Coumadin
Buy discount coumadin 5 mg online
If the patient’s symptoms cannot be managed arrhythmia update 2015 coumadin 5 mg line, the family needs to ask local providers to make home visits to provide support and advice and, if necessary, arrange for admittance to the appropriate level facility. At tertiary care settings, the team might include a gynaecologist, a radiotherapist, a radiotherapy technician, a psychologist or counsellor, a nutritionist, a physiotherapist, an oncology nurse, a pharmacist, a social worker and a palliative care nurse. In such settings, community health workers – supported, trained and supervised by primary and secondary-level health-care professionals – are the principal providers of palliative care. There should be a smooth transfer of medical information among the various health care professionals responsible for patient care. Where appropriate, this involves effcient exchange and sharing of medical records between community-level and tertiary care teams. All patients and family caregivers should be informed whom they can contact at which facility, if needed, and how they can reach him or her. Strategies need to be devised to allow community health workers to link the patient and her family with staff at the primary-, secondary and tertiary-level facilities. Communication is best if a system is formally established and willingly implemented by all team members, including tertiary care specialists, before the patient is discharged from the treatment facility. Health-care providers at all levels need to be trained to use the same words and nontechnical, culturally sensitive language when in the presence of patients and their family and community members, and to have the resources necessary to manage the most common physical and psychosocial problems, with special attention to pain control. The health-care provider should ensure that the patient and her family understand the nature and prognosis of the disease and the recommended treatment. With the help of community health workers, the family will be empowered to participate in the decision-making, and will be kept informed of medical decisions, 6 In this context, “family” includes anyone the patient considers to be signifcant to her. Palliative care including changes in caregivers and treatment, and should be guided in best practices of palliative care. The patient’s family and other caregivers can be taught to 7 provide home-based care. Clinical care can be provided by health workers trained in the use of recommended medicines within the national legal framework. Providers of palliative or home-based care, with continual back-up from the primary care provider. In this case, money for food, supplies and medicines for her care may be obtained by the family from local and regional nongovernmental and faith-based organizations. It is very useful for community health workers to have established links with these organizations before they are needed, so that patients can be referred to them as needed. Also there is an immense range of behaviours, feelings and beliefs Counselling regarding death that are affected by cultural context and that should be taken into consideration. Palliative care A trained palliative care worker enables the patient and her support circle to make decisions about the patient’s care. The patient and her family will feel that they are in control, with full support from the health-care team, whose task it is to provide appropriate information and advice and to support informed decisions. Prescribe, provide, supervise, support and maintain supplies (including medicines) for those community health workers who do home visits for women with cervical cancer, 7 or directly for patients and their caregivers for immediate use or to be used if and when needed. The delegation of some tasks to primary-level providers must only be implemented if there are adequate systems in place to legally protect both health-care providers and patients. Some countries have already changed their policies and regulations in order to allow nurses and clinical offcers to prescribe opioid medicines in order to provide improved coverage for pain relief. Additional documented evidence is needed to inform policy-makers about possible strategies for increasing coverage of services while maintaining quality of care. Use compassionate and culturally sensitive language when addressing death and dying with patients, families and their communities. Anticipating practical issues It may be diffcult for many families to prepare for the likelihood that their ill relative will die while they are still hoping for remission or prolongation of life. Health-care providers should be very sensitive to the patient’s and the family’s ability to deal with the reality of the situation and should adjust their interventions depending on the readiness of the patient and her family to take practical steps to prepare for anticipated death. Acknowledging the need for hope while planning for the worst do not have to be mutually exclusive. It is helpful to discuss important issues with the patient and with her family, if she consents to this. Discussing and assisting with these practical steps, according to the prevailing cultural context, may also allow for the completion of the family’s emotional tasks. Preparing for death Encouraging communication within the family can make a death less stressful and ease bereavement (see Chapter 6, section 6. At times, the patient may express anger or other strong emotions towards her closest family members and health-care providers; such outbursts need to be accepted and not taken personally. Reactions to impending death are always affected by the cultural context; thus, sensitive assessment of her willingness to discuss these issues is needed before starting the conversation. Always remember that attentive listening and calming body language can be most important. Palliative care Together with the family, the trained health-care provider can contribute to supporting the dying woman by: 7. When considering the possibility of transferring the patient to the hospital, the patient’s wishes are the primary consideration if she is conscious; if she is unconscious, her family’s wishes can be considered. If death is not expected in the immediate future, and the family needs some respite, consideration may be given to transferring her to the secondary-level hospital or to a hospice, if available and affordable. Death At the time of death, it is essential to respect local rites, rituals and customs, as well as any expressed personal wishes of the patient or family concerning care of the body, funeral arrangements and other issues. Bereavement Bereavement care is support given to the family after a patient’s death, to help them cope with the loss of their loved one. Home-based and clinic-based care providers involved in a woman’s end-of-life care can share the family’s sorrow, by encouraging them to talk and express their memories. Workers should not offer false comfort but should be supportive, take time to listen, and try to arrange practical support with neighbours and friends. Palliative care services usually include some ongoing follow-up care with bereaved families to support effective grieving and continuing community support, as well as to assess and assist families where prolonged grief may interfere with adjustment back to adaptive functioning. Pain is almost always part of the constellation, 7 and its relief should always be part of palliative care. The vast majority of women with cervical cancer will most likely suffer from moderate to severe pain. Moderate and severe pain should always be addressed, and opioid analgesics are often essential for pain treatment. It is very useful to have collaboration and regular communication between patients and their home-based caregivers as well as with clinical providers at all levels of the health system; home-based caregivers are most in touch with the patient’s needs, while clinical providers can offer support and medicines. Out of date national norms and guidelines: these norms and guidelines may not be regularly updated in accordance with international drug control conventions and 7 guidelines. Graduates of training institutions may not have learnt to feel confdent with the use of suffcient opioids to control pain and may lack knowledge on common side-effects and their management. For example, they may believe that long-term use of opioids will hasten a patient’s death and/or cause dependency. Where opioid analgesics are available, national rules and regulations must be followed. However, they should be carefully checked to see whether they allow pain relief to be administered adequately. If not, medical and non-medical people need to join forces to advocate for patients’ palliative care to include freedom from pain. Today, in many countries, the approach is, however, to skip the second step and to use low dosages of strong opioids like morphine instead, in order to manage pain in a timely and effective manner. Palliative care 207 arthritis, menstrual cramps, sore muscles following exercise, and tension headaches. Opioids can originate from the poppy plant or they can be synthesized and they can even be made by the body itself (endorphins); they may or may not be chemically related to morphine. The analgesic (pain relieving) effects of opioids are due to a decreased perception of pain and decreased reaction to pain, as well as increased pain tolerance. The more common side-effects of opioids include constipation, nausea, sedation, respiratory depression, euphoria and drowsiness. Opioids can also cause cough suppression, so coughing is another indication for administering an opioid. Systematic review of the evidence suggests that fentanyl, morphine, hydrocodone, oxycodone and methadone are equally effective.
Cheap coumadin online
Because treatment failure Infants and children aged ≥1 month who receive a diagnosis usually cannot be reliably distinguished from reinfection with of syphilis should have birth and maternal medical records T hypertension 6 weeks postpartum buy generic coumadin canada. Infants and children aged Failure of nontreponemal test titers to decline fourfold within ≥1 month with primary and secondary syphilis should be 6–12 months after therapy for primary or secondary syphilis managed by a pediatric infectious-disease specialist and might be indicative of treatment failure. Optimal Persons who have syphilis and symptoms or signs suggesting management of persons who have less than a fourfold decline neurologic disease. Because treatment failure might be the result of unrecognized Treatment should be guided by the results of this evaluation. Data to support use of alternatives to penicillin in the Latent Syphilis treatment of primary and secondary syphilis are limited. However, several therapies might be effective in nonpregnant, Latent syphilis is defined as syphilis characterized by penicillin-allergic persons who have primary or secondary seroreactivity without other evidence of primary, secondary, syphilis. Persons who have latent syphilis and who 14 days (411,412) and tetracycline (500 mg four times daily acquired syphilis during the preceding year are classified as for 14 days) have been used for many years. Persons likely to be better with doxycycline than tetracycline, because can receive a diagnosis of early latent syphilis if, during the tetracycline can cause gastrointestinal side effects and requires year preceding the diagnosis, they had 1) a documented more frequent dosing. Azithromycin as a single 2 g oral dose has been treponemal tests whose only possible exposure occurred during effective for treating primary and secondary syphilis in some the previous 12 months, early latent syphilis can be assumed. Nontreponemal resistance and treatment failures have been documented in serologic titers usually are higher early in the course of syphilis multiple geographical areas in the United States (417–419). However, early latent syphilis cannot be reliably Accordingly, azithromycin should not be used as first-line diagnosed solely on the basis of nontreponemal titers. All treatment for syphilis and should be used with caution only persons with latent syphilis should have careful examination when treatment with penicillin or doxycycline is not feasible. Careful clinical and serologic follow-up foreskin in uncircumcised men) to evaluate for mucosal lesions. Treatment Persons with a penicillin allergy whose compliance with Because latent syphilis is not transmitted sexually, the therapy or follow-up cannot be ensured should be desensitized objective of treating persons in this stage of disease is to prevent and treated with benzathine penicillin. Skin testing for complications and transmission from a pregnant woman to her penicillin allergy might be useful in some circumstances in fetus. Although clinical experience supports the effectiveness of which the reagents and expertise are available to perform the penicillin in achieving this goal, limited evidence is available test adequately (see Management of Persons Who Have a to guide choice of specific regimens or duration. In addition, birth Management of Sex Partners and maternal medical records should be reviewed to assess See Syphilis, Management of Sex Partners. For those with congenital syphilis, treatment should Special Considerations be undertaken as described in the congenital syphilis section in this document. Those with acquired latent syphilis should Penicillin Allergy be evaluated for sexual abuse. Persons who receive a diagnosis of latent syphilis tetracycline (500 mg orally four times daily), each for 28 days. Clinical experience suggests that an interval of have not been defined; treatment decisions should be discussed 10–14 days between doses of benzathine penicillin for latent in consultation with a specialist. Persons with a penicillin syphilis might be acceptable before restarting the sequence of allergy whose compliance with therapy or follow-up cannot injections. Skin testing for penicillin allergy might be useful that an interval of 7–9 days between doses, if feasible, might in some circumstances in which the reagents and expertise are be more optimal (420–422). Missed doses are not acceptable available to perform the test adequately (see Management of for pregnant women receiving therapy for latent syphilis (423). Guidelines for all forms of syphilis, even in the absence of clinical neurologic findings. Special Considerations If compliance with therapy can be ensured, the following Penicillin Allergy alternative regimen might be considered. Providers should ask patients about known allergies to Alternative Regimen penicillin. Leukocyte count is a sensitive test results and delayed appearance of seroreactivity have also measure of the effectiveness of therapy. The magnitude of these risks is Penicillin Allergy not defined precisely, but is likely small. Careful follow-up after therapy cephalosporins is negligible (428–431) (see Management is essential. The use of antiretroviral therapy as per current of Persons Who Have a History of Penicillin Allergy). Other regimens have not been adequately Recommended Regimen evaluated for treatment of neurosyphilis. Persons with penicillin allergy whose the recommended benzathine penicillin treatment regimen compliance with therapy or follow-up cannot be ensured for primary and secondary syphilis. Certain studies have demonstrated that among only in conjunction with close serologic and clinical follow-up. Recommended Regimen for Late Latent Syphilis Follow-Up Benzathine penicillin G, at weekly doses of 2. In these circumstances, the need for additional therapy should be performed and treatment administered accordingly. Even after retreatment, serologic titers Management of Sex Partners might fail to decline. Special Considerations Syphilis During Pregnancy Penicillin Allergy All women should be screened serologically for syphilis early the efficacy of alternative nonpenicillin regimens in in pregnancy (106). Antepartum be ensured should be desensitized and treated with penicillin screening by nontreponemal antibody testing is typical, but (See Management of Persons Who Have a History of treponemal antibody testing is being used in some settings. Any woman who has a fetal death after 20 weeks’ Follow Up gestation should be tested for syphilis. For women with a history of obstetric attention after treatment if they notice any fever, adequately treated syphilis who do not have ongoing risk, contractions, or decrease in fetal movements. Women without a history a rare complication of treatment, but concern for this of treatment should be staged and treated accordingly with a complication should not delay necessary treatment. Missed doses are not acceptable for pregnant women lacks signs or symptoms of primary syphilis, has a partner receiving therapy for late latent syphilis (423). Pregnant with no clinical or serologic evidence of syphilis, and is likely women who miss any dose of therapy must repeat the full to follow up, repeat serologic testing within 4 weeks can be course of therapy. If follow-up is not possible, women without a history of treated syphilis should be treated according to the Coordinated prenatal care and treatment are vital. Serologic titers can be checked Treatment monthly in women at high risk for reinfection or in geographic Penicillin G is the only known effective antimicrobial for areas in which the prevalence of syphilis is high. Providers preventing maternal transmission to the fetus and treating fetal should ensure that the clinical and antibody responses are infection (443). Evidence is insufficient to determine optimal, appropriate for the patient’s stage of disease, although most recommended penicillin regimens (444). Inadequate maternal treatment is Recommended Regimen likely if delivery occurs within 30 days of therapy, clinical signs Pregnant women should be treated with the penicillin regimen of infection are present at delivery, or the maternal antibody appropriate for their stage of infection. Management of Sex Partners Other Management Considerations See Syphilis, Management of Sex Partners. For women who have primary, secondary, or early latent syphilis, a second dose of Penicillin Allergy benzathine penicillin 2. When syphilis is diagnosed during the second half of have a history of penicillin allergy should be desensitized and pregnancy, management should include a sonographic treated with penicillin. However, this dose challenge might be helpful in identifying women at risk evaluation should not delay therapy. Sonographic signs of for acute allergic reactions (see Management of Persons Who fetal or placental syphilis. Erythromycin accompanied by these signs should be managed in and azithromycin should not be used, because neither reliably consultation with obstetric specialists. Data insufficient to recommend specific regimens for are insufficient to recommend ceftriaxone for treatment of these situations. Additional testing at for stillborn infants, skeletal survey demonstrating typical osseous 28 weeks’ gestation and again at delivery is warranted for lesions might aid in the diagnosis of congenital syphilis. Moreover, evaluation and treatment of neonates born to women who as part of the management of pregnant women who have have reactive serologic tests for syphilis during pregnancy. Routine screening of newborn sera or the neonate for congenital syphilis in most scenarios, except umbilical cord blood is not recommended, as diagnosis at when congenital syphilis is proven or highly probable (See this time does not prevent symptomatic congenital syphilis in Scenario 1). No mother or newborn infant should leave Scenario 1: Proven or highly probable congenital the hospital without maternal serologic status having been syphilis documented at least once during pregnancy, and preferably again at delivery if at risk. Other causes of elevated values should be considered when an immunoglobulin (IgM) test can be recommended.

Purchase coumadin 5 mg with amex
Berberis-Homaccord (exhausted suprarenal glands) Arsuraneel (serious exhaustion wide pulse pressure in young adults buy genuine coumadin online, psychic depression) Aletris-Heel (exhaustion) Spascupreel and Colocynthis-Homaccord (muscular pains) Gelsemium-Homaccord (neuralgia) Traumeel S tablets (enzyme regeneration after therapeutical damage) Injection therapy Glandula suprarenalis suis-Injeel and Funiculus umbilicalis suis-Injeel with Tonico Injeel as mixed injection on Mondays, i. Musculus suis-Injeel, Strychninum phosphoricum-Injeel and Selenium-Homaccord as mixed injection on Thursdays, i. Lathyrus sativus-Injeel, Rhus toxicodendron-Injeel S and Ignatia-Injeel as intermediate injection. Coenzyme compositum, possibly alternating with Ubichinon compositum (enzyme regeneration after therapeutical damage), possibly also Tonsilla compositum and Cerebrum compositum (depression of the defensive functions and vegetative dystonia), in addition to , or alternating with Testis compositum (hormonal functions in men) or Ovarium compositum (for women) and collective pack of the catalysts of the citric acid cycle, possibly with the above for progressive auto-sanguis therapie. Fertility, disturbances of (Germinodermal impregnation or degeneration phase) (Main remedy: Galium-Heel) Psorinoheel 8-10 drops in the morning Galium-Heel 8-10 drops at midday Phosphor-Homaccord 8-10 drops in the afternoon Lymphomyosot 8-10 drops in the evening possibly the above preparations taken together 2-4-6 times daily. Testis compositum (often specifically effective) in place of the above 2-3 times weekly i. Testis suis-Injeel, Ductus deferens suis-Injeel and Hypophysis suis-Injeel for progressive auto-sanguis therapy as well as once weekly i. Coenzyme compositum (in cases resistant to therapy), possibly also the collective pack of catalysts of the citric acid cycle interpolated. Fever (Mainly mesenchymal reaction phase) Fever is a sign that the defensive system of the organism is engaged in a feverish struggle with homotoxins. Fever, therefore, should not be suppressed symptomatically but the biotherapeutics indicated (Gripp-Heel, Traumeel S, Arnica-Heel, Belladonna Homaccord and, in particular, also Echinacea compositum (forte) S) are to be administered daily s. Lwoff demonstrated that viruses are destroyed solely by a rise in temperature (by splitting the Iysosome membrane with the consequent fermentative decomposition of the virus) (Biologische Medizin No. Siegert (Marburg) recommends: “In no case of feverish virus infection should the body be set back with antipyretics or hormones of the steroid group” (Med. Fibroma of the breast (fibrocystic breast disease) (Mesenchymal or ectodermal deposition or dedifferantiation phase) (Main remedy: Galium-Heel) Lymphomyosot 8-10 drops in the morning Galium-Heel 8-10 drops at midday Hormeel S 8-10 drops in the afternoon Psorinoheel 8-10 drops in the evening possibly the above preparations taken together 2-4-6 times daily. Traumeel S tablets (regeneration of the sulphide enzymes) Aesculus compositum (regulation of the peripheral circulation) 8-10 drops 3-6 times daily, additionally or at intervals. Injection therapy Sulfur jodatum-Injeel (forte) as resorptive agent, possibly mixed with Silicea-Injeel (forte). Galium-Heel, Hormeel S, Psorinoheel alternating or mixed with Carbo animalis-Injeel forte, Cimicifuga-Homaccord, Ranunculus-Homaccord, Conium-Injeel (forte) S, Phytolacca-Injeel (forte) S, Calcium carbonicum-Injeel forte or Calcium fluoratum-Injeel forte i. Sutoxol-Injeel (forte), Lac caninum-Injeel (forte), and Trichomonaden Fluor-Injeel (forte) at intervals for nosode therapy. Placenta compositum (regulation of the peripheral circulation) as well as possibly Coenzyme compositum and possibly Ubichinon compositum (suspicion of precancerous state), when there is a suspicion of an incipient neoplasm phase, also Glyoxal compositum (single injection, awaiting subsequent effect). Fistulae (Usually mesenchymal reaction phase) (Main remedies: Traumeel S, Cruroheel S) Mercurius-Heel S or Traumeel S, 1 tablet at 8 a. Psorinoheel and Galium-Heel in chronic cases Proctheel for anal fistulae, likewise Paeonia-Heel Cruroheel S for fistulae of the leg (fractures), fistulizing otitis Osteoheel S (fistulae of the bone) Traumeel S ointment externally Injection therapy Acidum fluoricum-Injeel, Silicea-Injeel (forte) and Traumeel S in alternation or mixed i. Osteomyelitis-Nosode-Injeel and Mastoiditis-Nosode-Injeel for fistulae of the bone. Flat foot, inflammatory (Osteodermal reaction phase) (Main remedy: Arnica-Heel) Arnica-Heel 8-10 drops at 8 a. Cruroheel S and Arsuraneel in cases of relapse, Traumeel S ointment or also Zeel T ointment to be rubbed in. Injection therapy Echinacea compositum (forte) S, possibly with Traumeel S and Neuralgo-Rheum-Injeel alternating or mixed i. Medorrhinum-Injeel (inability to tolerate prolonged standing up, always having to change from one foot to the other, in a continuous state of unrest and haste). Discus compositum (irritative remote symptoms of osteochondrosis of the vertebral column), possibly also Cerebrum compositum (central regulation), otherwise Os suis Injeel and Medulla ossis suis-Injeel in chronic cases. Flatulence (Entodermal deposition phase) Diarrheel S 1 tablet 3-4 times daily Nux vomica-Homaccord possibly interposed Gastricumeel for meteorism in the epigastrium Hepeel to stimulate the hepatic function Injection therapy Hepeel, Erigotheel, Carbo vegetabilis-Injeel, Injeel-Chol and Argentum nitricum-Injeel alternating or mixed i. Hepar compositum (disturbances of the hepatic function and liver damage), possibly also Coenzyme compositum (enzyme damage in general) and possibly Ubichinon compositum (pronounced enzyme damage). Coxsackie-Virus-A9 or B4-Injeel (forte) are possibly effective See also meteorism. Flittering scotoma (Ectodermal or neurodermal impregnation phase) (Main remedy: Kalium bichromicum-Injeel) Gelsemium-Homaccord 8-10 drops in the morning Kalium bichromicum-Injeel 1 ampoule taken orally at midday. Spigelon 1 tablet in the evening possibly the above preparations taken together 2-4-6 times daily. Injection therapy Kalium-bichromicum-Injeel and Nervus opticus suis-Injeel alternating or mixed i. Aurum-Injeel (colloidale-Injeel) for hemiablepsia As intermediate remedy, possibly also Psorinoheel i. Focal toxicoses (Usually neurodermal impregnation phases) (Main remedy: Traumeel S) On a devitalized tooth with granuloma formation. In the case of scars, the resultant circulatory disturbances also have an impregnating effect. The consequent disorders correspond to focal toxicoses (reflexes as described by Reilly, Speransky and Ricker). As the tonsils, as a result of repeated retoxic treatment of tonsillitis, can also exhibit such impregnation foci, extirpation may also be indicated. Here, however, possibilities are offered of provoking regressive vicariation (tonsillitis), by means of which such impregnation phases in the tonsils can be disintegrated and cured. It should be attempted in every case to achieve these regressive vicariations and to effect a cure by means of the following prescription. Mercurius-Heel S as auxiliary remedy for tonsillitis, Barijodeel for Iymphatism, chronic tonsillitis. Injection therapy Echinacea compositum (forte) S (stimulation of the defensive system) or Engystol N, Galium-Heel alternating i. Staphisagria-Injeel (forte S) for reflexes from scars after operations and incised wounds. Acidum formicicum-Injeel or D200 for general deallergization, Granuloma dentis-Injeel, Tonsillarpfröpfe-Injeel, Tonsillitis Nosode-Injeel, possibly also Streptococcus haemolyticus-Injeel and Staphylococcus-Injeel for chronic tonsillitis and focal diseases originating from the tonsils or teeth. Folliculitis (Ectodermal reaction phase) (Main remedy: Mercurius-Heel S) Arnica-Heel 8-10 drops at 8 a. Lymphomyosot for canalization of the mesenchyme in chronic cases, possibly with Cruroheel S and Arsuraneel. Mercurius praecipitatus ruber-Injeel (forte S) for nodular, deep sycosis of the beard. Tartarus stibiatus-Injeel and Cicuta virosa-Injeel recommended for deep sycosis of the beard. Cutis compositum (therapeutic agent for affections of the skin functions), possibly alternating with Echinacea compositum (forte) S (antitoxic effect), otherwise Cutis suis Injeel and possibly Funiculus umbilicalis suis-Injeel i. Frigidity (Germinodermal deposition or impregnation phase) (Main remedy: Hormeel S) Gynäcoheel 8-10 drops at 8 a. Traumeel S tablets (regeneration of the sulphide enzymes) Injection therapy Ovarium compositum regularly at first twice weekly, later only once weekly i. Funicular neuralgia (Inflammation of a funicle, especially the spermatic chord) (Germinodermal impregnation phase) (Main remedy: Rhododendroneel S) Berberis-Homaccord 8-10 drops at 8 a. Injection therapy Berberis-Homaccord with Zincum valerianicum-Injeel (forte), possibly also Tonico Injeel alternating or mixed i. Coenzyme compositum and Ubichinon compositum (stimulation of the enzyme functions) Cerebrum compositum (for neural disturbances provoked at a distance), Discus compositum (irritation emanating from the spinal column) Testis compositum Ampoules (regulation of the hormonal functions), otherwise also Ductus deferens suis-Injeel i. Furuncular otitis (Ectodermal reaction phase) (Main remedy: Traumeel S) Traumeel S 1 tablet at 8 a. Psorinoheel 8-10 drops 3 times weekly in the evening Possibly the above preparations taken together 2-4-6 times daily. Echinacea compositum (forte) S (stimulation of the defensive system) See also furunculosis, eczema of the auditory meatus, otitis externa, etc. Furunculosis (Ectodermal reaction phase) (Main remedy: Belladonna-Homaccord) Belladonna-Homaccord 8-10 drops at 8 a. Lymphomyosot for mesenchymal canalization Psorinoheel in extremely chronic cases Traumeel S ointment locally Injection therapy Echinacea compositum (forte) S (stimulates the defensive system), otherwise, Belladonna-Homaccord and Traumeel S alternating i. Sutoxol-Injeel, Pyodermie-Nosode-Injeel, Bacillinum-Injeel (furuncle in the nostrils), Staphylococcus-Injeel, Anthracinum-Injeel, Pyrogenium-Injeel (also as forte) in long-standing cases as nosode therapy. Ganglion cyst (Mesenchymal deposition phase) Graphites-Homaccord 8-10 drops 3 times daily Rhododendroneel S (in addition as alternating remedy) Traumeel S tablets (resorptive mercury and enzyme regenerating sulphide effect) Traumeel S ointment, occasionally Zeel T ointment which is more effective (massaged in once to twice daily). Injection therapy Graphites-Homaccord, Hypericum-Injeel (forte) and Ammonium carbonicum-Injeel forte alternating or mixed i. Acidum benzoicum Injeel and Ruta-Injeel (forte), possibly with Traumeel S for a ganglion on the wrist joint.
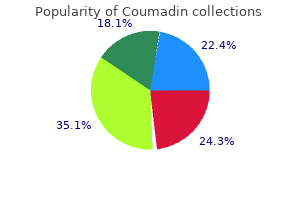
Safe 5 mg coumadin
Preliminary data from the acupuncture treatment study show that veterans reported significant reductions in pain and both primary and secondary health complaints blood pressure guidelines by age order coumadin australia, with results being more positive in the bi-weekly versus weekly treatment group. Acupuncture in combination with restorative sleep and yoga practice for Gulf War-related chronic multisymptom illness is being explored by M. Symptomatic Gulf War veterans will be recruited and randomized to receive acupressure treatment or no treatment for 12 sessions over six weeks. Symptoms will be evaluated across both groups, and before and after treatment in the veterans randomized to the acupressure treatment arm. In this procedure, the sinuses are flooded with either saline or a medicated Xylitol solution to improve functioning of the nasal cavity. Rabago and colleagues at the University of Wisconsin are implementing a 26-week randomized controlled trial using Gulf War veteran subjects, where one-third will receive saline nasal irrigation, one-third will receive Xylitol nasal irrigation and another third will receive routine medical care only. Sinus symptoms, quality of life measures and cytokine quantification will be used as outcomes. Some physicians and scientists believe that prolonged exposure to complex mixtures of chemicals such as pesticides, nerve gas agents, and smoke from oil fire create ongoing sensitivities to everyday chemicals found in the home environment. Carpenter at State University of New York Albany, a detoxification study is underway in which Gulf War veterans will participate in a program that Gulf War Illness Treatment Research | 75 includes exercise, vitamin and mineral supplementation, and low-heat sauna. Measures of fatigue, pain, mental health and cognitive function will be assessed in those that complete the program and in randomly assigned wait listed controls receiving usual care. Mindfulness interventions and cognitive therapies may be effective in reducing symptoms of chronic disease (Merkes, 2010), sleep disorders (Winbush et al. Symptom severity and measures of neurocognitive function will be assessed before and after treatment. After 6 hours of treatment over 3 weeks, subjects will complete follow up questionnaires to determine the efficacy of therapy programs. Golomb (University of California at San Diego) has received funding for a treatment study survey of Gulf War veterans to determine which, if any, treatment interventions have been used and found effective. Treatment studies using animal models of Gulf War illness Animal studies of potential treatments such as antibiotics or other medications offer the opportunity to test the safety and efficacy of medical interventions for Gulf War illness. Since 2008, only one study on antibiotics has been published that may translate into treatment developments for Gulf War veterans. O’Callaghan from Centers for Disease Control is currently studying minocycline as a potential treatment to reduce neuroinflammation in an animal model of Gulf War illness. A number of other ongoing studies are using animal models of Gulf War illness to explore potential treatments in humans. Abou-Donia from the Duke University Medical Center has been testing flupirtine in animals exposed to pesticides, which can recreate many symptoms seen in Gulf War veterans. Flupirtine has been shown to improve learning, memory and cognition while diminishing muscular pain. Rats exposed to the pesticides and to subsequent daily doses of flupirtine will undergo sensorimotor and behavioral function tests, as well as be evaluated for signs of oxidative stress, apoptosis and abnormal neuronal morphology in the brain. Drugs used to treat neurological and psychiatric diseases in human patients are also being explored in animal models of Gulf War illness. Anti-depressants are being investigated as treatments for the central nervous system impairments associated with Gulf War illness by A. Shetty and colleagues at the Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Medicine and the Central Texas Veterans Health Care System. After exposing mice to stress, pyridostigmine bromide and two pesticides, the anti-depressant fluoxetine is being administered in combination with one of two antioxidants, either resveratrol or curcumin, both of which are believed to have anti-inflammatory effects. In separate trials, both the medication and dietary supplements are combined with voluntary exercise. The efficacy of each treatment arm will be assessed using cognitive behavioral tests, neural stem cell proliferation and measures of oxidative stress. Drugs 76 | Gulf War Illness and the Health of Gulf War Veterans used to treat Alzheimer’s disease are also being explored in a sarin exposure-based animal model by M. Drug discovery and development studies are underway to determine if cognitive enhancers that improve memory and treat mood disorders such as depression could be used in symptomatic Gulf War veterans. In conclusion, comparisons between the 2008 Committee report and the current report reveal a shift in the number and diversity of studies exploring treatments that either directly or indirectly address symptoms documented in Gulf War veterans. It will continue to be important to explore both conventional medical approaches (such as medications or devices) as well as alternative therapies such as meditation, mindfulness training and acupuncture/acupressure. Treatments based on proposed mechanisms of illness presentation and on specific symptoms are under development and must be pursued urgently. Published Studies Assessing Treatments for Gulf War Veterans: 2009-2013 Study Groups Studied Parameter(s) Evaluated Key Findings Amin et al. Recommendations the Committee believes that the first priority of federal Gulf War illness research must be the identification of effective treatments to improve the health of Gulf War veterans and to protect the health of current and future American servicemen and women at risk of similar exposures. Treatment outcomes must be clearly defined so that it is possible to quantify improvements associated with interventions. Where possible, treatment outcomes should include improvement in measures associated with expressions of underlying pathology (abnormal laboratory and functional assays). Effective treatments of Gulf War illness could also lead to significant breakthroughs in the treatment of other exposure-related occupational and environmental health problems. Information from veterans with Gulf War illness and their treating physicians on effective treatments should be collected and published. This study was transformed into a literature review of treatments for mainly mental health problems by a group with no experience in treating Gulf War illness. Congress should maintain its funding to support the effective treatment-oriented Gulf War Illness Research Program at the DoD Office of Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs, for openly competed, peer-reviewed studies to identify: 1. Gulf War Illness Treatment Research | 79 Research Priorities and Recommendations Epidemiologic research on Gulf War illness, ill health, medical disorders, disability and mortality in Gulf War veterans Based on current knowledge about ill health in Gulf War veterans and given the limitations of epidemiologic research conducted to date in this population, the committee offers the following research recommendations. In the absence of a consensus case definition of Gulf War illness 23 years after the appearance of this condition, it remains difficult to assess and compare research findings in epidemiological, pathobiological or treatment research on the disorder. The Committee recommends the following approaches to the development of such a definition. Evaluation of health outcomes in Gulf War veteran subgroups of importance—for example, subgroups defined by relevant exposure history or location in theater. In evaluating risk factors for Gulf War illness and other health outcomes, use of analytic 80 | Gulf War Illness and the Health of Gulf War Veterans 5. Methods that control as fully as possible for confounding effects of multiple exposures and etiologic factors that may be associated both with the exposures and outcomes of interest. Monitoring the health of Gulf War veterans Ongoing monitoring and surveillance of the Gulf War veteran population is critical as this veteran group ages. Such surveillance should include outcomes described in this document, including Gulf War illness; neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease; autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis; brain, lung and other cancers; cardiovascular disorders and dysfunction; sleep dysfunction; adverse reproductive outcomes and birth defects; general ill health and disability; mortality, and other disorders and outcomes that emerge as important during the surveillance process. Ongoing assessment of Gulf War illness and its impact on the health and lives of Gulf War veterans is critical. Survey data should be used to flag conditions of possible importance and followed up with detailed investigation, including the clinical evaluations that are required to determine specific medical diagnoses affecting Gulf War veterans at excess rates. A study on the prevalence of “multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and brain cancers, as well as central nervous system abnormalities that are difficult to precisely diagnose” in Gulf War and recent Iraq/Afghanistan war veterans was required by Congress in 2008 (Public Law 110-389, 2008, Section 804) and should be carried out. These assessments should be repeated and published at a minimum of 5-year intervals. Systematic assessment of overall and disease-specific mortality in all Gulf War veterans and in specific subgroups of interest is essential. Evaluation of health outcomes in Gulf War veterans in subgroups of potential importance is critical as some health outcomes are related to specific exposures and experiences in theater. These subgroups can be defined by suspected or documented exposures in theater, geographical locations in the Gulf War theater, or other predictors. Research Priorities and Recommendations | 81 Research into the causes of Gulf War illness, ill health and disability in Gulf War veterans: Human studies Exposure studies in Gulf War veterans to identify the etiologic agents that may have been causative in Gulf War illness remain important because they clarify the physiological basis of the disorder and may help to determine treatment targets for Gulf War illness and other health problems in Gulf War veterans. Applicable methods might include genomic, genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, lipidomic and metabolomic assays to explore suspected physiological effects and to identify novel, unsuspected pathways of illness. Mixed exposures include not only mixtures of chemicals but also chemicals combined with heat, dehydration, infection, and other environmental stressors. Research into the causes of Gulf War illness, ill health and disability in Gulf War veterans: Animal models Studies that utilize animal models (multiple types of species and genetically altered rodents) to characterize persistent molecular, cellular, systemic, and behavioral effects of individual and combined exposure to pyridostigmine bromide, pesticides and insect repellants used in the Gulf War, as well as low level sarin or sarin surrogate, and environmental stressors such as heat and dehydration, all have been informative to date. Research using animal models in Gulf War illness should continue to examine the immediate, delayed, and persistent effects of acute exposures to chemicals and chemical mixtures. Studies that characterize persistent effects of Gulf War-related exposures, alone and in combination, on proinflammatory processes in the central nervous system, autonomic nervous system and peripheral target organs, including those that encompass mitochondrial dysfunction and accumulation of reactive oxygen species.
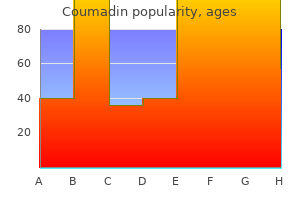
Order 1mg coumadin with mastercard
It was decided not to cover all 6 possible order combinations as this would mean smaller groups with less statistical power yaz arrhythmia order coumadin overnight delivery. This population was chosen as they had experience of refraction (which was needed to operate the phoropter head), and they were motivated to learn about the phoropter head as most had no previous experience and some may be required to 128 use the instrument in their upcoming pre-registration period. Students were asked to volunteer for the project to ensure that they would be motivated enough to attend four sessions. Students who were already qualified as contact lens opticians, and therefore already experienced in refraction, were excluded from this study. In order to estimate the power that would be given by this sample size, the expected standard deviation was required. The most similar previous study assessed the most effective means of teaching anterior eye imaging (Hunt & Wolffsohn, 2007), in which optometrists were asked to self-rate their knowledge following three methods of training. The students were then randomly allocated to one of four groups, A, B, C or D, who received training in the orders shown in table 5. After all participants have received the three methods of training, they were asked to return for a fourth visit at which no training would be given and, as previously, they would carry out a refraction of one eye in up to 30 minutes. This was done 4-6 weeks after the final training session in order to assess long-term learning. A B C Baseline Setup 0 0 2 Operation 0 0 2 Procedure 0 0 2 Overall 0 0 2 Session 1 Setup 5 3 3 Operation 7 4 4 Procedure 8 6 4 Overall 7 4 4 Accuracy 10 9 5 Session 2 Setup 7 4 6 Operation 8 3 6 Procedure 8 5 4 Overall 7. In order to determine whether the subjects’ overall subjective scores of their ability were a reliable measure, the accuracy of their refraction was measured objectively by a qualified optometrist (using the scoring system shown in table 5. This shows that the subjects’ subjective scores of their performance were positively correlated with the accuracy of their refraction as shown in figure 5. This compared the differences in overall subjective scores from the baseline to the follow-up as shown in figure 5. This showed no significant difference between any groups at the 95% confidence level (p=0. Results were then analysed comparing the change in score between each consecutive session to measure the effects of the different forms of training. Jonckheere-Terpstra tests were carried out where Mann-Whitney tests proved significant, to determine whether there was a trend in the most effective methods of training and the effect size of the trend. In order to measure the long-term learning effects from the training, changes in overall subjective score from session 3 to the follow-up session were analysed. No 134 significant difference emerged between the four groups (Kruskal Wallis test p=0. The test showed that, after all four training sessions, there was no significant difference between the groups (p=0. As with the subjective scores, the accuracy scores were also analysed by the change in score between each session. Two factors showed that hands-on training gave significantly higher improvement in scores than both computer-based training (factor 1 p=0. This was true for ‘understanding of phoropter head setup’ (factor 1) and ‘understanding of phoropter head operation’ (factor 2). For the final factor, ‘understanding of test procedure’, hands-on training scores were significantly higher than both computer-based (p=0. Each method of training was then analysed to determine whether all factors were taught equally well, or whether there was greater improvement in one factor. Understanding of test procedure (factor 3) showed the least improvement of the three factors with hands-on and computer based training but the highest improvement with self taught training. This may be because practice alone improves the subject’s knowledge of the order of tests, whilst understanding of the phoropter head operation and setup require more thorough explanation. The study found that although computer-based learning was more effective than self-taught learning, hands-on training is still the most beneficial form of training. The order in which subjects received the three methods of training had no significant effect on the overall scores, and results across all groups showed lasting effects when measured again at a follow-up session 4-6 weeks later. The results show that from baseline scores to final scores, the order in which subjects received the three types of training did not show any significant differences in the outcomes, both subjective and objective. When long-term learning, carried out at 4-6 weeks after the third session, was investigated, again no significant differences emerged, however Group A showed a slight increase in overall subjective score compared to Groups B, C and D. As Group A received hands-on training in week 1 this may be due to gaining a good level of knowledge early in the study on which they could build with computer-based and self-taught learning. Group A showed less improvement in session 2, when they received computer based learning, which may be due to their already high level of knowledge from hands-on training in week one. This may explain the anomaly in Jonckheere’s test which shows a trend of self-taught learning as more effective than computer-based learning. This contradicts the results from sessions 1 and 3 where the trend is that hands-on training is most effective followed by computer-based learning and lastly self-taught learning. The change in score from baseline to session one is the most accurate indicator of the effectiveness of each method of training as the subjects have received no other forms of training at this point. Hands-on training was the most effective, and computer-based training was significantly better than self-taught learning in session one. When the three factors that subjects were asked to score were individually analysed, two of the three factors showed that hands-on training was significantly more effective than both computer-based and self-taught learning, and that computer-based learning was significantly more effective than self-taught learning. This study shows that hands-on training is still the ideal method of delivering training; its advantages include the ability for immediate feedback and to learn at the trainee’s own pace. However, computer-based learning is more effective than self taught learning and could be incorporated in addition to hands-on training. An alternative combining both distance learning and hands-on training may be audio-teleconferencing as has been used in rural areas of Queensland. This involves a slide presentation, workbook and discussion (Wildsoet et al, 1996) and overcomes some disadvantages of the computer-based learning used in this study. It gives the opportunity for the trainee to ask questions and interact with the trainer and other learners, however it is not as flexible as a computer-based presentation which the trainee can view at their own pace and at a time which suits them. When evaluating how effective the training has been, a cost benefit analysis must also be taken into account (Rae, 1991). The costs incurred in delivering hands-on training from an instrumentation company to a high-street customer could include. In the case of distance learning, if the practitioner can complete their training at a convenient time for the practice, for example if an appointment is cancelled or after practice hours, the practice does not suffer this loss of earnings and may only have to pay for the cost of the practitioners time. The only costs incurred by the trainer are for the time taken to produce the material and to deliver it to the practitioner (by post or via the internet). A number of assumptions are made: firstly, that there is no charge for the training, secondly that the computer based training takes a day (8 hours) to prepare (this may be shorter if training has already been prepared and needs no alteration), that no accommodation is required and the training provider travels by car, that the training lasts an hour in both instances and that the computer-based training is completed outside of normal testing hours though the optometrist is still paid for their time. If the trainer has to travel further and accommodation is required, the costs of hands-on training will be significantly higher. It also assumes that the accuracy and subjective scoring is a linear scale which is unlikely as a small improvement in ability may lead to a large increase in score as the participant gains confidence. However, the training provider must consider whether to provide the best possible training at increased cost in order to deliver high levels of customer service. Visiting a practice in order to deliver the hands-on training has the added 143 benefit of building the relationship between the instrumentation company and the customer, and may allow the trainer to discuss other instrumentation purchase intentions. This was launched in November 2009 (College of Optometrists, 2010) to enable optometrists to record their professional development online which will be particularly relevant if and when revalidation is introduced. Revalidation will require optometrists to demonstrate that they are fit to practice every few years rather than only at the point of registration. Professional development based on analysing weaknesses and learning from managing complex cases in practice enables practitioners to progress towards an expert level of knowledge rather than simply maintaining a baseline standard (Faucher, 2011). As discussed earlier, practitioners favour distance learning and hands on workshops but find time and location to be constraints. When applying these results to optometrists across the country it is worth considering that the subjects are all final year undergraduates who are familiar with computer based learning as part of their degree and therefore may be more computer literate than an average optometrist. However, the preliminary study results with optometrists who had graduated between 5 and 7 years previously also showed the same pattern of results, with hands-on training the most effective 144 followed by computer-based then self-taught learning. Older practitioners and those who were unfamiliar with computer-based learning may not be as comfortable with computer-based learning therefore may show differences in their preferences, however, as subjects were only required to view a PowerPoint presentation, the training did not require anything more than a basic knowledge of computer operation. The participants were selected as they had a broadly similar baseline level of knowledge, therefore this study tested the effectiveness of the training rather than the participants’ own learning and experience. Subjects were randomly allocated to the four groups, however to ensure the groups were comparable, the study could be improved by matching the groups by age, educational level and refractive error of the participants. Further research into training in optometry could investigate interactive computer based learning, and video rather than the presentation used in this study. The long term effect of the training could also be measured several months later.

Purchase coumadin 5 mg with visa
Thanks to Olfrid Gilberg pulse pressure in septic shock generic 5mg coumadin amex, Astrid Åmot Andersen, Siss Lekang, Hege Ellefsen and Vigdis Johnsen for practical help, distribution and mailing of the questionnaires. I am also grateful to Synnøve Solberg, for your support and aesthetic design of my figures and tables. My thank goes also go to my social-worker colleagues at Sunnaas Rehabilitation hospital and their enthusiastic leader Jannike Kathrine Vikan for academic courses and discussions. I also want to thank Professor Maryann Olsson from Karolinska Institute who was a great inspiration of the first paper. I very am grateful to professor Berth Danermark, who has answered all my questions and provided me very valuable thoughts and feedback on the philosophy of science and epistemological perspectives of this thesis. Thanks to professor, Vidar Halvorsen, for your sharp academic view and important contributions to my thesis. Thanks to Anne Thorsen, senior advisor and administrative coordinator of PhD programs at Faculty of Social Sciences, for being helpful, informative and accessible. Finally, to the most important persons in my life, my husband Gunnar, my son Martin and my daughter Camilla and her partner Jonathan for their support, curiosity, patience and acceptance of the study. To my husband Gunnar, for your engagement, discussions and conceptual clarifications. To my dear Martin, for always calming me down when the pc clicked and helping me restore it. To my dear Camilla, for your repeated proofreading of my English documents and interesting discussion of statistical analysis. I cannot express my gratitude to you all for keeping me company all these years working in the evenings, weekends and holidays. There is no medical cure but improvement in medical management and surgery has resulted in increased life expectancy. The meta theoretical perspective of this study is based on critical realism, and different models and theories within social work and health science are combined to provide better understanding and explaining of the results of the study. The questionnaire was subsequently evaluated in focus groups discussion and pilot study. Paper V: Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to examine the association between chronic pain and associated factors. Some studies also indicate that the subjective perception of discomfort does not necessarily match the medical severity of the disease. Only severe fatigue, lower educational level and higher age were significantly associated with decreased work participation in the regression analyses. This confirms the view that fatigue is a major issue for this patient group, but the associations are complex. This research project highlights that medical social work plays an important role in the field of chronic illness and disability, and biopsycosocial approach is recommended. Studies of rare diagnoses are challenging due to small sample sizes and recruiting challenges. International collaborative studies, using the same study design and validated tools, and only including people with verified diagnosis are recommended. Det finnes ingen helbredende behandling, men behandling med ȕ-blokkere eller annen blodtrykksmedisin og operasjon med innsettelse av kunstig hovedpulsåre har ført til økt livslengde. Studien tar utgangspunkt i et meta-teoretisk perspektiv basert på kritisk realisme. Ulike modeller og teorier innenfor sosialt arbeid og helsevitenskap er kombinert for å gi økt forståelse og innsikt i de problemstillingene som diskuteres ut fra resultatene fra studien. Multippel logistisk regresjonsanalyse ble benyttet for å undersøke sammenheng mellom kronisk smerte og andre faktorer. Noen studier vektla også at folks subjektiv opplevelse av ubehag ikke nødvendigvis samsvarer med den medisinske alvorlighetsgraden av diagnosen. Både prevalens av kronisk smerter og fatigue var signifikant høyere i studiegruppen enn blant befolkningen generelt, men tilsvarende eller lavere enn for andre tilsvarende pasientgrupper. Mange beskrev at både kroniske smerter og fatigue begrenset dagliglivet, og smerter hadde signifikant sammenheng med fatigue. Til tross for at mange har omfattende helseplager ser det ut til at de mange mestrer å leve godt med diagnosen. Mye tyder på at fatigue er det helseproblemet som i størst grad er assosiert med lavere arbeidsdeltakelse og nedsatt fornøydhet med livet. Dette bekrefter at fatigue er et utbredt problem for pasient gruppen, men at sammenhengen er kompleks. Studien bekrefter at medisinsk sosialt arbeid er viktig i arbeidet med kronisk syke og funksjonshemmede, og en biopsykososial tilnærming vil være hensiktsmessig. Studier av sjeldne diagnoser er utfordrende på grunn av liten populasjon og rekrutteringsutfordringer. Internasjonale samarbeidsprosjekter som benytter sammen studie design, validerte instrumenter og inkluderer personer med verifisert diagnoser vil være en fordel. Journal of Quality of Life Research 2016; 25(7):1779-1790 Paper V Velvin G, Bathen T, Rand-Hendriksen S, Østertun Geirdal A. Background and choice of theme «My health is good, but I have many health complains. Aortic rupture can cause sudden death, lens luxation can lead to visual impairment and skeletal abnormalities may result in a particular appearance, chronic pain, fatigue and reduced physical capacity. The stories varies, some people grow up in Marfan-affected families; while others are diagnosed after an acute aortic surgery in adulthood. People of all ages describe psychosocial challenges in education, work, family planning and dealing with the health and social services. These treatments may cause frustration, inactivity, increased body mass index and can limit their choice of careers. Many individuals also report visual problems, chronic pain and fatigue and some experience that these symptoms are not understood or emphasized by the professionals in health and social services, or by their relatives. The Marfan Association in Norway is concerned with the psychosocial aspects of the diagnosis and has emphasized the need for more research particular on issues such as education, work participation, quality of life, chronic pain, fatigue and monitoring from social-and health services. The purpose was to gain more knowledge about the psychosocial aspects of living with Marfan syndrome. Chapter 2 is devoted to locating social work in health and disability studies and previous research related to the current issues. The theoretically oriented chapter 3 presents the meta-theoretical perspective and a set of middle range theories that are used as frameworks for better understanding and explaining the results of the study. Thereafter, the “methodology and material” chapter 4 consist of descriptions of the design, user participation, the study sample, the methodology used in the different parts of the study and ethical considerations. Further, in chapter 6 on the discussion of the findings, the methodological considerations of the review studies and the cross-sectional studies are presented. Then a more comprehensive discussion about the main results from each of the issues focused in study is elaborated. At last, in chapter 7 a conclusion with implications for medical social work, and for the health and social services institutions are outlined, along with suggested avenues for further research. Individuals with pertinent diagnoses may register as users and gain access to services, the multi disciplinary outpatient clinic, courses, and monitoring in cooperation with local health-and social services. Most scientific projects emanate from the clinical work and are planned in collaboration with the relevant user associations. Challenges in research on rare disorders There are several challenges of doing research on rare disorders, and in this study four different challenges will be outlined. Despite these similarities, different conditions have different courses, different challenges and different treatment regimens. In Norway, Sweden and Finland the definition of a rare disease is when the prevalence is less than 100 known individuals of one million inhabitants. In Denmark and Iceland, the definition is less than 200 cases out of one million inhabitants. Combined with rare non-genetic conditions, rare diseases affect approximately 6 to 10% of the population in Europe [Kole & Faurisson, 2009]. The third challenge worth mentioning is that research on rare disorders has received little attention, due to lack of marked interest. There have been several debates about the profitability, cost and whether it is economically justifiable to conduct research on rare disorders. It seems likely that research on rare disorders has not been given priority when it comes to allocating research funding. The research is characterized by scarce and scattered research resources and experience [Nortvedt, 2016]. During recent decades, research on rare diseases has been the object of increased interest, primarily concerning the genetic, medical and physical aspects.
Diseases
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Koebner type
- M?llerian aplasia
- Christian Johnson Angenieta syndrome
- Langer Nishino Yamaguchi syndrome
- Inborn amino acid metabolism disorder
- Chronic polyradiculoneuritis
- Carotid artery dissection
- Marinesco Sigren like syndrome
- Phosphomannoisomerase deficiency
- Aortic aneurysm
5 mg coumadin for sale
Efficacy of the to males between the ages of 18 and 30 Quickert procedure for involutional entropion: the first case tichiasis blood pressure medication for pilots discount coumadin online master card. Temporary management of judgment, with most incidents occurring involutional entropion with octyl-2-cyanoacrylate liquid bandage 3,5-8 scarring from chemical injuries and lid application. The role of senile are the most common causes of unilateral enophthalmos in involutional entropion. Upper eyelid between the ages of 30 to 60 years, with entropion and dry eye in cicatricial trachoma without trichiasis. Pathogenesis of involutional ectropion and entropion: the with a history of blunt-force trauma, such on presentation—the following physical involvement of matrix metalloproteinases in elastic fiber degrada as being struck with a projectile, like a tion. Grasp the lower eyelid skin microscopy of trachoma in relation to normal tarsal conjunctiva. Long-term efficacy impact of an air bag or the contact of an between the inferior border of the tarsal of botulinum toxin A for treatment of blepharospasm, hemifacial object following a fall. Entropion in associated with post-traumatic uveal children with isolated peripheral facial nerve paresis. Conservative close his or her eyes while releasing the management of upper eyelid entropion. Observe for evidence of entro tears, spastic entropion and for dysthyroid upper eyelid retrac movement of the eyes are all common. Botulinum toxin for lower lid entropion subconjunctival hemorrhage, ruptured correction. Acquired lateral upper lid entro globe, corneal abrasion, conjunctival lac published study of 12 consecutive patients, pion in a child treated with Botulinum toxin. The most challeng ing aspect of beginning an examination on patients that have encountered facial blunt-force injury is getting the eye open for inspection. Facial and orbital swelling or orbital emphysema can literally force the lids shut. Here, a lid retractor can be Left: Blowout fracture will characteristically be accompanied by marked physical injury on gross examination. The injury can must have imaging to rule out con optic neuropathy and optic nerve avulsion. Seidel testing is essential to rule out producing a shock wave causing “bone perforating injuries. Topical anti-infective Pathophysiology buckling;” the force may be transmitted drops can be prescribed for any observed the seven bones of the orbit include the to the eyeball, causing the globe to strike conjunctival/corneal laceration or abrasion frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, ethmoid, sphe one of the orbital walls such that it frac and topical and oral anti-inflammatory noid, lacrimal and the pterygopalatine. Topical and the sphenoid; the lateral wall is composed ized increased orbital content pressure oral nonsteroidal medications can assist of the zygomatic bone and the greater or a “hydraulic” effect resulting in bone with inflammation and analgesia. This produces what is known as the the maxilla, the lacrimal, the ethmoid and tal plane, the vector of the striking force “coup” injury, from the French/Scottish body of the sphenoid. For these reasons, dilated fundus which maintain structural stability and mechanism are often limited to the ante evaluation ruling out vitreous hemorrhage, resist fractures of the medial orbital wall, rior part of the orbital floor. Treatment of blowout fractures may include the ethmoidal air cells (anterior, When it gives way, the globe and its not be emergent. Compressive threats to middle and posterior), the sphenoidal attached components become unsupport the optic nerve via swelling and retrobul sinuses, the maxillary sinuses and the fron ed, slipping down into the vacant sinus bar hemorrhage will require referral for an tal sinuses. Typically, surgical inter be used to prevent infection of the orbital to center around a chronic, recalcitrant red vention is postponed until orbital health contents from the sinus. Orbital floor fractures: evalu ment unless large amounts of soft tissues ation, indications, approach and pearls from an ophthalmolo tearing to the point of overflow—is often are incarcerated in the bony rupture. Pure orbital blowout fracture: a simple watery consistency to full-blown new concepts and importance of medial orbital blowout frac ditionally has been accomplished through ture. Ocular injuries in will report previous therapy with topical patients with major trauma. Incidence of emergency depart the classic biomicroscopic sign asso surgeons have begun to evaluate an endo ment-treated eye injury in the United States. Epidemiology of oculoplastic punctum, although it may not be seen Endoscopy offers a hidden incision and and reconstructive surgeries performed by a single specialist in all cases. A clinical analysis of bilateral punctal orifice, such that it resembles a orbital fracture. However, the most (repositioning technique), numerous fractures and associated ocular symptoms. Correction of medial tered through lacrimal probing, although In cases that are seen before an orbital blowout fractures according to the fracture types. Considerations for the man finding is the so-called “wrinkle sign”; as agement of medial orbital wall blowout fracture. Orbital blowout overlying skin of the medial canthus may fractures: experimental evidence for the pure hydraulic theory. Epidemiology and manage Jones test for fluorescein dye disappear ment of orbital fractures. Orbital blow-out fractures: surgical timing and a robust lacrimal lake secondary to poor technique. Long-term outcomes of ultra-thin porous polyethylene implants used for reconstruction of orbital emphysema. While history, signs and symptoms Canaliculitis may be described as a pri may suggest an orbital fracture, neuroim mary or secondary condition. Performing smears and/or cultures Management of the retrieved material may be helpful Many cases of canaliculitis are diagnosed in determining the correct pharmacologic only after a seemingly benign case of course, as postoperative antimicrobial blepharoconjunctivitis fails to resolve with therapy is generally indicated. Low-grade In cases of bacterial canaliculitis, oral infections can sometimes persist for long penicillin or ampicillin is commonly pre periods of time because the clinician fails scribed for several weeks following surgical to observe the subtle signs of canaliculitis. In some cases, simple lacrimal cally associated with the formation of and the use of topical antibiotics for sev irrigation can dislodge the plug and effect intracanalicular concretions, sometimes eral weeks. This is the pro referred to as dacryoliths (from the Greek (n=7) series was 100%, although most cedure recommended by the SmartPlug dakryon, meaning “tear,” and lithos, mean subjects required multiple irrigations. On histologic analysis, these Another study evaluated the intracana noted that irrigation also introduces a risk deposits are composed of basophils and licular injection of ophthalmic tobramycin of creating an occlusion more distally in eosinophils associated with a variety of 0. In some cases, concretions lid from the punctal orifice down to the in the canthal region; it is treated with can form around or adjacent to retained level of the common canaliculus (approxi systemic antibiotics alone and generally plugs. Mycobacterium occur with or without keratouveitis and chelonae canaliculitis associated with SmartPlug use. Actinomyces Chronic corneal inflammation (three to canaliculitis: diagnosis of a masquerading disease. Clinical characteristics and thy, the production of corneal epithelial factors associated the outcome of lacrimal canaliculitis. Intracanalicular antibiot younger than 60 years of age often pres ics may obviate the need for surgical management of chronic can leave the nasolacrimal system scarred suppurative canaliculitis. New elevated intraocular pressure (trabeculitis) successfully reestablish lacrimal outflow. The most frequently affected branch of tion is possible, creating the potentially the trigeminal nerve in herpes zoster oph life-threatening complication of orbital 1. Primary and second sion (V1) with its supraorbital, lacrimal coma, scleritis, episcleritis and optic neu ary lacrimal canaliculitis: a review of literature. Primary canaliculitis: the incidence, clinical features, outcome and long-term epiphora tic respect for the midline, consistent with this phenomenon is known as post after snip-punctoplasty and curettage. Canaliculitis: the the skin manifestations begin as an the literature estimates that herpes incidence of long-term epiphora following canaliculotomy. Prevalence of fluid and begin to form scabs after about time; approximately 10% to 20% of these canaliculitis after Smartplug insertion during long-term follow-up. Novel therapy for primary canaliculitis: a pilot study of intracanalicular ophthalmic corti ropathic pain (one-sided headache) but ly 3. Clinical features and surgical is challenging to diagnose; the headache the disease shows a slight preponderance outcomes of primary canaliculitis with concretions. Medicine may be prodromal to an eventual rash for females over males likely due their (Baltimore). A pathological analysis of In addition to the dermatologic find with the highest rates observed among canaliculitis concretions: more than just Actinomyces. Aggregati vitis, superficial and/or stromal keratitis bacter aphrophilus chronic lacrimal canaliculitis: a case report. Additional sequelae include subconjunc the age of 60, 90% of the United States 18. Analysis of inorganic ele Corneal involvement may appear as virus becomes latent, residing in gangli ments in a dacryolith using polarised X-ray fluorescence spec trometry: a case report.

Cheap 5 mg coumadin visa
For instance fetal arrhythmia 34 weeks discount 2 mg coumadin amex, the total number of lymph nodes examined must be reported, but only if nodes are present in the specimen. The use of this protocol is not required for recurrent tumors or for metastatic tumors that are resected at a different time than the primary tumor. Use of this protocol is also not required for pathology reviews performed at a second institution (ie, secondary consultation, second opinion, or review of outside case at second institution). The response for any data element may be modified from those listed in the case summary, including “Cannot be determined” if appropriate. These optional elements may be 3 clinically important but are not yet validated or regularly used in patient management. These optional elements may be 4 clinically important but are not yet validated or regularly used in patient management. Other Tissue/ Organ Involvement (select all that apply) Note: Any organ not selected is either not involved or was not submitted. These optional elements may be 8 clinically important but are not yet validated or regularly used in patient management. Any other involved nodes should be categorized as metastases (pM1) and commented on in the distant metastasis section. Only the applicable T, N, or M category is required for reporting; their definitions need not be included in the report. The categories (with modifiers when applicable) can be listed on 1 line or more than 1 line. Includes all macroscopically visible lesions, even those with superficial invasion. These optional elements may be 9 clinically important but are not yet validated or regularly used in patient management. These optional elements may be 10 clinically important but are not yet validated or regularly used in patient management. Tumor Size Measurement Tumors should be measured in 3 dimensions in all cases, namely the depth of invasion and 2 measurements of horizontal extent (longitudinal/length and circumferential/width). Larger tumors are more accurately measured grossly, while smaller tumors and some larger tumors with a diffusely infiltrative pattern or with marked fibrosis are best measured microscopically. It is best to report only 1 set of tumor measurements based on a correlation of the gross and microscopic features to avoid confusion. In situations where carcinomas are exclusively or predominantly exophytic, there may be little or no invasion of the underlying stroma. The depth of invasion below the level of the epithelial origin should not be provided in these cases as this may not truly reflect the biological potential of such tumors. Horizontal extent: the longitudinal extent (length) of horizontal extent is measured in the superior-inferior plane (ie, from the endocervical to ectocervical aspects of the section), whereas the circumferential extent (width) is measured or calculated perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the cervix. Histologic Grade A wide variety of grading systems, including some that evaluate only the extent of cellular differentiation and others that assess additional features such as the appearance of the tumor margin, the extent of inflammatory cell infiltration, and vascular invasion, have been used for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. However, there is no consensus emerging from the literature that any of these systems are reproducible or that they provide useful prognostic information. Resection Margins Margins can be involved, negative, or indeterminate for carcinoma. If indeterminate, the reason should be specified (eg, cautery artifact in electroexcision specimens may preclude evaluation of the status of the margin). If an invasive tumor approximates but does not directly involve a resection margin, the distance between the tumor and the margin should be measured in millimeters. If the tumor involves the uterine corpus, a determination of whether the cervix or corpus is the primary site should be made. Lymphovascular Invasion Many gynecologists feel that the presence of vascular/lymphatic vessel invasion is important because it may change the extent of their surgical treatment. Examination of Bladder and Rectum Currently, pelvic exenterations are rarely seen, but typically when performed indicate advanced tumor stage. To evaluate these features, sections of the rectum and bladder should be taken perpendicular to the mucosa directly overlying the tumor in the cervix. A method that provides excellent orientation of the tumor to adjacent structures consists of inflation of the urinary bladder and rectum with formalin and fixation of the specimen for several hours. If a biopsied tumor is not resected for any reason (eg, when technically unfeasible) and if the highest T and N categories or the M1 category of the tumor can be confirmed microscopically, the criteria for pathologic classification and staging have been satisfied without total removal of the primary cancer. The “y” prefix indicates those cases in which classification is performed during or following initial multimodality therapy (ie, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both chemotherapy and radiation therapy). That is, tumor involving the resection margin on pathologic examination may be assumed to correspond to residual tumor in the patient and may be classified as macroscopic or microscopic according to the findings at the specimen margin(s). However, the size criteria for micrometastasis and macrometastasis is adopted from the experience in breast carcinoma. Examination of Parametria the parametria may be measured grossly, but their width varies according to the elasticity of the tissue. Careful microscopic examination of the parametria is important for evaluation of the lateral margins and/or soft tissue extension. Immunohistochemistry: Endocervical versus Endometrial Adenocarcinoma Immunohistochemistry can also be helpful in the differential diagnosis between endocervical and endometrial carcinoma, especially in curettage specimens, as endometrial carcinomas may show mucinous differentiation. Takeda N, Sakuragi N, Takeda M, Okamoto K, Kuwabara M, Negishi H, Oikawa M, Yamamoto R, Yamada H, Fujimoto S Multivariate analysis of histopathologic prognostic factors for invasive cervical cancer treated with radical hysterectomy and systematic retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy. Immunohistochemical staining in the distinction between primary endometrial and endocervical adenocarcinomas: another viewpoint. Cervical cancer Number of women aged 20-69 who have been screened for cervical cancer within the past three years (or according to the specific screening frequency recommended in each screening country) divided by the number of women aged 20-69 answering the survey question (for survey-based data) or eligible for an organised screening programme (for programme-based data). Note: Countries are invited to supply both survey data and programme data when these two sources are available. Programme data Source of data: There are no data for the cervix cancer screening coverage since 2013. The reason is that there were changes in the reimbursement rules, and there is currently no agreement on the way to compute the coverage. Coverage: Observed data for cervical cancer screening are available for the periods 1996-2000, 2002-2012. Estimation method: Data for other years than 1996-2000 and 2002-2012 are estimated using observed screening data and total annual consumption of cervical cytology by year (National Institute of Health Insurance) based on a linear regression imputation method. Analysis of individual health insurance data pertaining to Pap smears, colposcopies, biopsies and surgery on the uterine cervix (Belgium, 1996-2000). Analysis of 13 million individual patient records pertaining to Pap smears, colposcopies, biopsies and surgery on the uterine cervix (Belgium, 1996-2000). Analysis of individual health insurance data pertaining to Pap smears, colposcopies, biopsies and surgery on the uterine cervix (Belgium, 2002-2006). Bulgaria Breast cancer screening (mammography) Survey data: Source of data: National Statistical Institute, European Health Interview Survey 2008, harmonised questionnaire was used. Reference period: 2013 2015 Programmes: “Stop and check yourselves” – 2013-2014 National programme for prevention of chronic non-communicable diseases (2014-2020) Coverage: Data refer to women aged 50-69 National coverage Numerator: Number of women aged 50-69 who received a mammography through the organised breast cancer screening programme. In order to define the target group additional administrative data sources were used – the National Civil Registration System, the National Health Insurance Fund, and the National Cancer Registry. The denominator does not include women already registered in the National Cancer Registry with the relevant cancer and those who have undergone prophylactic check in the last 12 months. Reference period: 2016, 2017 National programme for prevention of chronic non-communicable diseases (2014-2020) 2016 and 2017 data Coverage: Data refer to women aged 50-69 National coverage Numerator: Number of women aged 50-69 who received a mammography through the organised breast cancer programme. The data does not include women who have had a mammography elsewhere, outside the screening programme. Cervical cancer screening Survey data: Source of data: National Statistical Institute, European Health Interview Survey 2008 and 2014, harmonised questionnaire was used. Reference period: November – December 2008 October – December 2014 Coverage: All persons aged 15 and over within the selected non-institutionalised households are surveyed. Denominator: Number of women aged 25-60 who were invited to the organised screening during the year. These districts have the highest incidence rate of oncological diseases per 100,000 of the population according to the National cancer registry 2015 data. For the screening only persons with family burden as well as without age restrictions have been covered. Coverage: National representative sample survey of population aged 15 years old and over. Programme data Source of data: Breast Cancer Screening Database (Institute of Biostatistics and Analyses, Faculty of Medicine and the Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, Programme data Source of data: Administrative data from all health insurance companies (aggregated and analysed by Institute of Health Information and Statistics of the Czech Republic and Institute of Biostatistics and Analyses, Faculty of Medicine and the Faculty of Science, Masaryk University,

Purchase cheap coumadin on-line
You may be able to recognize a deformed You should be able to demonstrate 90% of carcinomas duodenal ampulla while you screen heart attack the song coumadin 1 mg with amex, but you will see with simple screening. Be sure to use a long plate With experience, you will recognize enlargement of the to get the whole oesophagus on to it, and do not centre the duodenal loop (as by carcinoma of the head of the Xray tube on only one part of it. A mouthful of contrast medium and one large film will Suggesting gastric outlet obstruction: pyloric delay usually show an advanced tumour. If possible watch the movement of barium and air on Prepare the patient with oral bowel preparation and a rectal screening, and expose plates of critical areas. Sterilize the skin of the neck on both sides and infiltrate 2ml 1% lidocaine under the skin over the pulsations of the carotid artery. Do not put in too much, otherwise palpation of the artery You will probably be able to demonstrate the large bowel as far as will be difficult. If you have an ultrasound, this is very the hepatic flexure without much difficulty; the ascending colon is more difficult. Puncture the carotid artery directly from the front Lay the patient supine on the Xray table, and ask the with a 19G 5-8cm long lumbar puncture needle (38-4), patient to flex and abduct the hips. Lubricate the flatus tube well with a plastic connection, already attached, to which you can fit lubricant, and push it through the anus, as far as it will go the syringe with the contrast medium. Inject barium and air, of contrast and take films whilst you are injecting, as required, to show the large bowel up to the caecum. The limiting factor is the Being careful not to displace the needle, turn the patient’s distension of the large bowel with barium and air, head on its opposite side, and repeat the injection of 10ml and the urge to defecate that this produces. Finally, when you are satisfied with the quality of the films, remove the needle and press on the puncture site for a full 1min, without occluding the flow in the carotid artery. If you suspect a fistula to extend from skin to the large bowel, use bowel preparation beforehand. Make sure you plug the sinus or fistula, so that when you inject contrast it does not spill back out: you can use stoma paste for this, or pass a small Foley catheter and inflate the balloon to secure it in place. If during cholecystectomy, you feel a stone or if you have lost a stone in the common bile duct, or there has been a Look for displacement of the anterior cerebral artery from history of jaundice, or the common bile duct is dilated. Look for a the cystic duct, attach a 20ml syringe with saline to a fine ‘tumour blush’ or vessels displaced around a lesion. Remove instruments and swabs from the operative field, (1),Progressive neurological limb deficit suggestive of an and cover the wound with a sterile towel. Withdraw bile into the cannula to make sure it (3) Sciatica not improving with conservative treatment. Gallstones appear as filling defects, so it is vital that air (2) Septic lesions on the back. Place the patient in the lateral position with the the gallbladder, because you may want to do a lumbar spine well flexed but not crooked, with a pillow cholecystojejunostomy (15. Administer prophylactic tetracycline You will find a large variety of ultrasound scanners and metronidazole beforehand. Therefore, if you want to buy as the Leech-Wilkinson screw-in type (the Miller cannula one, make sure you order an instrument of a specification causes less trauma to the cervix, but does not make such a that will allow you to get useful data from it. It may be good seal with it) or a very small size Foley catheter but better to have no scanner than to have one that gives poor this needs a special syringe to provide a proper seal. Prepare a suitable 20ml syringe filled with a probe for cardiological examinations. Lie her supine on the Xray table your hand correctly so the image on the screen with her hips and knees flexed, and the plate under her corresponds with the patient’s position and is not back to pelvis. Increase in gain brightens the image; increase in ratchet; this should cause little discomfort. If it remains the specifications for a general purpose ultrasound scanner are as loculated, this suggests adhesions and impaired fertility. A transducer which is curvilinear (convex), or a combination of linear and sector. Overall sensitivity (gain or Unlike radiographic images, sonographic pictures are not transmitter power) and time-gain-compensation should be an generated by radiation but by sound waves of frequency integral part of the circuit. The lower the frequency, the shorter the gain-compensation is at the correct level for obstetrics, with a wavelength and so the greater the penetration. A frame rate 15-30Hz for the linear probe and at least 5-10Hz for the sector probe. At least one pair of electronic omni-directional calipers with quantitative tissues/structures due to various sound transmission readout, to measure lengths on the screen. A reasonable weight, so that an average adult can move it over at least passing through) between the tissues. However, Consequently fluids like blood, urine, pleural fluid appear the more your machine is mobile, the more easily it may be stolen! Protection for the local climate, and against dust, damp, and extremes could be reflected. It should be possible to use the scanner continuously and bone reflect almost all the sound waves obscuring any within a temperature range of 10-40°C and 90 % relative humidity. Connection to the local power supply and be compatible with the voltage, image from what lies behind the air or bone. It should be able to stabilize However, you can usually get round this problem a voltage variation of ±10%. Many ultrasound scanners incorporate biometric tables But the quality and reliability depends, more than in other. Biometric tables may knowledge of the examiner, and the quality of the not be universally applicable and should be adjusted for local conditions. You can use petroleum jelly for the around, ask him to teach you; it’s worthwhile to learn this transducer if special jelly is too expensive. The margin will applications, note the simple phenomena which appear on appear rounded if the liver is enlarged. Throughout the an image due to the physical characteristics of sound: parenchyma of the liver you will find porto-venous Some artefacts are useful. This results in blackish bands behind such structures which make evaluation there impossible. Use this effect in atherosclerotic plaques and to reveal stones in the gallbladder, kidney & bladder! If the transducer has poor contact with the skin of the patient there will be black bands through your image, too. But these ones start right at the skin level and they will disappear upon using more air-displacing gel. Carefully distinguish this from layered material like blood clots or small concretions which change their localisation after turning the patient around! Try to give your patient continuous breathing instructions and don’t forget to allow him to breathe out Fig. B, ultrasound image of a stone in the apply the transducer a little bit to the right side in the gallbladder. Usually you don’t need to be worried if the cyst appears anechoic and fulfils the cyst Method: Expect a healthy liver and kidney to have a criteria (see below). If a cyst is not anechoic any more but the liver is typical of a fatty liver whereas an apparently displays internal echoes you need to think of intracystic reduced brightness is in most cases due to an increased haemorrhage or of a parasitic hepatic cyst with septation. A common infection is due to Echincoccus granulosus these fatty infiltrations can look quite solid but are always (15. Although it is good idea of oedematous wall thickening, polyps or stones difficult to differentiate such lesions from abscesses, and tumours (which are actually extremely rare). While you scan the parenchyma of the liver, pay attention Stones usually generate acoustic shadowing, but tumours to any kind of focal lesions which appear and disappear do not. Most often they lie in the most dependent Although metastases in the liver present with a wide part of the gallbladder and move about when the patient’s variety of echogenicity, a very typical sonographic sign is position changes, unless they are impacted together and fill a dark narrow rim around the lesion which is called a the gallbladder completely. Especially in fast growing metastases you can sometimes find a cystic hypoechoic centre caused by Peri-vesicular fluid will appear as a black fringe around central necrosis. If a focal lesion has the same brightness the gallbladder as a sign of inflammation, perforation or as the liver parenchyma you may only detect it due to ascites. If you press directly with the probe on the liver borders or jaundice in your patient because of fundus of the gallbladder, and this causes acute pain, compression of the biliary ducts. Focal lesions which it is a true ‘Murphy’s sign’ and a very reliable sign of present brighter compared to liver tissue can be harmless acute cholecystitis. It is crucial to recognize any air in the homogeneously hyperechoic, have a sharp but possibly gallbladder due to a colonic fistula or to infection with irregular demarcation and typically display a bright narrow gas-producing bacteria, as this is associated with a high rim.
Order coumadin 2mg on-line
The scarring could be due to the death of the microflariae or as the result of a reaction to the presence of living microflariae wide pulse pressure icd 9 generic 5mg coumadin with visa. In the early stages of punctate keratitis, the corneal lesions are reversible but once more advanced scarring due to sclerosing keratitis develops, the visual loss is permanent. The fact must be emphasized that the disease is essentially conjunctival, and when the cornea is affected it is the conjunctival element of the cornea—the epithelium and the superfcial layers underlying it—which suffers. B from Jay H Krachmer, Mark J Mannis, Edward J Holland, phlyctens but cause much pain and refex blepharospasm eds. In severe cases associated with systemic autoimmune disorders, systemic steroids and cytotoxic drugs may be indicated. Marginal Ulcer (Catarrhal Ulcer) these ulcers occur near the limbus, especially in old Chronic Serpiginous Ulcer people. Erosion is initiated by autoimmune lysis of the epithelium Clinical Features: They are typically located at the with consequent release of collagenolytic enzymes. Sometimes they heal rapidly but recur break down, forming small ulcers that spread and sooner just as rapidly, so that the process tends to drag on indef or later coalesce. Frequently the ulcers become vascularized and the l the ulcer undermines the epithelium and superficial vessels persist. Associated blepharitis must be treated adults, while a milder, usually unilateral, less painful with hot fomentation, lid massage, cleaning of the lid mar form is seen in elderly patients. Excision of a 4–7 mm strip of adjacent conjunc tiva may prove successful by eliminating conjunctival sources of collagenase, proteoglycanase and other infam matory mediators. If perforation occurs, ulcer debridement, cyanoacrylate adhesive and soft contact lenses may be tried. Interstitial Keratitis this is an infammation affecting chiefy the stroma of the cornea. Cogan syndrome: Interstitial keratitis and deafness (Cogan syndrome) is a rare disease affecting young adults. Syphilitic (luetic) interstitial keratitis: l Interstitial keratitis due to inherited syphilis, most commonly affects children between the ages of 5 and 15 years. Clinical features: After slight irritative symptoms with some ciliary congestion, one or more hazy patches appear in the deep layers of the cornea near the margin or towards the centre. In 2–4 weeks the whole cornea is hazy with a steamy peripheral cornea with round, white stromal opacities. It is important to surface, giving a general ground glass appearance in which recognize this diagnosis because early treatment with systemic corticoste denser spots can always be seen. Approximately 10% of patients visible, but in the severest of cases the whole cornea with Cogan’s syndrome have evidence of a systemic vasculitis. As the cloudiness disappears the patches’) wherein separate vessels can be seen only with vessels become obliterated; although they cease to carry diffculty. The opacity extends a little beyond the vessels, blood they remain permanently as fne opaque lines known which seem to push the opacity in front of them and at as ‘ghost vessels’, the characteristic radial course of which the height of the condition the vessels run in radial bundles indicates the previous occurrence of the disease. There Since the infltration of the cornea is almost entirely is often a moderate degree of superfcial vascularization, limited to the deeper layers lying immediately anterior to but it never extends far over the cornea, and at the limbus Descemet’s membrane, the corneal surface rarely becomes the conjunctiva may be heaped up. It is frequently stippled, steamy and slightly un After the disease has reached its height, the cornea even, and this condition may persist. In the worst cases the clears slowly from the margin towards the centre, which cornea may be thickened but it usually improves with some may remain hazy for a long time, but fnally improves useful vision. Sometimes there is severe cyclitis, as tion which persists for weeks or many months, leaving a shown by the presence of keratic precipitates on the back of permanent opacity. The cornea may become anaesthetic the cornea, and not infrequently a choroiditis, particularly but ulceration does not occur. It is associated with itis, and the keratitis, which clinically masks the uveitis, is some degree of uveitis. It is important to understand the pathogenesis, It is completely a diffcult condition to treat, but gener as treatment must be directed to avoiding the deleterious ally the symptoms and the extent of the permanent opacity results of iridocyclitis rather than those of keratitis. The cornea takes weeks or months to clear, but little improvement can be expected Corneal dystrophies are non-infammatory, hereditary after 18 months. They mainly affect a particu congenital syphilis and positive serological reactions. A variety of classifcation systems Treatment: It is doubtful if antisyphilitic remedies have have been used in the past. The International Committee any infuence over the course of the keratitis, partly because for Classifcation of Corneal Dystrophies (1C3D) estab the cornea is non-vascular and partly because the reaction lished in 2005 has devised a current and accurate nomencla is probably largely allergic. It is possible, however, that in ture supplementing the anatomic classifcation with updated tensive systemic treatment with penicillin may shorten the clinical, pathologic and genetic information. Local treatment in the form of lubricants, topical ste Epithelial and Subepithelial Dystrophies roids and cycloplegics to control the uveitis is helpful in the acute stage. In the later stages the best results are obtained these involve the anteriormost layer of the cornea, gener by corneal grafting of the penetrating type, which generally ally present in adults, who may be asymptomatic or suffer has a good prognosis. They are of obscure origin involving the central area of the cornea, rarely affect ing the corneal margin. The lesions are characterized by the development of discrete areas of opacifcation, mainly in the superfcial layers of the stroma, essentially due to hyaline deposits between the corneal lamellae. They tend to increase in number and density until Bowman’s membrane becomes eroded and the epithelium desquamates. Relatively symp tomless and without infammatory reaction, they progress slowly until the vision becomes seriously impaired, usually above the age of 40 years. The intervening cornea between the opacities and periph eral cornea remain clear. Histopathological examination of the cornea by special stains after keratoplasty demon strates the nature of the material deposited. Characteristically, patients complain of seeing halos in the morning, which disappear later in the day as the massaging effect of refex blinking and evaporation leads to subsidence of corneal epithelial oedema. Periodic rupture of the epithelial bullae can be painful and the eye is prone to secondary infection. Treatment is diffcult; of S Kashyap) stained with Congo red shows amyloid deposition in the hypertonic solutions such as sodium chloride 5% eye drops stroma. They are distin guished from dystrophies as being non-hereditary and usually unilateral. Histological section (By categories: primary degenerations, secondary degenera courtesy of S Kashyap) stained with colloidal iron shows deposits of muco tions depending on long-standing changes in the eye itself, polysaccharide glycosaminoglycans in the stroma. It is almost universally present to some extent in people Endothelial Corneal Dystrophies who are above 60 years of age. It commences as a crescen these occur rarely, the most common being the endothe tic grey line or whitish arc concentric with the upper and lial dystrophy of Fuchs (Fig. It is seen in elderly lower margins of the cornea, the extremities of which people, particularly females, and is due to changes in the fnally meet so that an opaque line, thicker above and endothelium with the formation of hyaline excrescences on below, is formed completely round the cornea. It is charac Descemet’s membrane (cornea guttata) and the eventual terized by being separated from the margin by a narrow atrophy of the endothelial cells. These deep changes are zone of comparatively clear cornea, being sharply defned on the peripheral side, fading off on the central. It is never more than about 1 mm broad, is of no importance either from the point of view of vision or of the vitality of the cornea (see Fig. If it appears below the age of 40 years, a serum lipid profle is indicated to eliminate a hereditary anomaly with a serious prognosis for life. The characteristic diagnostic feature is the presence of a line of clear cornea between the opacity and the limbus. Chapter | 15 Diseases of the Cornea 215 at the inner and outer sides and progressing until it forms a continuous band across the cornea, interspersed with round ‘holes’ or cleaves in the band itself (Fig. Close to the limbus, however, the cornea is generally rela tively clear, as in so many degenerative conditions, proba bly owing to the better nutrition close to the blood vessels. The condition is due to hyaline infltration of the superf cial parts of the stroma, followed by the deposition of calcareous salts. Treatment: Improvement of vision may be obtained by scraping off the opacity, which is usually calcareous and quite superfcial, or dissolving it with the sodium salt of ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (sodium edetate). Climatic Droplet Keratopathy Also called oil droplet keratopathy or actinic droplet kera Terrien Marginal Degeneration topathy, this form of degeneration is common in those ex Terrien marginal degeneration is usually bilateral, but may posed to a hot, dry, dusty environment and outdoor activity be unilateral.

