Actoplus Met
Order actoplus met 500 mg visa
The increase in risk may be due to a longer lifetime exposure to the hormones estrogen and progesterone diabetes protocol cheap actoplus met 500mg with mastercard. Going through menopause after age 55 Women who have had more menstrual cycles because they went through menopause later (after age 55) have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer. The increase in risk may be because they have a longer lifetime exposure to the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Having radiation to your chest 6 Women who were treated with radiation therapy to the chest for another cancer (such as Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma) when they were younger have a significantly higher risk for breast cancer. The risk is highest for women who had radiation as a teen or young adult, when the breasts are still developing. Radiation treatment in older women (after about age 40 to 45) does not seem to increase breast cancer risk. Last Medical Review: September 10, 2019 Last Revised: September 10, 2019 Lifestyle-related Breast Cancer Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that increases your chances of getting a disease, such as breast cancer. Other lifestyle-related risk factors include decisions about having children and taking medicines that contain hormones. For information on other known and possible breast cancer risk factors, see: q Breast Cancer Risk Factors You Cannot Change q Factors with Unclear Effects on Breast Cancer Risk q Disproven or Controversial Breast Cancer Risk Factors Drinking alcohol 1 Drinking alcohol is clearly linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. Women who have 1 alcoholic drink a day have a small (about 7% to 10%) increase in risk compared with non-drinkers, while women who have 2 to 3 drinks a day have about a 20% higher risk than non-drinkers. Being overweight or obese 3 Being overweight or obese after menopause increases breast cancer risk. Before menopause your ovaries make most of your estrogen, and fat tissue makes only a small part of the total amount. After menopause (when the ovaries stop making estrogen), most of a womans estrogen comes from fat tissue. Having more fat tissue after menopause can raise estrogen levels and increase your chance of getting breast cancer. For instance, the risk of breast cancer after menopause is higher for women who gained weight as an adult, but the risk before menopause is actually lower in women who are obese. For example, being overweight after menopause is more strongly linked with an increased 10 American Cancer Society cancer. Not being physically active Evidence is growing that regular physical activity reduces breast cancer risk, especially in women past menopause. Some studies have found that even as little as a couple of hours a week might be helpful, although more seems to be better. Exactly how physical activity might reduce breast cancer risk isnt clear, but it may be due to its effects on body weight, inflammation, hormones, and energy balance. Not having children Women who have not had children or who had their first child after age 30 have a slightly higher breast cancer risk overall. Having many pregnancies and becoming pregnant at an early age reduces breast cancer risk. For example, the risk of breast cancer is higher for about the first decade after having a child, particularly for 7 hormone receptor-negative breast cancer (including the less common triple-negative breast cancer). Not breastfeeding Most studies suggest that breastfeeding may slightly lower breast cancer risk, especially if its continued for a year or more. But this has been hard to study, especially in countries like the United States, where breastfeeding for this long is uncommon. The explanation for this possible effect may be that breastfeeding reduces a womans 11 American Cancer Society cancer. Birth control Some birth control methods use hormones, which might increase breast cancer risk. Oral contraceptives: Most studies have found that women using oral contraceptives (birth control pills) have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than women who have never used them. Once the pills are stopped, this risk seems to go back to normal within about 10 years. Birth control shot:Depo-Provera is an injectable form of progesterone thats given once every 3 months for birth control. Some studies have found that women currently using birth-control shots seem to have an increase in breast cancer risk, but other studies have not found an increased risk. Hormone therapy after menopause Hormone therapy with estrogen (often combined with progesterone) has been used for many years to help relieve symptoms of menopause and help prevent osteoporosis (thinning of the bones). Progesterone is needed because estrogen alone can increase the risk of cancer of the uterus. For women whove had a hysterectomy (who no longer have a uterus), estrogen alone can be used. A womans breast cancer risk seems to go back down within 5 years of stopping treatment. Bioidentical hormone therapy:the word bioidentical is sometimes used to describe versions of estrogen and progesterone with the same chemical structure as those found naturally in people (as opposed to the slightly different versions found in most medicines). The use of these hormones has been marketed as a safe way to treat the symptoms of menopause. But because there arent many studies comparing bioidentical or natural hormones to synthetic versions of hormones, theres no proof that theyre safer or more effective. Until then, the use of these bioidentical hormones should be considered to have the same health risks as any other type of hormone therapy. It does lower the risk of colorectal cancer and osteoporosis, but this must be weighed against the possible harms, especially since there are other ways to prevent and treat osteoporosis, and 8 screening can sometimes prevent colon cancer. Breast implants Breast implants have not been linked with an increased risk of the most common types of breast cancer. However, they have been linked to a rare type of non-Hodgkin 13 American Cancer Society cancer. This lymphoma appears to happen more often in implants with textured (rough) surfaces rather than smooth surfaces. Breast cancer and breastfeeding: Collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50302 women with breast cancer and 96973 women without the disease. Type and timing of menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk: Individual participant meta analysis of the worldwide epidemiological evidence. Health risks and benefits 3 years after stopping randomized treatment with estrogen and progestin. Effect of depo-medroxyprogesterone acetate on breast cancer risk among women 20 to 44 years of age. Obesity as a risk factor for triple-negative breast cancers: A systematicreview and meta-analysis. American Cancer Society guideline for diet and 15 American Cancer Society cancer. Last Medical Review: September 10, 2019 Last Revised: June 9, 2020 Factors with Unclear Effects on Breast Cancer Risk There are some things that might be risk factors for breast cancer, but the research is not yet clear about whether they really affect breast cancer risk. For information on other known and possible breast cancer risk factors, see: q Lifestyle-related Breast Cancer Risk Factors q Breast Cancer Risk Factors You Cannot Change q Disproven or Controversial Breast Cancer Risk Factors 16 American Cancer Society cancer. Results of some studies have shown that diet may play a role, while others have not found that diet influences breast cancer risk. Studies of women in the United States have not found a consistent link between high fat diets and getting breast cancer, although some studies have found a possible link between high-fat diets and a higher risk of dying from breast cancer. Studies have also found that breast cancer is less common in countries where the typical diet is low in total fat, low in polyunsaturated fat, and low in saturated fat. Studies comparing diet and breast cancer risk in different countries are complicated by other differences (such as activity level, intake of other nutrients, and genetic factors) that might also affect breast cancer risk. We do know that high-fat diets can lead to being overweight or obese, which is a known breast cancer risk factor. And intake of certain types of fat is clearly linked to a higher risk of heart disease. Some studies have also suggested that diets high in fruits and vegetables and calcium-rich dairy products, but low in red and processed meats might lower the risk of breast cancer. Several studies looking at women in Asian countries have found that diets high in soy products might lower breast cancer risk.
500 mg actoplus met free shipping
Preliminary report: efect of encainide and fecainide on mortality in a randomized trial of arrhythmia suppression after myocardial infarction diabetic diet app generic 500mg actoplus met with mastercard. In clinically stable patients who have durable virological suppression for more than two years, clinicians may extend the interval to six months. Stasis dermatitis is commonly treated with antibiotic therapy, which may be a result of misdiagnosis or lack of awareness of the pathophysiology of 3 the disease. The standard of care for the treatment of stasis dermatitis afecting lower extremities is a combination of leg elevation and compression. Elevation of the afected area accelerates improvements by promoting gravity drainage of edema and infammatory substances. The risk of antibiotic-associated 5 adverse efects exceeds the beneft (if any) from prophylactic antibiotic therapy. Limited use of prophylaxis will likely reduce the unwanted selection of antibiotic-resistant strains and their unintended consequences such as C. The Committee identifed a preliminary list of inappropriate and overused clinical practices. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in adults. Reducing antibiotic overuse: a call for a national performance measure for not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria. Adult appropriate antibiotic use summary: physician information sheet (adults) [Internet]. Infective endocarditis rationale for revised guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis. We achieve this by collaborating with partner with the Choosing Wisely physicians and physician leaders, medical trainees, campaign to raise awareness of health care delivery systems, payers, policymakers, inappropriate, wasteful clinical consumer organizations and patients to foster a shared actions that harm patients and lead to costly health care. North American Spine Society Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question Dont recommend imaging of the spine within the frst 6 weeks of an acute episode of low back pain in the absence of red fags. Failure to use appropriate imaging may result in inappropriate placement of the medication, thereby decreasing the efcacy of the procedure and increasing the need for additional care. Opioid prescriptions should be for a limited period with the lowest efective dose that provides meaningful pain relief and improved function with manageable side efects. Dont recommend bed rest for low back pain; patients should remain as active as possible and be encouraged to fnd positions of comfort 5 and engage in activities that dont worsen symptoms during an acute episode. In patients with low back pain, bed rest has not been shown to be benefcial and has been shown to delay recovery. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Advice to rest in bed versus advice to stay active for acute low-back pain and sciatica. Interventions available over the counter and advice for acute low back pain: systematic review and meta analysis. Treatment should be based on the individual patients need and physicians professional judgment. We achieve this by collaborating with highest quality, ethical, value-based physicians and physician leaders, medical trainees, and evidence-based spine care through health care delivery systems, payers, policymakers, education, research and advocacy. American College of Radiology; Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography; Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance; American Society of Nuclear Cardiology; North American Society for Cardiac Imaging; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Interventional Radiology. American College of Radiology; Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography; Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance; American Society of Nuclear Cardiology; North American 4 Society for Cardiac Imaging; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Interventional Radiology. American College of Radiology; Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography; Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance; American Society of Nuclear Cardiology; North American 5 Society for Cardiac Imaging; Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions; Society of Interventional Radiology. Therefore, testing should generally be limited to patients with changes in clinical status (for example: new symptoms or decreasing exercise tolerance). Rare exceptions would be a signifcant left main coronary artery lesion or a >90% proximal lesion in a major coronary artery. The Committee extracted this list from these documents, which have been developed by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association and other professional societies over the past four years. After three days, laboratory and radiology information is available and antibiotics should either be deescalated to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic based on culture results or discontinued if evidence of infection is no longer present. When antibiotics are used for longer than necessary, they increase the risk of infection with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and C. Sources Core Elements of hospital antibiotic stewardship programs from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Strategies to prevent Clostridium difcile infections in acute care hospitals: 2014 update. We achieve this by collaborating with professionals around the world with physicians and physician leaders, medical trainees, expertise in healthcare epidemiology, health care delivery systems, payers, policymakers, infection prevention and antimicrobial stewardship. Specifc testing for antiphospholipid antibodies, when clinically indicated, should be limited to lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies and beta 2 glycoprotein antibodies. Dont use progestogens for preterm birth prevention in uncomplicated multifetal gestations. There are multiple studies documenting untoward efects of routine activity restriction on the mother and family, including negative psychosocial efects. When low-risk results have been reported on either test, there is limited clinical value of also performing the other screen. Dont perform maternal serologic studies for cytomegalovirus and toxoplasma as part of routine prenatal laboratory studies. Serologic screening during pregnancy for both diseases should be reserved for situations in which there is clinical or ultrasound suspicion of maternal or fetal infection. Most importantly, there are currently no additional treatment options for a short cervix after cerclage. The relationship of the factor V Leiden mutation and pregnancy outcomes for mother and fetus. Cerclage for short cervix on ultrasonography: meta-analysis of trials using individual patient-level data. Progesterone and preterm birth prevention: translating clinical trials data into clinical practice. Failure of 17-hydroxyprogesterone to reduce neonatal morbidity or prolong triplet pregnancy: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Prevention of preterm birth in triplets using 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone caproate: a randomized controlled trial. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal Fetal Medicine Unit Network. The risk of stillbirth and infant death stratifed by gestational age in women with 7 gestational diabetes. The role of routine cervical length screening in selected high and low-risk women for preterm birth prevention. We achieve this by collaborating with dedicated to the optimization of pregnancy and physicians and physician leaders, medical trainees, perinatal outcomes. There are currently about 2,000 active members of adopt the tenets of professionalism in practice. The Society hosts an annual scientifc meeting in which new ideas and research in the area of maternal-fetal medicine are presented. The Society is also an advocate for improving public policy and expanding research funding and opportunities in the area of maternal-fetal medicine. Lab tests to look for a clotting disorder will not alter treatment of a venous blood clot, even if an abnormality is found. Refrain from percutaneous or surgical revascularization of peripheral artery stenosis in patients without claudication or critical limb ischemia. No evidence exists to support improving circulation to prevent progression of disease. Dont screen for renal artery stenosis in patients without resistant hypertension and with normal renal function, even if known 5 atherosclerosis is present. Performing surgery or angioplasty to improve circulation to the kidneys has no proven preventive beneft, and shouldnt be considered unless there is evidence of symptoms, such as elevated blood pressure or decreased renal function. A committee, consisting of four members of the Board of Trustees, narrowed an initial list down to seven recommendations. Incidence of recurrent venous thromboembolism in relation to clinical and thrombophilic risk factors: prospective cohort study.
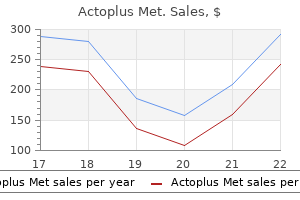
Generic actoplus met 500mg mastercard
Also diabetes prevention program uk order generic actoplus met from india, more patients given tion: Acuvail (Allergan) comes as a BromSite were free of inflammation at 15 days post-cataract surgery com preservative-free unit-dose indicated pared with patients given only the vehicle. Because Pro also approved to treat ocular allergy, well tolerated; however, be aware that lensa is a solution and not a suspen along with a number of other appli Bromday was discontinued in 2013. As a general rule, we never enzymatically converted to amfenac dispensed as 3ml in a 4ml bottle. It is dosed three identical to the bottle used by Tra tion of cystoid macular edema, which times a day. Both are dosed once daily: lowing for a decreased concentration the day before surgery, the day of (0. This may inhibit prostaglandin production in the anterior segment, explain, in part, their decreased anti-inflammatory effects especially when compared to topical administration. We typically just maintain Lotemax sonable lengths of time in appropriate patients with proper gel once or twice a daily for most of these patients. Their main use is in currently using Celebrex for four to gastrointestinal tissues. Aggres should pay heed to the black box edema concurrent with a potent cor sive use of Durezol and therapeutic warning of cardiovascular risk. For the relative efficacy of the topical that reason, we always end steroids, starting with the most effi our patient treatment en cacious: counters with a statement 1. Note that the anterior two thirds of less frequent dosing than with pred the cornea is heavily infiltrated, which nicely explains why the overlying epithelium is nisolone formulations, and provides secondarily compromised. This defect is near ery two hours initially, rather than the limbus, which is very fertile soil for inflammatory events. The antibiotic is for the benefit of the doctor; the steroid is for the 1% also has good anti-inflammatory benefit of the patient! This non-settling eye when you have specified Dispense Next in clinical efficacy are Lotemax drop does not require shaking before as Written on the Rx. Patients, practitioners and pharmacists may mix up these two medicines, so Lotemax Ointment, left). Though called a gel, this comes in a dropper as an off-label treatment for our dry bottle, like a solution. However, inside the bottle it is indeed eye patients, but we also use it to treat a highly viscous, semisolid gel formulation. But, through a many other chronic, recurrent, inflam process called adaptive viscosity, it becomes a liquid when matory conditions such as stromal squeezed out of the dropper. While loteprednol may not be quite Still, the drop is rather thick upon instillation, and will cause as efficacious as prednisolone and Du a moment of initial blur until the gel fully converts into a liq rezol, it has significantly lower pro uid. This generic steroid is an excel Lotemax ointment is indicated for the treatment of postoperative inflamma lent choice when a potent, relatively tion and pain, but is also appli inexpensive steroid is needed. Because cable in many other cases in this is a solution, it does not require which an ointment is useful for shaking and may be an especially good suppression of inflammation. Our Take We have encountered numerous epithelial defects over the years that were non-healing until we added a ste roid that quelled the corneal inflammation preventing re-epithelialization. The nature and cause of the epi thelial defect must be understood in order to properly select therapeutic intervention. If the epithelial defect is present as a result of subepithelial inflammation, as evidenced by leukocytic anterior stromal disease, then adding a steroid to suppress the underlying inflamma tory process can promote re-epithelialization. We know that inflammation and superficial punctate keratitis commonly coexist in dry eye disease, yet the proper A mild steroid will suffice for Thygesons superficial application of a steroid can help restore and enhance punctate keratopathy. Our Take There are three conditions in which a topical steroid is commonly used daily for a lifetime: corneal transplants, chronic uveitis and chronic herpetic stromal disease. Our Take There are those stubborn patients who simply will not abandon contact lens wear in the face of symptomatic giant papillary conjunctivitis. We reluctantly, but successfully, have had to use a steroid eye drop (loteprednol is our clear favorite here) four times a day for a week or two, then twice daily for an additional week or two, to properly care for such patients. We always try to put the patients in a daily disposable soft contact lens during and after the acute treatment. Myth Use steroids with great caution because they can cause glaucoma and cataracts. Our Take Well, contact lenses can cause corneal ulcers, an extremely serious consequence of lens wear, yet that doesnt seem to halt the use of these wonderful devices in a wholesale manner in the daily practice of optometry. First, steroids, even ester-based steroids, can increase intraocular pressure (usually by less than 10mm Hg), which reverts to baseline upon discontinuation of the steroid drop. No doubt, this has occurred through patient, pharmacy or doctor incompetence in appropriate patient management, but it is fully preventable. Regarding posterior subcapsular cataracts, we are unaware of a single case report of cataract formation resulting from the use of loteprednol. Cataract formation would certainly be much more common with the use of older, traditional, ketone-based steroids. The patient should have been asked by his physician or pharmacist about this approach, or perhaps he should have read the package insert himself. Myth Oral prednisone should be used with extreme care, as it can have a multitude of side effects. Our Take this is certainly true for long-term use; however, for short-term use (a few days), this statement is simply false. We have prescribed oral prednisone regularly over our careers with excellent success and no therapeutic mis adventures. Safety and efficacy of loteprednol etabonate for treatment of papillae in contact lens-associated giant papillary conjunctivitis. We are currently staying longer within artificially corneal epithelial healing-related problems or secondary created environments, such as office buildings, shopping infections as potential side effects from steroid use. The acetate moiety comfortable using it long-term as we episcleritis, as discussed above. More Bausch + Lomb) suspension, both of being temporarily unavailable in vari over, the 0. Corticosteroids also reduce substitutes are not sufficient or suppress capillary dilation, fibroblast to protect the ocular surface in proliferation and collagen deposition. Thus, this treatment could be administered occasion hyperemia, whereas no obvious effects were observed with ally to such patients expecting to undergo adverse environ polyvinyl alcohol artificial tears. Once the ocular surface inflammation is controlled, clini In contrast, polyvinyl alcohol artificial tears had no effect on cians should consider ongoing maintenance of inflammation hyperemia. However, the approved), Lotemax gel or fluorometholone, depending negative impact of benzalkonium chloride in terms of corne upon patient response. It is indicated for livery systems (suspensions, solutions, is indicated for postoperative inflam inflammation of the palpebral and bul emulsions, gels and ointments), know mation and pain, but also has many bar conjunctiva, cornea and anterior ing the clinical efficacy of these drugs off-label clinical uses: dry eye, al segment of the globe, and any of the is important. This merit frequent clinical use in the oint or episcleritis, contact dermatitis and is a dermatologic preparation that ment formulation include: other inflammatory conditions. Notice we did not use the term glau for many years to treat contact blepha coma, because that is exceedingly rare. It comes in 15g and 30g enough, and is mostly seen with protracted use of ketone-based steroids, tubes, each costing less than $10 in most notably dexamethasone, prednisolone and difluprednate. This would only occur if a doctor did not sched the side of the tube is the statement ule appropriate follow-up or the patient failed to return for scheduled follow Not For Ophthalmic Use, but that up visits in a timely manner (or at all), or a naive, non-optometric physician re the medication is perfectly fine to use prescribed a steroid. In oth associated red eye); retained lens fragments in the remote recesses of the er words, if some of the triamcinolone superior cul-de-sac; corneal infiltrates; infectious keratitis; and other condi cream gets into the patients eyes, its tions.

Actoplus met 500mg otc
Largely because of their greater size diabetes medications canada 500mg actoplus met sale, particlesthe particles of the dispersed phase are usu in a coarse dispersion have a greater tendency to ally solid materials that are insoluble in the dis separate from the dispersion medium than do persion medium. Most solids in dispersed phase is a liquid that is neither soluble dispersion tend to settle to the bottom of the nor miscible with the liquid of the dispersing container because of their greater density than phase. Emulsication results in the dispersion the dispersion medium, whereas most emulsi of liquid drug as ne droplets throughout the ed liquids for oral use are oils, which generally dispersing phase. In the case of an aerosol, the have less density than the aqueous medium in dispersed phase may be small air bubbles which they are dispersed, so they tend to rise throughout a solution or an emulsion. Complete and sions also consist of droplets of a liquid (solution uniform redistribution of the dispersed phase is or suspension) in air. For a properly prepared dispersion, widely in size, from large particles visible to the this should be accomplished by moderate agita naked eye down to particles of colloidal dimen tion of the container. Athe focus of this chapter is on dispersions of discussion on the difference between particles drugs administered orally or topically. The same and molecules is provided in Physical Pharmacy basic pharmaceutical characteristics apply to Capsule 14. Particles consist of numerous molecules, generally in a solid state (but can be liquid or gaseous). Dissolution is the solid to liquid transformation that converts solid drug particles to individual, dissolved liquid molecules. Most nonprotein or small molecule organic drugs have formula weights ranging from 150 to 500. For example, certain drugs are containing nely divided drug particles (the chemically unstable in solution but stable when suspensoid) distributed somewhat uniformly suspended. In this instance, the suspension throughout a vehicle in which the drug exhibits ensures chemical stability while permitting a minimum degree of solubility. For many patients, the liquid sions are available in ready-to-use form, that is, form is preferred to the solid form of the already distributed through a liquid vehicle same drug because of the ease of swallowing with or without stabilizers and other additives liquids and the flexibility in administration of. This is particularly advanta dry powders intended for suspension in liquid geous for infants, children, and the elderly. Generally, this type of product is athe disadvantage of a disagreeable taste of powder mixture containing the drug and certain drugs in solution form is overcome suitable suspending and dispersing agents to when the drug is administered as undissolved be diluted and agitated with a specied quan particles of an oral suspension. Drugs that are unstable if bility in a desired vehicle for the sole purpose maintained for extended periods in the pres of preparing a palatable liquid dosage form. A properly prepared pharmaceutical suspen sion should settle slowly and should be read ily redispersed upon gentle shaking of the container. The particle size of the suspensoid should remain fairly constant throughout long peri ods of undisturbed standing. These main features of a suspension, which of insoluble forms of drugs in suspensions depend on the nature of the dispersed phase, greatly reduces the difficult taste-masking the dispersion medium, and pharmaceutical problems of developmental pharmacists, and adjuncts, will be discussed briey. For the most part, oral suspensions are aqueous prep-the various factors involved in the rate of settling arations with the vehicle flavored and sweet of the particles of a suspension are embodied in ened to suit the anticipated taste preferences the equation of Stokes law, which is presented in of the intended patient. A number of factors can be adjusted to enhance the physical stability of a suspension, including the diameter of the particles and the density and viscosity of the medium. This enhanced effect is a result of the d factor in Stokes equation being squared. If a different dispersion medium, such as glycerin, is used in place of water, a further decrease in settling will result. As is evident from this table, a change in dispersion medium results in the greatest change in the rate of settling of particles. However, dispersed phase rather than through great the basic concepts of the equation do give a valid changes in the dispersion medium. In most indication of the factors that are important to instances, the dispersion medium supports the suspension of the particles and a clue to the pos adjusted dispersed phase. These adjustments sible adjustments that can be made to a formula are concerned mainly with particle size, unifor tion to decrease the rate of sedimentation. Also, the greater the density of the particles, the Probably the most important single consider greater the rate of descent, provided the density ation in a discussion of suspensions is the size of of the vehicle is not altered. In most good pharmaceutical sus vehicles are used in pharmaceutical oral suspen pensions, the particle diameter is 1 to 50m. If the particles were less dense than the the dispersed phase into the dispersion medium. For still ner particles, not generally desirable, because it pours with under 10m, uid energy grinding, sometimes difficulty and it is equally difficult to redisperse referred to as jet milling or micronizing, is quite the suspensoid. By this process, the shearing action of suspension is increased, it is done so only to a high-velocity compressed airstreams on the par modest extent to avoid these difficulties. The particles may be altered not only by the vehicle used, but to be micronized are swept into violent turbu also by the solids content. As the proportion of lence by the sonic and supersonic velocities of solid particles in a suspension increases, so does the airstreams. The viscosity of a pharmaceutical high velocities and collide with one another, preparation may be determined through the use resulting in fragmentation. This method may be of a viscometer, such as a Brookeld Viscometer, employed when the particles are intended for which measures viscosity by the force required parenteral or ophthalmic suspensions. A spray dryer is a suspensoid can also affect caking and product cone-shaped apparatus into which a solution of stability. It has been shown that symmetrical a drug is sprayed and rapidly dried by a current barrel-shaped particles of calcium carbonate of warm, dry air circulating in the cone. It is not pos asymmetrical needle-shaped particles of the sible for a pharmacist to achieve the same same agent. The needle-shaped particles formed degree of particle-size reduction with such com a tenacious sediment cake on standing that could minuting equipment as the mortar and pestle. One common method of in the particle size of a suspensoid is benecial to preventing rigid cohesion of small particles of a the stability of the suspension because the rate suspension is intentional formation of a less rigid of sedimentation of the solid particles is reduced or loose aggregation of the particles held together as the particles are decreased in size. However, one should avoid a occule, with occulated particles forming a type reducing the particle size too much, because ne of lattice that resists complete settling (although particles have a tendency to form a compact cake ocs settle more rapidly than ne, individual par upon settling to the bottom of the container. The ticles) and thus are less prone to compaction than result may be that the cake resists breakup with unocculated particles. The solid content of a suspension intended for For instance, in the preparation of an oral sus oral administration may vary considerably, pension of a drug, clays such as diluted bentonite depending on the dose of the drug to be adminis magma are commonly employed as the occulat tered, the volume of product to be administered, ing agent. The structure of the bentonite magma and the ability of the dispersion medium to sup and of other clays used for this purpose also port the concentration of drug while maintaining assists the suspension by helping to support the desirable features of viscosity and ow. When clays are unsuitable as the usual adult oral suspension is designed to sup agents, as in a parenteral suspension, frequently ply the dose of the particular drug in a convenient a oc of the dispersed phase can be produced by measure of 5mL or 1 teaspoonful. Pediatric sus an alteration in the pH of the preparation (gen pensions are formulated to deliver the appropri erally to the region of minimum drug solubility). The are accompanied by a calibrated dropper, whereas carefully determined concentration of nonionic other packages have the drop capability built into and ionic surface-active agents (surfactants) can the container. On administration, the drops may also induce occulation of particles in suspen be placed directly in the infants mouth or mixed sion and increase the sedimentation volume. Because many of the suspensions of antibiotic drugs intended for pedi atric use are prepared in a highly avored, sweet Dispersion Medium ened, colored base, they are frequently referred Oftentimes, as with highly occulated suspen to by their manufacturers and also popularly as sions, the particles of a suspension settle too rap syrups, even though in fact they are suspensions. In many commer cial suspensions, suspending agents are added to the dispersion medium to lend it structure. When polymeric substances and hydrophilic colloids are used as suspending agents, appropriate tests must be per formed to show that the agent does not interfere with availability of the drug. These materials can bind certain medicinal agents, rendering them unavailable or only slowly available for therapeu tic function. Also, the amount of the suspending agent must not be such to render the suspension too viscous to agitate (to distribute the suspensoid) or to pour. A summary of the concepts of rheology is designs of a built-in dropper device and a calibrated dropper found in Physical Pharmacy Capsule 14. Materials are divided into two general categories, Newtonian and non-Newtonian, depending on their ow characteristics. Newtonian ow is characterized by constant viscosity, regardless of the shear rates applied. Non-Newtonian ow is characterized by a change in viscosity characteristics with increasing shear rates.

Order actoplus met in india
Theory of mind disruption and Perception of complex sounds: abnormal recruitment of the right hemisphere during 35 Boddaert N diabetes jugendalter test order discount actoplus met, Chabane N, Belin P et al. Autism severity and temporal lobe brain overgrowth in autism associated with an do not attend. Autism at the beginning: biomarker for language impairment in cortex during word processing in autism: an microstructural and growth abnormalities autism. White Decreased left posterior insular activity neuroimaging of speech perception during a matter integrity and pictorial reasoning in during auditory language in autism. A comparison of hemispheric asymmetries in left temporal cortex to specialize for language Diffusion tensor imaging in autism spectrum speech-related brain potentials of autistic and is an early emerging and fundamental property disorder: a review. Speech and language Combining functional and anatomical reasoning in high-functioning adults with impairments in autism: insights from behavior connectivity reveals brain networks for autism: evidence for impaired exception and neuroimaging. Natl the superior temporal gyrus and temporal stem white matter fber tract development present Acad. Infant speech perception Lateralization of phonetic and pitch comprehension in autism: thinking in activates Brocas area: a developmental discrimination in speech processing. Structural and functional 121 Pulvermuller F, Huss M, Kherif F, Moscoso del taking in high-functioning autism. Brain brain development in autism: the impact of Prado Martin F, Hauk O, Shtyrov Y. The nature and origins of ambient language interactions underlying syllable production. On the relation connectivity: an investigation applied tothe geometric structure of the brain fber of speech to language. Keywords: Mucosal protection, Prostaglandin, Ulcer, Prostanoids Accepted on May 05, 2017 Introduction Table 1. This is understandable when considering also markedly increased by indomethacin in wild-type mice. In addition, the acid-induced duodenal damage was important in the local control of this secretion. In addition, several studies suggest a pathogenic expression was also up-regulated in the small intestine after role for enterobacteria in experimental colitis and infammatory ulceration, peaked at day 3 and then declined. Roles of prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in cytoprotective action of prostaglandin E2 24. Roles of prostaglandin E-receptor subtypes in gastric and duodenal bicarbonate 25. Gastric cytoprotection by prostaglandin E2: prostaglandin E receptors in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Inhibition of vagally prevent etodolac or indomethacin-induced gastrointestinal mediated gastric acid secretion by activation of central damage in the rat. Dilatation and mucosa by prostacyclin: possible mediation by increased constriction of rat gastric mucosal microvessels through mucosal blood fow. Nitric oxide, superoxide mechanism of duodenal bicarbonate secretion: Roles of radicals and mast cells in pathogenesis of indomethacin endogenous prostaglandins and nitric oxide. Prostanoids stimulation of anion secretory and mucosal ulcerogenic responses in the rat secretion in guinea-pig gastric and ileum mucosa is mediated duodenum. Treatment of ulcerative suppressing the expression of infammatory mediators via colitis using fecal bacteriotherapy. Cyclooxygenase cyclooxygenase-2 selective and nitric oxide-releasing 2-regulated vascular endothelial growth factor release in nonsteroidal anti-infammatory drugs on gastric ulcerogenic gastric fbroblasts. Vascular on ulcerogenic and healing responses in rat gastrointestinal Endothelial growth factor induction by prostaglandin E2 mucosa. Koji Takeuchi, PhD General Incorporated Association Kyoto Research Center for Gastrointestinal Diseases Karasuma-Oike, Kyoto 604-8106 Japan Tel: +81-077-545-5562 E-mail: takeuchi@mb. While available treatments benefit about 50%-60% of patients, there is a sizeable group that does not respond adequately. Bipolar depression often presents a very significant challenge for clinical management as treatment responses are often inadequate. The pathophysiology of depression is not agreed on but there is evidence for contributions of neuroinflammation and disturbed brain arachidonic acid metabolism. Furthermore, an increasing body of evidence documents a role for increased oxidative stress in brain neurons as a putative mechanism involved in neuronal damage and possibly in the pathophysiology of mood disorders. A controlled study testing the potential of aspirin in symptomatic schizophrenic patients found promising results. Available treatments help a substantial proportion of patients but are not beneficial for an estimated 40%-50% [1, 2]. Over the past two decades, several alternatives have been developed [1, 5-9] [10, 11][12-19]. Preliminary clinical studies suggest a therapeutic effect of aspirin in mood disorders. One study reported that aspirin ameliorated mood in males undergoing coronary angiography [46]. A retrospective clinical pharmacoepidemiological study reported that chronic aspirin reduced the incidence of clinical worsening in patients taking lithium [47]. Additionally, a randomized double blind placebo-controlled trial reported that adjuvant aspirin therapy (1000 mg/day, 12-weeks) reduced symptoms of schizophrenia spectrum disorders, in which neuroinflammation likely plays a role [48, 49]. Increased oxidative stress may be involved in pathophysiology of mood disorders [50]. If abnormalities in oxidative stress are key mechanisms involved in pathophysiology of mood disorders, it is compelling to hypothesize that effective antioxidant drugs will have effects in alleviating the symptoms or changing the course of the illness. Lithium and valproate have been shown to have important effects on glutathione-mediated processes [52]. In a clinical trial, lithium was shown to have effects on markers of oxidative stress in patients with bipolar disorder in the manic state [53]. Recently, results of an open label study also revealed positive results on bipolar depression during a two month extension period [55]. Our study will include measurements of cytokines, inflammatory factors and markers of oxidative stress at baseline, at 8 wks and at 16 wks to test the hypothesis that these are mediators or modulators of therapeutic response. Need for efficient drug development studies Most conventional, medication-development trials in psychiatry have employed standard, fixed, parallel-group designs, involving only a few drug conditions and very large sample sizes. Trials designed in this manner have been criticized for being exceedingly long, expensive, and often uninformative if initial drug or dose selection proved to be incorrect. Two ways in which the clinical trial enterprise may be enhanced are the implementation of adaptive clinical trial designs and the application of Bayesian statistical approaches in monitoring and analyzing clinical trials [57, 58]. Adaptive designs permit critical mid-trial design modifications, based on interim analyses, without undermining the validity and integrity of the trial [59]. Adaptations to the trial are pre-specified (by design); not made in an unplanned or ad hoc manner. These adaptations are aimed at providing (1) better treatment of patients by limiting exposure to non-effective drugs or drug combinations and increasing exposure to more effective drugs or drug combinations; (2) more efficient drug development; and (3) better use of available resources. An interim analysis plan specifies the criteria for dropping doses that fail to show clinically meaningful efficacy over placebo. This adaptive pruning permits the randomization of remaining participants to the drug condition(s) which demonstrate the most promise. The recommended analysis strategy when using adaptive trials is Bayesian [57] which permits statements about the probability that treatment confers benefit. This yields a posterior distribution from which statements about the probability of a given effect size can be made. As treatment outcomes accumulate over the course of the trial, posterior probabilities are used to estimate treatment effects and inform the pruning of less effective treatments based on a priori decision rules. Designing an adaptive trial typically begins with a simulation study to address issues such as timing and frequency of interim analyses, and to understand the operating characteristics associated with the criteria for dropping conditions [57]. Using simulated data, the design performs well as demonstrated by adequate power and Type I error rates. After the first 8 week of the double blind treatment, the responders will keep taking the same study drug, whichever it is.
Eberesche (Mountain Ash). Actoplus Met.
- Kidney diseases, diabetes, arthritis, swelling, vitamin C deficiency, purifying the blood, menstrual problems, diarrhea, lung conditions, and other conditions.
- How does Mountain Ash work?
- Dosing considerations for Mountain Ash.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Mountain Ash?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96568
Purchase actoplus met american express
New Antithrombotic Drugs: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis managing diabetes on the road buy discount actoplus met 500 mg online, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Aplastic Anemia: First-line Treatment by Immunosuppression and Sibling Marrow Transplantation. Treatment of Patients With Persistent Heartburn Symptoms: A Double-Blind, Randomized Trial. Bousvaros, A, et al, Treatment of ulcerative colitis in children and adolescents UpToDate. American Society of Clinical Oncology treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer guideline: update 2003. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on the treatment of glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, 2nd edition. Explicit criteria for determining inappropriate medication use in nursing home residents. American Geriatrics Society updated Beers criteria for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. Variability among nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Incidence of serious upper gastrointestinal bleeding/perforation in the general population: review of epidemiologic studies. The outline defines the body of knowledge from which the Subboard samples to prepare its examinations. The content specification statements located under each category of the outline are used by item writers to develop questions for the examinations; they broadly address the specific elements of knowledge within each section of the outline. Pediatric Endocrinology Each Pediatric Endocrinology exam is built to the same specifications, also known as the blueprint. This blueprint is used to ensure that, for the initial certification and in-training exams, each exam measures the same depth and breadth of content knowledge. Similarly, the blueprint ensures that the same is true for each Maintenance of Certification exam form. The table below shows the percentage of questions from each of the content domains that will appear on an exam. Know the sources of glucose from: digestion and absorption of dietary carbohydrates; endogenous release of glucose from the liver b. Know the enzyme systems (glycogenolysis, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, tricarboxylic acid cycle, and pentose phosphate shunt) involved in the storage, oxidation, and production of glucose c. Understand the processes and regulation of nutrient and substrate metabolism in the fasted and fed states with regard to glycogen, glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies, amino acid, and protein metabolism d. Know effects of insulin on protein synthesis and proteolysis; lipolysis and ketogenesis; glucose production and utilization. Know the effects of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity on beta cell function and insulin resistance 2. Know the criteria for a normal blood glucose concentration in children, and adolescents, and the definitions of biochemical hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia at these ages b. Know the rate of glucose production (expressed as glucose infusion rate) in normal neonates, children, and adolescents, and the factors which regulate it c. Know the duration of time glycogen stores and gluconeogenesis can maintain normal blood glucose concentrations in normal neonates, children and adolescents B. Know the structural homology of insulin-like growth factor (and other growth factors) with insulin c. Know the importance of the sulfonylurea receptor, chromium picolinate, the potassium channel, and the role of calcium flux in insulin secretion 3. Know the interactions of medications and other exogenous substances that regulate insulin secretion with beta cell receptors and channels d. Know the plasma membrane location, structure, and function of the insulin receptor b. Know the role or lack thereof of insulin on glucose transporters in different tissues c. Recognize histologic appearance of islets early and late in the course of type 1 diabetes with preferential destruction of beta cells and late persistence of alpha and delta cells 3. Know the current concepts of the role of autoimmunity including cell mediated immunity and cytoplasmic and surface autoantibodies and insulin autoantibodies in the pathogenesis and prediction of type 1 diabetes 4. Know the rationale for the use of immunomodulating agents for the treatment of early type 1 diabetes 5. Know the prevalence of glutamic acid decarboxylase, islet cell, and insulin antibodies in recent-onset type 1 diabetes and in individuals of various ages b. Know the different prevalence rates of type 1 diabetes in people of different ethnicities 2. Know the risk of type 1 diabetes development in identical twins, other siblings, offspring, and parents of patients who have type 1 diabetes 3. Understand the clinical differentiation of ketoacidosis from other causes of altered states of consciousness, such as hypoglycemia and nonketotic hyperosmolar coma, in diabetes mellitus 4. Understand the pathogenesis of ketoacidosis and disturbances in body fluid, electrolytes, substrates, and acid-base balance (pH, O2 dissociation), and the significance of relevant laboratory findings in type 1 diabetes 5. Recognize the mechanism, presentation, and natural history of neonatal diabetes c. Recognize the stages of clinical development of type 1 diabetes with progressive carbohydrate intolerance, and the pathophysiology of the polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, and fatigue d. Know the rationale and strategy for monitoring blood glucose, serum electrolytes, acid-base balance and ketone concentrations in the management of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis 3. Know when and how to change to subcutaneous insulin and oral intake in patients recovering from diabetic ketoacidosis 4. Know the complications (cerebral edema, hyperkalemia, hypokalemia, renal failure, hyperchloremia, hypoglycemia, persistent hyperglycemia, thrombosis, and/or ketonemia), pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and management in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis 5. Recognize that repeated episodes of ketoacidosis in a child or adolescent are most likely a result of failure to administer insulin regularly rather than dietary indiscretions or infectious illness 6. Know the methods, rationale, consequences, and principles of administration of fluid and electrolytes in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis 7. Know the methods, rationale, consequences, and principles of administration of glucose in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis 8. Know the formulations and action profiles of rapid, short, intermediate, and long-acting insulins 2. Recognize blood glucose values requiring insulin dose adjustments in patients with diabetes using home glucose monitoring 3. Understand the effects of meals, exercise, illness, trauma, and surgery on blood glucose concentration and insulin requirements of patients who have diabetes 4. Know the use and significance of glycosylated hemoglobin and factors other than blood glucose concentration (eg, hemolytic anemia) that affect or alter its value in the management of patients with diabetes 5. Know how to calculate an insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio for determination of insulin dosing for patients with diabetes 7. Be able to identify patients with type 1 diabetes who will succeed with insulin infusion pump therapy and know the steps required to prepare a patient for insulin pump therapy 8. Know how to calculate an initial basal and bolus insulin dose for a patient beginning insulin pump therapy 9. Know the pros and cons of intensification of diabetes management with both multiple daily insulin doses and with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy 10. Know how to make insulin dose adjustments in patients with type 1 diabetes using home glucose monitoring 11. Understand the rationale and appropriate use of continuous glucose monitoring devices in children with type 1 diabetes, including clinical indications and limits 12. Know how to convert insulin dose from intermediate/rapid-acting insulin regimens to basal-bolus regimens using long-acting insulin analogues 13.
Syndromes
- Your child holds his or her breath during tantrums, especially if he or she faints
- People who have unprotected sex, especially with people who have other high-risk behaviors, are HIV-positive, or have AIDS
- Prescribe extra potassium for you to take every day.
- Using tampons
- Abnormal "wall" of tissue (septum) in the vagina that may either partly or completely divide the vagina across or straight up and down
- X-rays
- Use of diuretic medications
Cheap actoplus met 500 mg visa
Table 16 Recommendations for the management of hypertension Delivery a b Recommendations Class Level Induction of delivery is indicated in gestational hypertension with proteinuria with adverse conditions such as visual disturbances blood sugar problems symptoms order actoplus met 500mg on line, Non-pharmacological management for pregnant coagulation abnormalities, or fetal distress. Bromo gestational hypertension or with hypertension criptine, which is used to suppress lactation, may induce hyperten and subclinical organ damage or symptoms at sion. Methyldopa should be avoided oedema, nitroglycerine given as an intravenous I C post-partum because of the risk of post-natal depression. Women experiencing hypertension in their rst pregnancy are at Women with pre-existing hypertension increased risk in a subsequent pregnancy. The relative risk of developing ischaemic heart disease after pre-eclampsia is more than twice as high compared with women with normal preg 10. Venous thrombo-embolism nancies, and the risk of developing hypertension is almost four 229 during pregnancy and the fold. Women with early-onset pre-eclampsia (delivery before 32 weeks of gestation), with stillbirth, or fetal growth retardation puerperium 229 are considered to be at highest risk. Risk factors before preg nancy for the development of hypertensive disorders are high 10. Therefore, identication of risk factors in the individual Mid-cavity or rotational forceps patient is important for risk assessment and choice of preventive Prolonged labour (>24 hours) strategies. Peripartum haemorrhage (>1 L or transfusion) Table 17 provides a suggested checklist for documentation of Transient risk factors 238 this risk assessment. On the basis of the type and the total Current systemic infection number of risk factors present in the individual patient, three risk groups can be identied (high, intermediate, and low risk Immobility groups) and preventive measures applied accordingly (see Table 19). This complicates recommendations and but there are no studies available on the optimal dose and weight calls urgently for multicentre, prospective studies. Subjective clini centration for each trimester compared with the previous cal assessment of pulmonary embolism is, however, more difficult, one. Patients with: Low In low risk patients early mobilization and avoidance of risk dehydration is recommended. Several risk scores for identication of patients at different risk levels have been developed,240 yet all risk scores, including the above, still need validation in prospective studies. It is favoured measured in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism, in patients with renal failure and when urgent reversal of anticoa followed by bilateral compression ultrasonography. If this is gulation by protamine is needed, as well as in the acute treatment normal in the presence of negative D-dimer levels, then pulmon of massive pulmonary emboli. In patients with acute pulmonary embolism with haemo In patients with suspected pulmonary embolism, positive dynamic compromise, i. Fetal loss of 6% and 6% pre-term delivery Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is markedly lower with 250 were reported. Whereas it is therefore not been evaluated, and is not recommended in preg considered necessary in patients with mechanical valves in nant patients. Indications for vena cava lters are the same as in nancy progresses to maintain a certain therapeutic anti-Xa non-pregnant patients. Vitamin K antagonists may be started on the second day pregnancy and puerperium after delivery and continued for at least 3 months or for 6 months if pulmonary embolism occurred late in pregnancy. Isolated iliac vein thrombosis may manifest with isolated pain in In intermediate risk patientsd post-partum the buttock, groin, ank, or abdomen. In women with a high pre-test probability, a positive D-dimer and a normal initial compression ultrasound magnetic aClass of recommendation. Drugs during pregnancy and be applied, weight adjusted, twice daily (see treatment of pulmon ary embolism). There are no uniform rec thrombo-embolism in pregnancy and ommendations for the treatment of pregnant women yet. As drug treatment in pregnancy concerns the mother Category D: there is evidence of human fetal risk, but the benets and the fetus, optimum treatment of both must be targeted. Category X: studies in animals or human beings have demonstrated In case of emergency, drugs that are not recommended by the fetal abnormalities, or there is evidence of fetal risk based on pharmaceutical industry during pregnancy and breastfeeding human experience, or both, and the risk of the use of the should not be withheld from the mother. The potential risk of a drug in pregnant women clearly outweighs any possible drug and the possible benet of the therapy must be weighed benet. Different sources of evidence can be used for risk classication of drugs applied during pregnancy. Category B: either animal reproduction studies have not demon strated a fetal risk but there are no controlled studies in preg 11. For this and for legal reasons, drugs are frequently considered Category C: either studies in animals have revealed adverse effects prohibited during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Drugs should be given only if potential benets justify the potential risk to the 11. Acenocoumarola Vitamin K antagonist D Yes Yes (no adverse effects Embryopathy (mainly first trimester), reported) bleeding (see further discussion in Section 5 for use during pregnancy). Acetylsalicylic acid Antiplatelet drug B Yes Well-tolerated No teratogenic effects known (low dose) (large datasets). Adenosineb Antiarrhythmic C No No No fetal adverse effects reported (limited human data). Aminoglycosides, Antibiotics D Unknown Unknown Risk to the fetus exists quinolones (reserved for vital indications). Clopidogrel Antiplatelet drug C Unknown Unknown No information during pregnancy available. Colestipol, Lipid-lowering drugs C Unknown Yes lowering fat May impair absorption of fat-soluble cholestyramine soluble vitamins vitamins. Hydralazine Vasodilator C Yes Yese (maximum 1%) Maternal side effect: lupus-like symptoms; fetal tachyarrhythmias (maternal use). Isradipine Calcium channel blocker C Yes Unknown Potential synergism with magnesium sulfate may induce hypotension. Labetalol / blocker Yes Yese Intrauterine growth retardation (second and third trimester), neonatal bradycardia and hypotension (used near term). Phenprocoumona Vitamin K antagonist D Yes Yes (maximum 10%), well Coumarin-embryopathy, bleeding (see tolerated as inactive further discussion in Section 5 for use metabolite during pregnancy). Acknowledgements the Task Force who so generously shared their knowledge, as It has been a great privilege for the Chair of this Task Force to have well as the referees for their tremendous input. Finally I scientists in the eld at the European level and to give these Guide would like to express my greatest appreciation of the Guidelines lines to the community of cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons, team at the heart house, especially Veronica Dean and Nathalie gynaecologists, and all specialists involved in the care of pregnant Cameron for their extremely helpful support. Regitz-Zagrosek V, Gohlke-Barwolf C, Geibel-Zehender A, Haas W, Kruck I, September 1995). Al-Nawas B, Block M, Ertl G, Franzen D, Gohlke-Barwolf C, Herrmann M, Euratom for nuclear medicine. Damilakis J, Theocharopoulos N, Perisinakis K, Manios E, Dimitriou P, Vardas P, Plicht B, Wahl G, Werdan K. Conceptus radiation dose and risk from cardiac catheter abla der European Society of Cardiology zur Infektiosen Endokarditis (Neuauage tion procedures. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease: the Task patient for nonobstetric conditions: algorithms and radiation dose consider Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society ations. Prospective multicenter Przybylski A, Urbanek P, Kusmierczyk M, Kozluk E, Sacher F, Sanders P, study of pregnancy outcomes in women with heart disease. Peripartum cardiomyopathy: National Heart, Lung, and Blood review of the accuracy of rst-trimester ultrasound examination for detecting Institute and Office of Rare Diseases (National Institutes of Health) workshop major congenital heart disease. Combined Doppler and echocar diographic measurement of cardiac output: theory and application in pregnancy.

Discount actoplus met 500 mg
In c re a s e d Sin ce m o st o f t h e p r o t ein -b o u n d ca lciu m co m b in es w it h serum calcium albumin diabetic diet for a 5 year old order actoplus met canada, total serum calcium is signi cantly altered by Feedback serum albumin levels. For example, when the arterial pH increases in alkalosis, more cal 3 35,37 cium becomes bound to protein. It stimulates the absorption of serum calcium remains unchanged, the ionized portion calcium, and to a lesser extent phosphorus, from the decreases. Calcium is stored in bone and excreted by the ++ Approximately 40% of serum calcium is bound to kidney. Another 10% is com plasma into the glomerulus and then selectively reab plexed. Another fac through reduced gastric acid production (proton-pump ++ 38,39 tor that in uences Ca reabsorption by the kidney is inhibitors, histamine 2-blockers). The opposite occurs with reduction fusion of plasma and platelets, which have high citrate 3 in serum phosphorus levels. Most persons with mild H ypocalcemia represents a total serum calcium level of hypocalcemia are asymptomatic, whereas large or ++ less than 8. A pseudo neuromuscular excitability and cardiovascular effects 3,35,36,38 hypocalcemia is caused by hypoalbuminemia. Before a diagnosis of ability, thereby making nerve cells less sensitive to hypocalcemia can be made, the total calcium should be stimuli. The severity of the manifestations mobilize calcium from bone due to hypoparathyroid depends on the underlying cause, rapidity of onset, ism, and increased protein binding or chelation such accompanying electrolyte disorders, and extracellular that greater proportions of calcium are in the nonion pH. Because of the inverse relation between severe hypocalcemia, laryngeal spasm and seizures. Contraction of cemia is dif cult to treat with calcium supplementa the ngers and hands. Hypocalcemia is also a common problem Cardiovascular effects of acute hypocalcemia include in acute pancreatitis in which fat necrosis and precipi hypotension, cardiac insuf ciency, cardiac arrhythmias tation of calcium soaps produce a decrease in serum (particularly heart block and ventricular brillation), calcium. Acute hypocalcemia is an emergency situ situations where an increase in pH, such as occurs with ation, requiring prompt treatment. Elevations in free fatty Chronic hypocalcemia is treated with oral intake of acids suf cient to alter calcium binding may occur calcium. O ral calcium supplements of carbonate, gluco 35 during stressful situations that cause elevations of epi nate, or lactate salts may be used. Long-term treatment nephrine, glucagon, growth hormone, and adrenocorti may require the use of vitamin D preparations, espe cotropic hormone levels. The active form of vitamin D is admin Hy p e rc a lc e m ia istered when the liver or kidney mechanisms needed Hypercalcemia represents a total serum calcium con for hormone activation are impaired. Increased serum albumin levels may also elevate the total serum calcium but not affect the ion ized calcium. H ypercalcemia occurs when calcium movement into the circulation overwhelms calcium regulatory hor mones or the ability of the kidney to remove excess calcium ions. The two most common causes of hyper calcemia are increased bone resorption due to hyper 40 parathyroidism and neoplasms. H ypercalcemia is a common complication of malignancy, occurring in approximately 20% to 30% of persons with advanced 40,41 disease. A number of malignant tumors, including carcinoma of the lung, have been associated with hyper calcemia. Some tumors destroy the bone, while others produce humoral agents that stimulate bone resorption or inhibit bone formation. Less common causes of hypercalcemia include pro longed immobilization, increased intestinal absorp A B tion of calcium, excessive doses of vitamin D, or the 41 effects of drugs such as lithium and thiazide diuretics. Intestinal absorption of calcium by in ating a blood pressure cuff above systolic blood pressure. Loop diuretics commonly is characterized by hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, are used rather than thiazide diuretics, which increase alkalosis, and progressive renal failure. Drugs that are women who are overzealous in taking calcium prepa used to inhibit calcium mobilization include bisphos 3,40 rations for osteoporosis prevention. The the antacid repairs the alkalosis and increases calcium bisphosphonates, which act mainly by inhibiting osteo elimination. Calcitonin of lithium to treat bipolar disorders has been shown to inhibits osteoclastic activity, thereby decreasing bone cause hyperparathyroidism and hypercalcemia in some resorption. The thiazide diuretics increase calcium reab of vitamin D to its active form and are used to treat sorption in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Dis ord ers of P hospho rus Bala nc e Phosphorus is mainly located in bone (about 85%) Manife s tatio ns. In the adult, the normal serum of the kidneys to high concentrations of calcium phosphorus level ranges from 2. Levels in children are greater, prob ness, stupor, weakness, and muscle accidity. Behavioral ably because of increased levels of growth hormone and changes may range from subtle alterations in personality decreased levels of gonadal hormones. The heart responds to elevated lev els of calcium with increased contractility and ventricu Re g u la t io n o f Ph o s p h o ru s Ba la n c e lar arrhythmias. Gastrointestinal symptoms include constipation, Phosphorus is ingested in the diet and eliminated in the anorexia, nausea, and vomiting, re ecting a decrease in urine. This causes salt and water diuresis the urine is directly related to phosphate concentrations and an increased sensation of thirst. Most of the intracellular phosphorus is in the H yperparathyroidism and malignant disease are the organic form. Contributing factors include poor food intake and the effect that chronic alcohol use Hy p o p h o s p h a t e m ia has on the renal threshold for phosphate reabsorption, causing more phosphate to be eliminated in the urine. H ypophosphatemia is commonly de ned by a serum Administration of hyperalimentation solutions with phosphorus level of less than 2. Serious depletion of phosphorus may exist with levels and increased phosphate excretion. M any of the manifestations of phos restricted, dietary intake and intestinal absorption of phorus de ciency result from a decrease in cellular phosphorus are usually adequate. The Prolonged ingestion of antacids may also interfere with decrease in cellular energy can cause altered neural func intestinal absorption. Antacids that contain aluminum tion, disturbed musculoskeletal function, and hemato hydroxide, aluminum carbonate, and calcium carbonate logic disorders (Table 8-7). N eural manifesta ished persons increases the incorporation of phosphorus tions (intention tremors, paresthesias, hypore exia, into nucleic acids and phosphorylated compounds in stupor, coma, and seizures) are uncommon but serious the cell. Usually the Chronic phosphorus depletion interferes with min hypophosphatemia does not become apparent, how eralization of newly formed bone matrix. In growing ever, until insulin and uid replacement have reversed children, this process causes abnormal endochondral the dehydration and glucose has started to move back growth and clinical manifestations of rickets. Sevelamer, a recently approved calcium and aluminum-free phosphate binder, is as Tr e a t m e n t. The treatment of hypophosphatemia is effective as a calcium-based binder, but lacks its adverse 3 usually directed toward prophylaxis. H emodialysis is used to reduce phosphate levels accomplished with dietary sources high in phosphorus in persons with chronic kidney disease. M oderate hyperphosphatemia exists when serum Re g u la t io n o f Ma g n e s iu m Ba la n c e phosphate is in the range of 4. The kidney kidneys to excrete excess phosphate, rapid redistri is the principal organ of magnesium regulation. B ecause only about 3% is excreted in the urine, although this phosphorus is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, amount can be in uenced by other conditions and medi hyperphosphatemia due to impaired renal function 48 cations. The administration of excess phosphate brane pump, membrane stabilization, nerve conduction, containing antacids, laxatives, or enemas can be and ion transport. Serious and even fatal hyperphosphatemia has M agnesium also participates in potassium and cal reportedly resulted from administration of phosphate cium channel activity. M any of the signs and symptoms as a smooth muscle relaxant by altering calcium levels of a phosphate excess are related to a calcium de cit that are responsible for muscle contraction. Because of the reciprocal relationship of its smooth muscle relaxing effect, there has been a between calcium and phosphorus levels, a high serum recent interest in the use of magnesium in the treatment phosphate level tends to lower serum calcium levels, 56 of severe bronchial asthma.
Buy actoplus met 500 mg otc
Nervous System: Anxiety diabete 2 symptoms buy actoplus met 500 mg with amex, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo. Skin and Appendages: Alopecia, bruising, desquamation, erythema, photosensitivity, sweat. Urogenital System: Cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, hyperkalemia, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure. Cardiovascular System: Arrhythmia, exacerbation of angina, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis. Hemic and Lymphatic System: Agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia. Nervous System: Akathisia, convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis, mood alterations. Skin and Appendages: Angioedema, toxic epidermal necrosis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, onycholysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria, vesiculobullous reaction. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60-100 g in adults, 1-2 g/kg in children) and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated. The long plasma half-life of piroxicam should be considered when treating an overdose with piroxicam. Experiments in dogs have demonstrated that the use of multiple-dose treatments with activated charcoal could reduce the half-life of piroxicam by more than 50% and systemic bioavailability by as much as 37% when activated charcoal is given as late as 6 hours after ingestion of piroxicam. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding. Syndromes are composed of multiple malformations thought to be etiologically and/or pathogenetically related. Syndromes that have cleft lip and/or cleft palate as one of the features are of interest in the quest for etiologic and pathogenetic factors, and it is estimated that 30% of cleft cases are syndromic. Studies suggest that associated anomalies occur with a frequency of 44 % to 64 % in patients with clefts (Cohen, 1978). There is however considerable variation in these figures in different populations. Clefts occur proportionately more often among the Asian populations than am ong African populations. Known data comes mainly from the city of La Paz, at 4000 meters above sea level, with a large proportion of its population being of Amerindian ethnic background. The role of both environmental (chronic hypobaric hypoxia from altitude) and genetic (M ongolic Amerindian ethnicity) etiologic factors and their interactions are still unknown (Castilla, Lopez-Camelo & Campana, 1999). The populations of two Asian countries, Japan (Neel, 1958) and the Philippines (M urray et al. Such exceptional situations 16 Global registry and database on craniofacial anomalies m ay be reflecting operational differences in ascertainm ent or case definition, or micro ethnic situations such as geographical clusters. Heterogeneity within and among could be due to registries was tested using the chi square test. Considering the 5th and 95th centile of the rate distribution, the rates varied from a low of 2. Higher values were found in Asian (China, Japan) and South American (Bolivia, Paraguay) countries, while Israel, South Africa and Southern European countries showed the lower values. It has been reported that about 20% of liveborn infants with facial clefts have associated malformations, and the figure is much higher among 18 Global registry and database on craniofacial anomalies stillbirths. The study of associated anomalies is useful in identifying pathogenetically homogeneous patterns of malformations and hence contributes to more powerful etiologic studies and better public health monitoring. The definitions Out of 6454 cases of multi-malformed infants, the study found 739 cases of associated (11. To distinguish between isolated and associated cases in birth-defect epidemiology it is useful to provide clues for the etiology of the defect. The definitions of associated anomalies may vary among researchers, and the completeness of the identification and registration of such anomalies will depend on the data-collection method and the length of follow-up time. Findings in literature show that the most frequent defects associated with facial clefts are malformation of the limbs, followed by cardiovascular and other facial anom alies. This is a significant research project, unique for the extent of its coverage of collected cases and the variety of races and ethnic groups represented. Furthermore, Registry an attempt was made to classify unidentified, multi-malformed cases as syndromes or associations. This was done by referring them either to the regional multiple congenital abnormality examination centres or the so called registry diagnoses in well-defined multiple-congenital abnormality entities. Finally, the remaining unidentified multi-malformed cases were evaluated on the basis of their component abnormalities. These cases, all with two to eight component abnormalities, were evaluated together on the basis of different pairs of component abnormalities in the hope that this approach might help to identify and/or delineate syndromes or associations, thus reducing the proportion of random com binations of congenital abnorm alities. The form allowed for the recording of at least 500 differentthe diversity hereditary diseases, autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and of hereditary X-linked recessive, in approximately the same proportion as they are presented in Victor M cKusicks Catalogue for M endelian Phenotypes syndromes with in M an (M cKusick, 1998). Team former Soviet Union m em bers visited every fam ily, excluding those where cases were evidently nonhereditary; the team subsequently com piled the was broad. Finally, the study revealed the prevalence rates for autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive and X-linked recessive disorders, as well as the spectrum of hereditary diseases in the population that had been investigated. In 1976-1984, a similar study was conducted on a population of almost one million people in the Central Asian Republics of the former Soviet Union. The same methodology was used and more than 420 families, with 1114 people affected with different hereditary disorders, were revealed in the course of the study. In 1985, further studies were conducted in Northern, Central and Southern regions of the European part of the former Soviet Union. A study that included other ethnic groups, namely Adigean, Chuvashian and M ari, investigated a population of more than 1. The prevalence rates for autosomal dominant, as well as for recessive disorders, were approximately two times higher in rural populations than they were in the urban populations of all the territories investigated, except for Krasnodar Province. Prevalence rates for X-linked pathology were approximately equal in both urban and rural populations. It should be mentioned that values of prevalence rates for hereditary pathology of rural populations in the study were close to the values of the frequencies of M endelian disorders in the highly respected Register for Handicapped Individuals of British Columbia. Am ong those, M arfan syndrome and trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1, showed local accumulation, the latter among the Adigean population. Given the public health importance of birth defects, it is necessary for birth-defect surveillance systems to monitor and detect trends in birth defects, provide data for etiologic studies of birth defects, and provide the basis to plan and evaluate the effects of prevention activities. These purposes are best accomplished through surveillance system s that use m ultiple data sources, possess accurate and precise diagnostic criteria, perform timely data analysis, provide timely dissemination of the data, and use personal identifiers for Surveillance follow-up and data linkage. It is important to collect this information given the variation in these characteristics and in the prevalence of some birth yearly births. The major activities of these centres are to participate in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study and expand and improve the birth-defect surveillance systems in their respective states. For example, 36 cooperative agreements have been awarded to enhance state-based birth-defect surveillance activities. These cooperative agreements provide the opportunity for state-based birth-defect surveillance system s to share data and increase the information on rare birth defects and geographical variation. Although differences between each states approach for birth-defect surveillance system s sometimes creates such limitations, the diversity of approaches serves as a useful resource for guiding the development of surveillance systems for other childhood conditions. Furthermore, distinct subgroups within these conditions seem to exist according to severity, sidedness, and associated anomalies. The reasons the number of ratios was different, malformation by malformation, were that several registries did not contribute data for a few malformations and some expected ratios were not computable. The number of computed ratios was very high so a certain number (about 5%) of significant ratios can be expected by chance. Some situations could even be intermediate between the above-mentioned macro and micro ethnicity, as for instance those of Finland (Saxen and Lathi, 1974) or the Philippines (M urray et al.

