Perindopril
Cheap 8 mg perindopril with mastercard
The movements of pendular or jerk nystagmus may be horizontal blood pressure chart daily order online perindopril, vertical, torsional, oblique, circular, or a combination of these. The amplitude of nystagmus is the extent of the movement; the rate of nystagmus is the frequency of oscillation. Generally speaking, the faster the rate, the smaller is the amplitude and vice versa. Nystagmus is usually conjugate but is occasionally dysconjugate, as in convergence-retraction nystagmus and seesaw nystagmus. Nystagmus is also occasionally dissociated (more marked in one eye than the other), as in internuclear ophthalmoplegia, spasmus nutans, monocular visual 688 loss, and acquired pendular nystagmus and with asymmetric muscle weakness in myasthenia. Physiology of Symptoms Reduced visual acuity is caused by inability to maintain steady fixation. The patient may complain of illusory movement of objects (oscillopsia), which is usually indicative of acquired rather than congenital nystagmus and is particularly severe in vestibular disease. The head is turned toward the fast components in jerk nystagmus or set so that the eyes are in a position that minimizes ocular movement in pendular nystagmus. Head nodding may occur in congenital nystagmus and is a characteristic feature of spasmus nutans. Nystagmus is noticeable and cosmetically disturbing except when excursions of the eye are very small. End-Point (End-Gaze) Nystagmus Normal individuals may have nystagmus on extreme horizontal gaze, which disappears when the eyes are moved centrally by a few degrees. It is primarily horizontal but may have a slight torsional component and greater amplitude in the abducting eye. Optokinetic Nystagmus this type of nystagmus may be elicited in all normal individuals, usually with a rotating drum with alternating black and white lines but by any repetitive targets in the visual field, such as repetitive telephone poles as seen from a window of a fast-moving vehicle. The slow component follows the object, and the fast component moves rapidly in the opposite direction to fixate on the succeeding object. A unilateral or asymmetric horizontal response usually indicates a deep parietal lobe lesion, especially a tumor. Anterior cerebral (ie, frontal lobe) lesions may inhibit this response only temporarily when an acute saccadic gaze palsy is present, which suggests the presence of a compensatory mechanism that is much greater than for lesions situated farther posteriorly. Since it is an involuntary response, this test is especially useful in detecting functional visual loss. Stimulation of Semicircular Canals the three semicircular canals of each inner ear sense movements of the head in space, being primarily sensitive to acceleration. The neural output of the vestibular system, after processing within the vestibular and related brainstem nuclei, is a velocity signal. In the unconscious subject with an intact brainstem, this leads to a tonic deviation of the eyes, whereas in the conscious subject, a superimposed corrective fast-phase movement, returning the eyes back toward the straight ahead position, results in a jerk nystagmus. These tests are useful methods of investigating vestibular function in conscious subjects and, in the case of caloric stimulation, brainstem function in comatose patients. Rotation, such as in a Barany chair, then leads to horizontal jerk nystagmus with the compensatory slow-phase eye movement opposite to the direction of turning and the corrective fast phase in the direction of turning. Due to impersistence of the vestibular signal during continued rotation, the nystagmus abates. Once the rotation stops, there is a vestibular tone in the opposite direction, which results in a jerk nystagmus with the fast phase away from the original direction of turning (postrotatory nystagmus). Since the 690 subject is stationary, postrotatory nystagmus is often easier to analyze than the nystagmus during rotation. Water irrigation of the auditory canal generates convection currents predominantly within the horizontal rather than the vertical semicircular canals. Cold water irrigation induces a predominantly horizontal jerk nystagmus with a fast phase opposite to the side of irrigation, and warm water irrigation induces a similar jerk nystagmus with a fast phase toward the side of irrigation. It is important to verify that the tympanic membrane is intact before performing irrigation of the external auditory canal. Congenital Nystagmus Congenital nystagmus is nystagmus present within 6 months after birth. Ocular instability is usual at birth, due to poor visual fixation, but this abates during the first few weeks of life. Congenital impairment of vision or visual deprivation due to lesions in any part of the eye or optic nerve can result in nystagmus at birth or soon thereafter. Causes include corneal opacity, cataract, albinism, achromatopsia, bilateral macular disease, aniridia, and optic atrophy. By definition, congenital idiopathic motor nystagmus has no associated underlying sensory abnormality, although visual performance is limited by the ocular instability. Typically it is not present at birth but becomes apparent between 3 and 6 months of age. At one time it was thought that congenital pendular nystagmus was indicative of an underlying sensory abnormality whereas congenital jerk nystagmus was not. Eye movement recordings have shown this not to be true, with both 691 pendular and jerk waveforms being seen whether or not there is a sensory abnormality. Indeed, in many cases, a mixed pattern of alternating pendular and jerk waveforms is seen. Congenital nystagmus, particularly the idiopathic motor type with its potential for better visual fixation, generally undergoes a progressive change in its waveform during early childhood. There is development of periods of relative ocular stability, that is, relatively slow eye velocity, known as foveation periods since they are thought to be an adaptive response to maximize the potential for fixation, and hence to improve visual acuity. In addition, congenital nystagmus with a jerk nystagmus has a characteristic waveform in which the slow phases have an exponentially increasing velocity. This can be a particularly useful feature in determining that nystagmus noted in adulthood is not of recent onset. The direction of any jerk component often varies with the direction of gaze, but an important feature in comparison to many forms of acquired nystagmus is that there is no additional vertical component on vertical gaze. In most patients with congenital nystagmus, there is a direction of gaze (null zone) in which the nystagmus is relatively quiet. If this null zone is away from primary position, a head turn may be adopted to place the eccentric position straight ahead. In a few cases, the position of the null zone varies to produce the congenital type of periodic alternating nystagmus. Congenital nystagmus is usually decreased in intensity by convergence, and some patients will adopt an esotropia (nystagmus blockage). Once congenital nystagmus has been noted, it is important to identify any underlying sensory abnormality, if only to determine the visual potential. Extraocular muscle surgery is predominantly indicated for patients with a marked head turn. Supramaximal recessions of the horizontal rectus muscles reduce the intensity of congenital nystagmus, but the effect is only temporary. Nystagmus with a latent component means that it increases in intensity when one eye is covered, which is a characteristic feature of congenital nystagmus. This may be because of loss of sight in one eye or even from the development of a divergent squint. Acquired Pendular Nystagmus Any child who develops bilateral visual loss before 6 years of age may also develop a pendular nystagmus, and indeed the acquisition of a pendular nystagmus during infancy necessitates further investigation. A specific syndrome of acquired pendular nystagmus in childhood is spasmus nutans. This is a bilateral, generally horizontal (occasionally vertical), fine, dissociated pendular nystagmus, associated with head nodding and an abnormal head posture.
Syndromes
- Blood loss
- Trauma to the back
- Roach powders
- Seizures
- Ethynodiol diacetate and ethinyl estradiol
- Fecal impaction
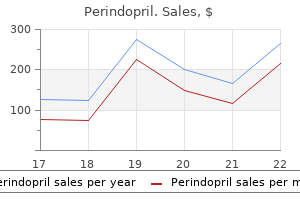
Cheap perindopril 8 mg visa
Photo- 5 fu arrhythmia discount perindopril 2 mg amex, osmo and phonophobia in the premonitory phase of migraine: mistaking symptoms for targeting these peptides or their receptors represent a triggersfi Characterising the premonitory a crucial time to maintain the momentum that has been stage of migraine in children: a clinic-based study of 100 patients in a specialist headache service. Premonitory symptoms in push forward towards safe, efcacious, and individualised migraine: a cross-sectional study in 2714 persons. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in microstructural and functional resting-state network correlation migraine patients with and without aura: a cross-sectional, analysis. Increased interictal visual spreading depolarizations in acute cortical lesion development: network connectivity in patients with migraine with aura. Cortical spreading depression closes paravascular space and 42 Santangelo G, Russo A, Trojano L, et al. Cognitive dysfunctions and impairs glymphatic fow: implications for migraine headache. The impact of cognitive the extracerebral circulation of humans during migraine headache. Prevalence of neck pain in migraine and tension-type in peripheral blood as a biomarker for chronic migraine. Pearls and pitfalls in human related to the frequency of migraine attacks: a cross-sectional study. Cephalalgia 2016; published online randomized, placebo controlled, dose-ranging trial. J Comp Neurol 2016; shunts, ischemic brain lesions, and persistent migraine activity. Investigation of the update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine attacks induced by in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-38. New therapeutic for the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, multicenter, approaches for the prevention and treatment of migraine. Exacerbation of headache during dihydroergotamine for Greater occipital nerve block for the acute treatment of prolonged or chronic migraine does not alter outcome. Canadian Headache Society systematic review and recommendations on the treatment of migraine pain in emergency settings. Dehydration refiects severity and should be monitored by established score Methods: the guideline development group formulated questions, systems. The latter were graded hypoosmolar solution is the major treatment and should start as soon as with the Muir Gray system and, in parallel, with the Grading of possible. Regular feeding should Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations system. Ultrarapid schemes of intravenous rehydration are not superior (e-mail: alfguari@unina. Key Words: acute gastroenteritis, child, children, definition of diarrhea, the work was supported by an unrestricted grant from the European Society guidelines for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. He has been paid by Dicofarm for the development of educational presentations; he received travel/accommo 1. The guidelines have had a major impact clinical investigator, and/or advisory board member, and/or consultant, on the management of gastroenteritis as judged by the number of and/or speaker for Arla, Biogaia, Biocodex, Danone, Dicofarm, Hipp, citations (a total of 160) and by several articles addressing their Nestle, Nestle Nutrition Institute, Nutricia, Mead Johnson, Merck, and Sequoia. In addition, an e-learning program was Copyright # 2014 by European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, created to implement their application. Hepatology, and Nutrition and North American Society for Pediatric We have now updated the guidelines to take account of the Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition evidence accumulated over the last 5 years. To reflect the changes that have occurred, we have, however, retained, the incidence of diarrhea ranges from 0. Gastroenteritis is a major reason for hospitalization in this Another novelty is a section on the management of children in range of age. Interested readers can Intestinal infections are a major cause of nosocomial access this material, which was used to produce the recommen infection. A comprehensive We applied the same approach we had used to develop the literature search in Western Europe showed an incidence of previous guidelines (see the 2008 guidelines for details). Hospitalization rates for rotavirus gastroenteritis ranged population for search purposes. Children with at-risk conditions, such as serotype predominance appears to change on a seasonal basis chronic disorders or immunodeficiency, are not covered. See additional information about methods in the licensed in Europe in 2006, were found to have good safety and Online Repository. In fact, the proportion of new (G12) or selected (G2P4) in the frequency of evacuations (typically! Acute diarrhea typically lasts <7 days and not gastroenteritis in countries with high rotavirus vaccine coverage >14 days. In Spain, severe clinical conditions were often outbreaks owing to new norovirus variants were recently reported in associated with rotavirus infections (24). In fact, there was a cases of extremely severe rotavirus diarrhea in Germany, which decline of Salmonella and an increase in the detection of norovirus included cases of rotavirus-related encephalopathy and deaths and sapovirus (18). In Although norovirus may induce frequent and severe vomit addition, Clostridium difficile infection, whose frequency is rapidly ing (25), norovirus and adenovirus infections are less severe than increasing worldwide, has been related to community-acquired those caused by rotavirus (13,25,27,28). Carriage of Giardia or Cryptosporidium in stool is low in Coinfection with different pathogens is associated with a more children living in Europe, namely 1% to 3% in day-care centers severe course of symptoms (29). However, no specific bacterial Asymptomatic carriage in stools of nonpathogenic protozoa species was associated with persistent diarrhea in more than is not rare in children returning from tropical countries. Therefore, it was suggested that there is not sufficient evidence to justify the routine use of anti microbials for children with persistent diarrhea when etiology is 5. In 1 study the etiology of diarrhea differed between infants (weak recommendation, low-quality evidence) and children age >2 years as follows: viral (98% vs 44%), bacterial (23% vs 50%), and parasitic (0% vs 31%) (23). Similarly,prolongedantigenemiaduringrotavirusinfectionwas reported in stem cell transplant recipients (49). In children who underwent renal transplantation, exposure to enteric pathogens and to risk of severe or protracted Cryptosporidium should be suspected in this population (47). The risk of nosocomial diarrhea is related to young age Protein energy malnutrition, vitamin A deficiency, poor and increases with duration of hospitalization; it may reach 70% in folate status, and prior antibiotic use are risk factors for persistence young children staying in hospital for 6 days (7,66,67). Nosocomial cases tended to be less severe than community acquired cases (69), and can be easily prevented by adherence to hand-hygiene measures (70). Stringent hygiene measures (including diaper changing, (weak recommendation, very low-quality evidence). Postillness self-limiting condition, although it may occasionally evolve into a weight gain is considered the criterion standard for the assessment serious illness. Questions to caregivers should be specific and easy derives from a compromise between accuracy and reliability on one to understand, and should focus on the following: side, and operators and setting on the other. It seems reasonable that different scoring systems are used in outpatient and inpatients. Several scoring systems assess Recent medical history dehydration based on clinical signs and symptoms (eg, capillary How long (hours or days) has the child been ill refill, skin turgor, urinary output) (dehydration scales). Other scores the number of episodes of diarrhea or vomiting, and the evaluate the global clinical features based on a cluster of symptoms approximate amount of fiuids lost (eg, diarrhea, vomiting, fever) and the need of hospital stay or Whether the child is able to receive oral fiuids follow-up (severity scores).
Order cheap perindopril
It presents with arthralgia/arthritis arteria gastrica sinistra generic perindopril 4 mg free shipping, abdominal pain, kidney disease, and palpable purpura in the absence of thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy. In the skin, these deposits lead to subepidermal hemorrhages and small vessel necrotizing vasculitis producing the purpura. IgG autoantibodies directed at mesangial antigens may also play a role in pathogenesis. Current management/treatment Treatment is supportive care including hydration, rest, and pain control. Platelet recovery time, incidence of thrombotic events, and length of hospital stay were similar in the early group and controls, but were longer/higher in the late group. Plasmapheresis in the management of exchange, plasmapheresis and cardiopulmonary bypass for articles heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Plasma exchange for heparin-induced penia requiring urgent insertion of a left ventricular assist device thrombocytopenia: is there enough evidencefi No difference in adverse events and no signifi cant difference in total treatment costs were observed (the higher cost of erythrocytapheresis was offset by a significant reduction in lost work productivity due to phlebotomy visits). Compared to lymphoid blasts, myeloid blasts are larger, less deformable, and their cytokine products are more prone to activate inflammation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression. This could however be in part due to higher risk of the patients undergoing leukapheresis. Others studies have reported no benefit and raised concerns that leukocytapheresis might delay start of induction chemotherapy. Limitations to the primary studies include the retrospective, observational nature of the publications, the number of which was small and having moderate to high risk of confounding bias. Chemotherapy should not be postponed and is required to prevent rapid reaccumu lation of circulating blasts. Cytapheresis in the treatment of cell-affected blood tial management of hyperleukocytosis on early complications disorders and abnormalities. Leukapheresis and cranial irradiation in patients with types and promyelocytes in the development of leukostasis syn hyperleukocytic acute myeloid leukemia: no impact on early drome. Complications and outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic Reliability of leukostasis grading score to identify patients with leukemia with hyperleukocytosis. Leuka ment outcome of children with newly diagnosed acute myeloid pheresis in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with leukostasis leukemia and hyperleukocytosis. Adequate information was not provided to ascertain the comparability of the two groups. Therapeutic plasma tic plasma exchange in patients with severe hypertriglyceride exchange in patients with hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Gubensek J, Buturovic-Ponikvarfi J, Marn-Pernat A, Kovac J, of hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis. Plasmapheresis for severe lipemia: treated with plasma exchange: an observational cohort study. Other manifestations include congestive heart failure (related to plasma volume overexpansion), respiratory compromise, coagulation abnormalities, anemia, fatigue, peripheral polyneuropathy, and anorexia. IgM is 80% intravascular and serum viscosity rises steeply with increasing IgM levels. Technical notes Conventional calculations of plasma volume based on weight and hematocrit are inaccurate in M-protein disorders because of plasma vol ume expansion. Evidence-based focused review of manage Tedeschi A, Gika D, Merlini G, Kastritis E, Sonneveld ment of hyperviscosity syndrome. The Canadian experience using Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline plasma exchange for immune thrombocytopenic purpura. An increased level of plasma IgA alone, however, is insufficient to generate mesangial IgA deposits. Case reports and case series from previous decades have addressed the treatment of the rapidly progressive form. This trial is representative of the experiences reported in case series and case reports. All patients were receiving concurrent corticosteroids or immunosuppressant therapy. The phenotype of these disorders is variable, affecting predominately individuals in the third decade of life. For Cellsorba, venous whole blood is processed at 50 mL/min through the column for 60 min. The Adacolumn is relatively selective for removing activated granulocytes and monocytes. Treating inflammatory bowel disease by adsorptive tive apheresis in patients with ulcerative colitis positive for leucocytapheresis: a desire to treat without drugs. Adsorptive granulocyte/ Efficacy, safety and cost analyses in ulcerative colitis patients monocyte apheresis for the maintenance of remission in patients undergoing granulocyte and monocyte adsorption or receiving with ulcerative colitis: a prospective randomized, double blind, prednisolone. Antibody levels do not correlate with severity, but may decrease as the disease improves in response to immunosuppressive therapy. It blocks fast voltage-gated potassium channels, prolonging presynaptic depolarization and thus the action potential, resulting in increased release of acetylcholine and also resulting in increased calcium entry into presynaptic neurons. In one series, 8 out 9 patients (Newsom-Davis, 1984) had increase in electromyographic muscle action potential (P < 0. It also inhibits tissue factor pathway inhibitor, which results in enhanced coagulation and inhibition of fibrinolysis, producing a prothrombotic state.
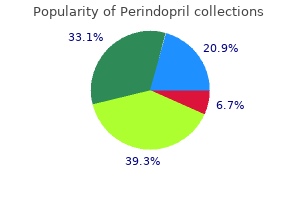
Buy discount perindopril 4 mg line
Sepulveda et al studied 368 twin pregnancies at 10 to 14 weeks gestation nhanes prehypertension discount 4mg perindopril amex, classifying them as monochorionic if there was a single placental mass in the absence of the lambda sign at the inter-twin mem brane-placental junction and dichorionic if there was a single placental mass but the lambda sign was present or the placentas were not adjacent to each other. In 81 (22%) cases, the pregnancies were classified as mono chorionic and in 287 (78%) as dichorionic. All pregnancies classified as monochorionic resulted in the deliv ery of same-sex twins and all different-sex pairs were correctly classified as dichorionic. Other authors suggest counting the number of layers of fetal membranes to determine chorionicity, however this strategy is not always possible and should be used in conjunction with other sonographic crite 20,21,22,23,24,25 ria. Membrane thickness is also occasionally useful to predict the type of placentation. Thick 26,27,28 membranes suggest dichorionic placentation while thin membranes suggest monochorionic placentation. There is a small risk, however, of a cytogenetic change that could result in monozygotic twins presenting as a boy and a girl. The most common cause of this rare anomaly is the early loss (during the embryo stage) of a Y chromosome in a cell line that eventually becomes a Turner syndrome. In rare instances, not only the primordial fertilized egg divides but one of the 2 daughter cells also looses genetic material (and more commonly the Y chromosome) resulting in a heterokaryotypic monozygotic twin pregnancy consisting of a boy and a Turner girl. Death of one twin may have serious 37,38,39, 40,41,42,43,44 implications for the survivor because of the increased risk of preterm delivery as well as the risk neurological handicap secondary to hypotensive episodes caused by hemorrhage from the live fetus into 45,46,47,48 the dead fetoplacental unit through vascular anastomoses. Monoamniotic twins Definition Monoamniotic twins are those that share not only the chorion (the outer membrane) but also the amnion (the 49 inner membrane) and thus are in the same gestational sac. They result from splitting between 7 to 13 days 50, 51 52, 53,54 after fertilization and represent 1% of twin pregnancies. Absence of a dividing membrane between two fetuses that are intimately in contact. Close approximation of the cord insertions 13 Cord entanglement (power Doppler on top, and gray-scale bottom) Counting twins with different chorionicity by counting the number of gestational sacs is easier in the first trimester when thick layers of tissue separate the sacs. However, differentiating monochorionic diamniotic 58 from monochorionic monoamniotic twins is not easy. The amniotic membrane is very thin, and unless the ultrasound beam is perpendicular, it may be difficult to observe. A simple trick that is convincing when pre sent is to roll the patient to the side and observe the passive motion of the embryos. If they both gravitate to the bottom of the gestational sac no matter what decubitus position, the suspicion of monoamniotic twin is 59 high. This must 60 be an accurate diagnosis since it identifies patients at higher risk for cord accidents. Differential diagnosis Monoamniotic twins can easily be confused with monochorionic diamniotic twins, especially when there is twin-to-twin transfusion and one of the twins is stuck (see elsewhere in this chapter). A careful search for a membrane, in particular between the limbs and the body, is the only way to ascertain the diagnosis. The ab sence or reduced amniotic fluid around the stuck twin should raise the suspicion of a diamniotic gestation as well. Associated syndromes Monoamniotic twins may be affected by multiple pathological conditions including twin-to-twin transfusion 61,62,63 (although less commonly and less severe than in monochorionic diamniotic twins), tangled umbilical 64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73 74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82 cords and increased risk of congenital anomalies (15-20%). Cord entan glement occurs in 40-70% of monoamniotic twins because of their increased mobility in the second trimester. Cord entanglement appears to be a pathognomonic sign of monoamnionicity and can be seen as early as the first trimester. The presence of a notch in the umbilical artery velocity waveform may reflect hemodynamic alterations in the fetal-placental circulation secondary to narrowing of the umbilical vessels involved in cord entanglement. Due to these complications the overall,87, 88, 89, 90, 91 mortality for monoamniotic twins can be as high as 50-60%. Fetal growth Intrauterine growth restriction is a pathological situation, caused in the majority of the cases by placental insufficiency. Poor maternal-fetal exchange reduces the offer of nutrients to the fetus, which grows slower than normal. This condition is seen in 25% of twin gestations, a rate ten times higher than that found in the general population. Growth rate in multiple gestations during the first and early second trimesters parallels the growth rate of singleton pregnancies, dropping off during the late second and third trimesters. Serial growth assessment is the most accurate method to diagnose intrauterine growth retardation. Some con troversy remains concerning the use of growth nomograms derived from the general population in multiple pregnancies. Twins commonly experience decreased growth after 26-28 week, and, as in this set, the effect may be more pronounced on the smaller of the twins. Head 92 Reece et al reported that the growth of the fetal head was not significantly different from that observed in singleton pregnancies. According to his findings nomograms derived from singleton pregnancies remains useful for twin gestations. Although a difference in fetal growth between these two groups was found, the authors concluded it was not statistically significant to justify the generation of separate nomograms for twins. Abdomen Neonatal differences in abdominal circumference from the normal singleton population are frequently identi fied. It is still unclear if these differences occur due to genetic differences in growth potential of twins or if they are secondary to decrease supplies. Our personal impression is that it is better to consider twin growth with singleton measurement. Using special twin chart increases the risk that the nomograms be established on fetuses with less then adequate growth and thus mask the presence of growth restriction in the index fetus. Despite the controversies regarding the use of nomograms in twin gestations, concordant growth should be expected between fetuses. In these dark old days they only had a scale, so they only could measure the weights after birth. The term should thus be abandoned because it promulgates confusion, and unnecessary testing. Fetal growth discrepancy is defined as a greater than 20% difference in the inter-twin estimated fetal weight. The definition of growth discrepancy should be categorized with respect to gestational week since the level of discrepancy varies at different stages 102 of pregnancy. Most cases of growth discrepancy are diagnosed at the second half of the pregnancy. Sonographic features the standard care for twin pregnancy includes serial sonographic evaluations to assess the growth of each 105,106 fetus. Cases of pre-term twin gestations with severe dis 121,122,123 crepancy are associated with a higher morbidity rate. Differential diagnosis 136,137,138,139 Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome is the main differential diagnosis. Observation of discordant 140 sexes or dichorionic placentation excludes this possibility. In general, twin-twin transfusion syndrome is 141 associated with the polyhydramnios-oligohydramnios and/or anemia-polycythemia sequences. Differences in genetic growth potential between the twins are another possibility: both twins would have normal growth but significant size discrepancy. These cases have adequate growth on serial sonographic analysis plotted in a growth chart, normal amniotic fluid volume and birth weight usually above 2500g. Associated syndromes Growth discrepancy can be associated with low amniotic fluid volume in the sac of the growth-restricted 143 fetus.
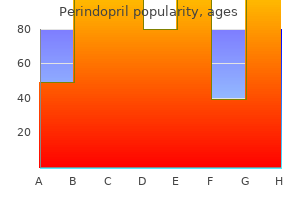
Discount 8 mg perindopril fast delivery
A meta-analysis of 16 studies blood pressure medication valsartan buy perindopril 8 mg on line, which included 1748 children Clinical failure rate was 0. Several countries, antibiotic therapy is effective and strongly recommended well-designed controlled studies have shown that appropriate anti inall ofthechildrenwithshigellosis. Itshouldbenoted,however,that biotic treatment of Shigella gastroenteritis significantly reduced the this finding has not been demonstrated in outpatients. Antibiotic treatment or if present local microbiologic data suggest susceptibility. Antibiotic treatment significantly reduces the duration nistered, both for 5 days. When Shigella isolates are susceptible to of fecal excretion of Campylobacter spp, and thus its infectivity. Azithromycin is the drug of choice in most locations, when no other alternative is feasible. The recommended first-line although local resistance patterns should be closely monitored parenteral treatment is ceftriaxone for 5 days (191). The treatment is nonspecific and administration of antibiotics could have adverse effect (Vb, D) (weak recom Antibiotic therapy is not effective on symptoms and mendation, very low-quality evidence). It is associated with a pro Antibiotic therapy for Shiga toxin-producing E coli is longed fecal excretion of Salmonella. Therefore, antibiotics not recommended (Vb, D) (strong recommendation, low-qual should not be used in an otherwise healthy child with Salmo ity evidence). A Cochrane systematic review showed that antibiotic therapy Antibiotic treatment of gastroenteritis caused by enterotoxigenic E of Salmonella gastroenteritis does not significantly affect the coli or by enteropathogenic E coli significantly shortens the clinical duration of fever or diarrhea in otherwise healthy children or adults course (mainly the duration of diarrhea) and fecal excretion of the compared with placebo or no treatment Moreover, antibiotics were pathogen. Rifaximin, a broad-spectrum, nonabsorbed antimicrobial associated with a significant increase of carriage of Salmonella, agent, can be used in children >12 years for nonfebrile watery although other adverse events were not reported. This is an emerging agent of diarrhea whose role is limited or questionable in children age <36 months. Hypervirulent strains may induce severe symptoms and should Antibiotic therapy for Campylobacter gastroenteritis is be treated with oral metronidazole or vancomycin (200). Anti recommended mainly for the dysenteric form and to reduce biotic-associated diarrhea is often caused by C difficile. The effect was more pronounced if treatment started within 3 days of illness onset (193) and in children with Campy Appropriate antibiotic treatment of cholera reduces the lobacter-induced dysentery. In a parallel group, assessor-blind trial, durations of diarrhea by approximately 50% and fecal shedding testing for inequality in 130 children with Campylobacter jejuni/ of V cholerae by approximately 1 day. A randomized, controlled study common causes are Shigella spp, Campylobacter spp, and Salmo demonstrated that a single 20 mg/kg azithromycin dose is more nella enterica. It is important to treat hospitalized children and efficacious clinically and microbiologically than ciprofloxacin children attending day-care centers to reduce transmission of (201); it is the drug of choice for children age <8 years. Antibiotic Extraintestinal Organs therapy is usually not needed for the uncommon cases of gastro enteritis caused by noncholera Vibrio spp, Aeromonas spp, or Plesiomonas shigelloides. Antibiotic therapy is recommended for the rare but severe extraintestinal infections caused bacterial enteric patho gens (Vb, D) (strong recommendation, low-quality evidence). Antibiotic therapy is not generally needed for antibiotic associated diarrhea, but should be considered in moderate-to severe forms (Vb, D) (weak recommendation, very low-qual Occasionally enteric bacterial pathogens can spread and ity evidence). It occurs during (early onset) or 2 to 6 weeks after (late onset) antibiotic treatment (204,208). Antiparasitic treatment is generally not needed in other wise healthy children; however, it may be considered if 9. Antibiotics are not recommended unless epi remains the first-line treatment (209). Albendazole (once daily demiology suggests shigellosis (Vb, D) (weak recommen for 5 days) is probably as effective as metronidazole in achieving dation, low-quality evidence). A recent trial in adults with Giardia monoinfec mended (Va, D) (strong recommendation, low-quality evi tion showed equivalence of the 2 drugs in terms of parasitological dence) for: cure and improving symptoms (210). Patients unable to take oral medications (vomiting, stupor, similar results; nitazoxanide was found to be less effective etc) (209,211). Severe toxemia, suspected or confirmed bacteremia require only oral rehydration (22,212). Invasive gastroenteritis is defined as tories must distinguish between Entamoeba dispar (nonpathogenic) acute onset of bloody/mucous diarrhea (or fecal polymorphonuclear and E histolytica, which requires rapid treatment with metronida leukocytes when the examination is available) with high fever. Guidelines on acute gastroenteritis in demonstrated that oral administration of immunoglobulin (300 mg/ children: a critical appraisal of their quality and applicability in primary kg) may be beneficial for rotaviral infection and is associated with a care. Evidence-Based Health Care: How to Make Health poultry hens were found to be strongly reactive to several rotavirus Policy and Management Decisions London: Churchill Livingstone; serotypes. Rules of evidence and clinical adjunct to general supportive therapy in pediatric patients (218). Burden of community were observed at 7 days, but no benefit was found for length of acquired and nosocomial rotavirus gastroenteritis in the pediatric hospital stay or hospital cost (219). Effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in prevention of hospital admissions for rotavirus gastro occurs in children with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, enteritis among young children in Belgium: case-control study. Rotavirus genotypes circulating in Australian compromised hosts (220); however, although the most appropriate children post vaccine introduction. Rotavirus vaccine effective features could benefit from ganciclovir therapy (221). Updated norovirus outbreak manage duration, and a moderate-to-severe degree of dehydration (222). Characterization of norovirus reported for the nitazoxanide and probiotic groups. Mean durations of diarrhea gastroenteritis in the United Kingdom over 15 years: microbiologic and of hospitalization were significantly shorter in the nitazoxanide findings from 2 prospective, population-based studies of infectious group than in controls. Clostridium difficile infection: an update on mendations on the management of acute gastroenteritis can be epidemiology, risk factors, and therapeutic options. Asymptomatic carriage of and middle income countries: systematic review of randomized con protozoan parasites in children in day care centers in the United trolled trials. Etiology of acute gastro coli virulence markers: positive association with distinct clinical char enteritis in children requiring hospitalization in the Netherlands. Intestinal protozoal center prospective study yolostrumfi the role of rotavirus on acute infestation profile in persistent diarrhea in children below age 5 years gastroenteritis in Spain. Complications in hospitalized diarrhea reduce growth and increase risk of persistent diarrhea in children with acute gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus: a retrospective children. Cryptosporidiosis in paediatricrenal immunodominant Cryptosporidium gp15 antigen and gp15 polymor transplantation. Yet in primary headache, that signal goes hay in a young woman of childbearing age, especially if further wire, and the brain needs to be taught to stop listening to the history suggests a gradual onset, perimenstrual headaches, false signal.
Egypt Fenugreek (Fenugreek). Perindopril.
- Diabetes, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, stomach upset, decreased appetite, constipation, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), gout, sexual problems (impotence), fever, baldness, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Fenugreek?
- Dosing considerations for Fenugreek.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Fenugreek work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96717
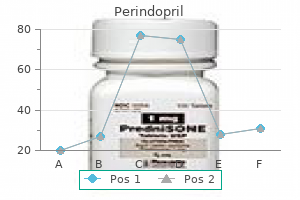
Discount perindopril 4 mg without prescription
Light that does not scatter and is aimed directly on the print or task is preferred best blood pressure medication kidney disease safe perindopril 8 mg. Such systems encourage a natural reading posture and are a good choice for school children to help them see their class work and view graphs, diagrams, or photos. The devices have built-in illumination and allow for contrast enhancement, color display, and 1011 variable magnification. Some have a built-in distance camera to allow viewing of signs, arrival and departure boards at airports, and classroom lectures. Electronic portable reading devices can download printed material such as books and newspapers, which can be read or listened to using text to speech options. The rapid development of devices for the general population has benefited visually impaired patients by increasing choice and reducing cost, allowing them to regain their independence more easily. The type and strength of visual aid are influenced by the type and extent of the deficit. Useful parameters of visual function include visual acuity, glare, and contrast sensitivity. Modification of illumination and attention to details of room and task lighting are most important. Antireflective lens coatings and neutral gray lenses reduce light intensity (and therefore glare). Contact lenses, keratoplasty, corneal laser refractive surgery, posterior capsulotomy, and cataract surgery may also be indicated. If cataract seems to be interfering with optimal function, a combination of contrast sensitivity and glare tests may indicate the best time for surgery. The surgeon may wish to discuss overcorrecting the power of the implant by a few diopters. The resulting myopia will provide clear intermediate distance vision without correction, which is more important for a visually impaired person than clear far distance vision. Other causes are macular holes, myopic macular degeneration, and congenital macular disorders. In the early stages of atrophic age-related macular degeneration, patients most often report blurred or distorted central vision. The loss of central vision interferes with reading and seeing details, including facial features. Dense scotomas are not present in atrophic macular degeneration and usually not in exudative disease unless there is retinal fibrosis following choroidal or subretinal hemorrhage. Macular degeneration generally does not hinder safe travel because the preserved peripheral vision is effective for orientation purposes. Effective treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration has increased the number of patients with macular degeneration who can benefit from low-vision rehabilitation. The ability to move the scotoma may be demonstrated to a patient during the Amsler grid test. Magnifying lenses enlarge the retinal image, allowing use of eccentric fixation by compensating for lower retinal sensitivity in the parafoveal area. The power of the lens is related to the contrast sensitivity, as well as location and density of the scotoma. Most people learn to use low-vision aids successfully, particularly after instruction sessions to reinforce correct usage. The peripheral field is essential for orienting oneself in space, detecting motion, and awareness of potential hazards in the environment. A person with a constricted field may be able to read small print yet need a cane or guide dog to get around. Telescopes and spectacle magnifiers may enlarge the image beyond the useful field. Hand magnifiers and closed-circuit television or computers may be the equipment of choice because the size of the image can be adjusted to match the size of the field. Mainly for patients with homonymous hemianopia, various training techniques, such as vision restoration therapy and explorative saccade training, have been advocated and are being evaluated. Forooghian F et al: Visual acuity outcomes after cataract surgery in patients with age-related macular degeneration: Age-Related Eye Disease Study Report No. Lighthouse Information and Resource Service: Information and pamphlets about eye conditions, visual impairment, and blindness. MacKeben M et al: Random word recognition chart helps scotoma assessment in low vision. It is an administrative definition that does not mean that the patient is unable to see anything. Loss of vision reduces the ability to perform activities of daily living, and affects safety and quality of life. In developed countries, and increasingly in developing countries, the majority of irreversible vision loss occurs in the elderly and will represent an ever increasing part of ophthalmic practice (see Chapter 20). Unfortunately, many patients and caregivers still consider vision loss as an inevitable result of aging and often do not seek the help that is available. Dysfunction at the different stages of visual processing causes different problems that require different solutions. The first is the optical stage, which puts an image of the outside world on the retina. The second is the receptor stage, which translates the optical image into neural impulses. The third stage is neural processing, which starts in the inner retina and proceeds via the visual cortex to higher cortical centers, where it eventually gives rise to visually guided behavior. Letter chart acuity is a good tool to evaluate this stage, and magnification devices (see Chapter 24) are the natural choice to counteract this type of vision 1021 loss. This eccentric area will have a reduced receptor density, which causes further reduction of visual acuity. Normal vision involves constant eye movements, which may move the object of attention in and out of the best-functioning area. This scotoma interference, which may be apparent as hesitation during testing, is not quantified by visual acuity and cannot be remedied with magnification devices. This may be provided by occupational therapists or vision rehabilitation specialists, but it is up to ophthalmologists to recognize the need for this training and to make the appropriate referral. Awareness of vision problems related to the processing of visual information is increasing. In this area, the ophthalmologist may need to cooperate and communicate with social workers and educators. Some cerebral defects produce obvious impairments of visual acuity and visual field (visual impairment). More subtle defects (visual dysfunction) may exist in the presence of normal performance on standard clinical testing. A patient with optical or retinal problems may stumble over a curb because of lack of contrast, whereas a patient with a cerebral injury may be able to detect the change in contrast but may be unable to decide whether this is a line on the ground or the edge of a step. In this case, vision enhancement (better illumination, contrast) will not help, and vision substitution (use of senses other than vision such as a cane to tactically determine the step) may be more appropriate. Full assessment of impaired cerebral processing may involve other professionals and neuropsychological testing, but preliminary assessment by ophthalmologists can often be the starting point.
Purchase perindopril 2 mg without a prescription
Usually arrhythmia uk discount perindopril 2mg without a prescription, Case history Chief complaint in a divergent squint an object towards the right in the feld of vision will be fxed with the right eye, in the left Onset and duration of the feld by the left eye, while the converse may occur Previous treatment in convergent squint (cross-fxation). Treatment goals and expectations the next step is to differentiate a comitant squint from an Diagnostic Visual acuity and monocular fxation pattern incomitant squint. In comitant squints, when either eye is covered and then uncovered, the deviation Determine details of deviation (Table 26. In acute comitant squint a patient may report diplo Management Estimate prognosis pia but the distance between the images is the same in all plan Patient/parent counselling directions. It must be remembered, however, in performing this test in a marked squint of long duration that the eyes do not move as much as usual in the direction opposite to that of the deviation. Thus, in convergent squint it may be very diffcult to get the eyes to move outwards to the full extent so Estimating the deviation: In assessing the deviation an that on maximum attempted abduction of the affected eye the important step is to ensure that any apparent deviation is margin of the cornea may still lie inside the lateral canthus. This may mistakenly be diagnosed as a left lateral may prove valuable in such cases. The infant is seated on the rectus paresis if one is not aware of this phenomenon. The light tive range of eye movement is due to muscle weakness or a beam must be wide enough to illuminate both eyes simulta physical restriction is the forced duction test. When the patient is orthotropic, the colour and especially the Forced Duction Test brightness of the fundus refex is equal in the two eyes. The patient is asked to tent or constant, alternating or unilateral, convergent or look in the direction in which movement is being tested divergent, comitant or incomitant the cover test is useful and the maximum range noted. If one eye habitually fxes and the is possible to passively rotate the eye fully with the forceps. Chapter | 26 Comitant Strabismus 419 Hirschberg test No obvious squint Manifest squint Cover either eye (Cover test) Cover the fixing eye (Cover test) Other eye moves to No movement Other eye remains Other eye moves to take up fixation deviated take up fixation Blind Eccentric Immobile Pseudosquint Microtropia Intermittent squint eye fixation Remove cover Remove cover (Uncover test) Squint remains momentarily and then eyes fuse or become straight. Cover test: cover apparently fixing eye and watch movement of suspected deviating eye. If corrective movement is outwards, the squinting eye was convergent or esotropic. A negative result on testing forced duction implies a para fracture of the orbit, where both muscle entrapment and lytic or innervational squint. Force Generation Test Assessment of Binocular Vision An additional useful test in immobile eyes is the active force generation test. Cover the apparently fixing eye with an occluder and observe the response of the other eye. The patient is asked to look at the light; an infant does convergence/ this refexly. The commonly used methods are (i) the Hirschberg tained is centred on the pupil of the squinting eye. Prism Bar Test this is the most commonly used method in routine clinical practice. Patients without In very young children or in recent squinters in whom any degree of binocular function will be treated for purely the habit of suppression has not become fxed, the less cosmetic reasons. The treatment options for strabismus drastic procedure of instilling atropine into the fxing eye can be either conservative or surgical. Since the position of rest is usually one of slight the only satisfactory method of ensuring this is by com divergence, some degree of heterophoria is almost universal plete occlusion, affected by a patch covering the better eye and few people are orthophoric. If the latent deviation is fxed on the skin by adhesive material to prevent the child one of convergence the condition is called esophoria, removing it. Occlusion should be total since, if both eyes are impossible to be sure whether there is absolute hyperphoria used together, active inhibition of the squinting eye rapidly of one eye or hypophoria of the other, the condition being undoes any improvement achieved. The younger the child, the higher the risk of occlusion am blyopia; the alternation should be more frequent. In very Symptoms young children less than 1 year of age, part-time occlusion is tried initially, i. Beyond 8 years the symptoms of heterophoria may be considerable since of age, constant occlusion can be prescribed. Symptoms of eye occluded for a time in the hope that foveal fxation will strain are, therefore, encountered in the higher degrees; develop in the other. This is due to relaxation of the over-strained mus are placed with their axes horizontal, the red line will be cles, when the eyes momentarily assume the position of rest, vertical. If there is hyperphoria, the red line will be eyes dissociate and the latent deviation appears; when below or above the spot depending upon whether the rela the screen is removed, this eye moves at once to regain the tive hyperphoria is associated with the eye with the rod in position of binocular fxation. By convention the Maddox rod is always placed over the right eye, and the patient is asked to fixate on a bright white light either at distance or near. Top row, to evaluate horizontal ocular deviations, the bars on the Maddox rod are aligned horizontally, so the patient sees a vertical red line with the right eye. If there is no horizontal deviation, the patient perceives the red line passing through the white light (depicted in yellow for illustrative purposes). Bottom row, to evaluate vertical deviations, the bars on the Maddox rod should be oriented vertically, so the patient will see a horizontal red line with the right eye. The red line passes through the white light when there is no vertical deviation, while a red line perceived below the light implies a right hyperdeviation, and a white light perceived below the red line indicates a left hyperdeviation. Note that this test will characterize the ocular misalignment, but by itself, in the setting of paralytic or restrictive strabismus, does not indicate which eye has the abnormal motility. An exophoria, manifesting only for distance or showing a marked increase for distance as compared to near could be a manifestation of a mild sixth nerve paresis, particularly a mild bilateral sixth nerve paresis, which A B may occur in patients with raised intracranial pressure or multiple sclerosis. The felds which are exposed to each eye are sepa rated by a diaphragm in such a way that they glide tangen C tially into each other. The im Besides the actual measurement of the deviation in la ages selected for viewing are different depending on the pur tent strabismus, the strength of the muscles involved should pose for which the instrument is being used. If symptoms are apparent after any error of refraction has been corrected with spectacles, a rational treatment of eso or exophoria consists in exercising the weak muscles against prisms (with the base of the prism in the direction of deviation), or by the use of the synoptophore. Unfortu nately, this is usually not or only temporarily benefcial, but relief, however, may be maintained by repeating the exercises at intervals, an activity which the patient can prac tice himself. If this is ineffective, the symptoms may be relieved by ordering prisms in spectacles to correct the defect, i. It is summarized as refraction, occlusion and way, as exercises are useless in this condition. Atropine until the distance at which diplopia occurs is gradually 1% eye ointment three times a day is then prescribed shortened. At the end of this period estimate the error the distance so as to relax his accommodation and conver of refraction by retinoscopy and confirm the result gence. Care should be each session the patient should attempt to relax his muscles taken to examine the fundus in detail as retinoblastoma by either closing both eyes or looking into the far distance or any other organic lesion may sometimes present as a for a few minutes. The angle of the squint should In all cases in which the deviation is large and unaf be measured again which is likely to be less under atro fected by such treatment, operation may be considered, pine than without a cycloplegic in case of hypermet one or other muscle being recessed or resected and the case ropes with a convergent squint or more in myopes with being treated as if it were a manifest squint. Great care must be taken to correct all astigmatism, especially in the squinting eye. The child should be examined at regular intervals to ensure that the squint is corrected by these measures Treatment until it is considered advisable to order spectacles. Hence, they are not popular and prescribed only when no the only exception to this rule is accommodative esotro other alternative is possible.

Order perindopril online
The majority angiotensin receptor blockers have been associated with of patients with chronic hypertension have lower blood renal abnormalities blood pressure 9862 best perindopril 2mg, dysmorphia and neonatal death. The reverse situation to become acquainted with the complications associated is rare and when the blood pressure rises at home it will with her condition and the testing necessary to evaluate usually be elevated at the clinic. Women with signifcant re surements at home are also the best index to measure the nal impairment (serum creatinine. Self monitoring reduces the with vascular involvement (Class R/F), cardiomyopathy, use of antihypertensives and need for hospitalization. The blood pressure re pregnancy can exacerbate their condition with potential for mains stable during the day and falls progressively during causing renal failure, cardiac failure or even death. This pattern is modifed by multiple patients if still plan to conceive should be managed in a variables, especially stressful conditions. Therefore, several tertiary care centre under a maternal fetal medicine special measurements throughout a 24-hour period give a better un ist and in conjunction with a medical specialist. Too Doppler waveform analysis of the umbilical artery is an much or too little weight gain is a concern. Excessive weight gain this type of placental compromise frequently occurs in may also be the consequence of unopposed methyldopa patients with chronic hypertension and fetal growth re action or the frst sign of superimposed preeclampsia. The prognosis for fetuses with normal umbilical Laboratory evaluation of patients with chronic hyper and uterine arteries Doppler is good. An important test is the normal umbilical and uterine Doppler suggests that there is hematocrit/hemoglobin, which is used to determine if plasma placental compromise and the potential for fetal hypoxia is volume expansion occurs. There is no need for monthly or not be used an indication for delivery except when exhibit periodic creatinine clearance tests and quantitative urinary ing absent or reversed diastolic fow. A high resistance fow protein determinations unless the serum creatinine level is in the umbilical artery Doppler has only prognostic value greater than 0. Chronic Assessment of severity is based on the magnitude of the blood hypertensives are prone for uteroplacental insuffciency. It is customary to initiate fetal well-being tests at 34 weeks and Determination of the severity of the hypertension is im earlier if fetal growth restriction or maternal complications portant to establish a prognosis. However, if growth restriction is not present and sion, the worse the prognosis and the greater the potential for superimposed preeclampsia is excluded, these tests of fetal complications. Failure of blood pressure to normalize in the well-being have not shown improved outcome. Sever any alteration in fetal growth or if the hypertension is inad ity assessment is also useful to determine the necessity for equately controlled, it is necessary to evaluate closely the fetal medications. Other factors which place the patient at high risk for vibroacoustic stimulation plus an ultrasonic determination of complications and poor outcome are listed in Box 13. Doppler studies of the uteroplacental and fetal placen Bed Rest tal circulation are important in the care of the pregnant Bed rest has been used for many years as an adjunct in the woman with chronic hypertension. Uterine artery Dop management of pregnant patients with chronic hyperten pler at 24 weeks is important to determine the risk of fetal sion. Blood pressure in the lateral recumbent position is growth restriction and that of developing preeclampsia. Bed rest increases the venous return that is integrity of the uteroplacental circulation while the impaired due to compression by the pregnant uterus and presence of early bilateral diastolic notching increases this permits mobilization of fuids, increases the urinary Chapter | 13 Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy 195 and severity of the associated complications. In addition, control of severe hypertension l History of abruptio placentae may permit prolongation of pregnancy and thereby im l History of stillbirth of unexplained neonatal death l History of previous deliveries of small for gestational age prove perinatal survival. However, there is no evidence infants that treatment of severe hypertension has any impact on l Older than 35 years or more than 15 years of hypertension reducing the risk of superimposed preeclampsia or abrup l Marked obesity tion placentae. In these patients, the most common maternal complications are wors output, decreases peripheral oedema, and improves placen ening of the hypertension, superimposed preeclampsia and tal perfusion. The fetus may be affected by growth Complete bed rest on the other hand may predispose to restriction, antepartum and intrapartum hypoxia and acidosis. Pregnant patients with chronic hypertension should duce the risk of progress to severe maternal hypertensive be instructed to avoid processed foods, to minimize con crisis but has not shown improvement in overall perinatal sumption of milk products, to scrutinize food labels for so outcome. Possible benefts include reduction in hospital ad dium content and to resist adding salt to their food. A reduction in blood pressure However, as opposed to benefts of antihypertensive of approximately 10 mmHg can be achieved in the nonpreg therapy in mild hypertensives, another meta-analysis of nant status by lowering the sodium intake to 90 mEq/day (4 treatment versus no treatment in mild chronic hypertensives g salt/day). However, obese hyper tensives and their blood pressure to be kept lower than tensive women should not lose weight during pregnancy. Pregnant hypertensive patients should Such uncomplicated chronic hypertensives should not lower avoid starting new exercise activities during pregnancy. The medi their blood pressure is above 150/100 mmHg or they have cation lowers the blood pressure within hours, and antihy other complicating factors (cardiac or renal) and to either pertensive effect is not modifed by changes in posture or stop or reduce medications in women who are already tak activity. In women with severe chronic hypertension (systolic the response and the side effects. Minor problems include An ideal antihypertensive drug should maintain the car fatigue, insomnia and bad dreams. It should are bronchospasm and a blunted response to hypoglycemia, not increase the heart rate or the plasma volume when the preventing its use in asthmatics and in brittle diabetics, re blood pressure drops and it should have no side effects. The largest experience does not cause bronchospasm and has a prolonged duration has been with methyldopa. Unfortunately, it has been associated with an in surfaced as frst line medications. Beta-Blockers Labetalol (a and nonselective b-blocker) has been 1 Beta-blockers act upon blood pressure by competing with extensively studied and is increasingly being prescribed endogenous catecholamines for the beta adrenergic recep during pregnancy. They leave alpha-mediated vasoconstriction unop good effcacy, labetalol is a good option for frst line treat posed. Different compounds have different affnities for beta ment of chronic hypertension. The drug has beta-1 and beta-2, and alpha-1 blocking Atenolol is predominately a beta-1 or cardioselective type of properties. The alpha to beta blockade ratio is 3:1 when beta-blocker while propranolol is noncardioselective. Once of Our present understanding of the haemodynamics of the main obstetrical uses of labetalol is for hypertensive mild chronic hypertension in pregnancy indicates that the emergencies in patients with severe preeclampsia. Labet majority of these patients have increased cardiac output and alol has replaced hydralazine for rapid reduction of blood hyperkinetic circulation. Propranolol reduces cardiac output pressure in preeclampsia, because it does not cause between 15 and 30% and suppresses rennin production by severe hypotension, headache, tachycardia and has no 60%. After a few weeks of treatment there is also a drop in effect on uteroplacental blood fow. These haemodynamic characteristics make therapy with Maximum dose per treatment cycle is 220 mg. Also, beta-blockers are safe in Labetalol is also used orally for long-term treatment of pregnancy, and there is abundant literature documenting the chronic hypertension. Approximately 75% of the drug is excellent outcome of pregnant patients treated with these inactivated in the frst liver pass. Propranolol is an effective drug for the treatment of l the initial dose is 100 mg twice daily. Methyldopa is one antihypertensive medication that has been submitted to controlled trials during pregnancy and l For severe hypertensive crisis, 10 mg initial oral dose has been shown to have benefcial effects.

Buy perindopril 4mg lowest price
Spontaneous expulsive phometric characteristics of traumatic choroidal rup choroidal hemorrhage: a clinicopathologic report of 2 tures associated with neovascularization hypertension thyroid generic perindopril 4mg with mastercard. Traumatic choroidal rupture with of the choroid associated with spontaneous expulsive late serous detachment of macula. Late macular compli rhagic ocular complications associated with the use of cations of choroidal ruptures. Retinal rior and Posterior Segment Surgery: Mutual Problems and pigment epithelial cells release an inhibitor of neovas Common Interests. Silicone oil tamponade in the manage ing sclerotomy: scleral puncture for postoperative sepa ment of severe hemorrhagic detachment of the choroid ration of the choroid. This is despite intensive efforts to heighten public Recent epidemiological data confirm the disturbing trend in the prevalence of severe ocular trauma. They also confirm that most eye financial implications, both personal and in terms of injuries are preventable, occurring in people who wear no eye protection. Even in most as the cause of severe and permanent visual cases with a discouraging visual prognosis, the benefits morbidity (Fig. Despite tremendous advances in therapy, the main Evaluation stay of tackling the global problem of ocular trauma Fundamental in the evaluation of any patient presenting (see Chapter 4) remains prevention. Time and again, it with ocular trauma is a comprehensive history and a has been shown that regardless of the setting, the cor careful physical examination (see Chapters 8 and 9). It is essential to establish the shape of the Closed Globe Injury agent, that is, blunt versus sharp. In cases of a projectile experimentally the effects of contusion resulting from 15 Pcausing ocular trauma, the foreign body high-speed pellets. The ocular damage resulting must be assumed intraocular until proved oth from the impact could be explained in four phases of globe deformation: erwise (see Chapter 24). Extreme traction on the vit should always be excluded despite a unilat reous base may cause its anterior border to be 2 eral presentation. It should be repeated periodically spot at the fovea mimicking that in acute central reti until the view improves or intraocular pathology nal artery occlusion may be seen. There may be asso ciated hemorrhage (preretinal, retinal, subretinal) and requiring surgical intervention is detected. The symptoms are determined primarily by the location of the lesion, for example, its relation to the macula. The presence of an anatomically normal ante As the retinal opacification resolves, vision may return rior segment, normal vision, or lack of pain to normal and there may be no ophthalmoscopic find should not deter the examiner from seeking ings after the resolution. Examination discloses retinal whitening in the posterior pole and in the periphery consistent with commotio retinae. A histopathologic study31,i in humans found the Pigmentary disturbance may occur following com motio retinae; with resolution of the edema, it may following. No leakage of fluorescein from retinal capillaries could be demonstrated at any time after injury. Commotio retinae is associ velocity missile penetrating the orbit and graz Pated not with extracellular edema but with 28 ing, but not perforating, the sclera. The bullet penetrated his right lower eyelid and was lodged in the inferior part of the orbit. Note the irregular pigmentary disturbances and the preretinal gliotic membrane involving the optic disk and macula as a result of indirect injury of the posterior pole. This is est description of the condition was in a book on war accompanied by retraction of these tissues to injuries published in 1872. In some areas, bare sclera clearing vitreous hemorrhage, which is more com may be evident. Vision is usually in the range of 20 100 to 20 400 following the development of a full-thickness macular hole. Occasionally, the hole may spontaneously close,54,l with or without full recovery of the visual acuity (Fig. In this patient, in addition to the large central full the surgeon to justify foregoing intervention. However, observation is a hyphema in 25%; chorioretinal atrophy in 25%; dubious initial treatment option, since most choroidal rupture in 20%; holes are not expected to close without surgi angle recession in 20%; cal intervention and may lessen the chance of peripheral retinal tears in 10%; and 53,m a good anatomical and functional recovery. The current standard treatment includes a three the pathognomic presence of vitreous base avul port pars plana vitrectomy, peeling of the posterior sion should alert the clinician to the likely possibility of hyaloid face from the posterior pole, intravitreal gas severe underlying ocular pathology. However, close follow-up is recommended until the ora serrata and pars plana area can be adequately visualized to rule out retinal dialysis or tears of the pars plana. As with surgery for idio Ppathic macular holes, removal of the mac Retinal Dialysis is probably more common than generally perceived. It may be defined lished data that early intervention has distinct as a break or separation occurring at the anterior edge advantages, possibly even more so than for an of the ora serrata and, unlike tears secondary to pos idiopathic macular hole. The favorable results may be due to the younger age of these patients and the shorter duration of the macular hole. Pdialysis location is the inferotemporal A retinal dialysis may be difficult to visualize ini 7,63,65,69 quadrant. However, because the dialysis tially because of the minimal separation between the retina and ora serrata. The difficulty in early detection can occur in any quadrant, thorough evaluation is borne out by published reports. Caution is advised at the initial evaluation Not all retinal dialyses lead to retinal detachment. If the surgeon elects not to Ptreat a retinal dialysis, regular follow-ups Retinal detachments related to dialysis are usually are mandatory, and the patient should be coun slow to develop,65 giving the ophthalmologist a win seled (see Chapters 5 and 8) with respect to this dow of opportunity to detect and treat them, pro management strategy. Peripheral Retinal Breaks are a common source of posttraumatic retinal detachment. The predilection for the inferotemporal and, to a lesser extent, superonasal quadrants has been con Tears from full-thickness retinal necrosis are usually firmed in several reports. They may progress to with the fact that the eye is a fluid-filled structure retinal detachment or seal spontaneously. Holes that have under gone spontaneous closure due to chorioretinal adhe sion can be observed but should be followed closely to detect possible progression to retinal detachment. Pically occurs for retinal detachments fol lowing retinal dialysis, evolving over several months or even years.
Order perindopril 2 mg fast delivery
Since the (wavy) collagenous structure of tissues is not active at low stresses (it does not store strain energy) we associate with the mechanical response of the non-collagenous matrix of the material (which is less stiff than its elastin fiber constituent) hypertension on a cellular level purchase line perindopril. Hence, the strain energy stored in the collagen fibers is taken to be governed by the polyconvex (anisotropic) function (5) where are stress-like material parameters and are dimensionless parameters. Due to the crimp structure of collagen fibers we assume that they do not support compressive stresses which implies that they are inactive in compression. If, for example, and, then the soft tissue responds similarly to a rubber-like (purely isotropic) material described by the energy function (4). However, in extension, that is when or, the collagen fibers are active and energy is stored in the fibers. The specific form of the proposed constitutive equation (7) requires the five material parameters whose interpretations can be partly based on the underlying histological structure, i. Note that in (7), orthotropic (,), transversely isotropic (or) and isotropic hyperelastic descriptions at finite strains are included as special cases. For an adequate model of arteries incorporat ing the active state (contraction of smooth muscles) see [22]. In addition, the arterial layers have different physiological tasks, and hence the artery is modeled as a thick-walled elastic circular tube consisting of two layers corresponding to the media and adventitia. In a young non-diseased artery the intima (innermost layer of the artery) exhibits negligible wall-thickness and mechanical strength. Hence, each tissue layer is considered as cylindrically orthotropic (already postulated in the early work [20]) so that a tissue layer behaves like a so-called balanced angle-ply laminate. We end up with a two-layer model incorporating six material parameters, three for the media, i. The invariants, associated with the anisotropic parts of the two tissue layers are defined by C A and C A. Small components of the (collagen) fiber orientation in the radial direction, as, for example, reported for human brain arteries [5], are neglected. If, for example, the media and adventitia are separated and cut in a radial direction the two arterial layers will spring open to form open (stress-free) sectors, which, in general, have different opening angles (see, for example, the experimental studies [29] for bovine specimens). In general, the residual stress-state is very complex, and residual stresses (strains) in the axial direction may also occur. For each 8 Reference (stress-free) Load-free (stressed) configuration Pure configuration bending R R r i ri fi Figure 4: Cross-sectional representation of one arterial layer at the reference (stress-free) and load-free (stressed) configurations. The importance of incorporating residual stresses associated with the load-free (but stressed) con figuration into the computation has been emphasized in, for example, [4], [12]. For analytical studies of residual stresses see, for example, the works [14], [22], which contain further references. One possible approach to consideration of the infiuence of residual stresses on the overall three dimensional stress behavior is to measure the strain energy from the load-free (stressed) configura tion and to include the residual stresses [19]. Another approach is to start with the energy function relative to the stress-free (and fixed) configuration, as assumed in the presented models, and deter mine the deformation required to reach the load-free (stressed) configuration. With the condition of incompressibility, the radius of an arterial layer in the load-free config uration may be computed from the radius of the associated reference configuration as [12] (14) where, are the internal radii associated with the two configurations. Hence, the (bell-shaped distribution of) collagen fiber orientations may be obtained from an image processing analysis of stained histological sections. How to use it the energy functions are well-suited for use in nonlinear finite element software, which enables complex boundary-value problems to be solved. Aspects of finite element implementation and nu merical analysis of the model are presented in [11]. Furthermore, computations may be carried out with some of the commercially available mathematical software-packages such as Mathematica or Maple, which allow symbolic computation. Table of parameters Values of the parameters correspond to the functions (10), (11) and are given for a representative carotid artery from a rabbit (experiment no. Media Adventitia Table 2: Table of parameters for a carotid artery from a rabbit (experiment no. Three-dimensional collagen organization of human brain arteries at different transmural pressures. A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. The use of strain energy to quantify the effect of residual stress on mechanical behaviour. The role of the fibrous components and ground substance in the mechanical properties of biological tissues: A preliminary investigation. Bending of blood vessel wall: Stress-strain laws of the intima-media and adventitia layers. Ogden, Aspects of stress softening in filled rub bers incorporating residual strains, Graz, October 1999. Schulze-Bauer, Phenomenological and structural aspects of the mechanical response of arteries, Graz, August 2000. Given the potential risks and inherent scarcity of human Departments of Pathology and Laboratory Services and Pediatrics, University of Ar immunoglobulin, careful consideration of its indications and kansas, Little Rock; gthe Department of Pediatrics, Allergy and Immunology, Mon administration is warranted. Harville has 2 line and centers on the use of standard immunoglobulin receivedconsultingfeesfromBaxalta. Others, however, are quite common, and rigorous scientific evaluation of immunoglobulin utility has been possible. Immunoglobulin holds great promise as a useful therapeutic agent Agammaglobulinemia due to the absence of B cells in some of these diseases, whereas in others it is ineffectual and Agammaglobulinemia due to the absence of B cells is the may actually increase risks to the patient. Several publications have suggested that immunoglobulin maternal IgG wanes over time. The implications for known whether a fatal infection may be the first presentation of clinical practice are that patients with hypogammaglobulinemia disease; therefore, clinical judgement, counseling, and close of unclear significance would be monitored closely over time follow-up are recommended as part of the decision to start immu 33 and that immunoglobulin would be initiated only after the full noglobulin replacement. Patients with the memory require additional laboratory data, specific histologic markers of phenotype are characterized as able to mount adequate concentra disease, or genetic testing (although genetic testing may be useful tions against polysaccharide antigen but in whom the response 34 36 in some, more complicated, cases). Antibody function, however, is initially partially specific-antibody production (selective antibody 40 impaired but ultimately typically intact. Immunoglobulin were treated with 400 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 2-3 months and replacement therapy should be provided when there is well followed up for 1-3 years. Sometimes immunoglobulin ther confidence interval for age), which may not be clinically signifi apy may be required. In this case, however, it would be prudent cant, in the absence of recurrent infections. Thus, while they are coincident and from secondary causes resulting from an increased loss of IgG, potentially compounding, focus should not be taken off of the se such as chylothorax, lymphangiectasia, or protein-losing lective IgG antibody deficiency as being the most relevant and enteropathy. In general, an IgG level < 150 mg/dL is widely accepted as A retrospective and prospective observational study evaluated severe hypogammaglobulinemia, for which additional testing the possible association of IgG and/or IgE anti-IgA with adverse apart from verification of the low level is not required prior to reactions in a subgroup of IgA-deficient patients receiving immu starting replacement therapy. In the retrospective well as poor antibody and cell-mediated responses to neoantigens > 56,57 study in 132 patients, 92 had a 50% reduction in the rate of such as keyhole limpet hemocyanin. Patients who completed a full year of treatment were Summary: Immunoglobulin in primary most likely to benefit (14 vs 36; P 5. On the other hand, 2 retrospective, on the costs and the values assigned to the clinical outcomes. Given the state of the the relationship between aging and the immune system has evidence, the current review panel recommends that recently attracted the attention of many researchers. Older age alone is not an indication of quent mixed results in larger-scale studies significantly changed immunoglobulin replacement; however, recurrent, severe, or 106-113 this practice over time. The immune function defects present in syndromic contraindicated in the immediate post-transplantation period in deficiencies may include B-cell, T-cell, phagocytic, complement, 106 103,104 patients with a history of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome. Immunoglobulin therapy should be administered in patients diagnosis and clinical presentation.

