Florinef
Buy florinef 0.1 mg line
Counseling from a practitioner with additional experience and expertise in extremely preterm and extremely low birth weight infants may be appropriate gastritis kidney pain purchase 0.1 mg florinef with mastercard. Disabilities in mental and psychomotor development, neuromotor function, or sensory and communication function are present in approximately one half of extremely preterm fetuses. When the extremely preterm newborn does not survive, support should be provided to the family by physicians, nurses, and other staff after the infants death. Management Retrospective studies addressing obstetric management on outcomes of extremely premature neonates have failed to document a benefit of cesarean delivery over vaginal delivery. The effect of antenatal steroid use in the extremely preterm fetus is unclear; however, it is recommended that all women at risk of preterm delivery between 24 weeks and 34 weeks of gestation be candidates for a single course of corticosteroids (see also Assessment and Management of Fetal Pulmonary Maturation earlier in this chapter). Maternal transport to a tertiary care center before delivery should be considered whenever possible. Management regarding the extent of resuscitative and supportive efforts should be based on gestational age and birth weight but should be further individualized based on the newborns condition at birth and the parents preferences. This information may be developed by each institution and should indicate the population used in determining estimates of survivability. Chorioamnionitis Chorioamnionitis or intra-amniotic infection is largely a clinical diagnosis that often is made presumptively during labor if a laboring woman develops a Obstetric and Medical Complications 251 fever for which there is no other obvious etiology. It is clear that neonates born to mothers with cho rioamnionitis have less infectious outcomes if their mother is treated in utero with appropriate antibiotics. Treatment for chorioamnionitis typically is the administration of ampicillin and gentamicin; treatment with only penicillin or ampicillin is never adequate for chorioamnionitis. Endocarditis Most cases of endocarditis are not attributable to an invasive procedure, but rather are the result of randomly occurring bacteremia from routine daily activi ties. Antibiotic prophylaxis may only prevent a small number of cases of infec tive endocarditis in women undergoing genitourinary procedures, and the risk of antibiotic-associated adverse events exceeds the benefit, if any, from prophy lactic antibiotic therapy. For these reasons, the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology no longer recommend infective endocar ditis prophylaxis for either vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery in the absence of infection, except possibly for the small subset of patients at highest potential risk of adverse cardiac outcomes who are undergoing vaginal delivery. Mitral valve prolapse is not considered a lesion that ever needs infective endocarditis prophylaxis. Prophylaxis Against Postcesarean Infection the single most important risk factor for infection in the postpartum period is cesarean delivery. When this is not possible (eg, need for emergent delivery), prophylaxis should be administered as soon as possible after the incision is made. A single dose of a targeted antibiotic, such as a first-generation cephalo sporin, is the first-line antibiotic of choice, unless significant drug allergies are present. For women with a history of a significant penicillin or cephalosporin allergy (anaphylaxis, angioedema, respiratory distress, or urticaria), a single-dose combination of clindamycin with an aminoglycoside is a reasonable alternative choice for cesarean delivery prophylaxis. Patients with lengthy sur geries or those who experience excessive blood loss should receive an additional intraoperative dose of the antibiotic used for preincision prophylaxis. A woman with postpartum fever should be evaluated by pertinent history, physical exam ination, blood count, and urine culture. Blood cultures rarely influence thera peutic decisions but could be indicated if septicemia is suspected. Cervical, vaginal, or endometrial cultures need not be routinely performed because the results might not indicate the infecting organism. One half of all maternal deaths occur within 24 hours of delivery and most commonly from excessive bleeding. Proper preparation and resources to manage maternal hemorrhage in a timely manner can be lifesaving. Policies to ensure the rapid availability of blood products for transfusion in the event of hemorrhage must be in place. Criteria of an esti mated blood loss of greater than 500 mL after a vaginal delivery or 1,000 mL after cesarean delivery are often used, but the average volume of blood lost at delivery can approach these amounts. Symptoms of hypotension, pallor, and oliguria typically do not occur until blood loss is substantial. In an effort to prevent uterine atony and associated bleeding, it is routine to administer oxytocin soon after delivery. In the presence of previa or a history of cesarean delivery, the obstetric care provider must have a high clinical suspicion for placenta accreta and take appropriate precau tions. Transfusion Transfusion therapy is used to prevent or treat hemorrhagic shock and its con sequences. Clinical judgment is an important determinant, given that estimates of blood loss often are inaccurate, determination of hematocrit or hemoglobin concentrations may not accurately reflect the current hematologic status, and symptoms and signs of hem orrhage may not occur until blood loss exceeds 15%. Accurate pregnancy dating is critical to the diagnosis (see also Estimated Date of Delivery in Chapter 5). Fetal risks include an increased perinatal mortality rate, uteroplacental insuf ficiency, meconium aspiration, intrauterine infection, low umbilical artery pH 256 Guidelines for Perinatal Care levels at delivery, and low 5-minute Apgar scores. Significant risks to the preg nant woman include an increase in labor dystocia, an increase in severe perineal injury related to macrosomia, and a doubling in the rate of cesarean delivery. Management Many authorities recommend prompt delivery in a postterm patient with a favorable cervix and no other complications. Although postterm pregnancy is defined as a pregnancy of 42 weeks or more of gestation, data suggest that rou tine induction at 41 weeks of gestation has fetal benefit without incurring the additional maternal risks of a higher rate of cesarean delivery. Delivery should be initiated if there is evidence of fetal compromise or oligohydramnios. Preterm Birth ^158^241 Preterm birth is defined as birth before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Spontaneous preterm birth includes preterm labor, preterm spontaneous rup ture of membranes, and cervical insufficiency. Preterm birth is the leading cause of neonatal mortality and one of the most common reasons for antenatal hospitalization. In the United States, approximately 12% of all live births occur before term, and preterm labor preceded approximately 50% of these preterm births. Women with a singleton gestation and prior spontaneous pre term birth should be offered progesterone supplementation starting at 16 weeks of gestation to reduce the risk of the recurrence of preterm birth. Fewer than 10% of women with the clinical diagnosis of preterm labor actually deliver within 7 days of presentation. The positive predictive value of a positive fetal fibronectin test result or a short cer vix alone is poor and should not be used exclusively to direct management in the setting of acute symptoms. Management of Preterm Labor Interventions to reduce the likelihood of delivery should be reserved for women likely to give birth and who are at a gestational age at which delay in delivery 258 Guidelines for Perinatal Care will provide benefit to the newborn. Historically, nonpharmacologic treatments to prevent preterm births in women who have preterm labor have included bed rest, abstention from intercourse and orgasm, and hydration. Evidence for the effectiveness of these interventions is lacking, and adverse effects have been reported. Proposed pharmacologic interventions to prolong pregnancy include tocolytic drugs to inhibit uterine contractions and antibiotics to treat intrauter ine bacterial infection. Therapeutics agents associated with improved neonatal outcomes include antenatal corticosteroids for fetal maturation and magnesium sulfate for neuroprotection. Tocolysis is contraindicated when the maternal and fetal risks of prolonging pregnancy or the risks associated with these drugs are greater than the risks associated with preterm birth. Antibiotic use intended only for pregnancy prolongation in women with preterm labor with intact membranes does not have short-term neonatal benefits and may be associated with long-term harm. Thus, antibiotics should not be used for this indication in women with preterm labor and intact mem branes. The most beneficial intervention for improvement of neonatal outcome in patients who deliver preterm is the administration of antenatal corticosteroids. The available evidence suggests that magnesium sulfate given before anticipated early preterm birth reduces the risk of cerebral palsy in surviving infants if administered when birth is anticipated before 32 weeks Obstetric and Medical Complications 259 of gestation. Hospitals electing to use magnesium sulfate for fetal neuroprotec tion should develop uniform and specific guidelines regarding inclusion crite ria, treatment regimens, concurrent tocolysis, and monitoring in accordance with one of the larger trials. It typically is associated with brief latency between membrane rupture and delivery, increased potential for perinatal infection, and in utero umbilical cord compression. Digital examinations should be avoided unless the patient is in active labor or immi nent delivery is planned.
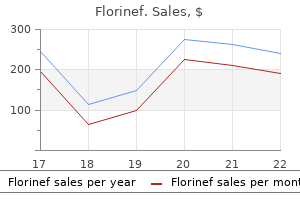
Purchase cheap florinef line
Similarly gastritis symptoms and duration generic florinef 0.1 mg on line, this association was not observed when the analysis was limited to high-grade glioma. There was also an association between mobile phone use and low-grade glioma in the regular use or long-term use subgroups. It is therefore necessary to conduct large sample, high quality research or better characterization of any potential association between long-term ipsilateral mobile phone use and glioma risk. Neurodevelopment for the first three years following prenatal mobile phone use, radio frequency radiation and lead exposure. Questionnaires were provided to pregnant women at 20 weeks of gestation to assess mobile phone call frequency and duration. Child neurodevelopment was assessed using the Korean version of the Bayley Scales of Infant Development-Revised at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months of age. Logistic regression analysis applied to groups classified by trajectory analysis showing neurodevelopmental patterns over time. The questionnaire included the average calling frequency per day and the average calling time per day. Mobile phone use, blood lead levels, and attention deficit hyperactivity symptoms in children: a longitudinal study. Electromagnetic Fields, Pulsed radiofrequency radiation, and epigenetics: How wireless technologies may affect childhood development. New epigenetic studies are profiled in this review to account for some neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioral changes due to exposure to wireless technologies. Technology benefits can be realized by adopting wired devices for education to avoid health risk and promote academic achievement. Conclusions Public health implications of wireless technologies are enormous because there has been a very rapid global deployment in homes, education, transportation, and health care in the last two decades. Even a small risk from chronic use wireless technologies may have a profound global health impact. Epigenetic mechanisms alone can change fetal development in profound ways, disrupting health by causing changes in gene activation and expression without change in gene sequences. Technology benefits can be realized by adopting wired devices for education, to avoid health risk and promote academic achievement. Abstract the use of digital technology has grown rapidly during the last couple of decades. No previous generation has been exposed during childhood and adolescence to this kind of radiation. An evaluation of the scientific evidence on the brain tumor risk was made in May 2011 by the International Agency for Research on Cancer at World Health Organization. With respect to health implications of digital (wireless) technologies, it is of importance that neurological diseases, physiological addiction, cognition, sleep, and behavioral problems are considered in addition to cancer. Well-being needs to be carefully evaluated as an effect of changed behavior in children and adolescents through their interactions with modern digital technologies. Concurrently, epidemiological studies have been documenting an increased cancer risk for people who use cell phones for 10 years or more [1,2] and for those who live near cell phone base stations [3,4,5], broadcast antennas [6,7], radar installations [8], or powerlines [9]. Health care authorities and physicists dismiss these studies because non-ionizing radiation doesnt have enough energy to break chemical bonds and, hence cannot cause cancer. The cerebellums of all animals were removed on postnatal day 47, sectioned and stained with cresyl violet for histopathological and stereological analyses. Ten gigahertz microwave radiation impairs spatial memory, enzymes activity, and histopathology of developing mice brain. Abstract For decades, there has been an increasing concern about the potential hazards of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields that are present in the environment and alarming as a major pollutant or electro-pollutant for health risk and neuronal diseases. Two weeks old mice were selected and divided into two groups (i) sham-exposed and (ii) microwave-exposed groups. After the completion of exposure, within an hour, half of the animals were autopsied immediately and others were allowed to attain 6 weeks of age for the follow-up study. Thereafter results were recorded in terms of various biochemical, behavioral, and histopathological parameters. Body weight result showed significant changes immediately after treatment, whereas non-significant changes were observed in mice attaining 6 weeks of age. Several other endpoints like brain weight, lipid peroxidation, glutathione, protein, catalase, and superoxide dismutase were also found significantly (p < 0. These significant differences were found immediately after exposure and also in follow-up on attaining 6 weeks of age in microwave exposure group. Although in probe trial test, sham-exposed animals spent more time in searching for platform into 424 the target quadrant than in opposite or other quadrants. Results from the present study concludes that the brain of 2 weeks aged mice was very sensitive to microwave exposure as observed immediately after exposure and during follow-up study at 6 weeks of age. The horn antenna was kept in H (Magnetic field) plane configuration, where electric field was perpendicular to the ground surface. Field was almost uniform because the dimension of the cage was of the order of wavelength. A power meter measured the emitted power of microwaves, which was a peak sensitive device. Similar experiment with same number of sham exposed animals was performed without energizing the microwave exposure system. After 30 days, serum and pancreatic tissue samples were harvested for biochemical, histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis. At the immunohistochemical examination, marked increase was observed in calcitonin gene related protein and Prostaglandin E2 expressions in pancreatic cells in this group. Effects of Intermittent and Continuous Magnetic Fields on Trace Element Levels in Guinea Pigs. Groups A and B were exposed to the magnetic field for a period of 4 h/day continuously (4 h/day) for 4 and 7 days, respectively. Groups C and D were exposed to the magnetic field for a period of 4 h/day intermittently for 4 and 7 days, respectively. Copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), and magnesium (Mg) levels were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy in serum, femur, brain, kidney, and liver tissues in all guinea pigs. When compared to the control groups, the changes in the levels of Cu in serum samples, femur, and kidney tissues of the treated groups were statistically significant. The same was also true for the levels of Mg in the brain, kidney, and lung tissues. Exposure to electromagnetic field in uterus has been hypothesized as possible preterm birth. The aim of the present study was to determine whether living closer to high voltage power lines increased the risk of preterm labor. The 150 control subjects were singleton term live birth in the same year of birth and city of residence using randomized-digit dialing. To test the association between the preterm births and the residential proximity to power lines, stepwise multiple logistic regression was used. Analogy: there is an increased risk in subjects exposed to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Asociacion entre las radiaciones de telefonos moviles y el riesgo tumoral en personas adultas. Methods A systematic search was conducted in Scopus, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, Medline and Cinahl of articles published in English and Spanish between January 2005 and February 2016 that analyse the risk of tumour associated with exposure to radiofrequency from mobile phones in adults. Most studies agree that it is not possible to determine a relationship in the short term, although long-term (over 10 years) radiofrequency emitted by mobile phones can cause tumour effects, with an increased risk by ipsilateral exposure and latency. Conclusions Although radiofrequency from mobile phones has tumour effects on humans, the available scientific evidence is not robust. More rigorous follow-up studies with larger sample sizes and broader periods are necessary to learn more about the long-term effects. Acute effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field emitted by mobile phone on brain function. A systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print December 9, 2016]. Modeled and Perceived Exposure to Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields From Mobile-Phone Base Stations and the Development of Symptoms Over Time in a General Population Cohort. Perceived exposure (0 = not at all; 6 = very much), nonspecific symptoms, and sleep disturbances were assessed by questionnaire. We performed cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses, including fixed-effects regression.
| Comparative prices of Florinef | ||
| # | Retailer | Average price |
| 1 | Ace Hardware | 516 |
| 2 | Trader Joe's | 789 |
| 3 | Price Chopper Supermkts | 779 |
| 4 | AutoZone | 991 |
| 5 | Lowe's | 781 |
| 6 | Rite Aid | 285 |
| 7 | YUM! Brands | 191 |
Purchase florinef 0.1 mg with mastercard
Short-duration therapy may be suboptimal agent as the intravenous antibiotic or the same drug class for patients with bacteremic S gastritis diet лего florinef 0.1 mg discount. Switching to a different class of agents simply the risk of associated endocarditis and deep-seated infection), because of its high bioavailability (such as a uoroquinolone) for those with meningitis or endocarditis complicating pneu is probably not necessary for a responding patient. An therapy, a switch to a macrolide alone appears to be safe for 8-day course of therapy for nosocomial P. Stud ies of duration of therapy have focused on patients receiving empirical treatment, and reliable data dening treatment du 32. A longer duration of therapy may be needed if initial spite adequate uid resuscitation should be considered for therapy was not active against the identied pathogen treatment with drotrecogin alfa activated within 24 h of or if it was complicated by extrapulmonary infection, admission. However, the survival advantage therapy in either inpatients or outpatients [276]. The small sample size in that trial, and the benet of the low-tidal-volume ventilatory and baseline differences between groups compromise the con strategy appeared to be equivalent in the population with pneu clusions. Although the criteria for steroid replacement therapy monia compared with the entire cohort. Patients who do not require immediate intubation but who Although difficult to dene, nonresponse is not uncommon. Noninfectious Mortality among nonresponding patients is increased sev Complication of pneumonia. Overall mortality rates as high as 49% have been reported Drug fever Deterioration or progression for an entire population of nonresponding hospitalized patients Early (! Empyema/parapneumonic Endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis Denition and classication. Lack of a clear-cut and validated Myocardial infarction denition in the literature makes nonresponse difficult to study. Persistent fever after the rst day of treatment differs signicantly from fever persisting (or recurring) at day 7 of tory failure or hypotension 172 h after initial treatment is often treatment. Nonresponse can be dened as absence of or delay sponse are seen in hospitalized patients [101]. The rst is pro in achieving clinical stability, using the criteria in table 10 [274, gressive pneumonia or actual clinical deterioration, with acute 294]. When these criteria were used, the median time to achieve respiratory failure requiring ventilatory support and/or septic clinical stability was 3 days for all patients, but a quarter of shock, usually occurring within the rst 72 h of hospital ad patients took 6 days to meet all of these criteria for stability mission. Deterioration and development of respira achieving this degree of clinical stability occurred in! A separate multicenter trial demonstrated similarndings further diagnostic testing, and (3) escalation or change in treat [297]. Decisions regarding further di used to refer to the conditions of patients who present with agnostic testing and antibiotic change/escalation are intimately persistence of pulmonary inltrates 130 days after initial pneu intertwined and need to be discussed in tandem. In a different study, independently associated with a better response in one study mortality among patients with microbiologically guided versus [84], whereas discordant antimicrobial therapy was associated empirical antibiotic changes was not improved (mortality rate, with early failure [81]. However, no antibioticchanges tective factors and their respective odds ratios are summarized. Although in the original study only 8 (16%) of 49 cases are major causes of apparent antibiotic failure. Therefore, the could not be classied [101], a subsequent prospective multi rst response to nonresponse or deterioration is to reevaluate center trial found that the cause of failure could not be deter the initial microbiological results. Overall failurea Early failureb Risk factor Decreased risk Increased risk Decreased risk Increased risk Older age (165 years) 0. Other family members or coworkers may have In addition, a positive pneumococcal antigen test result would developed viral symptoms in the interval since the patient was also help with interpretation of subsequent sputum/tracheal admitted, increasing suspicion of this cause. The evaluation of nonresponse is severely hampered if a Nonresponse may also be mimicked by concomitant or sub microbiological diagnosis was not made on initial presentation. Positive including pleural effusions, lung abscess, or central airway blood culture results in the face of what should be adequate obstruction. The pattern of opacities may also suggest al antibiotic therapy should increase the suspicion of either an ternative noninfectious disease, such as bronchiolitis obli tibiotic-resistant isolates or metastatic sites, such as endocarditis terans organizing pneumonia. Empyema and parapneumonic effusions are Despite the high frequency of infectious pulmonary causes important causes of nonresponse [81, 101], and thoracen of nonresponse, the diagnostic utility of respiratory tract cul tesis should be performed whenever signicant pleural uid tures is less clear. If the warranted because early colonization, rather than superinfec differential of nonresponse includes noninfectious pneu tion with resistant bacteria, is not uncommon in specimens monia mimics, bronchoscopy will provide more diagnostic obtained after initiation of antibiotic treatment. An etiology was determined by bronchoscopy alveolitis pointing toward virus or Chlamydophila infection. Stopping the b-lactam component of combination ther complications, household contacts of high-risk persons, apy to exclude drug fever is probably also safe [156]. Adapted from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [304]. Health care workers in inpatient and outpatient settings saccharide vaccine and inactivated inuenza vaccine are rec and long-term care facilities should receive annual in ommended for all older adults and for younger persons with uenza immunization. The effectiveness of the Coverage levels are lower for younger persons with vaccine vaccine against pneumococcal disease in immunocompromised indications. Ideally, patients should be vac been demonstrated, current guidelines do not suggest repeated cinated before developing pneumonia; therefore, admissionsfor revaccination. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine is under illnesses other than respiratory tract infections would be an investigation for use in adults but is currently only licensed for appropriate focus. However, its use in children important trigger for assessing the need for immunization. Patients with an acute fever should tors and on how closely the antigens in the vaccine are matched not be vaccinated until their fever has resolved. A systematic review a febrile reaction to immunization with recurrent/superinfec demonstrates that inuenza vaccine effectively prevents pneu tion pneumonia is a risk. A recent large for pneumonia is warranted for patients for whom outpatient observational study of adults 65 years of age found that vac follow-up is unreliable, and such vaccinations have been safely cination against inuenza was associated with a reduction in given to many patients. In long Inuenza and pneumococcal vaccines can be given at the same term-care facilities, vaccination of health care workers with time in different arms. Because the main virulence factors of inuenza for prevention and control of inuenza. Vaccination status should be assessed at the time of hos inuenza vaccine takes 2 weeks in adults; chemoprophylaxis pital admission for all patients, especially those with may be useful during this period for those with household medical illnesses. Vaccination may be performed either at hospital dis inuenza complications in the setting of a community outbreak charge or during outpatient treatment. Inuenza vaccine should be offered to persons at hospital vaccination for those who may not respond well to inuenza discharge or during outpatient treatment during the fall vaccine. Because it is unknown whether administering inuenza department about a condition of interest is the rst step to antiviral medications affects the performance of the new live getting public health professionals involved. Rules and regu attenuated intranasal vaccine, this vaccine should not be used lations regarding which diseases are reportable differ between in conjunction with antiviral agents. For pneumonia, most states require reporting for le Other types of vaccination can be considered. However, pneumonia is one of gation can determine whether others may be at risk and whether the major complications of pertussis. One-time vaccination with the new tetanus breaks caused by environmental contamination [130]. For most adults, In addition, any time avian inuenza (H5N1) or a possible the vaccine should be given in place of their next routine tet terrorism agent. In addition, pneumonia cases that are caused by path after their most recent tetanus/diphtheria booster. Smokers who will not quit should also be vaccinated for crowded settings of susceptible hosts, such as homeless shelters, both pneumococcus and inuenza.
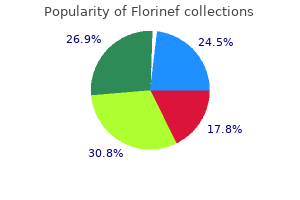
Order florinef 0.1 mg with amex
It is recommended that the mother continue the area where the plugged duct is located and the rest of the breast diet for gastritis sufferers order florinef 0.1mg mastercard. One out of 10 infants develops and breastfeed frequently to remedy and prevent this this condition. With increased feedings, the Poor Suckling condition usually improves within two weeks. An infant who does not appear to be correctly Q Breast milk jaundice is caused not by an infants lack attached to the breast, chews on the nipple, or of milk intake, but by substances in the mothers pushes the nipple out of his or her mouth may not milk that affect the ability of the infants body to rid be suckling effectively. The condition rarely causes improperly positioning an infant, incorrect use of the additional problems and usually subsides between 3 tongue while breastfeeding, nipple preference, and and 12 weeks of age as feedings continue. A expert who can provide assessment, counseling, and mother may feel these signs indicate that she is not follow-up services to correct suckling problems. Many mothers begin to supplement their feedings with infant 55 Jaundice formula, or even stop breastfeeding completely. After the birth of an infant, it is important to watch Mothers should not stop breastfeeding, and this the newborns health closely. One thing that the is why: the infant is actually signaling the mothers health care provider will monitor is jaundice. Mild body to produce more milk to meet the infants jaundice is common in most newborns and often growing needs. However, for moderate to keep the infant at the breast as often as the or severe cases of jaundice the infant may need infant demands to feed during this period. Jaundice is visible in the yellowing of feeding will increase her milk supply to meet her an infants skin and eyes. Jaundice occurs when a infants increased needs, and eventually the infant substance called bilirubin builds up in the infants will resume a more normal feeding pattern. Infants can continue to Q Infant nasal obstruction, gastroesophageal reflux breastfeed while growing teeth without causing disease, or teething pain to the mother. If the infant bears Efforts to restore or continue breastfeeding may down on the mother before the teeth come in, the take several days. Mothers will need reassurance to mother can discourage this behavior by slipping a continue the breastfeeding relationship and should finger in the infants mouth to break suction, then be encouraged to continue putting the infant to the removing the infant from the breast with a firm breast, especially when the infant shows signs of No (without yelling, which can scare the infant). Another option for mothers is to put the infant Mothers can also minimize distractions and increase down for a moment to show that biting brings a the amount of time holding or cuddling the infant, negative consequence; the infant can then be picked including using skin-to-skin contact. Infants learn be advised to maintain their milk supply by pumping quickly not to bite down if the feeding is stopped. Mothers should be instructed to to the infant before breastfeeding may also help provide the infant with pumped human milk in a cup, soothe the infants gums and prevent biting. When an infant does not Refusing to Breastfeed gain weight adequately, action should be taken to An infants sudden refusal to breastfeed is often increase weight and prevent premature weaning. It referred to as a nursing strike and may occur at is common for breastfed and formula-fed infants to any time. Mothers may perceive this as a personal lose a few ounces of weight in the first three or four rejection, and a nursing strike may lead to early or days of life. Many mothers never figure out stools and eliminate the extra fluids they are born what causes a nursing strike, but the following may with. After this period the infants weight loss should be among the reasons:57 reverse, and by the time the infant is 14 days old the birth weight should be exceeded. Night supplemented with water or any fluids other feedings are also important for the breastfeeding than human milk unless medically indicated. Artificial nipples on it is important to remind mothers that infants have bottles and pacifiers require different movements different feeding patterns with different time intervals. Bottles and pacifiers decrease the amount of time the infant spends Sleep deprivation is natural in the early weeks after breastfeeding, potentially leading to a mothers childbirth. Mothers can prevent this sleeping patterns is a learning process for parents by starting frequent breastfeeding immediately postpartum. After bottle-feeding, the sleep, but breastfeeding eliminates having to get up infant may become frustrated with the change and and prepare a bottle of formula. Some mothers may wish to partially bed in a bassinet, sleeping when the infant sleeps, breastfeed and feed some infant formula. Because resisting the temptation to do too much in the first the infant fills up on infant formula and suckles few weeks, and accepting help from others in order less from the breast, a reduction in the mothers to get more rest. Sleep through the night: Parents and caregivers have different definitions of what through the night means. Cluster feed: Also called bunch feed, this is when an infant feeds close together at certain times of the day, most commonly in the evening. Or, return will vary by circumstance and can include care only part time if possible in the early months after by relatives, center-based care, care provided birth. If a mother returns to work or school before in a temporary caregivers home, and care that time and is away from her infant for long provided in the infants home by another parent periods, she may have difficulty maintaining her or a temporary caregiver. A mother who is supports breastfeeding and, in the case of a comfortable expressing human milk manually childcare center, allows her to breastfeed if she (by hand) or mechanically (using a breast pump) visits. Instructions for the other parent or the can collect her milk while away from her infant. Department of Labor amended Section 7 of the Fair Labor Standards Act in the source given below. When a mother travels brief distances, to do most of their breastfeeding; this is not a such as to and from work or school, the pumped/ problem as long as the infant is consuming an expressed milk should be stored in a cooler or adequate amount to maintain proper growth. The mother should label each milk required for a mother to express adequate milk or container with the collection date and always use breastfeed during the day while she is working the oldest milk first. By that age, the mothers milk supply should be established and the infant should be able to move back and Flight Rules for forth between the mothers nipple and a bottle nipple. Many working on the plane whether or not the breastfeeding mothers begin giving formula to an infant because child is also traveling. Parents and caregivers they believe their milk production lessens when should know these points: they are not breastfeeding throughout the day. An infant 12 months or older may be given in infants being breastfed up to 1 year of age to 66 whole cows milk in a bottle and/or cup, depending on 34 percent. Some infants may infant from the breast is between each mother need to be weaned to a bottle because they are not and infant, the weaning process usually begins as developmentally ready to drink significant quantities of complementary foods are introduced and the infant liquid from a cup. Approach to Gradual Weaning Relactation Mothers who wish to wean their exclusively breastfed Either rebuilding a milk supply after it has been infants onto infant formula tend to experience less reduced or dried up, or building it from the start, is discomfort if the weaning process is gradual. Gradual weaning because she feels she is not producing enough milk also allows infants time to adjust to both the taste and therefore should feed her infant formula. If she of infant formula and to drinking from a bottle or decides to resume breastfeeding, relactation is easiest cup. Mothers can formally start weaning from the when attempted soon after weaning, especially if the breast by replacing a feeding of human milk with a infant is not yet 6 months of age (although it does feeding of infant formula (or whole cows milk if the work with older infants). Nonbirth feeding, the infant may be less interested in the next caregivers or parents who have never nursed can also breastfeeding and the mothers breasts may not feel relactate. The bedtime breastfeeding is often the last to guide on this process, which works best if the mother be eliminated. Gradually, over several days or even is motivated to follow the key steps, including breast weeks, additional breastfeedings can be eliminated. Relactation: Also called induced lactation, this is the process of a mother restarting her milk supply after she has weaned and her milk has dried up. The term can also be applied to a mother who has never nursed or to a nonbirth mother who wishes to develop a milk supply. Most women who desire to breastfeed can do so without Pharmacological Therapy problems. Under certain circumstances, a Few medications are contraindicated while physician will need to make a case-by-case breastfeeding; however, breastfeeding may not be assessment to determine whether a womans advised if the mother is receiving certain prescription environmental exposure or her medical condition medications for illness. The National gastrointestinal and urinary tract infections are Institutes of Health National Library of Medicine not contraindications to breastfeeding. More provides an online database with information about significant infectious diseases must be evaluated drugs and the implications for breastfeeding mothers, for the risk of transmission to the infant. If untreated, this disorder can lead to low blood sugar, vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, brain damage, and death. In fact, breastfeeding should be encouraged in most this section provides information on the use of cases. Additional assistance, monitoring, and cigarettes, alcohol, nonprescriptive drugs, caffeine encouragement should be provided during the containing products, herbal teas, and other products first few days and beyond to ensure sustained, during breastfeeding. If a pierced nipple was infected at any be an absolute contraindication to breastfeeding; time, scar tissue may have developed that could therefore, a mother who smokes cigarettes can make breastfeeding more difficult.
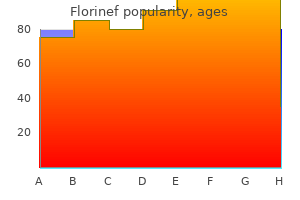
Discount florinef 0.1 mg mastercard
Determination of allergen speci erence serum gastritis symptoms ppt buy cheapest florinef, thereby enabling a uniform system of report ficity by inhibition of specific IgE binding is a unique at ing. Automated systems using multi ibration, an earlier specific IgE classification system was plexed allergen assays are being rapidly developed. The precise sensitivity of these cows milk are associated with Heiners disease, a non-IgE immunoassays compared with prick/puncture skin tests has disorder that presents in infants with pulmonary infiltrates. IgG and IgG subclass antibody studies; similar sensitivity ranges pertain when immunoas tests for food allergy do not have clinical relevance, are not says are compared with symptoms induced after natural or validated, lack sufficient quality control, and should not be controlled organ challenge tests. Although a number of investiga tation of specific IgE results requires correlation with the tors have reported modest increases of IgG4 during venom history, physical examination, and, in some cases, symptoms immunotherapy, confirmation and validation of the predictive directly observed after natural or laboratory exposure to al value of IgG4 for therapeutic efficacy of venom immunother lergens. The probability distribution of munotherapy on a history form submitted by the patient and specific IgE for several anaphylactogenic foods (peanuts, egg specific IgE results. Because the constitutive allerge as verified by double-blind oral challenge tests; similar rela nicity, potency, and stability are variable among commercial tionships have been defined for several respiratory allergens. Although allergens can be stan cells with essential roles in inflammatory and immune reac dardized either by radioimmunodiffusion or immunoassay tions, including the late-phase cutaneous response. Histamine and leukotriene re (B) lease measurements from human basophils after incubation Summary Statement 145. Other bioactive indices of cell with allergen are valuable research tools for in vitro investi mediated immunity include cytotoxic assays, cultures of gations of allergy. Proinflammatory cytokines or isolated basophils, mast cells, or other cultured cells. Abnormal serum and urine pro late highly with the diagnosis of allergic rhinitis, allergic teins, including cryoglobulins, may be associated with several asthma, and eosinophilic bronchitis. In some instances, functional assays of neutrophils flow cytometry is being evaluated for many IgE-mediated and macrophages may be necessary to pinpoint inflammatory disorders. Evaluation of complement acti function measure the ability of lymphocytes to (1) proliferate, vation with a decrease of C3 and C4 may indicate comple (2) produce inflammatory mediators and cytokines or chemo ment deficiency, drug reactions, or the presence of immune kines, (3) mount cytotoxic responses, and (4) regulate im complexes, which often are associated with increases in se mune responses. Autoantibody profiles offer im sponses may be evaluated by either nonspecific mitogens (eg, portant diagnostic adjuncts in the diagnosis of collagen vas phytohemagglutinin, concanavalin A, or pokeweed) or spe cular diseases, vasculitides, and cytotoxicity disorders. In vitro proliferative responses to evidence of diagnostic validity include cytotoxic tests, prov some soluble antigens, but not mitogens, have been shown to ocation-neutralization, electrodermal testing, applied kinesi correlate with in vivo delayed hypersensitivity. The role, ology, iridology, hair analysis, or food specific IgG, IgG4, however, of lymphocyte proliferation as measured in vitro in and IgG/IgG4 antibody tests. A well-designed skin test and epitopic determinants, more diffuse cross-reactivity due to laboratory ordering form should provide useful information plant profilins and cross-reactive carbohydrate determinants to the ordering physician, his/her staff, health care providers, may also be present. The skin prick/puncture test is prevalence in the air and concurrent allergy symptoms during superior to intracutaneous testing for predicting nasal allergic annually recurrent seasons when such pollens are expected to symptoms triggered by exposure to pollen. The clinical significance of a superior to intracutaneous testing for predicting allergic rhi single fungus test reagent may be difficult to ascertain be nitis and allergic asthma triggered by cat allergen exposure. The skin prick/puncture can be ences between spores, and hyphae and preferential ecologic used to rule out allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma triggered niches. Knowledge of allergen cross often characterized as outdoor (Alternaria and Cladosporium reactivity and local aerobiology is important in selecting species), indoor (Aspergillus and Penicillium species), or appropriate allergens and in minimizing the number of aller both (Alternaria, Aspergillus, and Penicillium species). In general, skin prick/puncture tracts are available for evaluation of anaphylactic reactions to testing is more sensitive for identifying sensitization to in honeybee, yellow jacket, yellow hornet, white faced hornet, halant allergens and confirming clinical allergy. A whole-body extract is the only currently specific IgE assays with defined quantifiable threshold levels available diagnostic reagent for fire ant sting allergy. Specific testing is well-characterized occupational protein allergens possesses guided by history of appropriate animal exposure. Selection of food tests for IgE (3-mm wheal diameter) can be used to rule out clinical mediated clinical sensitivity is usually tailored to the patients allergy. Although commercial skin tests ical IgE-mediated sensitization must undergo validation and for drugs, biologics, and chemicals are not available, special reproducibility in controlled studies using standardized anti ized medical centers prepare and use such tests under appro gens and assay protocols before these can be considered priate clinical situations. The primary tools available to grass, and weed pollens is essential in preparing an efficient evaluate patients adverse reactions to foods include history panel of test reagents. A small percentage of patients sensitive (generally 85%) but only modestly specific (ap (1%) with negative results to both skin and in vitro tests may proximately 40% to 80%) and therefore are well suited for experience anaphylaxis after a field sting. A skin test refractory period are not effective for indiscriminate screening (eg, using pan lasting up to 6 weeks after a venom sting has been demon els of tests without consideration of likely causes) and there strated by recent data. Intracutaneous (intradermal) skin sistencies of both skin and serum specific IgE tests, patients tests for foods are potentially dangerous, are overly sensitive, with a convincing history of venom-induced systemic reac increase the chance of a false-positive test result, and are not tions should be evaluated by both methods. Based on studies in infants and venoms is (1) extensive among vespid venoms, (2) consider children, increasingly higher concentrations of food specific able between vespids and Polistes, (3) infrequent between IgE antibodies (reflected by increasingly larger percutaneous bees and vespids, and (4) very limited between yellow jacket skin test size and/or higher concentrations of food specific and imported fire ants. A trial elimination diet may be endpoint titration with intracutaneous tests may be required. Graded oral food challenge is a once or twice at 3 to 6-month intervals to confirm the useful means to diagnose an adverse reaction to food. The rational selection, applica tion, and interpretation of tests for food specific IgE antibod supervised live insect challenge sting may confirm clinical ies require consideration of the epidemiology and underlying sensitivity. Nevertheless, most patients with suspected venom immunopathophysiology of the disorder under investigation, allergy do not require live stings. Evaluation of drug-specific IgE attributable to particular foods, and an understanding of the antibodies induced by many high-molecular-weight and sev test utility and limitations. Diagnostic skin and/or specific confirming the diagnosis and prediction of future IgE-medi IgE tests are used to confirm clinical sensitivity to venoms in ated reactions, such as anaphylaxis and urticaria. Although diagnostic tests identify for specific IgE antibodies are diagnostic of cytotoxic, im species specificity of venom sensitization, they do not reli mune complex, or cell-mediated drug-induced allergic reac ably predict severity of the sting reaction. Atopy patch tests, lymphocyte evaluation of imported fire sting allergy is a nonstandardized proliferation tests, and basophil activation tests are additional whole-body extract. In the case of a history of ana to confirm their clinical utility in the evaluation of drug phylaxis to Hymenoptera venoms, intracutaneous skin tests allergic patients. Skin testing is a useful diagnostic a procedure to determine if a drug is safe to administer and is tool in cases of perioperative anaphylaxis, and when skin intended for patients who are unlikely to be allergic to the testing is used to guide subsequent anesthetic agents, the risk given drug. In contrast to desensitization, a graded challenge of recurrent anaphylaxis to anesthesia is low. Skin testing for diagnosis of local lergy provided that the necessary reagents are available. The When performed with both major and minor determinants, gold standard for establishing a diagnosis of local anesthetic the negative predictive value of penicillin skin testing for allergy is the provocative challenge. Skin testing with penicilloyl and cases of corticosteroid allergy with negative skin test polylysine and penicillin G appears to have adequate negative results to the implicated corticosteroid have been reported. For most allergic reactions to tients (as determined by testing with major and minor deter additives, skin tests are of no diagnostic value, and placebo minants) may receive penicillin, and depending on which controlled oral challenges are required. Contact dermatitis is a common dose may need to be given via a test challenge with a lower skin disorder seen by allergists and dermatologists and can dose under observation. In the absence of validated skin (C) test reagents, the approach to patients with a history of Summary Statement 227. Factors that ternative antibiotic, (2) performing a graded challenge, and affect response to the contact agent include the agent itself, (3) performing penicillin desensitization. Tissue reactions to contactants skin test the implicated antibiotic and penicillin determinants. A positive skin test result suggests must be supported by a history of exposure to a putative agent the presence of drug-specific IgE antibodies, but the predic and subsequently confirmed by patch testing whenever this is tive value is unknown. Emphasis is patch test results should conform to principles developed by placed on reliability of reagents and devices. Quality assur the International Contact Dermatitis Research Group and the ance is also discussed in the context of reproducibility and the North American Contact Dermatitis Research Group. There are 7 generally acceptable independently introduced the intracutaneous test as a diag nostic method. Sir Thomas Lewis had exposure to plants is the result of specific cell-mediated first suggested the puncture technique as an alternative skin test. Allergic contact dermatitis due to Prick/Puncture Tests topical corticosteroids may occur in up to 5% of patients with Summary Statement 2. The role of detergents in hand Prick/puncture tests are widely used for confirmation of clin dermatitis is a reflection of their ability to disrupt the skin ical immediate hypersensitivity induced by a wide variety of barrier. Allergic contact dermatitis is a Under carefully defined circumstances, these tests are also significant clinical problem in children.
Syndromes
- Changes in your mitral valve are causing major heart symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting spells, or heart failure.
- Alopecia (hair loss)
- Cardiac catheterization (rarely needed, unless there are concerns of high blood pressure in the lungs)
- Muscle biopsy
- How tall are you? How much do you weigh?
- Try drinking water or sports drinks that contain electrolytes.
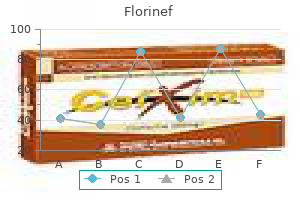
Buy cheap florinef
Navigational Note: Ileal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic gastritis child florinef 0.1mg discount, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the ileum and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Jejunal fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the jejunum and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Pancreatic fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between the pancreas and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Pancreatic hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the pancreas. Navigational Note: Pancreatitis Enzyme elevation; radiologic Severe pain; vomiting; Life-threatening Death findings only medical intervention indicated consequences; urgent. Navigational Note: Periodontal disease Gingival recession or Moderate gingival recession Spontaneous bleeding; severe gingivitis; limited bleeding on or gingivitis; multiple sites of bone loss with or without probing; mild local bone loss bleeding on probing; tooth loss; osteonecrosis of moderate bone loss maxilla or mandible Definition:A disorder in the gingival tissue around the teeth. Navigational Note: Rectal fissure Asymptomatic Symptomatic Invasive intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a tear in the lining of the rectum. Navigational Note: Rectal hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the rectal wall and discharged from the anus. Navigational Note: Salivary duct inflammation Slightly thickened saliva; Thick, ropy, sticky saliva; Acute salivary gland necrosis; Life-threatening Death slightly altered taste. Navigational Note: Salivary gland fistula Asymptomatic Symptomatic, invasive Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an abnormal communication between a salivary gland and another organ or anatomic site. Navigational Note: Neck edema Asymptomatic localized neck Moderate neck edema; slight Generalized neck edema. Navigational Note: Portal hypertension Decreased portal vein flow Reversal/retrograde portal Life-threatening Death vein flow; associated with consequences; urgent varices and/or ascites intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an increase in blood pressure in the portal venous system. Navigational Note: Portal vein thrombosis Intervention not indicated Medical intervention Life-threatening Death indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by the formation of a thrombus (blood clot) in the portal vein. Clinically, it presents with breathing difficulty, dizziness, hypotension, cyanosis and loss of consciousness and may lead to death. Navigational Note: Autoimmune disorder Asymptomatic; serologic or Evidence of autoimmune Autoimmune reactions Life-threatening Death other evidence of reaction involving a non involving major organ. Symptoms include fever, arthralgias, myalgias, skin eruptions, lymphadenopathy, chest marked discomfort and dyspnea. Navigational Note: Bacteremia Blood culture positive with no signs or symptoms Definition:A disorder characterized by the presence of bacteria in the blood stream. Navigational Note: Endophthalmitis Local intervention indicated Systemic intervention; Best corrected visual acuity of hospitalization indicated 20/200 or worse in the affected eye Definition:A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the internal structures of the eye. Navigational Note: Fungemia Moderate symptoms; medical Severe or medically significant intervention indicated but not immediately life threatening; hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by the presence of fungus in the blood stream. Unlike acne, this rash does not present with whiteheads or blackheads, and can be symptomatic, with itchy or tender lesions. Navigational Note:Synonym: Boil Rhinitis infective Localized; local intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an infectious process involving the nasal mucosal. Navigational Note: Fall Minor with no resultant Symptomatic; noninvasive Hospitalization indicated; injuries; intervention not intervention indicated invasive intervention indicated indicated Definition:A finding of sudden movement downward, usually resulting in injury. Navigational Note: Gastrointestinal anastomotic Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death leak finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition:A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a gastrointestinal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Gastrointestinal stoma Superficial necrosis; Severe symptoms; Life-threatening Death necrosis intervention not indicated hospitalization indicated; consequences; urgent elective operative intervention indicated intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a necrotic process occurring in the gastrointestinal tract stoma. Navigational Note: Intestinal stoma site bleeding Minimal bleeding identified Moderate bleeding; medical Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death on clinical exam; intervention intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent not indicated indicated intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding from the intestinal stoma. Navigational Note: Kidney anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition:A finding of leakage of urine due to breakdown of a kidney anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Pharyngeal anastomotic leak Asymptomatic diagnostic Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; invasive Life-threatening Death finding; intervention not intervention indicated intervention indicated consequences; urgent indicated operative intervention indicated Definition:A finding of leakage due to breakdown of a pharyngeal anastomosis (surgical connection of two separate anatomic structures). Navigational Note: Stomal ulcer Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; elective diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated operative intervention intervention not indicated indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a circumscribed, erosive lesion on the jejunal mucosal surface close to the anastomosis site following a gastroenterostomy procedure. Navigational Note: Uterine perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death indicated indicated consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a rupture in the uterine wall. Navigational Note: Wound complication Observation only; topical Bedside local care indicated Operative intervention Life-threatening Death intervention indicated indicated consequences Definition:A finding of development of a new problem at the site of an existing wound. Navigational Note:Also consider Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic failure Blood antidiuretic hormone Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Hospitalization indicated abnormal diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated intervention not indicated Definition:A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate abnormal levels of antidiuretic hormone in the blood specimen. Cardiac troponin T increased Levels above the upper limit Levels consistent with of normal and below the level myocardial infarction as of myocardial infarction as defined by the manufacturer defined by the manufacturer Definition:A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate increased levels of cardiac troponin T in a biological specimen. Report Cardiac disorders: Heart failure or Cardiac disorders: Myocardial infarction if same grade event. Navigational Note:Also consider Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Report Cardiac disorders: Left ventricular systolic dysfunction if same grade event. Navigational Note: Lymphocyte count increased >4000/mm3 20,000/mm3 >20,000/mm3 Definition:A finding based on laboratory test results that indicate an abnormal increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, effusions or bone marrow. Navigational Note:Also consider Investigations: Forced Expiratory Volume; Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory failure or Dyspnea Weight gain 5 <10% from baseline 10 <20% from baseline >=20% from baseline Definition:A finding characterized by an unexpected or abnormal increase in overall body weight; for pediatrics, greater than the baseline growth curve. Navigational Note: Anorexia Loss of appetite without Oral intake altered without Associated with significant Life-threatening Death alteration in eating habits significant weight loss or weight loss or malnutrition consequences; urgent malnutrition; oral nutritional. Navigational Note: Glucose intolerance Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; dietary Severe symptoms; insulin Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; modification or oral agent indicated consequences; urgent intervention not indicated indicated intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by an inability to properly metabolize glucose. Navigational Note: Hyperphosphatemia Laboratory finding only and Noninvasive intervention Severe or medically significant Life-threatening Death intervention not indicated indicated but not immediately life consequences; urgent threatening; hospitalization or intervention indicated. Navigational Note:Use term Investigations: Weight gain Tumor lysis syndrome Present Life-threatening Death consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by metabolic abnormalities that result from a spontaneous or therapy-related cytolysis of tumor cells. Navigational Note: Osteonecrosis of jaw Asymptomatic; clinical or Symptomatic; medical Severe symptoms; limiting self Life-threatening Death diagnostic observations only; intervention indicated. Navigational Note: Rhabdomyolysis Asymptomatic, intervention Non-urgent intervention Symptomatic, urgent Life-threatening Death not indicated; laboratory indicated intervention indicated consequences; dialysis findings only Definition:A disorder characterized by the breakdown of muscle tissue resulting in the release of muscle fiber contents into the bloodstream. Navigational Note: Skin papilloma Asymptomatic; intervention Intervention initiated not indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by the presence of one or more warts. Navigational Note: Tumor hemorrhage Mild symptoms; intervention Moderate symptoms; Transfusion indicated; Life-threatening Death not indicated intervention indicated invasive intervention consequences; urgent indicated; hospitalization intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by bleeding in a tumor. Navigational Note: Anosmia Present Definition:A disorder characterized by a change in the sense of smell. Navigational Note:Also consider Olfactory nerve disorder Aphonia Voicelessness; unable to speak Definition:A disorder characterized by the inability to speak. Navigational Note: Cognitive disturbance Mild cognitive disability; not Moderate cognitive disability; Severe cognitive disability; interfering with interfering with significant impairment of work/school/life work/school/life performance work/school/life performance performance; specialized but capable of independent educational services/devices living; specialized resources not indicated on part time basis indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a conspicuous change in cognitive function. Navigational Note: Dysphasia Awareness of receptive or Moderate receptive or Severe receptive or expressive expressive characteristics; not expressive characteristics; characteristics; impairing impairing ability to impairing ability to ability to read, write or communicate communicate spontaneously communicate intelligibly Definition:A disorder characterized by impairment of verbal communication skills, often resulting from brain damage. Navigational Note: Edema cerebral New onset; worsening from Life-threatening Death baseline consequences; urgent intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by swelling due to an excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain. Navigational Note: Ischemia cerebrovascular Asymptomatic; clinical or Moderate symptoms diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction (thrombosis or embolism) of an artery resulting in neurological damage. Navigational Note: Tendon reflex decreased Ankle reflex reduced Ankle reflex absent; other Absence of all reflexes reflexes reduced Definition:A disorder characterized by less than normal deep tendon reflexes. Typically, viability is achievable between the twentieth and thirty-seventh week of gestation. Navigational Note: Delayed orgasm Delay in achieving orgasm not Delay in achieving orgasm adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition:A disorder characterized by sexual dysfunction characterized by a delay in climax. Navigational Note: Delusions Moderate delusional Severe delusional symptoms; Life-threatening Death symptoms hospitalization not indicated; consequences, threats of new onset harm to self or others; hospitalization indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by false personal beliefs held contrary to reality, despite contradictory evidence and common sense. Navigational Note: Euphoria Mild mood elevation Moderate mood elevation Severe mood elevation. Navigational Note: Libido decreased Decrease in sexual interest Decrease in sexual interest not adversely affecting adversely affecting relationship relationship Definition:A disorder characterized by a decrease in sexual desire. Navigational Note: Psychosis Mild psychotic symptoms Moderate psychotic Severe psychotic symptoms Life-threatening Death symptoms. Navigational Note:Also consider Investigations: Creatinine increased Bladder perforation Invasive intervention not Invasive intervention Life-threatening Death indicated indicated consequences; organ failure; urgent operative intervention indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by a rupture in the bladder wall. Navigational Note: Hemoglobinuria Asymptomatic; clinical or diagnostic observations only; intervention not indicated Definition:A disorder characterized by laboratory test results that indicate the presence of free hemoglobin in the urine. Navigational Note: Proteinuria 1+ proteinuria; urinary protein Adult:2+ and 3+ proteinuria; Adult:Urinary protein >=3.
Order florinef now
In vitro assays for the diagnosis of logical assays for natural rubber latex-specific immunoglobulin E Ige-mediated disorders gastritis symptoms worse night buy discount florinef 0.1mg on line. In vitro demonstration of purified Hevea brasiliensis proteins in health care workers sensitized specific IgE in phthalic anhydride hypersensitivity. Conifer pollen allergy: Studies of induced airway syndromes: clinical and immunologic studies. J Al immunogenicity and cross antigenicity of conifer pollens in rabbit and lergy Clin Immunol. Role of skin prick test and of cross-reactive allergens in Kentucky bluegrass and six other grasses serological measurement of specific IgE in the diagnosis of occupa by crossed radioimmunoelectrophoresis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immu tional asthma resulting from exposure to vinyl sulphone reactive dyes. Serum albumins are the of purified DacgIandLol p I, the major allergens of Dactylis major site for in vivo formation of hapten-carrier protein adducts in glomerata and Lolium perenne pollens, using monoclonal antibodies. Mapping epitopes on PoapIand LolpIallergens with ducing hexahydrophthalic anhydride. Cross-reactivity among five logic evaluation of foundry workers exposed to methylene diphenyl major pollen allergens. Specific serum antibodies pollen, a significant aeroallergen: evidence for the lack of clinical against isocyanates: association with occupational asthma. Skin-prick testing as a diag allergy: multicenter latex skin testing efficacy study. False-negative food challenges in chil and double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges in children with dren with suspected food allergy. J allergen challenges in young children: a comparison of in vitro with in Allergy Clin Immunol. Comparison of results of development of tolerance to milk in children with cows milk hyper skin prick tests (with fresh foods and commercial food extracts) and sensitivity. Natural history of large levels in the diagnosis of immediate hypersensitivity to cows milk local reactions from stinging insects. Proper use of skin tests with food Insects of the American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunol extracts in diagnosis of food hypersensitivity. Immunologic mechanisms of penicillin allergy: a haptenic and in vitro tests in the diagnosis of imported fire ant sting allergy. Efficacy and safety of desen anaphylactic risk in patients with suspected yellow jacket hypersen sitization to allopurinol following cutaneous reactions. Hypersensitivity reactions to drugs: evaluation and after discontinuing venom immunotherapy. A controlled trial of desensitization for aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: a practice immunotherapy in insect hypersensitivity. Natural history of insect sting allergy: Relationship of nonimmediate allergic reactions to penicillins. J Allergy Clin lenge in 324 subjects with a previous anaphylactic reaction: Current Immunol. Lymphocyte transformation sensitive and efficient technique in diagnosing allergy to wasp venom. T cell reactions in carbohydrates is a frequent cause for double positivity to honeybee and yellow jacket venom in patients with stinging insect allergy. Hymenoptera venoms: composition, standardization, T lymphocytes in bullous cutaneous reactions caused by beta-lactam stability. J Investig Allergol menoptera venoms for immunotherapy based on patients IgE anti Clin Immunol. Prospective evaluation of determination of basophil activation induced by aspirin and other chymopapain sensitivity in patients undergoing chemonucleolysis. Penicillin allergy: prevalence of Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Clinical vague history in skin test-positive patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Im Trial to test the predictive value of skin testing with major and minor munol. A liquid chromatographic study nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: clinical and cross-reactivity of stability of the minor determinants of penicillin allergy: a stable studies. Prevention of anaphylactic reactions to anaes experience with a battery of skin-test reagents. Evaluation of penicillin threatening anaphylactoid reactions to propofol (Diprivan). Anesthe hypersensitivity: value of clinical history and skin testing with peni siology. J induction of general anesthesia: subsequent evaluation and manage Allergy Clin Immunol. Anaphylaxis during surgical and interventional examination: is this patient allergic to penicillin Anaphylaxis to challenge in patients with negative skin test responses to penicillin muscle relaxants: cross-sensitivity studied by radioimmunoassays reagents. The value of routine penicillin carboplatin administration are common but not always severe: a allergy skin testing in an outpatient population. Elective penicillin skin testing and amoxicillin challenge: hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin. Allergy to penicillin with good testing: a skin-testing protocol for predicting hypersensitivity to car tolerance to other penicillins; study of the incidence in subjects boplatin chemotherapy. Immediate allergic reactions to an intradermal skin test to predict for the presence or absence of amoxicillin. Int J Gy reactions to cephalosporins: evaluation of cross-reactivity with a panel necol Cancer. Aspirin-induced asthma: advances in among amide-type local anesthetics in a case of allergy to mepiva pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Sensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory thetics despite IgE deficiency: a case report. Allergic contact dermatitis and incremental challenge tests in patients with history of adverse from shellac in mascara. Cosmetic allergy: incidence, diagnosis, and investigation of allergy to local anesthetic agents. Allergic contact dermatitis in patients with causing false-positive results of local anesthetic skin testing or pro anogenital complaints. Anaphylactoid reaction to corticosteroid: Dermatitis Group patch test results for the detection of delayed-type case report and review of the literature. Common hyperpigmentation disor by the carboxymethylcellulose component of injectable triamcinolone ders in adults, part I: diagnostic approach, cafeau lait macules, diffuse acetonide suspension (Kenalog). Role of contact allergens in Prausnitz-Kustner reactions in metabisulfite-sensitive subjects. Occupational allergic contact subjects with experimentally induced allergic and irritant contact dermatitis from bisphenol A in vinyl gloves. Intraoperative anaphy using mass spectrometry as a new screening method for skin sensiti lactic shock associated with bacitracin irrigation during revision total zation. Contact sensitization in 1094 tion claims related to natural rubber latex gloves among Oregon children underlying patch testing over a 7 year period. Clinical presentation of patients sensitive to natural rubber children: strategies of prevention and risk management. Allergic contact dermatitis in children: a outcomes in health care workers with natural rubber latex allergy. Dzurella, Holly Canada, Sarah Laybourne, Chiara McKenney, Jeannie Darby, 1 James F. Quinn, Thomas Harter Center for Watershed Sciences University of California, Davis California Nitrate Project, Implementation of Senate Bill X2 1 Tulare Lake Basin and Salinas Valley Pilot Studies Prepared for: California State Water Resources Control Board July 2012 1 Corresponding author: thharter@ucdavis. Technical Report 2 in: Addressing Nitrate in Californias Drinking Water with a Focus on Tulare Lake Basin and Salinas Valley Groundwater. An electronic copy of this Final Report is available from the following website: groundwaternitrate. University policy also prohibits reprisal or retaliation against any person in any of its programs or activities for making a complaint of discrimination or sexual harassment or for using or participating in the investigation or resolution process of any such complaint. University policy is intended to be consistent with the provisions of applicable State and Federal laws. Disclaimer: the contents of this document are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of supporting agencies For further inquiries, please contact Thomas Harter, Ph.
Best florinef 0.1mg
Female rats exhibited a similar dose-dependent increase in severity of scores for the above indices gastritis left untreated purchase florinef 0.1mg overnight delivery, with 100% of animals being graded as severe for splenic congestion and increased extramedullary hematopoiesis. Increased brown pigmentation in red pulp was graded as severe in two and moderate in three female rats. Liver scores were graded as no change in all groups, except for the high-dose animals in both sexes. In high-dose males and females, increased extramedullary 41 hematopoiesis was moderate in five males and two females and exhibited no change in one male and three females. Brown pigmentation in Kupffer cells was moderate in five males and four females and severe in one male and one female. Absolute kidney weights in males were inconsistent with the histopathologic finding. In the highest dose group, brown pigmentation in tubular epithelium was reported as moderate in five animals and severe in one animal, but no change in absolute kidney weight was reported at the highest dose. In contrast, female histopathology of the kidney correlated with the absolute weight in that 100% of animals were graded with moderate brown pigmentation in tubular epithelium at the highest dose, and a 3% increase in absolute kidney weight was also observed at the highest dose. Decreased absolute testis weight correlated with severe degeneration of seminiferous tubular epithelium and severe atrophy of seminiferous tubule in 100% of male rats receiving 125 mg/kg nitrobenzene. Chronic Studies No studies were identified that addressed the chronic toxicity of nitrobenzene administered via the oral route. During the in-life phase of the 90-day study, behavioral signs were observed twice daily, and body weights were monitored weekly. At the end of the 90-day exposure period, animals were fasted overnight and then sacrificed following an i. Samples of blood were taken to measure hematologic and clinical chemistry parameters. Animals were examined for gross abnormalities at necropsy, and the weights of certain key target organs, such as the spleen, liver, kidney, testes, and brain, were recorded. Eight-hour urine samples were obtained from all animals after 60 days of exposure. Among the parameters assessed were color, turbidity, specific gravity, pH, protein, glucose, ketones, bilirubin, blood, and the presence of cells, casts, and crystals. Histopathologic examination was carried out in a full range of excised organs and tissues, including the epithelium lining the air passages of the nose and lungs. There were no compound-related effects on body weight, mortality, or the occurrence of behavioral signs in the subchronic 90-day study. By contrast, there was a statistically significant reduction in testis weight in male F344 rats exposed to 50 ppm nitrobenzene. Examination of the internal organs of exposed animals at necropsy confirmed that the liver, spleen, and testis were the primary target organs of nitrobenzene. For example, in high-concentration rats of either strain, males presented with testicular atrophy, enlarged spleens, and the presence of irregular blotches on the surface of the liver. Similarly, both sexes of B6C3F1 mice had enlarged spleens in response to nitrobenzene at 50 ppm. A number of statistically significant changes occurred in the hematologic parameters under investigation, but all were not obviously related to exposure concentration. However, in the rats, there was an increased incidence of hemolytic anemia in response to increased concentrations of nitrobenzene. Most marked among the potential compound-related changes in hematologic or clinical chemistry parameters were the increased concentrations of serum metHb (Table 4-17) and a 50% increase in the concentration of bilirubin in male F344 rats receiving 16 and 50 ppm nitrobenzene. Histologic sections of organs and tissues of nitrobenzene-receiving rats and mice demonstrated treatment-related lesions in the spleen, testis, liver, epididymides, kidney, and bone marrow, plus other possible target organs of nitrobenzene, such as the adrenals, 43 lymph nodes, and lungs. For example, in F344 rats, lesions in the spleen consisted of acute sinusoidal congestion, proliferative capsular lesions, and increases in extramedullary hematopoiesis. These effects were dose dependent with 10/10 animals of either sex affected in F344 rats exposed to 50 ppm. Histopathologic effects of nitrobenzene on the liver in F344 rats included disorganization of the hepatic cord architecture and centrilobular degeneration of the hepatocytes in 7/10 high concentration males but only in 1/10 high-concentration females. Other histopathologic effects evident in F344 rats included basophilia of the medullary cells of the adrenal in 5/10 high concentration males and in 3/10 high-concentration females, plus an increased incidence of bronchial hyperplasia in both sexes receiving the highest dose. All male F344 rats displayed degeneration of tubular epithelial cells in the testis. The condition was described by the authors as representing a cessation of maturation at the level of primary and secondary spermatocytes and was usually accompanied by interstitial edema and hyperplasia of Leydig cells. Instead, the presence of some apparently proteinaceous material was noted in the ducts. Kidney effects of nitrobenzene in F344 rats were characterized by a toxic nephrosis associated with an accumulation of droplets in the cytoplasm of proximal tubular epithelial cells. The droplets were described in the report as hyaline and eosinophilic, and the lesions increased in incidence and severity with dose in both sexes of F344 rats. The report makes no mention of whether or not kidney sections were stained for the male rat-specific protein, 2u-globulin. In the absence of this information and in view of the appearance of kidney lesions in both sexes of F344 rat, the kidney responses cannot be assigned to 2u-globulin-associated nephropathy (U. For example, the splenic lesions consisted of sinusoidal congestion, increased extramedullary hematopoiesis, and numbers of hemosiderin-laden macrophages infiltrating the red pulp. These features were evident in 1/10 subjects receiving 5 ppm nitrobenzene, 2/10 receiving 16 ppm, and 9/10 receiving nitrobenzene at the highest concentration. These lesions were characterized by the occurrence of lymphoid hyperplasia, inflammation, and the presence of interstitial and granulomatous pneumonitis, together with the presence of macrophages and lymphocytes in perivascular areas. The adrenal gland, liver, and spleen were also target organs of nitrobenzene in B6C3F1 mice, as judged by the range of histopathologic lesions observed in the study. In the liver, instances of centrilobular hyperplasia were noted in mid (4/9) and high-concentration (9/9) males, compared with 7/9 high-concentration females displaying these lesions. Animals were observed for clinical signs twice daily, with body weights determined weekly for the first 13 weeks and twice weekly thereafter. For the scheduled interim and final sacrifices, animals were fasted overnight, weighed, and then anesthetized using an i. In addition, a percentage metHb value was determined, and the relative and absolute differential cell counts were 46 determined microscopically. A wide range of tissues from high-concentration and control animals and all gross lesions were processed for histopathologic examination. Tissues considered to be specific targets of nitrobenzene, such as liver, spleen, and nose, were examined microscopically in all exposure groups. Additional tissues were examined where significant findings of toxicity had become evident in the high-dose group. Effects of nitrobenzene on clinical signs, body weight changes, and survival appeared to be sporadic and unrelated to dose. For example, during the first 2 weeks of exposure, nine B6C3F1 mice died (across all exposure groups) and were replaced with substitutes of the same age and shipment. The probability of survival was not statistically significantly affected by exposure to nitrobenzene since the actual percentage of mice available during final euthanasia was 55. After rejecting autolyzed specimens from animals that were found dead, all available tissues, including those from animals that were sacrificed in a moribund state, were fixed and evaluated microscopically. The numbers of examined lungs in mice were 68/70, 67/70, 65/70, and 66/70 in males and 53/70, 60/70, 64/70, and 62/70 in females of the 0, 5, 25, and 50 ppm nitrobenzene exposure groups, respectively. Other target organs in mice or rats also had similar or identical numbers of tissues examined per group as specified here for the mouse lung (Cattley et al. A summary of the positive findings of tumor formation in the study in animals with two years of exposure is shown in Table 4-19. Animals sacrificed at 15 months (interim) were not included in the analysis because they were deliberately removed from the study, rather than being removed due to nitrobenzene-induced effects. In male F344 rats, the incidence of combined adenomas and carcinomas in liver displayed a statistically significant trend and an increased incidence with dose (16/46 in males receiving 25 ppm compared with 1/43 in controls). Similarly, statistically significant trends for dose-dependent increases in combined adenomas and carcinomas in kidney and thyroid were observed in male F344 rats but not in females. However, there was a dose dependent trend and statistically significant increase in the incidence of endometrial polyps in female F344 rats (19/49 in rats exposed to 25 ppm versus 9/48 in controls).
Buy generic florinef 0.1 mg
It should be out of the parent for Infants or caregivers walking path chronic gastritis operation buy cheap florinef on line, away from shelving and objects that could fall, and away from It is important that parents and caregivers continually rocking chairs and other potential hazards. Parents items in the space should be lightweight for easy and caregivers should not only allow infants to handling and grasping, contain no pieces that move as freely as possible in a safe and monitored the infant can swallow, have no sharp points or environment, but also incorporate easy, fun, and edges, and be nontoxic. Solo playtime: When an infant plays alone in a safe environment with a parent or caregiver supervising nearby but not directly interacting. This should not include solo media use, such as allowing an infant to watch television. These can include lifting the health care provider regarding the appropriate age to head and neck to observe new surroundings; place an infant on his or her stomach. The back is a good shoulder and neck strength; this also puts the position for allowing the infant to stretch, for infant in the right position to practice crawling. A play mat with a See also: Make Moving Fun: Encourage a Playful toys suspended above the infant allows for the Infant! Talk along the furniture, holding the infants hands to the infant about the pretty colors of the toys while he or she practices (be sure to remove or and point to each one. Smile and give words of pad sharp-edged furniture); or encourage the encouragement as the infant focuses on the toys. Give continuous words of encouragement, and make sure stairs are off-limits with a gate or and then move the object into the infants grasp; be other safety blockade. For support, prop the infants back against a rolled-up towel and place a small, folded washcloth beneath Play Positions the infants head. Make sure that both arms It is important for every parent or caregiver to know are out in front of the infant, and then bring the the positions that best promote safety when an infants legs forward at the hips and bend the infant is playing actively and to provide walled knees for comfort. Change the infants position every 10 Chapter 6, Sleeping Patterns and Safe Sleep to 15 minutes during playtime. Whatever the position, dont forget to distract the infant with a fun toy or to Tummy to Play read an entertaining book or sing songs. Strive to expose the infant tummy time (lying on their stomach) to strengthen to a variety of all the positions throughout the day, their head, neck, and upper body muscles. Tummy including time spent in a parent or caregivers time helps to build the strength, coordination, and arms and on his or her lap. Remember, infants flexibility needed for rolling over, crawling, reaching, crave emotional interaction and connection with and playing. Interact with the infant in daily Parents and caregivers should create a safe play space physical activities that are dedicated to exploring for an infant to stretch, roll, and try new skill-building movement and the environment. Move infants from one position or place to another and introduce new toys and activities, and place the infant on a different colored towel or rug. When carrying the infant around the house, especially while doing chores, the infant should be strapped in an infant carrier. Otherwise the infant can arch his or her back and flip out of a parent or caregivers arms. Hide behind hands or a blanket and pop out at intervals; infants love anticipating the surprise. While playing or singing happy music, rotate or pump the infants legs as if riding a bicycle or dancing. Then try other dance moves with their arms, like rotating them or pumping them gently backward and forward. But try activities each day; gradually, infants become more comfortable with the positions and activities and can do them for longer periods of time. Use happy, age-appropriate songs and give the infant a rattle to shake or a pan to beat along with the rhythm. These should stimulate the senses and can include toys that make sounds and those with varied textures and colors. Rattles, large blocks, bubbles, balls, pans, wooden spoons, small boxes, and small stuffed animals are great examples. This is the most common accident associated with infant walkers, and it can result in broken bones and severe head injuries. An infant can reach higher in a walker, so he or she could pull a tablecloth off a table, causing any hot coffee or soup vessels on the table to fall; grab pot handles off the stove; or push fingers or toes into radiators, fireplaces, or space heaters. They can be in the fluids on a shelf are easier for an infant to reach in middle of family activity and interact with their a walker. An infant in a walker can move more than all times and to use the high chair appropriately, 3 feet in 1 second, and parents or caregivers simply mainly at mealtimes. They usually have seats that rotate, tilt, and bounce, 38 Media Use and Inactivity allowing the infant to use and develop large muscles. Examples of media activities are In addition to the danger of using a walker, the watching television and videos, playing computer or misuse of other infant equipment, including infant video games, or any other screen-based activities. Specifically, benefits to infants and toddlers are shown to be infants are programmed to learn from interacting limited, and inappropriate use can be harmful. The earlier they If parents and caregivers choose to engage their can begin healthy person-to-person interaction as infants with electronic media, they are encouraged opposed to media interaction, the better. That way, the parent or promote a calm family environment and caregiver can monitor the viewing time and help conversation that leads to relaxed eating and an the infant or child understand how the media infants increased recognition of satiety cues. Even for infants as young as 4 months programs are not necessary for the development of age, solo play, with the parent or caregiver of motor skills in infancy. An infant of drowning if a false sense of security around learns more from playing with soft, appropriate water is fostered. Additional concerns include the risk from watching a screen for the same amount of of gastrointestinal tract infections, dermatitis, time, because of the eye contact and interaction. Always child to new words,but with the television on, the consult a health care provider before entering an parent or caregiver is distracted and there is less infant in a swimming program. Maffulli, At What Age Should a Child Begin Regular Continuous Exercise at Moderate or High Intensity Krugman, Newborn Adiposity by Body Mass Index Predicts Childhood Overweight, Clinical Pediatrics 49, no. Gahagan, The Effect of Maternal Obesity on the Offspring, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology 57, no. Iotova, Early Growth Patterns and Long-Term Obesity Risk, Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 13, no. Stricker, Sports Physiology, American Academy of Pediatrics, last modified November 21, 2015, Staines, Locomotor Milestones and Babywalkers: Cross Sectional Study, British Medical Journal 324, no. Bartlett, Infant Motor Development and Equipment Use in the Home, Child Care Health and Development 27, no. Christakis, The Association between Television Viewing and Irregular Sleep Schedules among Children Less Than Three Years of Age, Pediatrics 116, no. Meltzoff, Associations between Media Viewing and Language Development in Children under Age of Two Years, Journal of Pediatrics 151, no. Because infants have immature immune systems, they are particularly sensitive to disease-producing microorganisms and toxins that may contaminate food. This chapter reviews the Q Clean hands and kitchens for importance of safe food preparation and storage, and it warns infant safety of the potential contaminants that can harm an infant. Be sure to lather the backs of hands, sanitizers as effectively as possible: between fingers, and under fingernails. As children grow, teach them when and how to wash Rub the product over all the surfaces of the their hands.

Order genuine florinef on-line
It will take time to determine whether conditional guidelines can be developed for Gram-negative drug entry and efux avoidance gastritis diet treatment infection buy genuine florinef. Meanwhile, practical and transparent knowledge-sharing mechanisms should be established to better inform discovery scientists on how to identify new chemical matter based on drug-like qualities and what is already known about the chemical properties of antibiotics. This would require collaborative research to facilitate new and directed approaches to generate and modify chemical matter. For example, working together across multiple disciplines, scientists may begin to develop new semi-synthetic antibiotic templates derived from fragment-based or natural products-based starting points that better target Gram-negative or Gram positive bacteria. Alongside a synthetic based approach, natural products may be identifed through alternative cultivation or novel screening methods and carefully vetted, then modifed through medicinal chemistry approaches for inclusion in these prototype libraries. Over the past two decades, despite the technical challenges and resource limitations, scientists have discovered novel natural products of interest. This indicates that new antibiotic starting points may be out there, but that fnding them will require ingenuity. Until recently, to generate natural products for testing, only a small fraction of bacteria could be grown or fermented under standard laboratory conditions. Early proof-of-concept studies indicate that new methods for the cultivation of bacteria in their native environment may aford new possibilities for natural products discovery, as might old techniques such as cell-based phenotypic screening, which have started to make a comeback in a more sophisticated form. Several researchers have devised genetic methods to express these silent gene clusters and produce natural products in heterologous hosts. Finding those rare novel natural products that are efective and nontoxic antibacterials will require a focused efort. Products that were approved for the clinic but withdrawn because of toxicity or antibiotic resistance issues could be revisited as well. As a part of this efort, medicinal chemists may take a second look at published natural product antibacterials, review their status, and evaluate whether problems, such as toxicity, metabolic issues, narrow spectrum of activity, or resistance issues, that may have prevented compounds from moving to clinical development can be overcome through chemical modifcation and testing. Once prototype libraries are established, conditional guidelines for drug entry and efux avoidance for Gram negative pathogens could be applied more broadly to build a curated resource of diverse chemical material for use by the broader scientifc community. The goal of this efort would not be to build massive compound collections, but to create a carefully vetted and annotated source of compounds tailored for antibiotic discovery. Unlike the prototype libraries described above, which would serve best as probes for testing conditional guidelines for drug entry and efux, scaled-up chemical libraries would be designed to serve as a source of antibiotic starting material and as a model for creating additional chemical libraries. Chemical synthesis to generate compounds could be carried out through contract research organizations or in partnership with synthesis and natural products laboratories. To build a diverse collection, work should 12 incorporate a variety of synthesis methods and draw from multiple synthetic and natural products sources. The number of compounds produced would be limited by established physicochemical properties and structural guidelines, but it could be large enough to carry out targeted screens for antibiotic starting points. Other biomedical initiatives, such Medicines for Malaria Venture, have generated freely available libraries tailored for specifc disease areas. Malaria Box, a collection of 400 diverse compounds with anti-malarial activity, was distilled from 20,000 hits generated from a screening campaign of around 4 million compounds from the libraries of St. This collection of compounds incorporates a broad cross-section of structural diversity and takes into account factors such as oral absorption and toxicity. The goal of this proposed efort is to spur the discovery of new classes of antibiotics, so considering that this objectives outcome could lead to the discovery of new antibiotic starting points, an intellectual property policy that encourages use of this resource, and maximizes public health benefts, would be required (see Models for antibiotic discovery). While Gram-positive antibacterial discovery is not the primary focus of this roadmap, it is important to consider the potential follow-on applications of the knowledge and tools generated through this initiative. Assays for measuring drug entry and efux for Gram-negative bacteria could be adopted for Gram-positive organisms. Similar compound collections designed for Gram-positive bacteria could be a useful resource for antibiotic discovery. Conduct key proof-of-concept studies for nontraditional therapies Alongside a scientifc program to underpin future antibiotic discovery is an opportunity to advance nontraditional therapeutic approaches, which include alternative small molecule therapy, such as anti-virulence drugs or molecules that reduce the emergence of resistance; non-small molecule approaches, such as monoclonal antibodies or probiotics; and new drug delivery methods, such as liposomes or nanoparticles. While there is some indication that nontraditional approaches may have a role in treating systemic bacterial infections, only a handful of companies are pursuing development of these types of alternative products (see Appendix B). For most nontraditional approaches, scientists face the same questions today as they did 30 years ago. For example, researchers have been working for years on polymyxin-based molecules that permeabilize or break down the outer membrane; the chemistry is not novel, but it remains unclear how these compounds should be combined with other drugs or whether their use will generate drug-resistant bacteria. Scientists have studied broad-spectrum siderophore-conjugated antibacterial agents, which work by hijacking bacterial iron uptake pathways, but lacked reliable in vitro tests to predict resistance rates in animal models. To address this concern, researchers at Pfzer and Hartford Hospital published 13 a study describing new in vitro assays that were predictive of efcacy in mouse models, providing a useful tool for researchers in the feld. There is no single solution given that there are a plethora of nontraditional approaches, each with its own challenges and limitations. At the same time, it is important to realize that in many cases, progression of nontraditional therapies has been hobbled by the same factors that impede the discovery and development of traditional antibiotics. Scientists working on nontraditional small molecule-based therapies that must enter the cytoplasm of bacterial cells to exert activity face the same barriers to drug entry and efux avoidance as scientists working on traditional antibiotic discovery. However, researchers working in alternative therapeutic felds may not have access to the consultation and support they need to validate a novel therapeutic approach and demonstrate clinical application. Chemotherapy drugs are also used in combination to decrease the likelihood that cancer cells will develop resistance. In addition, alternatives to traditional small molecule drug therapy have shown promise. For example, over the past few decades, immunotherapy, which uses a patients immune system to fght disease, has played an important role in treating some types of cancer. This efort would aim to develop key proof-of-concept studies for a variety of nontraditional therapeutic approaches, starting with combination therapy. In addition, it would provide advisory and resource support to scientists working on nontraditional approaches by bringing together leading experts from a diversity of felds to foster new perspective and insight to help validate the clinical potential of new therapies and bridge the divide between translational science and early development. Most systemic antibiotics in use today are not subject to high-level resistance resulting from single-step chromosomal mutations, primarily because they have more than one molecular target within the bacterial cell. Bacteria must generate multiple mutations to develop resistance against these types of drugs. Single-target inhibitors often lead to a high frequency of resistance and substantial decreases in the minimum inhibitory concentration. To date, there has been no comprehensive, standardized, and well-controlled in 14 vitro and in vivo study of characterized single-target drugs to assess whether a combination or cocktail of these compounds could help lower resistance rates in vitro or in vivo and how this might translate to the clinical setting. This objective aims to determine whether combinations of single-target antibacterials can, at least in principle, reduce the frequency of resistance in vitro. One approach to achieve this objective would be to carry out a comprehensive in vitro assessment of existing single-target antibacterials used in combination against a variety of bacterial pathogens to measure and compare the frequency of resistance. Sourcing of these compounds, which could include antibiotics in clinical use as well as compounds that have not been developed as drugs, may pose some challenges given that many inhibitors were at one point pursued by companies and some have entered into the development pipeline. Those that have published synthetic routes could be chemically generated, and others would have to be requested from industry or academic scientists. The dosing, timing, and distribution for each drug will vary, adding further complications to combination testing. For example, the hollow fber infection model* may be used to determine the appropriate dosing and timing for each antibacterial. Compounds could then be tested in pair-wise combinations and potentially in combinations of three or more. Given that there would likely be bacterial species-specifc variation in resistance rates, the scientifc team should examine both standard pathogens and clinical strains. The sheer number of combinatorial assays would require that methodologies for these studies be standardized and well-controlled to compare fndings across multiple experiments. Based on the results from these studies, the scientifc team would then evaluate whether combinations can be used to overcome resistance issues in vitro and what further studies should be done. Following the in vitro studies described above, a subset of promising antibacterial combinations would be further tested in animal models to assess whether results in hollow fber models are predictive of resistance rates in * the hollow fber infection model is a useful tool to carry out in vitro experiments under conditions that mimic changes in drug concentration over time, similar to what might occur in an animal model. In addition, studies have demonstrated that hollow fber models are efective tools for studying antibiotic combination therapies. Compound dosing and frequency of administration may be based on pre-existing knowledge of in vivo pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics parameters established by previous in vivo work. Animal models that mimic infection at diferent body sites could provide useful information on the potential efcacy of combination therapy for a particular clinical indication. Goal: Validate nontraditional therapies While each type of nontraditional therapy will have its own benefts and pitfalls, experts agree that the gap between late-stage translational science and early development remains a key scientifc bottleneck no matter the approach.

