheduled basis. Recent retrospective studies support the concept that virologic rebound is more likely to occur in patients with viral loads >200 copies/mL than in those with low-level viremia between 50 and 199 copies/mL [57,58]. Once virologic failure is suspected or confirmed, a thorough assessment is indicated to determine whether one or more of the factors below could have been the cause(s) of virologic failure. It is important to distinguish among the causes of virologic failure, as the approaches to subsequent therapy may differ. Clinicians should note that the lack of evidence of resistance in this setting does not exclude the possibility that resistance mutations may be present. Abacavir susceptibility could be compromise when the 184V mutation is present h Preliminary data from Botswana suggested that there is an increased risk of neural tube defects in infants born to those who were receiving dolutegravir at the time of conception [27]. Pregnancy testing should therefore be performed for those of childbearing potential prior to initiation of dolutegravir. Despite this progress, there remain patients who have experienced toxicities and/or developed resistance to all or most currently available drugs. Dolutegravir plus lamivudine maintains human immunodeficiency virus-1 suppression through week 48 in a pilot randomized trial. Efficacy and safety 48 weeks after switching from efavirenz to rilpivirine using emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-based single-tablet regimens. Immunologic and virologic evolution during periods of intermittent and persistent low-level viremia. We recommend against the use of cobicistat-containing regimens in pregnancy due to a lack of safety data. The tables have been adapted from the Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Click on the drug class below to link to the adverse reactions and recommendations pertaining to the agents in that class. We recommend against the use of cobicistat in pregnancy due to insufficient safety data. Emtricitabine intolerance in treatment-experienced patients switched from lamivudine: a method of assessing toxicity. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: is there a true difference in efficacy and safety Acute kidney injury caused by tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and diclofenac co-administration. Integrase strand transfer inhibitors and neuropsychiatric adverse events in a large prospective cohort. Surveillance for neural tube defects following antiretroviral exposure from conception the Tsepamo Study (Botswana). Ritonavir-boosted atazanvir exposure is associated with an increased rate of renal stones compared with efavirenz, ritonavir-boosted lopinavir and ritonavir-boosted darunavir. Cardiovascular disease and use of contemporary protease inhibitors: the D:A:D international prospective multicohort study. Impact of individual antiretroviral drugs on the risk of myocardial infarction in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-infected patients. An excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation. They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition. The "sequelae" include conditions specified as such; they also include residuals of diseases classifiable to the above categories if there is evidence that the disease itself is no longer present. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, etc. For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned. The "sequelae" include conditions specified as such; they also include the late effects of diseases classifiable to the above categories if the disease itself is no longer present Code first condition resulting from (sequela) of malnutrition and other nutritional deficiencies E64. F01 Vascular dementia Vascular dementia as a result of infarction of the brain due to vascular disease, including hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Includes: arteriosclerotic dementia Code first the underlying physiological condition or sequelae of cerebrovascular disease. The category is also for use in multiple coding to identify these conditions resulting from any cause Excludes1:congenital cerebral palsy (G80. The category is also for use in multiple coding to identify these conditions resulting from any cause. Pupillary occlusion Pupillary seclusion Excludes1:congenital pupillary membranes (Q13. Category of visual impairment Visual acuity with best possible correction Maximum less than: Minimum equal to or better than: 6/18 6/60 1 3/10 (0. The "sequelae" include conditions specified as such or as residuals which may occur at any time after the onset of the causal condition Excludes1:personal history of cerebral infarction without residual deficit (Z86. Excludes2: chronic (childhood) granulomatous disease (D71) dermatitis gangrenosa (L88) dermatitis herpetiformis (L13. The appropriate code from category O30, Multiple gestation, must also be assigned when assigning a code from category O31 that has a 7th character of 1 through 9. The appropriate code from category O30, Multiple gestation, must also be assigned when assigning a code from category O32 that has a 7th character of 1 through 9. The appropriate code from category O30, Multiple gestation, must also be assigned when assigning code O33. The appropriate code from category O30, Multiple gestation, must also be assigned when assigning a code from category O40 that has a 7th character of 1 through 9.
Discount baclofen 25 mg fast delivery
Given the high comorbidity of axis I disorders with borderline personality disorder muscle relaxant pregnancy purchase discount baclofen line, it is important to do a full axis I evaluation. If axis I disorders are present, both the axis I disorders and borderline personality disorder should be diagnosed. Because the personality of children and adolescents is still developing, borderline personal ity disorder should be diagnosed with care in this age group. Often, the presence of the disorder does not become clear until late adolescence or adulthood. However, some features of borderline personality disorder may overlap with those of mood disorders, complicating the differential diagnostic assessment. However, in borderline per sonality disorder, the mood swings are often triggered by interpersonal stressors. Depressive features may meet criteria for major depressive disorder or may be features of the borderline personality dis order itself. Depressive features that appear particularly characteristic of borderline personality disorder are emptiness, self-condemnation, abandonment fears, self-destructiveness, and hope lessness (91, 92). It can be particularly difficult to differentiate dysthymic disorder from bor derline personality disorder, given that chronic dysphoria is so common in individuals with borderline personality disorder. In other cases, what appear to be features of borderline personality disorder may constitute symptoms of an axis I disorder. A more in-depth consideration of the differential diag nosis or treatment of the presumed axis I condition may help clarify such questions. Although borderline personality disorder may be comorbid with dissociative identity disorder, the latter (unlike borderline personality disorder) is characterized by the presence of two or more distinct identities or personality states that alternate, manifesting different patterns of behavior. Borderline personality disorder is diagnosed predominantly in women, with an estimated gender ratio of 3:1. It is approximately five times more common among first-degree biological relatives of those with the disorder than Treatment of Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder 43 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. There is also a greater familial risk for substance-related disorders, antisocial personality disorder, and mood disorders. Early adulthood is often characterized by chronic instability, with episodes of serious affective and impulsive dyscontrol and high levels of use of health and men tal health resources. Later in life, a majority of individuals attain greater stability in social and occupational functioning. In the largest follow-up study to date (137), about one-third of patients with borderline per sonality disorder had recovered by the follow-up evaluation, having solidified their identity during the intervening years and having replaced their tendency toward self-damaging acts, in ordinate anger, and stormy relationships with more mature and more modulated behavior pat terns. One-half to three-quarters will have by that time achieved stable full-time em ployment. These studies concentrated on patients with borderline personality disorder from middle-class or upper-middle-class families. Patients with borderline personality disorder from backgrounds of poverty have substantially lower success rates in the spheres of intimacy and work. Virtually all of the studies involved adults with borderline personality disorder. While the results may be applica ble to adolescents, there is a paucity of research that has examined the efficiency of these treat ments for this age group. Although such studies are necessary to establish that a par ticular treatment is effective, there may be limits to how generalizable the study findings are. For example, inclusion and exclusion criteria result in particular types of patients being in volved in a study. When reviewing the data presented in this guideline, clinicians should con sider how similar their patient is to the population included in a particular study. This is particularly important because of the heterogeneous nature of borderline personality disorder symptoms. In addition, many studies have been rela tively short-term; longer-term treatment outcome studies are needed. Another issue to consider is that some studies are done in specialized research settings with more expertise and training in the treatment modality than is generally available in the com munity. In addition, the amount of treatment provided in a study may be greater than is actu ally available in the community. When evaluating studies of psychosocial treatments that consist of multiple elements, such as psychodynamic psychotherapy, it may be difficult to know which elements are responsible for the treatment outcome. Another factor to consider is that patients in certain studies of psy chosocial treatment were also taking prescription medication, and no steps were taken to con trol for these effects. Conversely, patients in some studies of medication efficacy also received psychotherapy, and no steps were taken to control for these effects. Therefore, the literature on the efficacy of any one particular treatment is often confounded by the presence of other simul taneous treatments. It can be difficult, then, to isolate the impact of a single modality in most treatment efficacy studies involving patients with borderline personality disorder. In clinical practice, a combination of treatment approaches is often used and appropriate. Few data are available on the complex treatment regimens often required by the realities of clin ical practice. Many clinically important and complex treatment questions have not been (and are unlikely to ever be) addressed in re search studies. Psychodynamic psychotherapy draws from three major theo retical perspectives: ego psychology, object relations, and self psychology. Most therapeutic approaches to patients with borderline personality disorder do not adhere strictly to only one of these theoretical frameworks. The approach of Stevenson and Meares (20, 138), for example, encompasses the self-psychological ideas of Kohut and the object relations ideas of Winnicott, whereas the technique of Kernberg et al. At the more exploratory end of the continuum, the goals of psychodynamic psychotherapy with patients with borderline personality disorder are to make unconscious patterns more consciously avail able, to increase affect tolerance, to build a capacity to delay impulsive action, to provide insight into relationship problems, and to develop reflective functioning so that there is greater appre ciation of internal motivation in self and others. On the supportive end of the continuum, the goals involve strengthening of de fenses, the shoring up of self-esteem, the validation of feelings, the internalization of the thera peutic relationship, and creation of a greater capacity to cope with disturbing feelings. Treatment of Patients With Borderline Personality Disorder 45 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. Of these interventions, only interpretation is unique to the psychodynamic approach. The more exploratory interventions (interpretation, confrontation, and clarification) may be fo cused on either transference or extratransference issues. In its simplest form, interpretation involves making something con scious that was previously unconscious. An interpretation is an explanatory statement that links a feeling, thought, behavior, or symptom to its unconscious meaning or origin.
Cheap 10 mg baclofen amex
Magnets Magnets are commonly used as an alternative treatment for musculoskeletal disorders spasms right flank cheap baclofen 10mg otc, including heel pain. Magnets are not invasive, have no adverse effects, and are low cost, but are not recommended for treatment of plantar heel pain. Thus, night splints are recommended for chronic and subacute plantar fascial heel pain. Author/Year Score Sample Comparison Results Conclusion Comments Study Type (0-11) Size Group Batt 5. Improvement less than 12 Study suggests rate, defined months lack of efficacy as decrease duration. No splints significant dorsiflexion true cross-over fasciitis used in either differences night splints design, rather group for final 4 found can be an treatment months of study. Recommendation: Custom Orthoses for Acute, Subacute, or Chronic Plantar Fasciitis There is no recommendation for or against the use of custom orthoses for acute, subacute, or chronic plantar fasciitis. Recommendation: Orthoses for Prevention of Plantar Fasciitis or Lower Extremity Disorders There is no recommendation for or against the use of orthotic devices for the prevention of plantar fasciitis or lower extremity disorders. Thus, there is limited evidence for short-term functional benefit from the use of orthoses and no evidence of long-term benefit. In comparison with other treatments, orthoses were demonstrated to be equivalent in efficacy to night splints,(212) (Roos 06) supportive shoes,(221) (Chalmers 00) Achilles and plantar stretching exercises,(219) (Pfeffer 99) electrical stimulation(222) (Stratton 09) and in a low-quality study, the airheel device. A low-quality randomized trial found demonstrated benefit in reducing acute leg and foot pain in referees during a tournament from the use of heel cups. These devices are non-invasive, have few adverse effects, and are generally low cost for devices that are not custom-made; therefore, they are recommended. There is insufficient evidence for orthotics for prevention and therefore, there is no recommendation for or against their use. All had Foot Health function and with mean of plaster molds of Status may also 12 months. All insert, 88%; 3) program, a stretching fasciitis groups received felt insert, 81%; prefabricated program. Regardless, there were no significant differences in outcomes at 3, 6, or 12 months. Those in the Achilles group were crossed over to plantar stretching, and improved significantly over a 2-year period, similar to the first group. Another moderate-quality trial comparing stretching to calcaneal taping, sham taping, and no treatment over a 1-week period found no benefit from gastrocnemius and plantar fascia stretching. One moderate-quality study used stretching as a treatment arm to compare efficacy of orthotic interventions. Author/Year Score Sample Comparison Results Conclusion Comments Study Type (0-11) Size Group Pfeffer 6. Each group 4) stretching prefabricated However, performed only, 72%; and shoe insert is percentages of Achilles and 5) custom more likely to improvement plantar fascia orthosis, 68%. Recommendation: Heel Taping for Acute or Subacute Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain the use of heel taping is recommended as a short-term treatment for acute or subacute plantar fasciitis or heel pain. Recommendation: Heel Taping for Chronic Plantar Fasciitis or Heel Pain There is no recommendation for or against the use of heel taping for the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis or heel pain. Taping was limited by high adverse events (28%) including taping too tight, new pain, and allergic reaction to the tape. Low-Dye taping is described as an adjunct to other treatment arms in one moderate-quality study,(188) (Osborne 06) but no conclusions regarding its efficacy compared to other interventions or to no treatment can be made. There is one moderate-quality trial comparing calcaneal taping to stretching, sham taping, and no treatment for short-term treatment of plantar heel pain. Data Treatment foot function, patients with suggest no effect general foot plantar heel differences in measured over health scores all pain. Acupuncture is minimally invasive, has minimal adverse effects, and, depending on numbers of treatments, is moderately costly. Author/Year Score Sample Comparison Results Conclusion Comments Study Type (0-11) Size Group Zhang 8. Both treatment with plantar limiting arms statistically fasciitis is generalizability. The mechanism of action is unknown, but shockwaves are purported to reduce pain and enhance healing. There have been challenges interpreting studies as the amount of energy delivered, method of focusing shockwaves, treatment frequency, timing, use of anesthetics, and outcomes vary among studies. Classification schemes for energy levels of shockwave therapy have been proposed by Mainz and Kassel,(236) (Speed 04) which are summarized in Table 9. Classification Schemes for Energy Levels of Shockwave Therapy Classification Energy Flux Density Range Energy Level 2 Scheme (mJ/mm) Low 0. What if any bearing the transmission area has on treatment in musculoskeletal disorders is not addressed in the medical literature. Described protocols consisted of 2 3 treatment sessions, with varied impulse energy density (0. There are three quality studies that demonstrated benefit from a single high-energy treatment session. Another moderate-quality trial compared perpendicular to tangential application of energy, which demonstrated no difference in outcomes as both groups improved the same. Energy and normal clinical Blinding >6 directed to activity (p symptoms and uncertain. Data >12 fluoroscopy; 60 reduction from finished, all but 9 suggest low 2 months, mJ/mm; low baseline: 75% vs. No p-values has a randomized conservati provided between recognized risk patients ve groups. Author of rupture of the included for treatments states number of plantar fascia training. Active change from safety and performed by fasciitis treatment of baseline: 12 effectiveness. No 2002 intractable applications of subjective the current pilot anesthesia was plantar 1000 impulses of variable for study revealed used.
Viola Odorata (Garden Violet). Baclofen.
- Bronchitis, asthma, coughs, colds and other lung problems; trouble sleeping (insomnia); hysteria; skin diseases; and other uses.
- What is Garden Violet?
- How does Garden Violet work?
- Dosing considerations for Garden Violet.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96463
Cheap baclofen 10mg
Therefore spasms neck buy baclofen toronto, patient-management and family management programs are urgently needed not only for patients but also for their families to satisfy their needs and enhance their capabilities to support and care for patients. This will happen if there is effective communication between patients, families and their healthcare providers, as well as by improving health literacy regarding their disease and enhancing their coping skills. Interaction between patients and healthcare professionals was considered an essential aspect for therapeutic relationships. The literature showed that communication with patients about their experienced symptoms had a positive influence on their health outcomes. Results showed that when discussion about experienced symptoms took place, patients were more satisfied with the provided care, less likely to worry after a visit, and had 332 greater symptom improvement two weeks post-visit. Self-management or self-care interventions have been found to be beneficial in health outcomes of patients with chronic diseases such as heart failure, cancer and asthma. However, their impacts on patients with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis are uncertain and need research. The only identified quasi-experimental study that was conducted among Iranian cirrhotic patients demonstrated that a self-care educational intervention could significantly improve abdominal symptoms, fatigue, systemic symptoms, activity, worry and emotional domains, without significant changes in disease severity. In this study, the majority of patients reported that depression, decreased appetite and joint pain limit their daily activities. Patients with chronic disease usually make daily decisions about how to self manage their illness. Thus, collaboration between the patient and healthcare professional has become an essential paradigm of providing and enhancing self management interventions. Self-management interventions complement traditional methods of care by supporting patients to be active members in managing their chronic condition. Traditional patient education offers only information and technical skills, while self-management education teaches problem-solving skills (Bodenheimer et a. The results supported the validity of these tools and their reliability among patients with cirrhosis in Egypt, and they can also be used in future research or clinical practice. Therefore, this study is the foundation for developing future research in symptom management. In 2008, the Egyptian Ministry of Health launched a National Control Strategy for treating and preventing viral hepatitis, including the opening of 20 national treatment reference centres providing antiviral hepatitis for free to those with national health insurance or who cannot pay (Guerra et al. There is a need to develop medical research that focuses on the treatment of viral hepatitis (Dalglish 2008), and to construct specific liver disease institutes. Bowling (2005) maintains that a medical model is no longer enough; particularly in cases of chronic or life threatening diseases. Thus, sufficient and qualified healthcare providers, nurses in particular, are considered the backbone of the healthcare system worldwide (Ma et al. In Egypt, the nursing sector faces many challenges; a shortage of nurses in general and qualified nurses in particular (Farag 2008). A brief background explanation will help to understand why the quality of nursing in Egypt is so low. The majority of qualified nurses prefer to work in private hospitals, a teaching career or migrate to countries where nurses are paid more (Farag 2008). Therefore, the majority of current nurses in the public health sector, which is the major sector in Egypt, are without a basic standard of nursing qualification. The reform process is still being implemented as it aims to increase the number of qualified nurses by improving the quality of university nursing education and by increasing the number of admitted students and to stop secondary school nursing (Ma et al. However, the reform has faced several obstacles such as financial restrictions and stakeholder resistance (Bossert and El Rabbat 2012). Thus, supporting patients to engage in their daily activities as far as possible can be achieved by providing self-management programs. Healthcare policy should support nurses by providing continuous development programs, and establishing evidence based infrastructure. For example in the one of the developed Western countries, the Scottish Government (2010, p. Therefore continuous upgrading of the healthcare system through staff development and training together with the provision of resources is important for increasing the quality of healthcare services. Delivering high quality healthcare that produces better health outcomes for patients requires qualified staff with skills and knowledge that makes them competent to deliver high quality care. The main problem was staff resistance to change especially in the areas of: (1) working as a team, (2) delivering care as an integrated team and (3) following standard procedures (El Hosseiny 2010). Thus, a person-centered approach with communication not only between healthcare professionals but also with patients and their family is at the heart of a quality healthcare strategy. Patient reported outcomes, patient experience of access, self-assessed general health and healthcare experience are some of the quality outcomes measures. Patients are the greatest source of information to help healthcare providers to decide whether a goal is achieved. However, patient experience regarding their disease or the medical intervention provided has not been routinely collected in clinical practice (Ware et al. Furthermore, lay people should be involved in the development of services to cover patient needs and expectations, as well as understanding barriers to 340 receiving appropriate care. Patients with high social support were more likely to report high adherence to self-care programs. Therefore, it is highly recommended to enhance the social support to people with liver cirrhosis in Egypt by developing effective intervention programs. Therefore, a qualitative approach is recommended to explore why cirrhotic patients in Egypt, particularly females, have lower perceived social support and higher severity of some symptoms, such as depression, than men. There are different sources of support: (1) natural or primary support provided by family and (2) professional support provided by healthcare professionals (Lanza and Revenson 1993). Perceived social support from healthcare providers has not been investigated in patients with liver disease or cirrhosis in Egypt or other chronic illnesses. Results showed that no participant reported a healthcare provider; therapist or counsellor in their social network, while only two listed a religious person. This suggests that Egyptian patients may not recognise that healthcare professionals 342 are a source of support. Therefore it may be useful to explore how cirrhotic or liver disease patients in general perceive the availability and adequacy of support from their healthcare provider and the types of social support available. Types of social support in general have been explored in people with other chronic diseases; however, they have not been investigated in patients with liver disease or cirrhosis, particularly in Egypt.
Purchase baclofen cheap
Blut 1984; Reactive haemophagocytic syndrome in children with in ammatory disorders spasms treatment discount 25 mg baclofen visa. Chocova Z, Hruskova Z, Mareckova H, Svobodova B, Duskova D, Bednarova V, International recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of patients with ac et al. Recent under gamma globulin as rst line therapy in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: an standing on diagnosis and management of central nervous system vasculitis in open study in 11 adult patients. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in a patient with lupus serositis and Neurology 1997;48:712-6. Mechanisms of action of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy disorder affecting neurotransmission of gamma-aminobutyric acid. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial: treatment of non-infectious uveitis. In amm Allergy Drug Targets 2013;12: intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with diffuse cutaneous sys 38-45. Ocul diffuse scleroderma successfully treated with high-dose intravenous immune Immunol In amm 2000;8:49-57. Ann Allergy 1989;63: steroids may improve clinical outcomes during hospitalization for Henoch 327-30. De ciency of IgG4 in children: association of purpura with response to intravenous immunoglobulin infusion. IgG3 de Intravenous immunoglobulin in Henoch-Schonlein purpura complicated by cere ciency: common in obstructive lung disease. Asthma and noglobulin infusion in polyarteritis nodosa: report on one case and review of the selective immunoglobulin subclass de ciency: improvement of asthma after literature. Intravenous gamma-globulin therapy in bronchial case of common variable immunode ciency syndrome associated with Takayasu asthma. Treatment of systemic and renal-limited vasculitic disorders with immunoglobulin in severe childhood asthma. Mechanisms of gluco treatment of systemic vasculitis with intravenous immunoglobulin. Intra steroid-sparing effect of intravenous immunoglobulin in children and adolescents venous immunoglobulin therapy for autoimmune diabetes mellitus. A preliminary trial of high-dose intravenous spective, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study on the effect of immunoglobulin to a patient with euthyroid ophthalmopathy. Thyroidology high-dose, intravenous immunoglobulin in children and adolescents with severe 1989;1:93-5. Autoimmune uveitis: clinical, asthma: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Serum IgG autoantibodies directed against the alpha chain of Fc epsilon matol Rep 2002;4:474-82. Mechanisms of autoimmune activation of basophils in gamma-globulin treatment for Kawasaki disease: the nationwide surveys in Japan. Effect of high-dose intrave Intravenous gamma-globulin treatment and retreatment in Kawasaki disease. Br J Dermatol 1998; diction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawa 138:101-6. Br J Dermatol 2003; of immunoglobulin plus prednisolone for prevention of coronary artery abnormal 149:836-40. Ann Dermatol Vene of non-responsiveness to standard high-dose gamma-globulin therapy in patients reol 2004;131:65-9. Analysis of potential risk factors associated with nonresponse to initial intrave 302. Omalizumab, an Anti-IgE mAb, receives approval for nous immunoglobulin treatment among Kawasaki disease patients in Japan. Long-term ef cacy of intravenous intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in Kawasaki Disease. Korean Circ J 2011; immunoglobulin therapy for moderate to severe childhood atopic dermatitis. J Acquir Immune De c Syndr 1999;22: globulin to treat severe atopic dermatitis in children: a case series. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin: a report of three patients and review of 2008;28:851-9, x. Pathophysiology of septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syn nereol 2003;83:433-7. A randomized controlled as adjunct therapy for severe group B streptococcal disease in the newborn. Am J evaluator-blinded trial of intravenous immunoglobulin in adults with severe atopic Perinatol 1990;7:1-4. Prevention of infection in multiple trauma patients by high-dose intra Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for severe Clostridium dif cile colitis. Intravenous immunoglobulin for suspected or subsequently Dis Colon Rectum 2006;49:640-5. Use of intravenous immune globulin in addition to antiviral therapy in the treat 344. Intraventricular gamma-globulin for the management of interstitial pneumonitis due to cytomegalovirus with ganciclovir and intrave of enterovirus encephalitis. Respira encephalitis and myositis-fasciitis with intravenous immune globulin therapy in a tory syncytial virus upper respiratory tract illnesses in adult blood and marrow patient with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Entero globulin for respiratory syncytial virus disease in adult bone marrow transplant viral meningoencephalitis in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: intensive immuno recipients. Treatment of potentially life-threatening enterovirus in evidence-based medicine. Discovery of ulin in adult varicella pneumonia complicated by acute respiratory distress syn structurally diverse small-molecule compounds with broad antiviral activity drome. Chronic enteroviral adenoviral pneumonitis with intravenous ribavirin and immunoglobulin. Thorax meningo-encephalitis in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia: favourable response 1995;50:1219-20. Successful treatment of chronic parvovirus B19 infection by high-dose immu immunoglobulins for treatment of acute rotaviral gastroenteritis. Intrauterine anemia due to parvovirus B19: successful treatment with intrave munoglobulins for treatment of protracted rotaviral diarrhea. Severe rotavirus nous immunoglobulin therapy in 3 cases of parvovirus B19-associated chronic fa associated diarrhoea following bone marrow transplantation: treatment with oral tigue syndrome. Intravenous immunoglobulin in acute rheumatic fever: a randomized human serum immunoglobulin in immunode cient patients with viral controlled trial. Dutch course of clinical response to intravenous immunoglobulin in chronic Guillain-Barre Study Group. Effect of methylprednisolone when added to standard treatment with intrave December 4, 2016. Overview of the pathogenesis and treatment of ized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic in ammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with intravenous immuno chronic in ammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; immunoglobulin treatment in children with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Outcome of severe Guillain-Barre syndrome in children: immunoglobulin treatment in patients with motor neuron syndromes associated comparison between untreated cases versus gamma-globulin therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychia immunoglobulin therapy for Guillain-Barre syndrome in Japanese children. Emerging drugs for Guillain-Barre syn taneous immunoglobulin therapy for multifocal motor neuropathy. Immunotherapy for IgM anti-myelin-associated placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Immunoglobulin treatment polyneuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Neurology versus plasma exchange in patients with chronic moderate to severe myasthenia 1990;40:209-12.
Buy 10 mg baclofen amex
A fasciotomy (surgi cal decompression with excision of the fascia) may be needed to relieve the constrictive muscle fascia muscle relaxant drugs flexeril buy baclofen visa. The wound remains open and covered with moist sterile saline dress ings for 3 to 5 days. Pre scribed passive range-of-motion exercises may be performed every 4 to 6 hours. In an open fracture, there is the risk of osteomyelitis, tetanus, and gas gangrene. Monitor the circulation and nerve function of the affected arm and compare with the unaffected arm to determine variations, F which may indicate disturbances in neurovascular status. Cau tion the patient not to elevate the arm above shoulder level until the fracture has healed (about 6 weeks). Encourage the patient to exercise the elbow, wrist, and ngers as soon as pos sible and, when prescribed, to perform shoulder exercises. Teach the patient to support the arm and immobilize it by a sling and swathe that secure the supported arm to the trunk. Inform the patient that residual stiffness, aching, and some limitation of range of motion may persist for 6 or more months. When a humeral neck fracture is displaced with required xation, exercises are started only after a prescribed period of immobilization. Use well-padded splints to initially immobilize the upper arm and to support the arm in 90 degrees of exion at the elbow, use a sling or collar and cuff to support the forearm, and use external xators to treat open fractures of the humeral shaft. Teach patient to perform pendulum shoulder exercises and isometric exercises as prescribed. Evaluate the patient for paresthesia and signs of compromised circulation in the fore arm and hand. Reinforce information regarding reduction and xation of the fracture and planned F active motion when swelling has subsided and healing has begun. Explain care if the arm is immobilized in a cast or posterior splint with a sling. Teach and encourage patient to do gentle range-of motion exercise of the injured joint about 1 week after inter nal xation. If the fracture is dis placed, reinforce the need for postoperative immobilization of the arm in a posterior plaster splint and sling. Encourage the patient to carry out a program of active motion of the elbow and forearm when prescribed. They are frequently seen in elderly women with osteoporotic bones and weak soft tissues that do not dissipate the energy of a fall. Reinforce care of the cast, or with more severe fractures with wire inser tion, teach incision care. Instruct patient to keep the wrist and forearm elevated for 48 hours after reduction. With a nondisplaced fracture, the n ger is splinted for 3 to 4 weeks to relieve pain and protect the ngertip from further trauma, but displaced fractures and open fractures may require open reduction with internal x ation, using wires or pins. Mon itor for hemorrhage and shock, two of the most serious con sequences that may occur. Palpate both lower extremities for absence of peripheral pulses, which may indicate a torn iliac artery or one of its branches. In male patients, do not insert a catheter until the status of the ure thra is known. Monitor for diffuse and intense abdominal pain, hyperactive or absent bowel sounds, and abdominal Fractures 311 rigidity and resonance (free air) or dullness to percussion (blood), which suggest injury to the intestines or abdominal bleeding. If patient has a fracture of the coccyx and experiences pain on sitting and with defecation, assist with sitz baths as prescribed to relieve pain, and administer stool softeners to prevent the need to strain on defecation. Frequently, these patients have associated multiple trauma and develop shock from a loss of 2 to 3 units of blood. Assist patient in performing active and passive knee exercises as soon as pos sible, depending on the management approach and the sta bility of the fracture and knee ligaments. Encourage patient to perform hip, foot, and knee exercises within the limits of the immobilizing device. Assist patient to cough and take deep breaths by splinting the chest with hands or pillow during cough. Reassure patient that pain associated with rib fracture diminishes signi cantly in 3 or 4 days, and the fracture heals within 6 weeks. Monitor for complications, which may include atelectasis, pneumonia, a ail chest, pneumothorax, and hemothorax. Acute gas tritis lasts several hours to a few days and is often caused by dietary indiscretion (eating irritating food that is highly sea soned or food that is infected). A more severe form of acute gastritis is caused by strong acids or alkali, which may cause the mucosa to become gangrenous or to perforate. Chronic gastritis is a prolonged in ammation of the stom ach that may be caused either by benign or malignant ulcers of the stomach or by bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori. G Medical Management Acute Gastritis the gastric mucosa is capable of repairing itself after an episode of gastritis. As a rule, the patient recovers in about 1 day, although the appetite may be diminished for an additional 2 or 3 days. If gastritis is due to ingestion of strong acids or alkali, dilute and neutralize the acid with common antacids (eg, aluminum hydroxide); neutralize alkali with diluted lemon juice or diluted vinegar. If corrosion is extensive or severe, avoid emet ics and lavage because of danger of perforation. Fiberoptic endoscopy may be necessary; emergency surgery may be required to remove gangrenous or perforated tissue; gastric resection (gastrojejunostomy) may be necessary to treat pyloric obstruction. Glaucoma the term glaucoma is used to refer to a group of ocular con ditions characterized by optic nerve damage.
Purchase baclofen online from canada
Since sensiti zation is considered crucial in the induction of autoimmune disease muscle relaxant drugs medication buy baclofen 10 mg with mastercard, the potential to induce sensitization should be considered a hazard. Although frequently used in experimental settings and as a screening assay, the test is not formally validated. Supporting its potential as a first-tier assay, the popliteal lymph node assay allows screening of a set of structurally related compounds so as to select the least sensi tizing, which is relevant in particular in case of drug evaluations. For instance, mercury-induced autoimmune glomerulonephritis in Brown Norway rats is transient and resolves spontaneously and cannot be induced again in the same animal. In contrast, the fact that low-dose tolerance occurs with certain chemicals suggests that a threshold exists. Chemicals affecting these known processes could be at increased potential for inducing autoimmune reactions. For example, laboratory studies have shown that thymolytic chemicals (such as cyclosporin) can induce autoimmunity when given neonatally by altering normal patterns of autoreactive T cell deletion, a process that occurs in the thymus early in life. Chemicals that form protein adducts or damage tissue in such a way as to allow expression of cryptic determinants. Common features associated with many drugs that induce autoimmune diseases include their ability to serve as myeloperoxidase substrates. The underlying biology for the latter associations is less clear but may involve formation of the specific antigenic epitopes responsible for the autoimmune response. With regard to the association with myeloperoxidase substrates, it has been suggested that many of the chemicals require metabolism in proximity to immune cells in order to be antigenic; immune cells such as monocytes contain high levels of myeloperoxidase. Also of potential concern are endocrine disruptors, as hormonal influences, particularly sex ster oids, appear to play a role in many autoimmune diseases. The disposition of a chemical in an organism is dependent upon the processes of absorption, distribu tion, metabolism, and excretion, defined as toxicokinetic data. Qualitative and quantitative information on each of these processes would be useful in risk assessment. For autoimmune diseases, toxicokinetic data may be helpful in identifying the potential organ systems that are likely to be involved or the responsible metabolite. There are special issues in designing and standardizing epidemiological studies for general risk assessment that also apply for chemical-induced autoimmune dis ease. Randomized trials of environmental exposures are generally not feasible or ethical. Epidemiological studies use methodologies developed for observational research to reduce the potential role of confounding, selection bias, and misclassification of exposure and of disease that may bias the estimates of disease association, increase the imprecision or uncertainty of the estimates, or limit the ability to apply the results to the general population. Prospective studies in which exposure assessment is determined prior to disease onset avoid the potential problem of a differential misclassification of exposure based on disease status. For both prospective and retrospective designs, however, the adequacy of exposure assessment, in terms of both sensitivity and specificity, is extremely important and has been demonstrated to affect not just the precision, but the magnitude and direction of observed associations between exposures and autoimmune diseases (Parks et al. In addition, there are some unique challenges in epidemiological studies for risk assessment in chemical-induced autoimmunity. Furthermore, there are no population-based disease registries for most auto immune diagnoses, and the diagnosis can be difficult to ascertain accurately. For example, most cases of a lupus-like illness caused by procainamide or hydralazine usually resolve when the drug is discontinued. Several forms of autoimmune disease, such as Hashimoto thyroiditis and Graves disease, may arise several weeks after delivery. Characteristically, these forms of postpartum auto immune diseases clear spontaneously after several months and, thus, may be difficult to capture in retrospective studies. As described in detail elsewhere in this document, a variety of intrinsic factors. While there is varia bility in the extent of female predominance and no strong association between degree of female predominance and type of disease or age at onset, sex and/or hormonal status clearly play a role in disease susceptibility. Although a majority of autoimmune diseases are less common in children and adolescents, the relative influence of early-life exposures to environmental chemicals or infectious agents on the incidence and severity of disease later in life is largely unexplored. When insufficent evidence exists pertaining to susceptibility, the assumption of equality is generally used. Studies have shown that genetic predisposition plays an impor tant role in susceptibility in the development of autoimmune diseases. The genetic basis for these differences is likely due to functional polymorphisms contained within multiple genes, each of which, by modulating corresponding protein expression, influences disease susceptibility. With the advent of genetic screening assays and their applica tion in population-based epidemiological studies, it may be possible in the near future to establish quantitatively the increased risk associated with these factors that can be applied to the risk assessment. Our lack of understanding regarding the contribution of these individual exposures to the risk of autoimmune disease in genetically suscep tible individuals and the potential for cumulative interactions of many of these components is a significant challenge for the risk assessment process. Thus, in addition to the prevalence of disease, considera tion of the burden of autoimmune disease should include mortality risk and the impact of morbidity (direct costs of health-care utiliza tion and indirect costs from effects of employment, overall quality of life, and burden on non-paid caregivers). The annual per patient direct costs of hospitalization, outpatient services, and medications in rheumatoid arthritis have been estimated as approx imately 2000 euros, with a range of approximately 5 to 10-fold. Substantial variability is seen across studies and countries (Rat & Boissier, 2004; Rosery et al. In a Canadian study of multiple sclerosis, the average cost associated with remission. There are few studies pertaining to costs of many of the other autoimmune diseases. The development of new therapeutic agents has led to a substantial increase in medication costs for rheu matoid arthritis and other diseases (Rubio-Terres & Dominguez-Gil Hurle, 2005; Sorensen & Andersen, 2005). Studies on several diseases have reported that a large percentage (30% or more) of patients are unable to work, and this figure increases with disease duration (Woolf & Pfleger, 2003; Lacaille, 2005; Alarcon et al. Furthermore, the indirect costs associated with job or produc tivity loss may be greater than the direct costs associated with health-care utilization (Phillips, 2004; Rat & Boissier, 2004; Hulsemann et al. In conclusion, much of the information needed to address the risk of chemical-induced autoimmune diseases is not available. Autoimmune diseases include a wide variety of illnesses tar geting many sites in the body. Furthermore, autoimmune mechanisms play a role in many other diseases; hence, more than these 5% will encounter autoimmune-associ ated health effects. Autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases are consequences of multifactorial phenomena. In addition to intrinsic factors, exogenous factors include infections, dietary factors, and phys ical and chemical agents. There is growing evidence that a wide array of environmental agents and therapeutics produce autoimmune-like diseases or exacerbate pre-existing autoimmune diseases. The interaction of intrinsic and environmental factors and their consequences for autoimmune disease are poorly understood. Drug-induced autoimmune diseases, autoimmune-like disorders, and hypersensitivity reactions are a major concern and have caused the withdrawal of drugs from the market or restriction of their use. There is inadequate information on the prevalence of the various diseases, particularly in countries other than Europe or North America. There is epidemiological evidence of increasing incidence and prevalence of certain autoimmune diseases in highly indus trialized countries, which cannot be attributed to better diag nostics alone. The utility of the available methods for clinical measurement of immune responses has not been validated for the identification of chemical-induced autoimmunity.

