Zudena
Order zudena overnight
So impotence nitric oxide generic 100 mg zudena with visa, the two components of the loss function are defined as follows: 1 = log 1 = 1 2 2 + where L is the total number of labels, K denotes the batch size. The results of automatically segmented tumors, denoted by A, can be compared with manually segmented tumors by human experts, denoted by B, which are considered as ground truth for evaluation. It measures states the similarity between two volumes A and B, corresponding to the output segmentation of the model and clinical ground truth annotations, respectively. Employing Sensitivity with Specificity can provide a good assessment of the segmentation result. This metric indicates the segmentation quality at the border of the tumors by evaluating the greatest distance between the two segmentation surfaces, and is independent of the tumor size. Mean, standard deviation, median and 25th and 75th percentile are given for Dice and Sensitivity metrics in Table 1 and for Specificity and Hausdorff distance in Table 2. In this1 context, we can compare our segmentation results with those of other participants. In these figures, boxplots show quartile ranges of the scores; whiskers and dots indicate outliers; and x indicates the mean score. Also, other interesting perspective consists to use ensemble learning methods, like Stacking and Blending, to improve segmentation per formance in tumor core and active tumor regions. The dense connec tivity pattern used in the segmentation network enables eective reuse of features with lesser number of network parameters. In a clinical setup this time consuming process is carried out by radiologists, however this approach becomes in-feasible when number of pa tients increase. Survival analysis is time prediction problem, which aids in better patient care and treatment planning. The training dataset comprises of 210 high grade glioma volumes and 75 low grade gliomas. Additionally on the training data, each subject was provided with pixel level segmentation. For the task of survival prediction, the training dataset included age, survival days and the resection status of 163 high grade glioma patients. The class imbalance among the various classes in the data was cir cumvented by extracting relatively more number of patches extracted from lesser frequent cases such as necrosis (class 1) when compared to edema. Figure 2 il lustrates the number of patches extracted around the pixel of each class. The network accepts an input of dimension 643 and predicts the class associated to all the voxels in the input. The dense connection between the various convolutional layers in the network aids in eective reuse of the features in the network. The presence of dense connections between layers lead to requiring more computational resources. This bottleneck is circumvented by keeping the number of convolutions to a small number say 4. To further address the issue of class imbalance in the network, the parameters of the network were trained by minimizing weighted cross entropy. The weight associated to each class was equivalent to the ratio of median of the class frequency to the frequency of the class of interest. The Table 1 lists the features extracted for survival analysis which is further elaborated below. This is the ratio of the volume of enhancing tumor region to the whole tumor volume. Hence, this is the ratio of edema and enhancing tumor regions volume to the whole tumor. Hence, this feature gives the ratio of volume of the tumor core to the volume of the whole tumor. Comparing the performance of network on the held out test data and the validation data, apart from generating good segmentation the network general izes well on the unseen data. Table 2: Performance of the segmentation on the held out test data (n=40) Whole Tumor Tumor Core Active Tumor Mean 0. In images d and e, Green, Yellow & Red represent Edema,Enhancing Tumor and Necrosis present in the lesion. In images d and e, Green, Yellow & Red represent Edema, En hancing Tumor and Necrosis present in the lesion. The network accepts patches of size 643 as the input and predicts the class associated to all the voxels forming the input. The false positives generated by the network were minimized by using 3-D connected component analysis. Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre operative scans of the tcga-gbm collection. S Bakas, H Akbari, A Sotiras, M Bilello, M Rozycki, J Kirby, J Freymann, K Fara hani, and C. Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre operative scans of the tcga-lgg collection. Spyridon Bakas, Hamed Akbari, Aristeidis Sotiras, Michel Bilello, Martin Rozycki, Justin S Kirby, John B Freymann, Keyvan Farahani, and Christos Davatzikos. Ad vancing the cancer genome atlas glioma mri collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Bjoern H Menze, Andras Jakab, Stefan Bauer, Jayashree Kalpathy-Cramer, Keyvan Farahani, Justin Kirby, Yuliya Burren, Nicole Porz, Johannes Slotboom, Roland Wiest, et al. Thus its precise eval uation is crucially important, however it requires time and is often per formed using 2D projections that reduces analysis complexity but in creases bias. On the other hand time consuming 3D evaluation like seg mentation is able to provide precise estimation of a number of valuable spatial characteristics giving us understanding about the course of the disease. Recent studies focusing at the segmentation task report superior perfor mance of neural network based methods compared with classical com puter vision algorithms, but still, it remains a challenging problem. In this paper we present two stage approach for automatic brain tumor seg mentation. Alike recent methods in object detection our solution is based on neural networks; we employ localization network at the rst stage of the pipeline and segmentation neural network at the second stage. Among its dierent applications, it is mainly used for decease di agnostics and treatment planing. Typically these scans are analyzed by clinical experts using two dimensional cut and projection planes. Test dataset is split into two parts: validation data proposed methods can be evaluated with throughout the challenge and testing data. The performance of the methods is evaluated using Dice coecient, Sen sitivity, Specicity and Hausdordistance. Above-named challenge made a signicant impact on the evolution of compu tational approaches for tumor segmentation. In the last few years variety of al gorithms addressed to solve this problem were proposed. Compared with other methods convolutional neural networks have been showing the best state of the art performance for computer vision tasks in general and for biomedical image processing tasks in particular. In this paper we present two-stage convolutional neural network based pipeline for brain tumor segmentation. At the rst stage the tumor is localized, cropped and then segmented at the second stage. We compare multiple approaches for dening localization network and report their performance. Besides this, we com pare 3d unet [5] with its cascaded counterpart described later in this paper. This pipeline consists of two stages: tumor localization and segmentation of localized region. Generally speaking there are two possible way to predict a bound box: explicit estimation of bounding box center and size; or solution of another task like seg mentation that can be used to extract information on bounding box. Regres sion of the spatial characteristics is done using Resnet18 [6] model and Resnet10 model with Dierentiable Spatial to Numeric Transform [11]. We use unet [5, 12] and proposed cascaded unet variant as a second type of algorithms that are able to implicitly estimate values described above. Regression In order to predict the bounding box coordinates Resnet18 [6] was employed. For size prediction we employed two layer fully connected network on top of Resnet 18 [6].
Order genuine zudena line
If blood in a specimen is caused by a subarachnoid hemorrhage erectile dysfunction cures over the counter buy zudena now, the color of the fluid will look the same in all the collection tubes. It is the result of the release of hemoglobin from hemolyzed red blood cells, which begins 1 to 4 hours after hemorrhage. If the spinal fluid appears clear, cell 422 Hematology counts may be performed in a hemocytometer counting chamber without using diluting fluid. Cell counts should be performed promptly since cells begin to disintegrate within about 1 hour. If delay in testing is unavoidable, the specimen should be placed in a refrigerator at 2-10oC and dealt with at the earliest opportunity. A predominance of polynuclear cells usually indicates a bacterial infection, while the presence of many mononuclear cells indicates a viral infection. Morphologic examination When the cell count is over 30 white cells per microliter, a differential cell count is done. This may be done on a smear made from the centrifuged spinal fluid sediment, by recovery with a filtration or sedimentation method, or preferably on a cytocentrifuged preparation (This technique requires the use of a special cytocentrifuge, such as the Cytospin). The supernatant is removed, and the sediment is used to prepare smears on glass sliders. If any tumor cells or unusual cells are encountered, the specimen should be referred for cytologic examination. With the low power objective, quickly scan both ruled areas of the hemocytometer to determine whether red cells are present and to get a rough idea of their concentration. Count five squares on each side, using the four corner squares and the center square. If the number of red cells is fairly high (more than 200 cells per ten squares) count fewer squares and adjust the calculations accordingly. If the fluid is extremely blood, it may be necessary to dilute it volumetrically with saline or some other isotonic diluent. It is preferable to count the undiluted fluid in fewer than 10 squares, if possible. Rinse a disposable Pasteur pipette with glacial acetic acid, drain it carefully, wipe the outside completely dry with gauze, and touch the tip of the pipette to the gauze to remove any excess acid. Mix the spinal fluid with the acid coating the pipette by placing the pipette in a horizontal position and removing your finger from the end of the pipette. With the low-power objective, quickly scan both ruled areas of the hemocytometer to determine whether white cells are present, and to get a rough idea of their concentration. The white cell nuclei will appear as dark, retractile structures surrounded by a halo of cytoplasm. Using the low-power objective, count the white cells in 10mm2, 5mm2 on each side of the hemocytometer using the four corner squares and the center square 7. Do a chamber differential as the white cells are counted by classifying each white cell seen as polynuclear or mononuclear. This chamber differential is inaccurate, and a differential cell counts on a stained cytocentrifuged preparation is preferred. If it appears that the number of white cells is more than 200 cells per ten squares, count fewer squares and adjust your calculations accordingly. These cavities are lined by a contiguous membrane that forms a double layer of mesothelial cells, called the serous membrane. The cavities are the pleural (around the lungs), pericardial (around the heart), and peritoneal (around the abdominal and pelvic organs) cavities. A small about of serous fluid fills the space between the two layers and serves to lubricate the surfaces of these membranes as they move against each other. The fluids are ultrafiltrates of plasma, which are continuously formed and reabsorbed, leaving only a very small volume within the cavities. Since normal serous fluids are formed as an ultrafiltrate of plasma as it filters through the capillary endothelium, they are transudates. In determining the cause of an effusion, it is helpful to 427 Hematology determine whether the effusion is a transudate or an exudate. In general, the effusion is a transudate (which is an ultrafiltrate of plasma) as the result of a systemic disease. An example of a transudate includes ascites, an effusion into the peritoneal cavity, which might be caused by liver cirrhosis or congestive heart failure. Transudates may be thought of as the result of a mechanical disorder affecting movement of fluid across a membrane. Exudates are usually effusions that result from an inflammatory response to conditions that directly affect the serous cavity. At least three anticoagulated tubes of fluids are generally collected and used as follows: 1. A sterile heparinized tube for Gram stain and culture Gross appearance Normal serous fluid is pale and straw colored. An abnormally colored fluid may appear milky (chylous or pseudochylous), cloudy, or bloody on gross 429 Hematology observation. A cloudy serous fluid is often associated with an inflammatory reaction, either bacterial or viral. Blood-tinged fluid can be seen as a result of a traumatic tap, and grossly bloody fluid can be seen when an organ such as the spleen or liver or a blood vessel has rupture. Bloody fluids are also seen in malignant diseases states, after myocardial infarction, in tuberculosis, in rheumatoid arthritis, and in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clotting To observe the ability of the serous fluid to clot, the specimen must be collected in a plain tube with no anticoagulant. Red and white Blood cell count Cell counts are done on well-mixed anticoagulated serous fluid in a hemocytometer. If significant protein is present, acetic acid cannot be used as a diluent for white cell counts, owing to the precipitation of protein. In this case, saline may be used as a diluent and the red and white cell counts are done simultaneously. A predominance of lymphocytes suggests viral infection, tuberculosis, lymphoma, or malignancy. Slides are generally stained with Wright stain, and a differential cell count is done. The white cells generally resemble those seen in peripheral blood, with the addition of mesothelial lining cells. Generally 300 cells are counted and differentiated as to percentage of each cell type see. If any malignant tumor cells are seen or appear to be present, the slide must be referred to a pathologist or 431 Hematology qualified cytotechnologist. Normal synovial fluid is an ultrafiltrate of plasma with the addition of a high molecular-weight mucopolysaccharide called hyaluronate or hyaluronic acid. The presence of hyaluronate differentiates synovial fluid from other serous fluids and spinal fluid. It is responsible for the normal viscosity of synovial fluid, which serves to lubricate the joints so that they move freely. This normal viscosity is responsible for some difficulties in the examination of synovial fluid, especially in performing cell counts. Normal synovial fluid Normal synovial fluid is straw colored and viscous, resembling uncooked egg white. About 1ml of synovial fluid is present in each large joint, such as the knee, ankle, hip, elbow, wrist, and shoulder. Since the fluid is an ultrafiltrate of plasma, normal synovial fluid has essentially the same chemical composition as plasma without the larger protein molecules. Aspiration and analysis the aspiration and analysis of synovial fluid may be done to determine the cause of joint disease, especially when accompanied by an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the joint (effusion). The joint disease (arthritis) might be crystal induced, degenerative, inflammatory, or infectious.
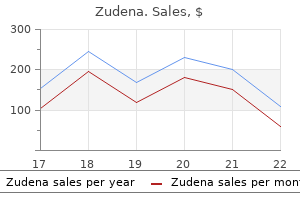
Buy zudena 100 mg low price
An athlete has relatively large muscle mass and needs an efficient oxygen delivery to the muscles when they are working erectile dysfunction daily pill buy zudena 100 mg line. If you had a high hematocrit, would you expect your hemoglobin determination to be high or low Heparin (in capillary tubes) and sodium citrate What is the bodys natural anticoagulant Calhoon: Blood drop and Blood drop and anti-A serum anti-B serum On the basis of these results, Mr. Explain why an Rh-negative person does not have a transfusion reaction on the first exposure to Rh-positive blood but does have a reaction on the second exposure. Describe the relationship between high blood cholesterol levels and cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, heart at tacks, and strokes. Attached thrombi or detached thrombi (emboli) are common causes of heart attack and stroke. Rh disease (Rh = Rhesus factor) (1) Genetics: Rh positive (+) denotes presence of D antigen. A sensitized Rh negative mother produces anti-Rh IgG antibodies that cross the placenta. Therefore, the Direct Antiglobulin test will be negative, but the Indirect Antiglobulin Test will be positive. Lewis antigen stimulates only IgM production, so maternal antibody screen may be positive, but fetus is not affected. In type O mothers, the antibodies are predominantly IgG, cross the placenta and can cause hemolysis in the fetus. The association of a type A or B fetus with a type O mother occurs in ~15% of pregnancies. Anticipate need for later ExTx for hyperbilirubinemia and have additional blood for these. Resuscitation: At birth, the major problems are cardiopulmonary and relate to effects of severe anemia, hydrops and prematurity. If ventilation is difficult, drain pleural and ascitic fluid; during paracentesis, take care to avoid puncturing the enlarged liver and spleen. Kernicterus occurs at lower levels of bilirubin in the presence of acidosis, hypoalbuminemia, prematurity and certain drugs. Although phototherapy may not eliminate the need for ExTx, it may delay ExTx and decrease the number required. In general, perform ExTx for cord bilirubin >5 mg/dL, for a rate of rise of bilirubin >0. Erythropoietin treatment will help prevent severe anemia and further transfusions (see P. The largest quantities of ferritin are found in the liver and reticuloendothelial cells. Specimen Serum is used for testing Normal concentration Serum ferritin 10-500 ng/ml Interpretation Serum ferritin levels are markedly decreased in iron deficiency anemia. Interpretation Elevated ferritin levels are common in iron overload states such as hemochromatosis and sideroblastic anemia Serum ferritin levels are elevated in patients with inflammatory diseases Precautions in interpretation When iron deficiency and inflammatory disease coexist, serum ferritin levels may be in the normal range Serum soluble transferrin receptor Principle the transferrin receptor is a transmembrane protein that transfers iron from plasma transferrin into cell. A truncated form of the tissue receptor that is complexed with transferrin is found soluble in the serum. Transferrin receptor levels reflect iron status, with receptor synthesis being rapidly induced by decreased iron levels. Specimen Serum is used Interpretation Levels of serum soluble transferrin receptors greater than 3. Describe the distribution & morphology of cells in certain common Blood Pictures Clinical Diagnostic Laboratories offer: 1. Cells are classified by morphology> Blasts Eosinophil, Lymphocyte & Neutrophil Neutrophil and Lymphocyte Neutrophils the main phagocytic cells of peripheral blood. The counter is able to plot a red cell volume histogram, and the mean is determined. Self-Assessment Question #3 Acute leukemia is characterized by presence of in the stained peripheral blood smear: a) blasts b) neutrophils c) lymphocytes d) platelet clumps e) basophils Explanation: the hallmark of acute leukemia is the increased presence of blasts in the bone marrow and in peripheral blood. Blasts are immature progenitor cells with characteristic morphology and cell surface markers. Their chronic nature makes them one of the 1 leading causes of morbidity and mortality in those countries. Objective: the aim of this study is to estimate the frequency of beta thalassemia among the students in Bahrain from 1999 to 2008. Setting: Bahraini Secondary Schools, genetic department and laboratory at Salmaniya medical complex. Preventive measures remain the best ways for lowering the incidence of these diseases. Bahrain Med Bull 2010; 32(2): Genetic diseases such as beta thalassemia are chronic in nature and require costly lifelong care and management strategies. They cause significant health care and psychosocial burdens 1-9 on the patient, the family, the health care system and the community. The frequency of this disease is high in Lebanon, Jordon, Iraq, Palestine, Egypt and other Arab countries. Nadkarni et al 1991, Al-Arrayed and 10 Haites 1995 have observed that beta thalassemia carrier rate of 2-4% in Bahrain population 23. The molecular diagnosis is essential in these diseases as the inheritance of beta thalassemia might be masked by coinheritance of sickle cell gene and/or alpha Thalassemia. Thalassemia major patient shows severe anemia in the first year of life, and are unable to maintain the hemoglobin level of 5 gm/dl. Hence, iron chelating treatment is necessary to prevent iron overload damage to the internal organs. In general, the disease may affect the spleen (often enlarged), and causes heart failure. In recent years, bone marrow transplant and stem cell transplant have shown success in some patients of thalassemia major. Most of the beta thalassemia heterozygote carriers are clinically asymptomatic with distinctive hematological phenotype represented by hypochromic, microcytic anemia and 8-9 characteristically raised levels of HbA2. Falciparum malaria was endemic in Bahrain until 1970, and soon afterward eradication was successful. The aim of this study is to estimate the frequency of beta thalassemia among the students in Bahrain. The project included planning, education sessions, blood collection, laboratory testing, and data processing, distribution of cards, data analysis and reporting. Table 1 and Figure 1 show the prevalence of beta thalassemia among these students. Only five cases of beta thalassemia homozygous status, were detected in the first year. Prevalence of beta thalassemia Trait: the number of carriers for beta thalassemia during the years 1999-2008 was 164, 212, 187, 219, 175, 212, 221, 231, 211 and 265 students respectively. Prevalence of beta thalassemia by Region in Bahrain: According to the result of 1999, some regions were observed to have a higher rate of this disease: Hidd 5. Other regions like Western region, Northern region, and Manama had only 2% prevalence rate. In the year 2008, there was a sudden increase in the frequency of beta thalassemia to 5%, which was not reported earlier. The cause of the rise of the carrier rate, and the future trend needs to be investigated.
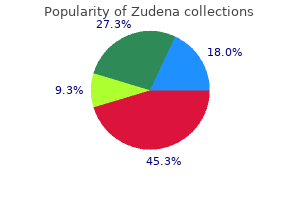
Purchase zudena 100mg line
Dosing and pressure distribution system designers and installers should provide homeowners with instructions that describe proper operation and maintenance of the system erectile dysfunction pump as seen on tv generic 100 mg zudena overnight delivery. If the system is already installed at a time of property transfer, a briefing with the previous owner of their experience with the system may be helpful. Keep trees away from the immediate area of the absorption field as their roots may enter and clog the system. Owners should consider increasing the size of an existing septic tank and absorption facilities when additions are made to homes (expansion bedrooms, installation of additional wastewater generating appliances and fixtures, etc. Groundwater diversion may also be necessary to alleviate high groundwater, which interferes with the proper operation of the facility. The absorption facility should be observed periodically for surface discharge or ponding of effluent. Observation ports can be installed at the distal end of the absorption trenches, as depicted in Figure 36, to allow monitoring of the trench system. Not used as designed for (more bedrooms, residents, vacation rental, home business, etc. Overuse of toxic chemicals or high-powered antibiotics that kill beneficial bacteria. Septic Tank: not pumped, not watertight or no outlet baffle, excess water or solids discharged. Poor fill material or compacted soil resulting in low permeability soil below the system. Failure to identify seasonal high groundwater depth; consequently the system becomes too close to or at times within the water table. Uneven distribution: part of the system overloaded (adjustment to the distribution box outlets). Uneven distribution: part of the system not used because of blockage, broken pipe or uneven settling. Failure to install trenches parallel to contours or failure to install trench bottoms level. Because a number of reasons can lead to system failure or overloading, a careful evaluation of the home, water use, plumbing, wastewater treatment system components and site conditions (soil type, groundwater depth, bedrock, drainage, etc. The solution may require simple less costly corrections or necessitate a costly system repair or replacement. Table 11 lists some common reasons for premature failure and some commonly used correction methods or designs. Designs may also need to account for additional factors that can effect daily discharge quantity and quality such as: installation of high water use products and fixtures. If the trench bottoms will be between grade and six (6) inches deep, conduct the test at six (6) inch depth. The slower of the two (2) percolation rates shall be used for design of the system. Bell should be set or siphon system purchased that will deliver the calculated dose volume only. If necessary, the total trench length of each lateral shall be rounded up to create equal trench lengths. The use of slowly permeable soils for the fill material will result in a trench system that will have a basal area larger than the minimum area calculated using the above application rates for the various treatment systems. A conventional absorption trench system is designed using the percolation rate of the fill material. A conventional absorption trench system is designed to distribute effluent evenly over the fill material basal area. Absorption Bed an absorption area comprised of a single shallow excavation, not more than 20 feet wide, that includes several distribution laterals for the distribution of wastewater effluent. Absorption Trench an absorption area comprised of long, narrow and shallow excavation(s) for the distribution of wastewater effluent. Aeration the process of transferring oxygen to wastewater treatment components or absorption areas through piping, diffusers, air source, vents or other devices. Aggregate washed gravel or crushed stone to 1 inches in diameter for absorption trench. Large washed gravel or crushed stone 2 to 4 inches in diameter is used for seepage pit annular ring. Alternate Aggregate Materials used as a substitute for conventional gravel or crushed stone aggregate when it can be demonstrated that the material provides at least the equivalent soil infiltration area and storage volume as conventional gravel or crushed stone aggregate. Application Rate the rate at which wastewater effluent is applied to a subsurface absorption 2 area expressed in gallons per day per square foot (gpd/ft) for design purposes. Baffle a flow deflecting device used in septic tanks, distribution boxes and drop boxes to inhibit the discharge of floating solids, reduce the amount of settleable solids that exit the component and reduce the exit velocity of the wastewater. The amount of oxygen, expressed in milligrams per liter (mg/L), required by bacteria to digest organic matter under aerobic conditions. Biomat a layer of biological growth and inorganic residue that develops at the infiltrative surface. Cleanout an opening providing access to wastewater treatment system components including the house sewer drain, distribution piping, distribution box, drop box and septic tank. Curtain Drain/Perimeter and Interceptor Drain/French Drain a subsurface drain designed and constructed to control ground water intrusion into the wastewater treatment system or sewer. Distribution Device a device used to uniformly distribute wastewater effluent to the absorption area or filtration area. Distribution Line the perforated pipe used to distribute wastewater effluent in the absorption area or filtration area. Diversion Ditch or Berm a designed and constructed excavation or filled area to control surface water intrusion into the wastewater absorption area on sloped sites. Drinking Water water whose physical, chemical, radiological, and biological quality is or is intended to be satisfactory for human consumption, food preparation or culinary purposes. Effective Grain Size a measure of the diameter of soil particles, when compared to a theoretical material having an equal transmission constant. It is the dimensions of that mesh screen which will permit 10% of the sample to pass and will retain 90 percent. Ground Water subsurface water occupying the saturation zone from which wells and springs are fed. Heavy Equipment all equipment that would result in the compaction of the design absorption area at a depth equivalent to the design depth of the distribution lines. House Sewer Drain Line the line that connects to the end of the house sewer drain and conveys wastewater to the first wastewater treatment system component. Infiltration the flow or movement of water into the interstices or pores of a soil through the soil interface. Invert the floor, bottom, or lowest point of the inside cross-section of a pipe or opening/slot/channel. Number 3A and 3 stone or gravel meets this size requirement and Number 3 is preferred. Local Health Department a city, county or part-county department of health or a State Department of Health District Office. Percolation the movement of water through the pores of a soil or other porous medium following infiltration through the soil interface. Rain Garden a planted depression that allows rainwater runoff from impervious areas like roofs, driveways, walkways, parking lots, and compacted lawn areas the opportunity to be absorbed. Scum the wastewater material which is less dense than water and floats on top of the water. Sewage the combination of human and household waste with water which is discharged to the 169 home plumbing system including the waste from a flush toilet, bath, shower, sink, lavatory, dishwashing or laundry machine, or the water-carried waste from any other fixture, equipment or machine. Sludge the wastewater material which is more dense than water and settles to the bottom in relatively quiescent areas. Stabilized Rate of Percolation the rate corresponding to two (2) consecutive equal or near equal percolation test results. Drainage areas, which contain water only during and immediately following precipitation or snowmelt, should not be considered a stream. Uniformity Coefficient a ratio of the diameter of soil particles obtained by sieving soil through standard U.
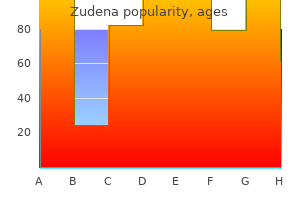
Generic zudena 100mg without prescription
Departments should agree on the conditions that are best treated in the labor and delivery area and those that should be treated in other hospital care units impotence homeopathy treatment order zudena on line amex. Qualified obstetric care providers should evaluate patients with medical or surgical conditions that could reasonably be expected to cause obstetric complications. A pregnant woman who comes to the labor and deliv ery area should be evaluated in a timely fashion. A patient with a transmissible infection should be admitted to a site where isolation techniques may be followed according to hospital policy. If a woman has received prenatal care and a recent examination has con firmed the normal progress of pregnancy, her admission evaluation may be lim ited to an interval history and physical examination directed at the presenting condition. Women who have not received prenatal care, had Intrapartum and Postpartum Care of the Mother 173 episodic prenatal care, or who received care late in pregnancy are more likely to have sexually transmitted infections and substance abuse problems. Social problems, such as poverty and family conflict, also may affect patients health. Routine obstetric screen ing tests (eg, hemoglobin level, blood type, and Rh factor), social intervention, and additional education may be needed within this limited period. Once the results of the examination have been obtained and documented, the health care pro vider responsible for the womans care in the labor and delivery area should be informed of her status. If electronic medical records are used, the electronic prenatal records should be accessible. At the time of a patients admission to the labor and delivery area, pertinent information from the prenatal record should be noted in the admission records. Because labor and delivery is a dynamic process, all entries into a patients 174 Guidelines for Perinatal Care medical record should include the date and time of occurrence. If the results of the womans antenatal laboratory evaluation are not known and cannot be obtained, blood typing, Rh D type determination, hepatitis B virus antigen testing, and serologic testing for syphi lis should be performed before the woman is discharged. Practices such as showers dur ing labor, placement of intravenous lines, use of fetal heart rate monitoring, and restrictions on ambulation should be reviewed in departmental policies. Obstetric department policies should include recommendations for transmitting to the nursery those maternal and fetal historical and laboratory data that may affect the care of the newborn. The lack of such data, perhaps because of a lack of Intrapartum and Postpartum Care of the Mother 175 prenatal care, also should be made known to the nursery personnel. The physi cian who will care for the newborn should be identified on the maternal medi cal record (see Appendix A). Health care professionals who provide anesthesia should be notified of women who may be at significant risk of complications from anesthetic procedures (eg, women with hypertension, morbid obesity, or receiving anticoagulation). Labor the onset of true labor is established by observing progressive change in a womans cervix in the setting of regular, phasic, uterine contractions. This may require two or more cervical examinations that are separated by an adequate period of time to observe change. A policy that both allows for adequate evaluation of patients for the presence of labor and prevents unnecessary admissions to the labor and delivery unit is advisable (see also Appendix G). False Labor at Term Uterine contractions in the absence of cervical change are commonly referred to as false labor. The patient may be discharged, after observation and evaluation by appropriate hospital-designated personnel and assurance of fetal well-being (see also Appendix G). Management may be dictated by the presence of overt intrauterine 176 Guidelines for Perinatal Care infection, advanced labor, or fetal compromise. In any labor occurring after rupture of membranes, vaginal examinations should be limited in number and attention paid to clean technique. Supportive laboratory testing includes vaginal pH, fern testing, and ultrasound estimation of amniotic fluid volume. These causes include leakage of alkaline urine, cervical mucus, bacterial vaginosis, and blood. However, at any gestational age, a patient with evident intrauterine infection, abruptio pla centae, or evidence of fetal compromise is best cared for by expeditious delivery. When the patient is in active labor, that health care provider should be readily available (see also Cesarean Delivery later in this chapter). Ideally, intravenous access should be secured when the active phase of labor begins. The progress of labor should be evaluated by periodic vaginal exami nations, and the obstetric provider should be notified of the patients labor progress. Sterile, water-soluble lubricants may be used to reduce discomfort during vaginal examinations. Antiseptics, such as povidone-iodine and hexa chlorophene, have not been shown to decrease infections acquired during the intrapartum period. Evaluation of the quality of the uterine contractions and pelvic examina tions should be sufficient to detect abnormalities in the progress of labor. This terminology should be used in both medical record entries and in verbal communication among obstetric personnel. Uterine contractions should be described as normal (five contractions or fewer in 10 minutes) or tachysystole (more than five contractions in 10 minutes) averaged over a 30-minute window. Fetal heart rate patterns are described by baseline rate, variability, accelera tions, and decelerations, which can be early, late, or variable. However, if there are indications for fetal scalp monitoring, it is reasonable in a woman who has a history of a recurrence of herpes simplex virus and no active lesions. The 2008 National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development workshop report on electronic fetal heart monitoring: update on definitions, interpretation, and research guidelines. Generally, induction of labor has merit as a therapeutic option when the benefits of expeditious delivery outweigh the risks of continuing the pregnancy. The benefits of labor induction must be weighed against the potential maternal and fetal risks associated with this procedure. Cervical ripening facilitates the process of cervical softening, thinning, and dilating with resultant reduction in the rate of failed induction and induction to-delivery time. Effective methods for cervical ripening include the use of Intrapartum and Postpartum Care of the Mother 181 mechanical cervical dilators and administration of synthetic prostaglandin E1 and prostaglandin E2. Indications for induction of labor are not absolute but should take into account maternal and fetal conditions, gestational age, cervical status, and other factors. The individual patient and clinical situation should be considered in determining when induction of labor is contraindicated. Generally, the contra indications to labor induction are the same as those for spontaneous labor and vaginal delivery. Each hospitals department of obstetrics and gynecology should develop written protocols for preparing and administering oxytocin solution or other agents for labor induction or augmentation. Personnel who are familiar with the effects of the agents used and who are able to identify both maternal and fetal complications should be in attendance during administration of the induction agent(s). The qualifications of personnel authorized to administer oxytocic agents for this purpose should be described. Because it is possible to introduce fluid into the uterus at too rapid a rate, each obstetric unit should 182 Guidelines for Perinatal Care establish a protocol for intrauterine pressure monitoring during amnioinfusion, or limitations of the volume and infusion rate when the technique is used. Analgesia or anesthesia during labor and delivery has no lasting effect on the physiologic status of the neonate. Available Methods of Analgesia and Anesthesia Available methods of obstetric analgesia and anesthesia include parenteral agents and regional, general, and local anesthesia. These agents can be given in intermittent doses on patient request or via patient-controlled administration. Patients exposed to high doses of narcotics are at increased risk of aspiration and respiratory arrest. There has been some concern about fetal safety with the use of nalbuphine hydrochloride; however, there is insufficient evidence at this time to recommend a change in practice with the use of this medication. Ambulation to some extent may be possible when using regional analgesia, depending on the technique used, the experience of the anesthesiologist, and the patients response. Thus, there seems to be little justification to withhold this form of pain relief from women in early labor until an arbitrary cervical dilation is achieved (ie, 4-cm cervical dilation).

Order zudena 100mg
Insect repellents can help reduce exposure to mosquito bites that may carry viruses such as West Nile virus that can cause serious illness and even death erectile dysfunction at 65 buy cheap zudena 100mg. Using insect repellent allows you to continue to play and work outdoors with a reduced risk of mosquito bites. If you are outdoors around these times of the day, it is especially important to apply repellent. Sweating, perspiration or getting wet may mean that you need to re-apply repellent more frequently. Repellents are effective only at short distances from the treated surface, so you may still see mosquitoes flying nearby. How does the percentage of active ingredient in a product relate to the amount of protection it gives Typically, the more active ingredient a product contains the longer it provides protection from mosquito bites. Actual protection will vary widely based on conditions such as temperature, perspiration, and water exposure. People who are concerned about using repellents may wish to consult their health care provider for advice. A wider selection may be available at outdoor stores or in hunting and camping sections. Using Repellents Properly What are some general considerations to remember when using insect repellents If you suspect a reaction to a product, discontinue use, wash the treated skin, and call a poison control center. There is a national number to reach a Poison Control Center near you: 1-800-222-1222. Parents should choose the type and concentration of repellent to be used by taking into account the amount of time that a child will be outdoors, exposure to mosquitoes, and the risk of mosquito-transmitted disease in the area. People can, and should, use both a sunscreen and an insect repellent when they are outdoors. While no recommendations are available at this time regarding products that combine other active ingredients and sunscreen, it is important to always follow the label on whatever product you are using. You can also apply insect repellent to your clothing, rather than directly to your skin. West Nile virus vaccine Is there a vaccine available to protect humans from West Nile virus Many scientists are working on this issue, and there is hope that a vaccine will become available in the next few years. Should people take the West Nile virus vaccine that is licensed for use in horses The effectiveness of this vaccine in preventing West Nile virus infections in horses has yet to be fully evaluated, and its effectiveness in humans is completely unknown. For these reasons, veterinary vaccines and other veterinary drugs should never be used in humans. People who live in or traveled to areas where West Nile virus activity has been identified are at risk of getting West Nile encephalitis; persons older than 50 years of age have the highest risk of severe disease. This blood test may not be positive when symptoms first occur; however, the test is positive in most infected people within 8 days of onset of symptoms. These additional tests require growth of the virus and may take a week or longer (plus shipping time) to conduct. What role do commercial laboratories play in diagnosing people with West Nile virus infection When a person goes to see a health care provider, and has symptoms of a West Nile illness a specimen may be sent to a commercial laboratory to determine if the person has been infected by West Nile virus. The results of the test will be sent to the doctor and the state health department will be informed if the results are positive. The state health department may choose to accept the positive results from the commercial lab, or they may choose to test the sample again in the state health department laboratory for confirmation of the infection. This is the first year that many of these tests have been widely used in commercial labs, and laboratories are learning more about the specific measurements used in each test. A false positive occurs when an initial tests indicates that a person does have a West Nile infection, but a later, more specific tests indicates that the person does not actually have the infection. There is no specific treatment that the person would receive due to West Nile virus infection. The person may want to work with their physician to see if another cause of the illness needs to be identified. In 2002, one case of transplacental (mother-to-child) transmission of West Nile virus was reported. Three additional pregnancies in which the expectant mother became infected with West Nile virus were detected and evaluated in 2002; none of these 3 resulted in fetal infection. In 2003 and 2004, the registry identified 77 women who acquired West Nile virus illness while pregnant. Pregnant women who become ill should see their health care provider, and those who have an illness consistent with acute West Nile virus infection should undergo appropriate diagnostic testing. Based on a 2002 case in Michigan, it appears that West Nile virus can be transmitted through breast milk. A new mother in Michigan contracted West Nile virus from a blood transfusion shortly after giving birth. Lactating women who are ill or who are having difficulty breastfeeding for any reason should, as always, consult their physicians. It is likely that the organ donor was infected by the bite of an infected mosquito, as he was reported to have spent time outdoors and infected mosquitoes were collected from a site near the persons home approximately 10 days before he died. Organ donors are screened to identify infectious risks on the basis of national organ procurement standards. There are several issues to consider: (a) time, (b) type of test and (c) potential biological differences. You should be aware of the potential risk for West Nile virus infection and the need to monitor your health. If you have symptoms of West Nile virus or other concerns you should contact your physician. If a patient who recently received a blood transfusion or organ transplantation develops a West Nile virus infection, that does not necessarily mean that the transfusion/ transplantation was the source of infection. Adulticides can be applied from hand held sprayers, truck-mounted sprayers or using airplanes. An integrated program is the most effective way to prevent and control mosquito-borne disease. An integrated mosquito management program should include several components: (1) surveillance (monitoring levels of mosquito activity, and where virus transmission is occurring), (2) reduction of mosquito breeding sites, (3) community outreach and public education, and (4) the ability to use chemical and biological methods to control both mosquito larvae and adult mosquitoes. People who are concerned about exposure to a pesticide, such as those with chemical sensitivity or breathing conditions such as asthma can reduce their potential for exposure by staying indoors during the application period (typically nighttime). This study found that "application of certain insecticides poses a low risk for acute, temporary health effects among person in areas that were sprayed and among workers handling and applying insecticides. Your local mosquito control program or health department can give information about the type of products being used in an area. Check with your health department or in the "blue" (government) pages of the phone book for the contacts in your area. Treatment would be supportive (managing symptoms, if present) and consistent with standard veterinary practices for animals infected with a viral agent. Does my dog/cat becoming infected pose a risk to the health of my family or other animals It is very unlikely that cats would be important in furthering the spread of the virus. There is also evidence that cats can become infected with the virus after eating experimentally infected mice. There is no reason to destroy an animal just because it has been infected with West Nile virus. West Nile Virus and Horses Has West Nile virus caused severe illness or death in horses
Diseases
- BANF acoustic neurinoma
- Cataract
- Cardiomyopathy spherocytosis
- Phocomelia Schinzel type
- Herrmann Opitz arthrogryposis syndrome
- Lennox Gastaut syndrome
- Duane syndrome
- Hirschsprung disease ganglioneuroblastoma
- Median cleft lip corpus callosum lipoma skin polyps
Order zudena 100mg fast delivery
Long-acting and sus excitability and suppress abnormal discharges in tained-release opioids are useful for patients with 98-100 pathologically altered neurons erectile dysfunction foundation purchase zudena 100mg overnight delivery. However, continuous pain, as they lessen the severity of the exact basis of their analgesic effects is end-of-dose pain and often allow the patient to 19 unclear. Product information (references 76-95) is from the Physicians Desk Reference, 55th edition. Therefore, additional contraindications, warnings, and side effects of that nonopioid drug apply. Also, titrate naloxone carefully to avoid profound withdrawal, seizures, and severe pain. Amitriptyline has the best-documented anal Table 26 summarizes other ways to prevent and gesic effects but also the most side effects. Antidepressants await formal evaluation in a randomized place bo-controlled trial. Mechanism of action and effects Antidepressants exhibit analgesic properties in iii. Approaches to Management of Antiepileptic Drugs, Tricyclic Antidepressants, and Local Anesthetic Side Effects Populations at Increased Risk Side Effect and Precautions Prevention and Management Sedation Elderly Titrate drug slowly and monitor drug levels, if recommended Consider changing dosing regimen or drug Administer drug at bedtime Eliminate other nonessential medications with sedating effects Consider use of mild stimulants during the day. However, this does evidence suggests that the lidocaine patch also not account for all drugs used in pain manage may be useful for other neuropathic pain, ment. These mastectomy pain, postthoracotomy pain, and include drugs used for arthritis pain. General Principles of Analgesic opioids play an important role in managing post 107 Therapy operative and obstetrical pain. However, pain stroke pain, or headache107,126-128 or, somewhat management can begin before the source of the more often, to anesthetize an upper extremity. Select the simplest approach to pain man used to manage neuropathic or cancer pain. Factors that guide this process include:19-20 encephalopathy, seizures) and cardiovascular. It may: methods of analgesia include tissue infiltration s Allow use of lower doses of some agents. Nerve blocks can be used for diag Common acceptable combination regimens nostic, prognostic, and therapeutic purposes. The goal is to use the No single route of drug administration is smallest dosage necessary to provide the desired effect with minimal side effects. However, most opioids do absorption, half-life) influence the selection of not have an analgesic ceiling, so the dosage can an appropriate route. Table 28 reviews advan be titrated upwards until pain relief occurs or tages and disadvantages of various routes of limiting side effects develop. A long Advantages: permits concomitant use of local anesthetic and shorter term catheter can be tunneled acting opioids, eliminates need for catheter reinjection, reduces under the skin or surgically rostral spread of analgesia, less risk of catheter contamination, greater implanted for long-term pain potency than systemic administration management. Signs of drug craving and/or aging common side effects of nonopioid, opioid, drug-seeking behavior. The general strategy to ments with after-hour calls for prescription managing side effects consists of:19 renewals; solicitation of prescriptions from mul s Changing the dosage or route of administra tiple physicians; reports of lost, destroyed, or tion (to achieve stable drugs levels), stolen medications; selling and buying drugs off s Trying a different drug within the same the street)19 should alert the clinician to such a class, and/or possibility. However, diagnosing addiction s Adding a drug that counteracts the effect requires extreme caution. Severe side condition and failure to treat it will hinder effects, on occasion, may require administration efforts to manage pain. However, optimal pain management decrease in the duration and/or degree of pain also includes psychological, physical rehabilita relief, which can be managed by increasing the tive, and in some cases, surgical treatment drug dose and/or frequency of administration. For example, the 1992 Agency for Combining opioids with nonopioids, or switch Health Care Policy and Research clinical prac ing to a lower dose of another opioid, may delay tice guideline on acute pain management recom the development of opioid tolerance. Such psychological interven to pain management include the pain type, dura tions may help assess and enhance patient tion, and severity; the patients preferences, cop adherence with treatment. Psychological Approaches and adaptation to pain, time constraints, reim bursement policies). Psychological interventions used in pain man agement include contingency management, cog nitive behavioral therapy, biofeedback, relax ation, imagery, and psychotherapy. In instruction sheets, audiotapes) can supplement, addition to relieving pain, such methods can but not replace, clinician efforts to instruct reduce fear and anxiety, improve physical func patients in these methods. Patients in whom psychological interventions Treatments used in physical rehabilitation may be most appropriate include those who include stretching, exercises/reconditioning (to express interest in such approaches, manifest improve strength, endurance, and flexibility), anxiety or fear, have inadequate pain relief after gait and posture training, and attention to appropriate pharmacologic interventions, or ergonomics and body mechanics. Surgical Approaches impede a positive response to medical interven 214 Most pain can be managed by simple nonin tion. However, more invasive typically an integral part of the interdisciplinary approaches, including surgery, are sometimes approach to the management of chronic pain. Orthopedic approaches to pain manage Because such management usually involves reha ment include both nonsurgical (conservative) bilitation, psychological approaches are typically approaches and various surgeries. Psychologists rarely treat pain directly but e One reason that medical interventions sometimes fail or mini rather work with other health care professionals mally succeed is poor patient adherence to treatment regimens. For exam population as a whole are relatively high (30% to 60%), and patients tend to underreport poor adherence and overreport good ple, a psychologist can improve communication adherence. Examples of Psychological Methods Used to Manage Pain Intervention Definition Purpose/Goals Uses Patient education Provision of detailed information about disease or Can reduce pain, analgesic Postoperative pain, interventions and methods of assessing and use, and length of hospital chronic pain managing pain. The patient or clinician controls stimulation using non-implanted system components. Examples of this section reviews the general approach to the treatment of acute pain, including treatment Multimodal Therapy goals, therapeutic strategies, and elements of pain management. Acute pain is more Benefits of multimodal analgesia include earli difficult to manage if permitted to become 1 er oral intake, ambulation, and hospital dis severe, so prompt and adequate treatment of charge for postoperative patients as well as high acute pain is imperative. Treatment goals and er levels of participation in activities necessary strategies for acute pain can be summarized as: for recovery. Compelling as multimodal analgesia or balanced analge evidence of the efficacy of preemptive analgesia sia. One example of multimodal thetic and opioid with or without clonidine) analgesia is the use of various combinations of may reduce the incidence of phantom limb pain in patients undergoing limb amputation. Moderate ence in the intensity and duration of postopera to severe acute pain should be treated with suffi tive pain after preemptive analgesia with a vari cient doses of opioids to safely relieve the pain. Nonpharmacologic approaches to acute pain management should supplement, but not replace, analgesics. Elements of Treatment severe trauma or burns) may limit the use of nonpharmacologic therapy. Pharmacologic management simple psychological methods (Table 30) such as Pharmacologic management is the corner relaxation and imagery are especially likely to stone of acute pain management. Most Physical methods of pain management can be acute pain is nociceptive and responds to nono helpful in all phases of care, including immedi pioids and opioids. Analgesics, espe divided into medications administered via sys temic routes (Table 34) and those administered a Nikolajsen and colleagues13 found that the rate and intensity regionally. However, the former did provide better relief of ment stump pain during the immediate postoperative period. They do not consider all of the risks this entails a comprehensive approach that associated with treatments or the needs of spe includes medication and functional rehabilita cial populations. It includes patient education, regular assessment, manage ment of contributing illnesses. Monitor neurological and neurovascular status continuously in patients with head injury or limb injury, respectively. Interdisciplinary approach to rehabilita decompression tion Sources: References 2, 28, 30, and 36-37. This refers to a process in which health intensive chronic pain rehabilitation are war care professionals with disparate training collab ranted. Team members represent a number of orate to diagnose and treat patients suffering health care disciplines and include physicians from difficult pain states.

Generic zudena 100 mg amex
A 52-year-old woman begins pharmacotherapy after being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus erectile dysfunction icd 9 code discount zudena 100 mg visa. Ten days later, she develops fever, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias, and erythema on her hands and feet. After being severely beaten and sustaining a gunshot wound to the abdomen, a 42-year-old woman undergoes resection of a perforated small bowel. Which of the following ligand > receptor pairs most likely played a primary role in the proliferation of the T lymphocytes present at the site of the rash in this patient Muscle biopsy specimens obtained from the subjects during the resting state show significantly increased concentrations of malonyl-CoA. A 63-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 4-day history of increasingly severe left leg pain and swelling of his left calf. During this time, he has had a 9-kg (20-lb) weight loss despite no change in appetite. Physical examination shows temporal balding and coarse dark hair on the upper lip and chin. Current medications are atorvastatin, glyburide, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, and warfarin. A 24-year-old man comes to the office because of a 2-day history of a red, itchy rash on his buttocks and legs. The pain tends to be more severe at night and occurs 1 to 3 hours after meals during the day. A photomicrograph of Steiner silver-stained tissue (400x) from a biopsy of the gastric mucosa adjacent to the ulcer is shown. A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being hit with a baseball bat on the lateral side of his leg immediately below the knee. A 46-year-old woman with active ankylosing spondylitis comes to the office for a follow-up examination. Physical examination shows lesions that are most numerous in the flexural areas including the axillae and groin. These blisters are most likely the result of adhesion failure involving which of the following A 17-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after her boyfriend found her unconscious next to an empty bottle of acetaminophen. A 72-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and cough. During the interview, he responds to the questions with a single word and sometimes with sarcastic answers. He does not engage in eye contact, and he frowns as he tells the physician that this is the third time he has been asked these questions. The husband says that she was well last night but when she awoke this morning, she had difficulty getting out of bed and her speech was slurred. She has a 20-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus well controlled with medication and diet. Which of the following labeled sites in the photograph of a cross section of a normal brain stem is most likely damaged in this patient Assuming there were no technical errors, the Southern blot analysis results demonstrate which of the following processes Physical examination shows a normal female body habitus, normal breast development, and normal appearing external genitalia. The physician explains that hormone therapy likely will help and explains the risks to the patient. Which of the following best represents the absolute risk reduction for vomiting among patients in the azithromycin group A 34-year-old woman with a 10-year history of hepatitis C comes to the physician because of progressive fatigue during the past month. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause of the ongoing hepatocyte injury in this patient Following pulmonary function testing, a biopsy specimen of the affected area of the lungs is obtained. A 43-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department because of a 12-hour history of nausea and vomiting. Physical examination shows muscle weakness of the distal portion of the feet and absent ankle jerk reflexes. The same nucleotide change is found in 15 of 200 individuals without Marfan syndrome. Compared with a healthy adult, which of the following findings is most likely in this patient The initial evaluation of this test shows: Tumor Present Absent Positive 40 20 60 Test Result Negative 10 30 40 50 50 100 Which of the following is the likelihood that a patient with a positive test from this sample has a tumor A 75-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension is brought to the office by her daughter because of a 4-month history of loss of appetite. If the efferent arteriole is constricted with a vascular clamp, which of the following Starling forces is most likely to change in the glomeruli His birth weight was 3500 g (7 lb 11 oz), and Apgar scores were 8 and 10 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. During the operation, moderate hemorrhaging requires ligation of several vessels in the left side of the neck. Her pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 105/60 mm Hg while seated; pulse is 95/min, and blood pressure is 99/59 mm Hg while standing. The patient says with disgust that the missing child is and always has been worthless. A 6-year-old girl is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-week history of constant increasingly severe neck pain and a 2-month history of severe headaches that occur three to four times weekly and last for 1 hour. Examination of a biopsy specimen of the retropharyngeal area shows aggregates of segmented neutrophils as well as evidence of Candida albicans. The mother says that she looked in his underpants and saw something move, which she captured. Gram stain of the exudate shows numerous neutrophils, many that contain intracellular gram-negative diplococci. She only takes an oral contraceptive, but she has not been sexually active for the past 6 months. A plain x-ray shows a fracture of the superior pubic ramus and retrograde urethrography is done to evaluate for a urethral disruption. Which of the following portions of the urethra would be at greatest risk for injury in this patient An 18-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of fever, dizziness, weakness, rash, nausea, and vomiting. Serum concentrations of gonadotropic hormones, estrogens, and testosterone are within the reference ranges. A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by paramedics 30 minutes after he was involved in a motor vehicle collision in which his face struck the steering wheel. A 23-year-old woman is brought to the medical tent 2 minutes after she collapsed at the finish line of a marathon. She has not lost consciousness; she is alert and coherent and says she feels dizzy and light-headed. A 27-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 3-hour history of pain around his navel. The patient says that his current symptoms are similar to those he had during the appendicitis episode. Results of laboratory studies are shown: Hemoglobin 12 g/dL Hematocrit 36% 3 Leukocyte count 18,000/mm 3 Platelet count 350,000/mm Serum Urea nitrogen 20 mg/dL Creatinine 0. A 14-year-old girl is brought to the physician after her mother learned that she began having sexual intercourse with various partners 1 month ago. She has begun smoking cigarettes, disobeying her curfew, and being truant from school.
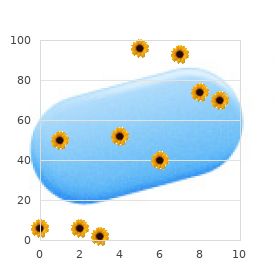
Buy zudena toronto
Many body sites have normal impotence for males purchase cheap zudena, com between the physicians, nurses, and laboratory staf should be mensal microbiota that can easily contaminate the inappro encouraged and open with no punitive motive or consequences. The diagnosis of infectious disease is best achieved by apply Therefore, specimens from sites such as lower respiratory ing in-depth knowledge of both medical and laboratory science tract (sputum), nasal sinuses, superficial wounds, fistulae, along with principles of epidemiology and pharmacokinetics and others require care in collection. Actual tissue, aspirates, and fluids are always specimens the result of strong partnerships between the clinician and the of choice, especially from surgery. This document illustrates and promotes of choice for many specimens because swabs pick up extra this partnership and emphasizes the importance of appropriate neous microbes, hold extremely small volumes of the speci specimen management to clinical relevance of the results. Swabs are expected from the nasopharynx and Medical Microbiology, the American Board of Pathology, or the to diagnose most viral respiratory infections. Flocked swabs American Board of Medical Laboratory Immunology or their have become a valuable tool for specimen collection and have equivalent certifed by other organizations. Clinicians should been shown to be more effective than Dacron, rayon, and cot recommend and medical institutions should provide this kind ton swabs in many situations. The flocked nature of the swab of leadership for the microbiology laboratory or provide formal allows for more efficient release of contents for evaluation. To request the laboratory to provide testing apart sibility of the medical personnel, not usually the laboratory, from the procedure manual places everyone at legal risk. It is the key to accurate laboratory diag biota changes and etiologic agents are impacted, leading to nosis and confirmation, it directly affects patient care and patient potentially misleading culture results. Susceptibility testing should be done only on clinically signif infection control, patient length of stay, hospital and laboratory icant isolates, not on all microorganisms recovered in culture. Clinicians and other medical personnel should consult accurate, significant, and clinically relevant. The laboratory should set technical policy; this is not the storage of patient specimens they collect are managed properly. Specimens must be labeled accurately and completely so Throughout the text, there will be caveats that are relevant to spe that interpretation of results will be reliable. Labels such as cific specimens and diagnostic protocols for infectious disease eye and wound are not helpful to the interpretation of diagnosis. However, there are some strategic tenets of specimen results without more specific site and clinical information management and testing in microbiology that stand as community (eg, dog bite wound right forefinger). Future modifications of the document are to at all times for all medical personnel to review or consult and it be expected, as diagnostic microbiology is a dynamic and rap would be particularly helpful to encourage the nursing staff to idly changing discipline. Pediatric parameters have been updated review the specimen collection and management portion of the in concordance with Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines and manual. Comments and recommenda tion personnel, who may know very little about microbiology or tions have been integrated into the appropriate sections. When the term clinician is used throughout require longer incubation periods; others may require special cul the document, it also includes other licensed, advanced practice ture media or non-culture-based methods. Another unique feature is that in most chapters, there fungi often require special broth media or lysis-centrifugation vials are targeted recommendations and precautions regarding select for detection, most Candida spp grow very well in standard blood ing and collecting specimens for analysis for a disease process. Within each chapter, didemia do not yield positive results in almost half of patients. The most common etiologic agents of period, such as 2 hours, it is expected that the sample should culture-negative endocarditis, Bartonella spp and Coxiella bur be refrigerated afer that time unless specifed otherwise in that netii, ofen can be detected by conventional serologic testing. It is a collaborative effort between clinicians and laboratory require >2 culture bottles depending on the system. For neonates experts focusing on optimum use of the laboratory for positive and adolescents, an age and weight appropriate volume of blood patient outcomes. When the term recommended is used in this should be cultured (see Table 3 below for recommended volumes). Infants and children: 2 As much blood as can be Organisms will usually survive in inoculated culture vials blood culture sets (see conveniently obtained even if not incubated immediately. Malassezia spp re above) from children; volume quire lipid supplementation; lysis-centrifugation is recom depends on weight of mended for their recovery. There may be circumstances in which it is prudent to omit the anaerobic vial and split blood spec imens between 2 aerobic vials. Such requests should be made in consultation with the microbiology laboratory director. The timing of blood culture orders should be dictated by Skin contaminants in blood culture bottles are common, very patient acuity. In urgent situations, 2 or more blood culture sets costly to the healthcare system, and frequently confusing to cli can be obtained sequentially over a short time interval (min nicians. To minimize the risk of contamination of the blood cul utes), afer which empiric therapy can be initiated. Recommended Volumes of Blood for Culture in Pediatric Patients (Blood Culture Set May Use Only 1 Bottle) Recommended Volume of Weight of Blood for Culture, mL Patient, Total Patient Total Volume % of Total kg Blood Volume, mL Culture Set No. Two recent studies have documented equiv the anaerobic bottle (faster time to detection). Infections Associated With Vascular Catheters povidone-iodine followed by alcohol is recommended. Tese procedures may include abbreviated iden of a positive culture from an indwelling catheter segment or tip tifcation of the organism, absence of susceptibility testing, and in the absence of positive blood cultures is unknown. The next a comment that instructs the clinician to contact the laboratory essential diagnostic component is demonstrating that the infec if the culture result is thought to be clinically signifcant and tion is caused by the catheter. This usually requires exclusion of requires additional workup and susceptibility results. Some investigators have Physicians should expect to be called and notifed by the concluded that catheter tip cultures have such poor predictive laboratory every time a blood culture becomes positive since value that they should not be performed [13]. Routine culture of intrave Key points for the laboratory diagnosis of bacteremia/ nous catheter tips at the time of catheter removal has no clinical fungemia: value and should not be done [13]. When a microbiologic diagnosis of less common etio tories): one from catheter or port and one from peripheral logic agents is required, especially when specialized techniques venipuncture obtained at the same time using lysis-centrifu or methods are necessary, consultation with the laboratory gation (Isolator) or pour plate method. In this section, infections are categorized to obtain the correct length (5 cm) of the distal catheter tip. Other routes of infection include direct extension tip or an endoluminal brush (not performed routinely in most from a contiguous structure, movement along nerves, or intro laboratories). Infected (Mycotic) Aneurysms and Vascular Grafts fora and should not be sent to the microbiology laboratory Infected (mycotic) aneurysms and infections of vascular grafts for direct smears, culture, or molecular studies. Pericarditis and Myocarditis culture and are required for optimal recovery of mycobacteria Numerous viruses, bacteria, rickettsiae, fungi, and parasites and fungi. When the specimen volume is less than required have been implicated as etiologic agents of pericarditis and for multiple test requests, prioritization of testing must be myocarditis. Whenever possible, specimens for whelming majority of patients with myocarditis, an etiologic culture should be obtained prior to initiation of antimicrobial diagnosis is never made and patients are treated empirically. If anaerobes are suspected, then the culture should consist of an aerobic and anaerobic bacterial culture. If anaerobes are suspected, then the culture should consist of both a routine aerobic and anaerobic culture. Serum should be separated from red cells as soon as from cultures is routinely performed unless contamination possible.
Buy 100 mg zudena
Cross References Automatism; Emotionalism erectile dysfunction houston 100 mg zudena fast delivery, Emotional lability; Pseudobulbar palsy Peduncular Hallucinosis Peduncular hallucinosis is a rare syndrome characterized by hallucinations and brainstem symptoms. Brainstem nd ings include oculomotor disturbances, dysarthria, ataxia, and impaired arousal. Cross Reference Hallucination Peek Sign One of the eye signs of myasthenia gravis: on attempted forced eye closure, orbic ularis oculi may fatigue such that the patient peeks through the partially open palpebral ssure. Cross References Metamorphopsia; Porropsia Pelvic Thrusting Pelvic thrusting may be a feature of epileptic seizures of frontal lobe origin; occa sionally it may occur in temporal lobe seizures. In acquired causes such as multiple sclerosis, this may pro duce oscillopsia and blurred vision. For example, a blow to the thenar eminence may produce involuntary and sustained exion of the thumb. Treatment of the associated lesion may be undertaken, otherwise periodic alternating nystagmus usually responds to baclofen, hence the importance of correctly identifying this particular form of nystagmus. Periodic respiration may be observed in unconscious patients with lesions of the deep cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, or upper pons, or with central or tonsillar brain herniation; it has also been reported in multiple system atro phy. Cross References Aphasia; Dysexecutive syndrome; Frontal lobe syndromes; Intrusion; Logoclonia; Palinopsia Personication of Paralyzed Limbs Critchley drew attention to the tendency observed in some hemiplegic patients to give their paralyzed limbs a name or nickname and to invest them with a per sonality or identity of their own. A similar phenomenon may occur with amputated limbs, and it has been reported in a functional limb weakness. Cross References Anosodiaphoria; Anosognosia Pes Cavus Pes cavus is a high-arched foot due to equinus (plantar exion) deformity of the rst ray, with secondary changes in the other rays. Patients may volunteer that they experience such symptoms when carrying heavy items such as shopping bags which puts the hand in a similar posture. Hyperextension of the wrist (reverse Phalens manoeuvre) may also reproduce symptoms. These are signs of compression of the median nerve at the wrist (carpal tunnel syndrome). The term was coined by Weir Mitchell in the nineteenth century, but parts other than limbs (either congenitally absent or following amputation) may be affected by phantom phenomena, such as lips, tongue, nose, eye, penis, breast and nipple, teeth, and viscera. Phantom phenomena are perceived as real by the patient, may be subject to a wide range of sensations (pressure, tem perature, tickle, pain), and are perceived as an integral part of the self. Reorganization of cortical connections follow ing amputation may explain phantom phenomena such as representation of a hand on the chest or face, for which there is also evidence from functional brain imaging. Phantom Vision this name has been given to visual hallucinations following eye enucleation, by analogy with somaesthetic sensation experienced in a phantom limb after amputation. Cross Reference Hyperacusis Phosphene Phosphenes are percepts in one modality induced by an inappropriate stimu lus. The perception of ashes of light when the eyes are moved has been reported in optic neuritis, presumably reecting the increased mechanosensitivity of the demyelinated optic nerve bres; this is suggested to be the visual equivalent of Lhermittes sign. Noise-induced visual phosphenes have also been reported and may be equivalent to auditory-visual synaesthesia. Cross References Auditory-visual synaesthesia; Gaze-evoked phenomena; Lhermittes sign; Photism; Synaesthesia Photism Photisms are transient positive visual phenomenon, such as geometrical shapes or brightly coloured spectral phenomena, occurring in the context of epilepsy, migraine, or in blind visual elds (hence overlapping with photopsia). Cross References Dazzle; Meningism; Retinitis pigmentosa Photopsia Photopsias are simple visual hallucinations consisting of ashes of light which often occur with a visual eld defect. Cross References Aura; Hallucination; Photism Physical Duality A rare somaesthetic metamorphopsia occurring as a migraine aura in which individuals feel as though they have two bodies. Cross Reference Geophagia, Geophagy Picture Sign the picture sign is present when a patient believes that individuals seen on the television screen are actually present in the home; indeed they may be reported 279 P Picture Within a Picture Sign to emerge from the television set into the room. Like the mirror sign, the picture sign may be classied as a misidentication phenomenon. Cross References Mirror sign; Misidentication syndromes Picture Within a Picture Sign Following a right parieto-occipital infarction, a patient complained of seeing people moving about in the left lower quadrant of the visual eld whilst vision was normal in the remainder of the visual eld, a phenomenon labelled the picture within a picture sign. Cross References Froments sign; Straight thumb sign Pinhole Test Impairments in visual acuity due to refraction defects (changes in shape of the globe or defects in the transparent media of the eye) may be improved or cor rected by looking through a pinhole which restricts vision to the central beam of light. Use of the term negative Babinskis sign or negative Babinski response to mean exor plantar response is incorrect and should not be used. This normal plantar response is a supercial cutaneous reex, analo gous to abdominal and cremasteric reexes, whereas the pathological response is often accompanied by activity in other exor muscles. In some individuals the toes do not move at all, in which case the response is labelled as mute or absent. Of these, perhaps the most frequently used are Chaddocks sign (application of a stimulus in a circular direction around the external malle olus or the lateral aspect of the foot from heel to little toe) and Oppenheims sign (application of heavy pressure to the anterior surface of the tibia from patella to ankle). If the plantar response thus elicited is upgoing, this suggests a spread of the receptive eld of the reex. It is often difficult to form a denite judgment on the plantar response and reproducibility is also questionable. There remains a persistent belief, particularly amongst trainees, that an experienced neurologist can make the plantar response go which ever way s/he chooses. Cross Reference Dystonia Plexopathy Lesions conned to the brachial, lumbar, or sacral plexi may produce a constella tion of motor and sensory signs (weakness, reex diminution or loss, sensory loss) which cannot be ascribed to single or multiple roots (radiculopathy) or periph eral nerves (neuropathy). It has also been described in disease of the retina and optic nerve and occasionally in normal individuals. The pathophysiology is unknown; suggestions include a defect of visual xation or of visual integration; the latter may reect pure occipital cortical dysfunction. Cross References Automatism; Seizures Porropsia Porropsia, or teliopsia, is a form of metamorphopsia characterized by the mis perception of objects as farther away from the observer than they really are (cf. Postural and righting reexes depend not only on the integration of labyrinthine, proprioceptive, exteroceptive, and visual stimuli, mostly in the brainstem but also involve the cerebral cortex. However, abnormalities in these reexes are of relatively little diagnostic value except in infants. One exception is extrapyramidal disease (parkinsonism, Huntingtons dis ease, but not idiopathic dystonia) in which impairment or loss of postural reexes may be observed. In the pull test the examiner stands behind the patient, who 284 Presbyastasis P is standing comfortably, and pulls briskly on the shoulders; if balance is normal, the patient takes a step back; with impaired postural reexes, this may provoke repetitive steps backwards (retropulsion, festination) or even en bloc falling, due to the failure of reex muscle contraction necessary to maintain equilibrium. Cross References Dystonia; Festinant gait, Festination; Parkinsonism; Proprioception; Rocket sign Pourfour du Petit Syndrome Pourfour du Petit syndrome is characterized by mydriasis, widening of the palpebral ssure, exophthalmos, hyperhidrosis. Cross References Frontal release signs; Primitive reexes Prayer Sign An inability to fully oppose the palmar surfaces of the digits with the hands held in the praying position, recognized causes of which include ulnar neuropa thy (main en griffe), Dupuytrens contracture, diabetic cheiroarthropathy, and camptodactyly. Presbycusis Presbycusis is a progressive sensorineural hearing loss, especially for high fre quencies, developing with increasing age, which may reduce speech discrimina tion. It is thought to be due to age-related attrition of hair cells in the organ of Corti and/or spiral ganglion neurones. Cross Reference Age-related signs Presbyopia Presbyopia is progressive far-sightedness which is increasingly common with increasing age, thought to be due to an age-related impairment of accommo dation. The eyes can be brought to the other side with the oculocephalic manoeuvre or caloric testing. In contrast, thalamic and basal gan glia haemorrhages produce forced deviation of the eyes to the side contralateral to the lesion (wrong-way eyes). There are also non neurological causes, such as haematological conditions (sickle cell anaemia, polycythaemia rubra vera) which may cause intrapenile thromboses. Primitive Reexes Reexes which are normally found in infancy but which disappear with brain maturation during childhood may be labelled as primitive reexes if they re emerge in adulthood as a consequence of pathological states. Cross References Babinskis sign (1); Corneomandibular reex; Frontal release signs; Grasp reex; Palmomental reex; Pout reex; Rooting reex Procerus Sign A focal dystonia of the procerus muscle, denoted the procerus sign, has been suggested to contribute to the astonished, worried, or reptile-like facial expression typical of progressive supranuclear palsy, which may also be char acterized by reduced blinking, lid retraction, and gaze palsy. Cross References Blinking; Dystonia; Hypomimia; Parkinsonism Pronator Drift Pronator drift is pronation of the forearm observed when the arms are held straightforward, palms up, with the eyes closed.

